MCQs for Chemistry Class 12 with Answers Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
Students of class 12 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 12 Chemistry NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 12 Chemistry. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 12 Chemistry examination
Chapter 3 Electrochemistry MCQ with Answers Class 12 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 12. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 12 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane directly into electrical energy is known as:
(a) dynamo
(b) Ni-Cd cell
(c) fuel cell
(d) electrolytic cell
Answer
C
Question. Which metal is used as electrode which do not participate in the reaction but provides surface for conduction of electrons?
(a) Cu
(b) Pt
(c) Zn
(d) Fe
Answer
B
Question. What flows in the internal circuit of a galvanic cell?
(a) Ions
(b) Electrons
(c) Electricity
(d) Atoms
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the use of electrolysis?
(a) Electrorefining
(b) Electroplating
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Several blocks of magnesium are fixed to the bottom of a ship to
(a) make the ship lighter
(b) prevent action of water and salt
(c) prevent puncturing by under-sea rocks
(d) keep away the sharks
Answer
B
Question. Using the data given in Q. 8 find out in which option the order of reducing power is correct.
(a) Cr3+ < Cl– < Mn2+ < Cr
(b) Mn 2+< Cl– < Cr 3+ < Cr
(c) Cr 3+ < Cl– < Cr 2 O72–< MnO–4
(d) Mn 2+ < Cr 3+ < Cl– < Cr
Answer
B
Question. Use the data given in Q. 8 find out the most stable oxidised species.
(a) Cr3+
(b) MnO4–
(c) Cr2O27
(d) Mn2+
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is always true about the spontaneous cell reaction in a galvanic cell?
(a) Ecell > 0, G < 0,Q > K o o D c
(b) Ecell < 0, G < 0,Q < K o o D c
(c) Ecell > 0, G > 0,Q > K o o D c
(d) Ecell > 0, G < 0,Q < K o o D c
Answer
D
Question. On increasing temperature,
(a) ionic conductance increases and electronic conductance decreases.
(b) ionic conductance decreases and electronic conductance increases.
(c) both ionic and electronic conductance increase.
(d) both ionic and electronic conductance decrease.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements about galvanic cell is incorrect
(a) anode is positive
(b) oxidation occurs at the electrode with lower reduction potential
(c) cathode is positive
(d) reduction occurs at cathode
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell?
(a) It does not participate in the cell reaction.
(b) It provides surface either for oxidation or for reduction reaction.
(c) It provides surface for conduction of electrons.
(d) It provides surface for redox reaction.
Answer
D
Question. If 0.5 amp current is passed through acidified silver nitrate solution for 100 minutes. The mass of silver deposited on cathode, is (eq.wt.of silver nitrate = 108)
(a) 2.3523 g
(b) 3.3575 g
(c) 5.3578 g
(d) 6.3575 g
Answer
B
Question. Charge carried by 1 mole of electrons is
(a) 6.023 × 1023 coulomb
(b) 9.65 × 104 coulomb
(c) 1.6 × 10–19 coulomb
(d) 6.28 × 1019 coulomb
Answer
B
Question. An aqueous solution of X is added slowly to an aqueous solution of Y as shown in Column I. The variation in conductivity of these reactions is given in Column II. Match Column I with Column II and select the correct answer us ing the codes given below the lists.

Codes
A B C D
(a) 3 4 2 1
(b) 4 3 2 1
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 1 4 3 2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following reactions cannot be a base for electrochemical cell?
(a) H2 + O2 → H2O
(b) AgNO3 +Zn → Zn(NO3] 2 + Ag
(c) AgNO3 + NaCl→ AgCl + NaNO2
(d) KMnO4 + FeSO4 + H2SO4→
K2SO4 + Fe2 (SO4 )3 + MnSO4 + H2O
Answer
D
Question. The electrochemical cell stops working after sometime because
(a) electrode potential ofboth the electrodes becomes zero
(b) electrode potential of both the electrodes becomes equal
(c) one of the electrodes is eaten away
(d) the cell reaction gets reversed
Answer
B
Question. In a galvanic cell, the electrons flow from
(a) anode to cathode through the solution
(b) cathode to anode through the solution
(c) anode to cathode through the extemal circuit
(d) cathode to anode through the extemal circuit
Answer
C
Question. What is the cell reaction occurring in Daniel cell (Galvaniccell)?
