DK Goel Solutions Chapter 9 Books of Original Entry Journal
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9 Books of Original Entry Journal. These answers and solutions to questions given in chapter have been prepared based on the latest Class 11 DK Goel Accountancy book issued for current academic year.
This chapter in DK Goel Accountancy Class 11 highlights a crystal clear picture instilling the knowledge about journal entries within the students.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9 also includes a lot of good quality questions which are very well designed and can be very helpful to understand the concepts for Class 11 students of Accountancy.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 11 Accountancy
Books of Original Entry Journal DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy Solutions
Students can refer below for solutions for all questions given in your DK Goel Accountancy Textbook for Class 11 in Chapter 9
Very Short Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9
Question 1:
Solution 1: Journal is a main entry book or an original entry book in which the event is first entered in a linear order or sequence. As all transactions are originally documented in it, the document is called the Book of Original Entry.
Question 2:
Solution 2: All the transactions are recorded firstly in the journal so it is called book of original entry.
Question 3:
Solution 3: The process by which the transaction is reported in the journal is called journalising.
Question 4:
Solution 4: The benefit of a report is the compilation of financial data in chronological order.
Question 5:
Solution 5: The journal’s only drawback is that it is difficult to document all the heavy and cumbersome transactions.
Question 6:
Solution 6: Every transaction has a short summary after each entry is known as the narrative.
Question 7:
Solution 7: Ledger Folio or L.F. It’s the number of the page where the journal poses. In the document, the page number is registered.
Question 8:
Solution 8: When, on the same day, two or more purchases belonging to one individual account take place. In this case, only one entry is passed, instead of logging different entries. This form of journal entry is known as the journal entry compound.
Question 9:
Solution 9: The first entry in the Journal is moved to the preceding year’s closing balances ledger. The opening entry is called it. The balance sheet prepared at the end of the year displays each asset and liability’s closing balances and forms the basis for this opening entry.
Question 10:
Solution 10: Below is the Journal of withdrawing of goods by the proprietor
| Drawings A/c | Dr. | ||||
| To Purchases A/c | |||||
| (Being goods withdrawing by the owner) |
Question 11:
Solution 11: Machine account is debited if wages are paid for the installation of a machine.
Practical Question for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9
Question 1:
Solution 1:

Point in Mind DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9 :-
Journal is a prime entry book or an original entry book in which the transaction is first entered in a linear order or sequence. As all transactions are originally documented in it, the document is called the Book of Original Entry.
Question 2:
Solution 2:
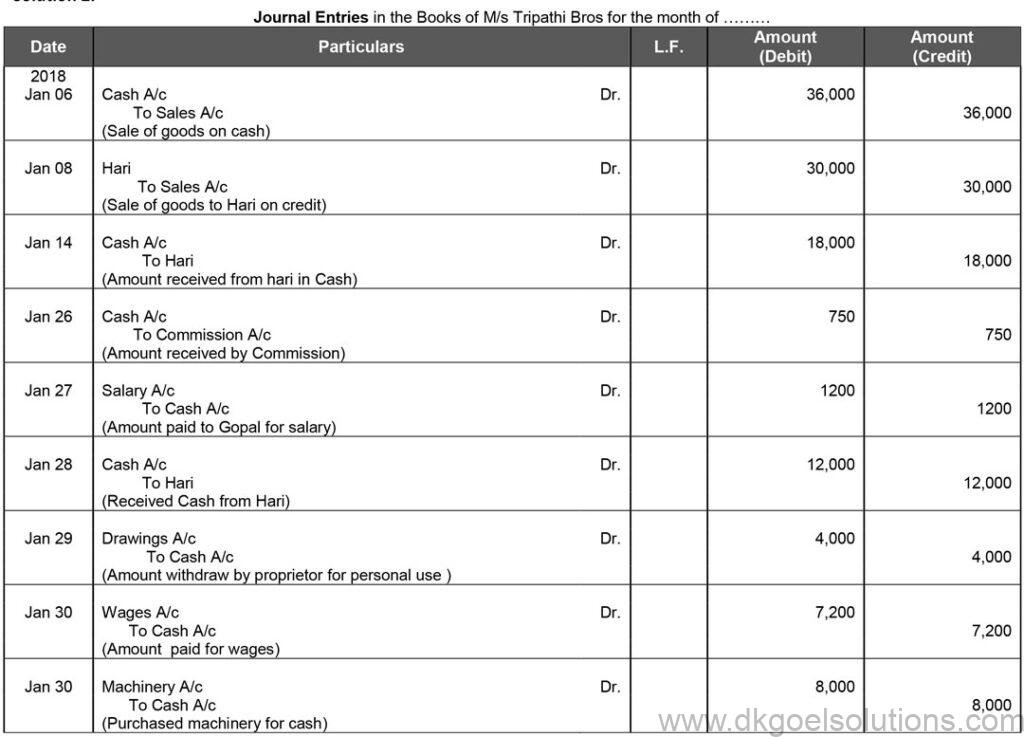
Point in Mind DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9 :- The first entry in the Journal is passed to record closing balances of the previous year. It is called the opening entry. The Balance Sheet prepared at the end of the year shows the closing balances of each asset and liability and forms the basis for this opening entry.