(a) Cu(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) ➔ CuSO4 (aq) + Zn(s)
(b) Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ➔ Cu(s) + ZnSO4 (aq)
(c) Ni(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) ➔ NiSO4 (aq) + Zn(s)
(d) 2Na(s) + CdSO4 (aq) ➔ Na2SO4 (aq)+ Cd(s)
Answer
B
Question. The best way to prevent rusting of iron is
(a) making it cathode
(b) putting in saline water
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Several blocks of magnesium are fixed to the bottom of a ship to
(a) keep away the sharks
(b) make the ship lighter
(c) prevent action of water and salt
(d) prevent puncturing by under-sea rocks
Answer
C
Question. The process of zinc-plating on iron sheet is known as
(a) annealing
(b) roasting
(c) galvanisation
(d) smelting
Answer
C
Question. Stainless steel does not mst because
(a) chromium and nickel combine with iron
(b) chromium forms an oxide layer and protects iron from rusting
(c) nickel present in it, does not rust
(d) iron forms a hard chemical compound with chromium present in it
Answer
B
Question. Corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon where the cell reactions are
(a) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and dissolved oxygen in water is reduced to OH–
(b) Fe is oxidised to Fe3+ and H2O is reduced to O2-2
(c) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and H2O is reduced to O–2
(d) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ and H2O is reduced to O2
Answer
A
Question. The quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from Al2O3 is ______________.
(a) 1F
(b) 6F
(c) 3F
(d) 2F
Answer
C
Question. On electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes, the product obtained at the anode will be
(a) hydrogen
(b) oxygen
(c) hydrogen sulphide
(d) Sulphur dioxide
Answer
B
Question. The standard emf of a galvanic cell involving 3 moles of electrons in a redox reaction is 0.59 V. The equilibrium constant for the reaction of the cell is:
(a) 1010
(b) 1020
(c) 1030
(d) 1015
Answer
C
Question. The SI unit of conductivity is
(a) Sm–1
(b) Scm–1
(c) Sm
(d) Scm
Answer
A
Question. Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Conductivity of solution depends upon size of ions.
(b) Conductivity depends upon viscosity of solution.
(c) Conductivity does not depend upon solvation of ions present in solution.
(d) Conductivity of solution increases with temperature.
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following conditions salt bridge is not required in a galvanic cell?
(a) When galvanic cell is used in geyser.
(b) When distance between oxidation half cell and reduction half cell is negligible.
(c) Electrolytic solutions used in both the half cells are of same concentration.
(d) When both the electrodes are dipped in the same electrolytic solution.
Answer
D
Question. Which device converts chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy?
(a) Galvanic cell
(b) Electrolytic cell
(c) Daniell cell
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Pt(s)| H2 (g, 0.1 bar)| H+ (aq., 1 M) | | Cu2+ (aq., 1M)| Cu
(b) Pt(s)| H2 (g, 1 bar) | H+ (aq., 1 M) | | Cu2+ (aq., 2M)| Cu
(c) Pt(s)| H2 (g, 1 bar) | H+ (aq., 1 M) | | Cu2+ (aq., 1M)| Cu
(d) Pt(s)| H2 (g, 1 bar) | H+ (aq., 0.1 M)| | Cu2+ (aq., 1M)| Cu
Answer
C
Question. The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu indicates that ______________.
(a) this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple.
(b) this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2.
(c) Cu can displace H2 from acid.
(d) Cu cannot displace H2 from acid.
Answer
B
Question. Standard electrode potential for Sn4+/Sn2+ couple is +0.15 V and that for the Cr3+/Cr couple is – 0.74 V. The two couple in their standard states are connected to make cell. The cell potential will be:
(a) +1.19 V
(b) 0.89 V
(c) +0.18 V
(d) +1.83 V
Answer
B
Question. The tendency of an electrode to lose electrons is known as
(a) electrode potential
(b) reduction potential
(c) oxidation potential
(d) e.m.f.
Answer
C
Question. The oxidation potentials of A and B are +2.37 and +1.66 V respectively. In chemical reactions
(a) A will be replaced by B
(b) A will replace B
(c) A will not replace B
(d) A and B will not replace each other
Answer
B
Question. An electrolytic cell contains a solution of Ag2SO4 and has platinum electrodes. A current is passed until 1.6 gm of O2 has been liberated at anode. The amount of silver deposited
at cathode would be
(a) 107.88 gm
(b) 1.6 gm
(c) 0.8 gm
(d) 21.60 gm
Answer
D
Question. When 9650 coulombs of electricity is passed through a solution of copper sulphate, the amount of copper deposited is (given at. wt. of Cu = 63.6)
(a) 0318g
(b) 3.18 g
(c) 31.8g
(d) 63.6g
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a merit of Ni–Cd cell over lead storage battery?
(a) Ni–Cd cell can be re-used.
(b) Ni–Cd cell is comparatively economical to manufacture
(c) Ni–Cd cell has comparatively longer life
(d) All the above are the merits of Ni–Cd cell over lead storage battery.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements regarding fuel cell is incorrect?
(a) These cells are eco-friendly.
(b) These cells convert energy of combustion of fuels like H2, CH4, CH3OH etc., directly into electrical energy.
(c) H2 – O2 fuel cell is used in Apollo space programme.
(d) Fuel cells produce electricity with an efficiency of about 100%.
Answer
D
Question. An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell when ____________.
(a) Ecell = 0
(b) Ecell > Eext
(c) Eext > Ecell
(d) Ecell = Eext
Answer
C
Question. To deposit one equivalent weight of silver at cathode, the charge required will be
(a) 9.65 × 104 C
(b) 9.65 × 103 C
(c) 9.65 × 105 C
(d) 9.65 × 107 C
Answer
A
Question. The volume of oxygen gas liberated at NTP by passing a current of 9650 coulombs through acidified water is
(a) 1.12 litre
(b) 2.24 litre
(c) 11.2 litre
(d) 22.4 litre
Answer
B
Question. Three faradays electricity was passed through an aqueous solution of iron (II) bromide. The weight of iron metal (at. wt = 65) deposited at the cathode (in gm) is
(a) 56
(b) 84
(c) 112
(d) 168
Answer
B
Question. Faraday’s laws of electrolysis will fail when
(a) temperature is increased
(b) inert electrodes are used
(c) a mixture of electrolytes is used
(d) None of these cases
Answer
D
Question. The electric charge for electrode decomposition of one gram equivalent of a substance is
(a) one ampere per second
(b) 96500 coulombs per second
(c) one ampere for one hour
(d) charge on one mole of electrons
Answer
D
Question. In electrolysis of dilute H2SO4 using platinum electrodes
(a) H2 is evolved at cathode
(b) NH2 is produced at anode
(c) Cl2 is obtained at cathode
(d) O2 is produced
Answer
A
Question. A silver cup is plated with silver by passing 965 coulombs of electricity. The amount of Ag deposited is :
(a) 107.89 g
(b) 9.89 g
(c) 1.0002 g
(d) 1.08 g
Answer
D
Question. If the H+ concentration is decreased from 1 M to 10-4 Mat 25°C for the couple MnO4 /Mn2+, then the oxidising power of the MnO–4 /Mn2+ couple decreases by
(a) -0.18 V
(b) 0.18 V
(c) 0.38 V
(d) – 0.38 V
Answer
C
Question. The reduction electrode potential, E of 0.1 M solution of M+ ions (ERP = – 2.36 V) is
(a) – 4.82 V
(b) – 2.41 V
(c) + 2.41 V
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Consider the following E° values
E°Fe3+ / F2+ = + 0.77 V, E°sn2+ / sn = – 0.14 V
Under standard conditions the potential for the reaction
Sn(s) + 2Fe3+ (aq) ➔ 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq) is
(a) 1.68 V
(b) 1.40 V
(c) 0.91 V
(d) 0.63 V
Answer
D
Question. Reduction potentials of A, B, C and Dare 0.8 V, 0.79 V, 0.34 Vand- 2.37Vrespectively. Which element displaces all the other three elements?
(a) B
(b) A
(c) D
(d) C
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements are correct concerning redox properties?