Question 3:
Solution 3:
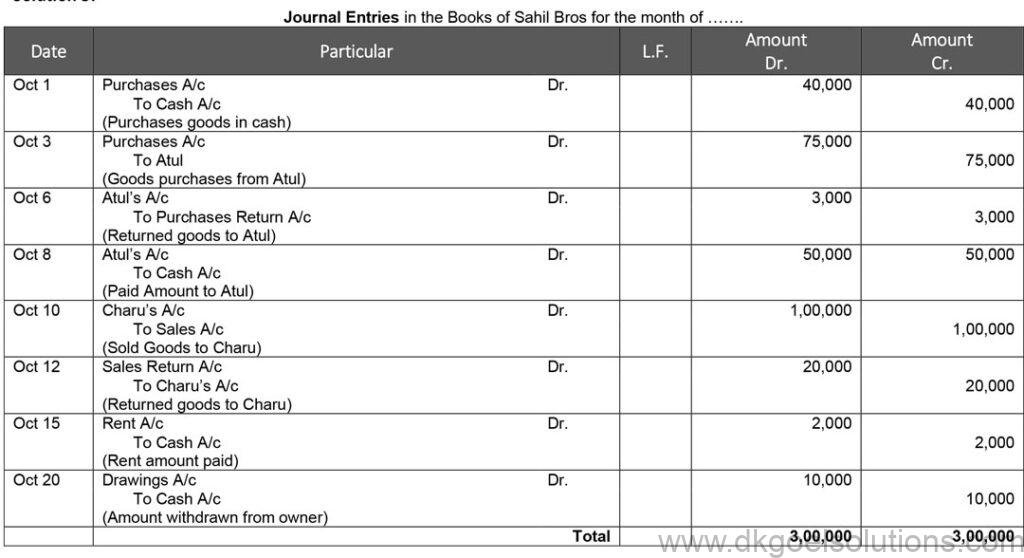
Working Note:-
1.) Sale = 1,00,000
Sales Return = Rs. 1,00,000 × 20% = Rs. 20,000
Question 4:
Solution 4:

Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 25,000
Calculation of Trade discount:-
Trade discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 25,000 × 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 5,000
Calculation Sales:-
Sales = Rs. 25,000 – Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 20,000
Question 5:
Solution 5:

Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of discount
Discount Amount = Rs. 10,000 × 5% = Rs. 500
Amount paid to Gopal = Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 500
= Rs. 9,500
Question 6:
Solution 6:

Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 50,000 and Trade discount = 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 50,000 × 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 7,500
Sales = Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 7,500
Sales = Rs. 42,500
2.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 60,000 and Trade discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 60,000 × 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 60,000 – Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 54,000
Point in mind:-
The following are the two advantages of allowing Trade Discount:
1.) Increased sales due to high quantity involved in sales.
2.) Increased customer base due to low prices and discount offers.