I. A metal M for which E° for the half reaction Mn+ + ne– = M, is very negative will be a good reducing agent.
II. The oxidising power of the halogens decreases from chlorine to iodine.
III. The reducing power of hydrogen halides increases from hydrogen chloride to hydrogen iodide.
(a) I, II and III
(b) I and II
(c) Only I
(d) II and III
(e) Only III
Answer
A
Question. Given the standard reduction potentials
Zn2+ /Zn = – 0.74 V, Cl2/ Cl– = 1.36 V
H+/1/2H2 = 0V and Fe2+/Fe3+ =0.77V
The order of increasing strength as reducing agent is
(a) Cl– ,Zn ,H2 , Fe2+
(b) H2 ,Zn ,Fe2+ ,Cl–
(c) Cl– ,Fe2+ ,Zn ,H2
(d) H2 ,Fe2+ ,Cl- ,Zn
(e) Cl– ,Fe2+,H2 ,Zn
Answer
E
Question. When Cu reacts with AgNO3 solution, the reaction takes place is
(a) oxidation of Cu
(b) reduction of Cu
(c) oxidation of Ag
(d) reduction of NO3
Answer
A
Question. The standard reduction potentials of Zn2+ l Zn, Cu2+ l Cu and Ag+ l Ag are respectively – 0.76, 0. 34 and 0.8 V. The following cells were constructed
I. Zn l Zn2+ ll cu2+ l Cu
TI. Zn l Zn2+ ll Ag+ l Ag
ITT. Cu l Cu2+ ll Ag+ l Ag
What is the correct order of E°cell of these cell ?
(a) II > III > I
(b) II > I > III
(c) I > II > III
(d) III > I > II
Answer
B
Question. Which will reduce zinc oxide to zinc?
(a) Mg
(b) Pb
(c) Cu
(d) Fe
Answer
A
Question. The metal that does not displace hydrogen from an acid is
(a) Ca
(b) AI
(c) Zn
(d) Hg
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following ions can be replaced by H+ ions when H2 gas is bubbled through the solutions containing these ions?
(a) Li+
(b) Ba2+
(c) Cu2+
(d) Be2+
Answer
C
Question. The emfofthe cell, (EZn2+ /Zn = – 0.76 V)
Zn l Zn2+ (lM) ll Cu2+ (lM)Cu
(ECu2+ /Cu = + 0.34 V)will be
(a) + 1.10 V
(b) – 1.10 V
(c) + 0.42 V
(d) – 0.42 V
Answer
A
Question. H2 cannot be displaced by
(a) Li+
(b) Sr2+
(c) N3+
(d) Ag+
Answer
D
Question. The number of coulombs required to reduce 12.3 g of nitrobenzene to aniline is :
(a) 115800 C
(b) 5790 C
(c) 28950 C
(d) 57900 C
Answer
D
Question. The amount of electricity that can deposit 108 g of Ag from AgNO3 solution is:
(a) 1 F
(b) 2 A
(c) 1 C
(d) 1 A
Answer
A
Question. A smuggler could not carry gold by depositing iron on the gold surface since
(a) gold is denser
(b) iron rusts
(c) gold has higher reduction potential than iron
(d) gold has lower reduction potential than iron
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following batteries cannot be reused?
(a) Lead storage battery
(b) Ni-Cd cell
(c) Mercury cell
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. In electrolysis of NaCl when Pt electrode is taken then H2 is liberated at cathode while with Hg cathode it forms sodium amalgam. This is because
(a) Hg is more inert than Pt
(b) more voltage is required to reduce H+ at Hg than at Pt
(c) Na is dissolved in Hg while it does not dissolve in Pt
(d) conc. of H+ ions is larger when Pt electrode is taken
Answer
B
Question. Electrolysis of fused NaCl will give
(a) Na
(b) NaOH
(c) NaClO
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Hydrogen-Oxygen fuel cells are used in space craft to supply
(a) power for heat and light
(b) power for pressure
(c) oxygen
(d) water
Answer
B
Question. The electrolyte used in the mercury cell is
(a) paste of NH4Cl and ZnCl2
(b) paste of HgO and carbon
(c) paste of KOH and ZnO
(d) paste of PbO and H2SO4
Answer
C
Question. Among the following cells: Leclanche cell
(i)Nickel-Cadmium cell
(ii)Lead storage battery
(iii)Mercury cell
(iv)primary cells are
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. The electrolyte used in Leclanche cell is
(a) paste of KOH and ZnO
(b) 38% solution of H2SO4
(c) moist paste of NH4Cl and ZnCl2
(d) moist sodium hydroxide
Answer
C
Question. A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane, directly into electrical energy is known as :
(a) Electrolytic cell
(b) Dynamo
(c) Ni-Cd cell
(d) Fuel Cell
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following cells can convert chemical energy of H2 and O2 directly into electrical energy?
(a) Mercury cell
(b) Daniell cell
(c) Fuel cell
(d) Lead storage cell
Answer
C
Question. Prevention of corrosion of iron by zinc coating is called
(a) electrolysis
(b) photoelectrolysis
(c) cathodic protection
(d) galvanization
Answer
D
Question. The best way to prevent rusting of iron is
(a) making it cathode
(b) putting in saline water
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called _________________.
(a) Cell potential
(b) Cell emf
(c) Potential difference
(d) Cell voltage
Answer
B
Question. A hypothetical electrochemical cell is shown below: A | A+(xM) || B+(yM) | B The emf measured is +0.20 V. The cell reaction is
(a) A + B+ → A++ B
(b) The cell reaction cannot be predicted.
(c) A+e– → A, B+ +e–→ B
(d) A++ B → A + B+
Answer
A
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Which of the following statements regarding given cell representation is/are correct?
Cd(s)/Cd2+(aq)//Ag+(aq)/Ag(s)
(i) In the given cell Cd electrode act as an anode whereas
Ag electrode acts as a cathode.
(ii) In the given cell Cd electrode acts as a cathode whereas
Ag electrode acts as a annode.
(iii)
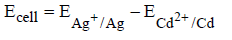
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (ii)
(c) Only (i)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
D
Question. Read the following statements.
(i) According to Faraday’s second law amounts of different substances liberated by same quantity of electricity passing through the electrolytic solution are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights.
(ii) 1 F = 96487 Cmol–1 = 96500 Cmol–1 (for more accurate calculation).
(iii) As per electrode reactions
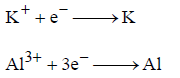
one mole of K+ and Al3+ require 1(1F) and 3(3F) mol of electrons respectively.
Which of the following is the correct coding for the above statements?
(a) TTT
(b) FFT
(c) TFT
(d) FTF
Answer
C
Question.
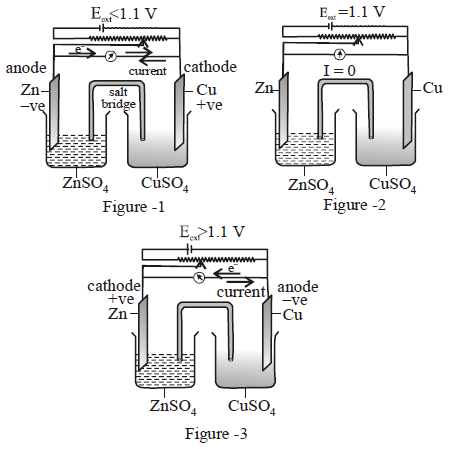
(i) Figure 1 represents electrochemical and Figure 3 represents electrolytic cell.
(ii) Figure 2 represents electrolytic and Figure 3 represents electrochemical cell.
(iii) Figure 2 represents a cell which is not working i.e. no current flows through the cell.
(iv) Energy conversion shown in Figure 1 is chemical to electrical whereas energy conversion shown in Figure 2 is electrical to chemical.
Which of the following is the correct coding for the statements above.
(a) TFTT
(b) TTTT
(c) TFFT
(d) FTFF
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/ are incorrect for corrosion of iron?
(i) Reaction occurring at anode is

(ii) Reaction occurring at cathode is

(iii) Rust is Fe2O3.xH2O
(iv) H+ involved in corrosion reaction is provided from H2CO3 which is formed due to dissolution of carbon dioxide from air in to water.
(a) (iv) only
(b) (i) only
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(i) Molar conductivity for strong electrolytes increases gradually and of weak electrolytes increases rapidly on dilution.
(ii) If α is the degree of dissociation of weak electrolytes.

(iii) Molar conductivity of CaX2 increases rapidly on dilution.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) only
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer
D
Question. Read the following statements carefully.
(i) According to a convention cell potential of hydrogen electrode (S.H.E.) is considered to be zero at all temperatures.