Question 7:
Solution 7:
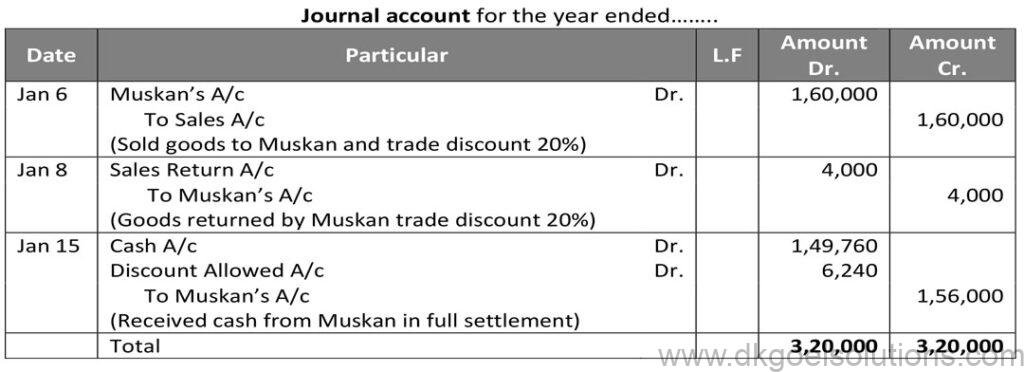
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 2,00,000 and Trade discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,00,000 × 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 40,000
Sales = Rs. 2,00,000 – Rs. 40,000
Sales = Rs. 1,60,000
Question 8:
Solution 8:
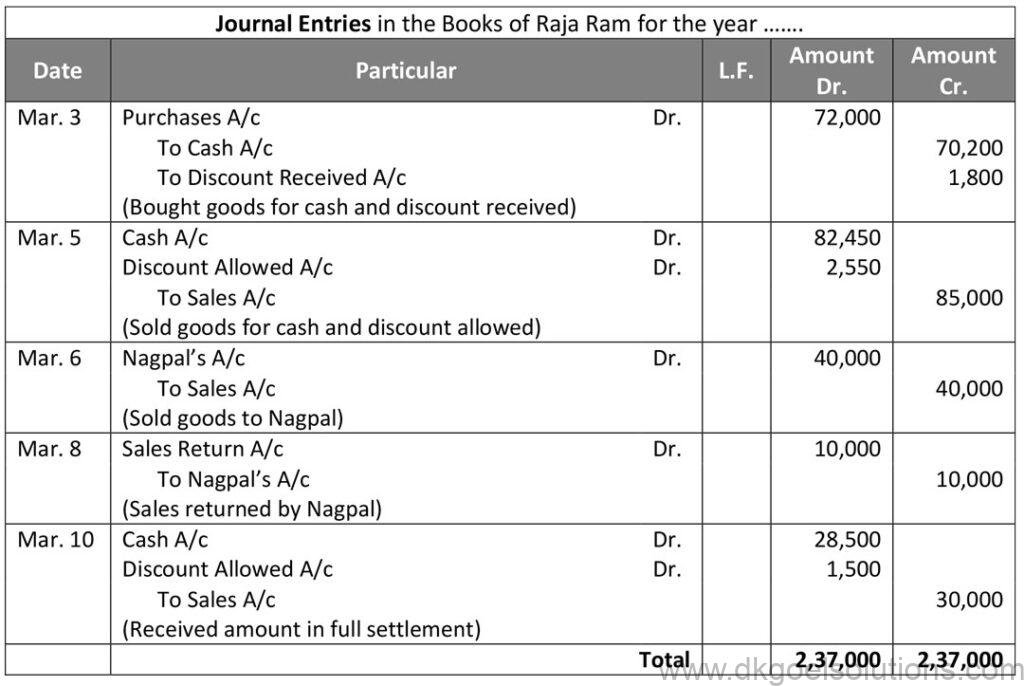
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 80,000 and Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 80,000 × 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 8,000
Sales = Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 8,000
Sales = Rs. 72,000
Cash discount = 2.5%
Cash discount = Rs. 72,000 × 2.5%
Cash discount = Rs. 1,800
Total Amount Received = Rs. 72,000 – Rs. 1,800
Total Amount Received = Rs. 70,200
Question 9:
Solution 9:
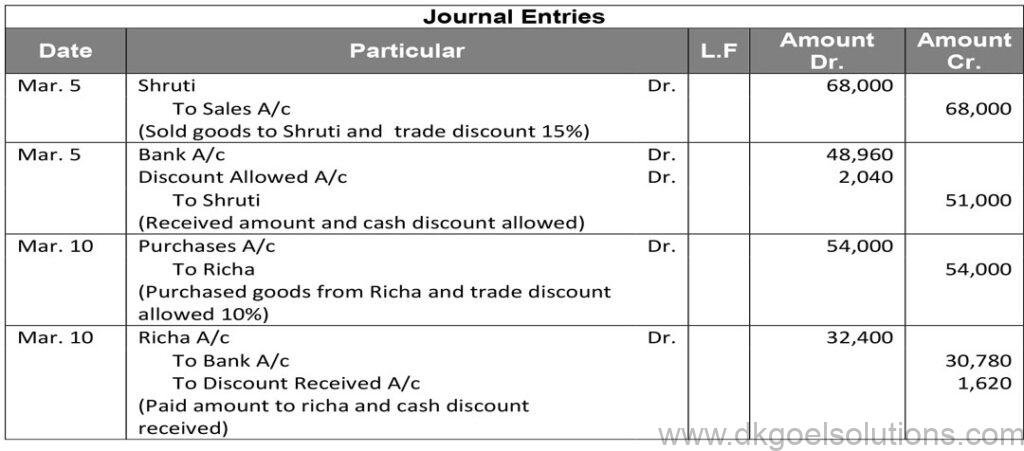
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 80,000 and Trade Discount = 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 80,000 × 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 12,000
Sales = Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 12,000
Sales = Rs. 68,000
Amount received = Rs. 68000 × 75%
Amount received = Rs. 51,000
Cash discount = 4%
Discount amount = Rs. 51,000 × 4%
Discount amount = Rs. 2,040
Amount Received = Rs. 51,000 – Rs. 2,020
Amount Received = Rs. 48,960
2.) Calculation of purchases price
List price = Rs. 60,000 and Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 60,000 × 10% = Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 60,000 – Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 54,000
Amount received = Rs. 54,000 × 60%
Amount received = Rs. 32,400
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 32,400 × 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,620
Amount Received = Rs. 32,400 – Rs. 1,620
Amount Received = Rs. 30,780
Question 10:
Question 10:

Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of amount paid to hanry:-
List price = Rs. 50,000 and Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 50,000 × 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 45,000
Amount received = Rs. 45,000 × 60%
Amount received = Rs. 27,000
Cash discount = 4%
Discount amount = Rs. 27,000 × 4%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,080
Amount Received = Rs. 27,000 – Rs. 1,080
Amount Received = Rs. 25,920
Question 11:
Solution 11:
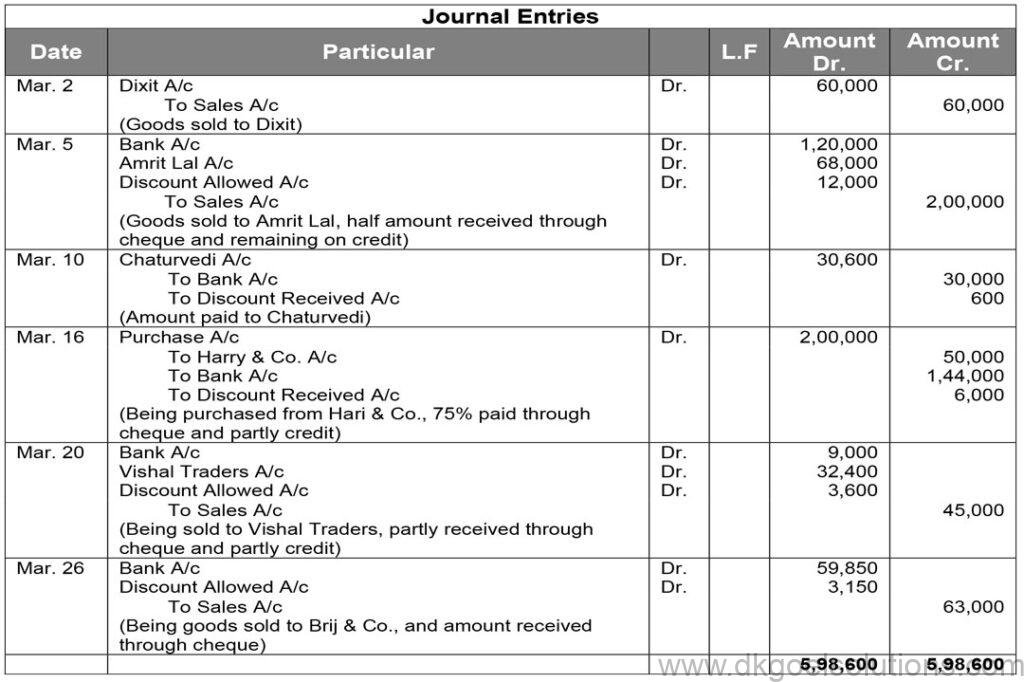