(ii) e.m.f. of the cell Pt(s)/H2(g, 1 bar)/H+(aq, 1 M) || Zn2+ (aq,1M) / Zn is – 0.76. This negative value indicates that Zn2+ ion reduces less easily then H+ ions.
(iii) Copper does not dissolve in HCl but dissolves in HNO3 as in nitric acid it gets oxidised by nitrate ion.
(iv) Inert metals like Pt or Au are used in certain electrodes i.e., these metals does not participate in reaction but provide surface for oxidation and reduction reactions.
(v) Fluorine has the highest electrode potential thereby making it strongest oxidising agent whereas lithium with lowest electrode potential is the weakest oxidising and strongest reducing agent.Which of the following is the correct coding for the statements above.
(a) TTTTT
(b) TTFTF
(c) FFTTT
(d) FFFTT
Answer
A
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Cell in which electrolyte (p) H2 – O2 fuel cell
is a paste of KOH and
ZnO. This cell is used in
low current devices like
hearing aids, watches, etc.
(B) Cell in which 38% H2SO4 (q) Mercury cell
solution is used as an
electrolyte.
(C) Cell in which vapours (r) Lead storage battery
produced during electrochemical
reaction were
condensed and added
to drinking water
(D) Cell having longer life (s) Nickel – Cadmium cell
than lead storage cell
and is expensive to
manufacture
(a) (A) – (r), (B) – (q), (C) – (p), (D) – (s)
(b) (A) – (q), (B) – (r), (C) – (p), (D) – (s)
(c) (A) – (q), (B) – (r), (C) – (p), D) – (s)
(d) (A) – (q), (B) – (r), (C) – (s), (D) – (p)
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns.

(a) (A) – (p), (B) – (s), (C) – (q), (D) – (r)
(b) (A) – (s), (B) – (p), (C) – (q), (D) – (r)
(c) (A) – (s), (B) – (q), (C) – (p), (D) – (r)
(d) (A) – (s), (B) – (p), (C) – (r), (D) – (q)
Answer
B
Question. Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below :
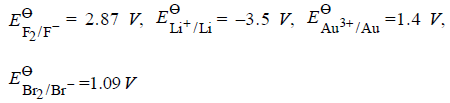
Column-I Column-II
(A) F2 (p) metal is the strongest reducing agent.
(B) Li (q) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+
(C) Au3+ (r) non metal which is the best oxidising agent
(D) Br– (s) metal ion which is an oxidising agent
(a) (A) – (r), (B) – (p), (C) – (s), (D) – (q)
(b) (A) – (p), (B) – (r), (C) – (s), (D) – (q)
(c) (A) – (q), (B) – (p), (C) – (s), (D) – (r)
(d) (A) – (r), (B) – (s), (C) – (p), (D) – (q)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.

(a) (A) – (p), (B) – (r), (C) – (q), (D) – (s)
(b) (A) – (s), (B) – (q), (C) – (r), (D) – (p)
(c) (A) – (r), (B) – (s), (C) – (q), (D) – (p)
(d) (A) – (s), (B) – (r), (C) – (q), (D) – (p)
Answer
D
Question. Match the Column-I (functioning of Daniel cell) with Column-II (value of Eext) and choose the correct option.
Column-I Column-II
(A) Flow of electrons from (p) E = 1.1 V
Cu to Zn and current
flows from Zn to Cu
(B) No flow of electrons (q) E < 1.1 V
or current
(C) Zn dissolves at anode (r) E > 1.1 V
and copper deposits at
cathode
(a) (A) – (q), (B) – (p), (C) – (r)
(b) (A) – (r), (B) – (p), (C) – (q)
(c) (A) – (p), (B) – (r), (C) – (q)
(d) (A) – (r), (B) – (q), (C) – (p)
Answer
B
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keep on increasing.
Reason : On increasing dilution, degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and molality of ions also increases.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Galvanised iron does not rust.
Reason : Zinc has a more negative electrode potential than iron.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The resistivity for a substance is its resistance when it is one meter long and its area of cross section is one square meter.
Reason : The SI units of resistivity is ohm metre (Ωm).
Answer
B

We hope the above multiple choice questions for Class 12 Chemistry for Chapter 3 Electrochemistry provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Electrochemistry is an important chapter in Class 12 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 12 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