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 2,50,000 and Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,50,000 × 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 50,000
Sales = Rs. 2,50,000 – Rs. 50,000
Sales = Rs. 2,00,000
Amount received = Rs. 1,20,000
Cash discount = 10%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,20,000 × 10%
Discount amount = Rs. 12,000
Amount Received = Rs. 1,20,000 – Rs. 12,000
Amount Received = Rs. 1,08,000
Question 12:
Solution 12:

Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of amount paid by bhushan:-
List price = Rs. 10,000 and Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 1,00,000 × 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 1,000
Sales = Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 1,000
Sales = Rs. 9,000
Point in Mind DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9:-
Trade Discount is allowed by the seller on the purchase of goods in large quantities. It is usually by the wholesalers to the retail shop owners who further sell the goods to the consumer. Trade Discount is deducted in the invoice from sale price and is not recorded in the books of account.
Cash Discount is allowed by the seller to the customers to encourage prompt or early payment. It is allowed as a per cent of invoice value or payment made say @ 5% of invoice value to the buyer. Cash discount is calculated after deducting trade discount from the invoice price.
Question 13:
Solution 13:
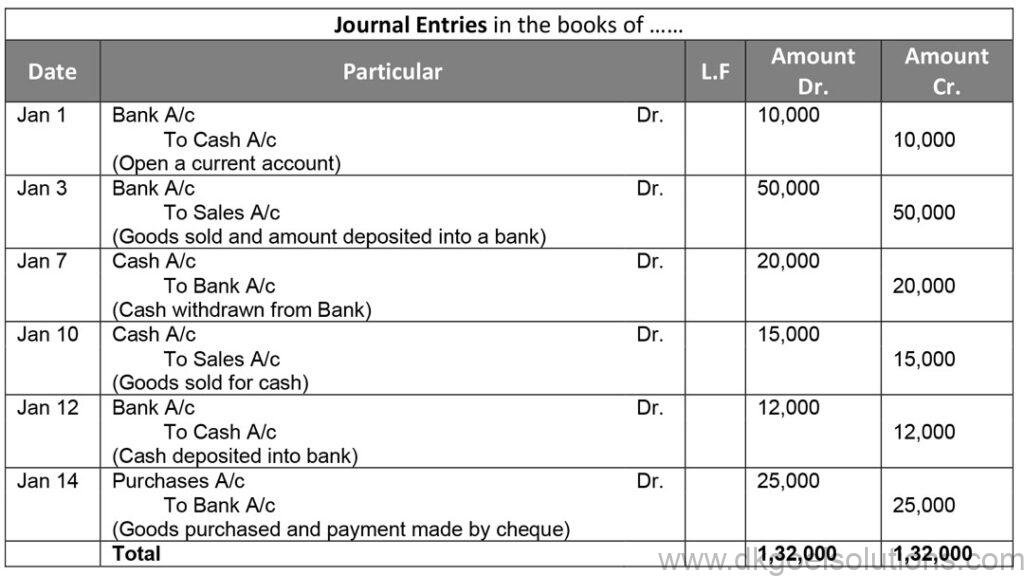
Point in Mind:-
- Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
- Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
Question 14 (A):
Solution 14 (A):
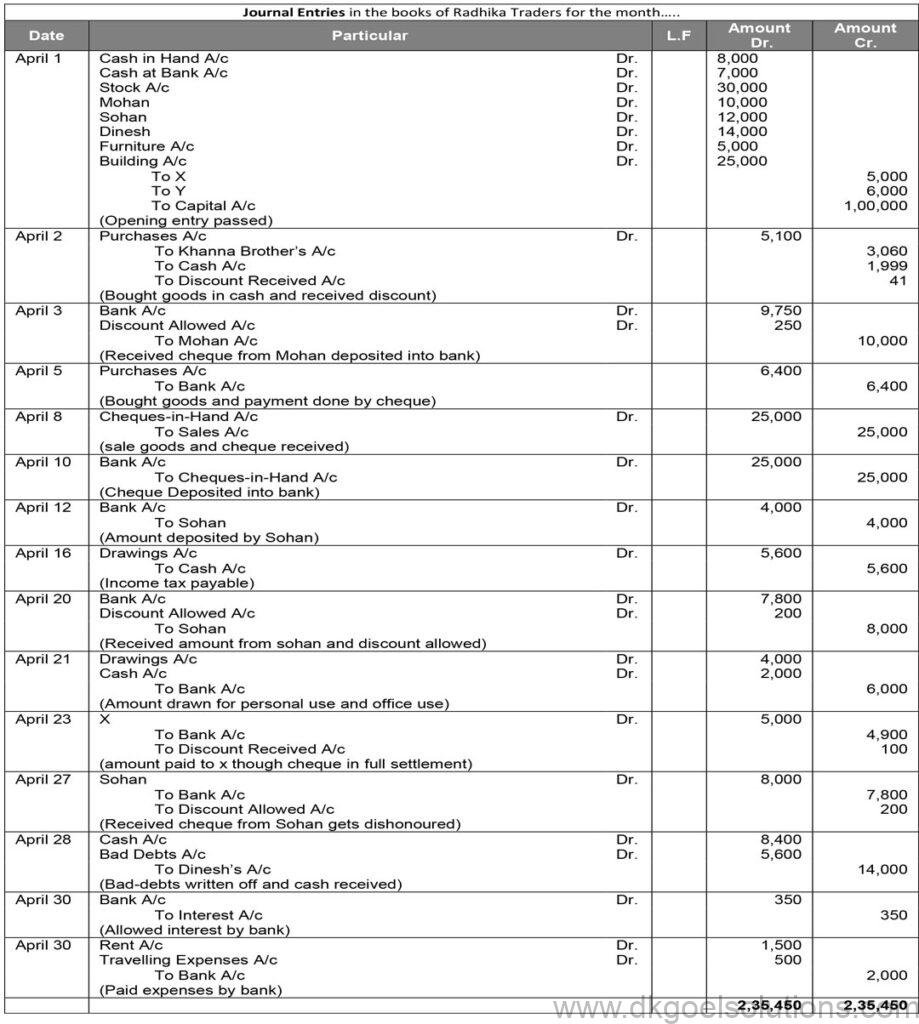
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of amount paid by bhushan:-
List price = Rs. 8,000 and Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 8,000 × 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 1,600
Sales = Rs. 8,000 – Rs. 1,600
Sales = Rs. 6,400
Point in mind:-
1.) Increased sales due to high quantity involved in sales.
2.) Increased customer base due to low prices and discount offers.
Question 14 (B):
Solution 14 (B):

Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 20,000 and Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 20,000 × 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 18,000
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 18,000 × 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 900
Amount Received = Rs. 18,000 – Rs. 900
Amount Received = Rs. 17,100
Question 15:
Solution 15:

Question 16:
Solution 16:
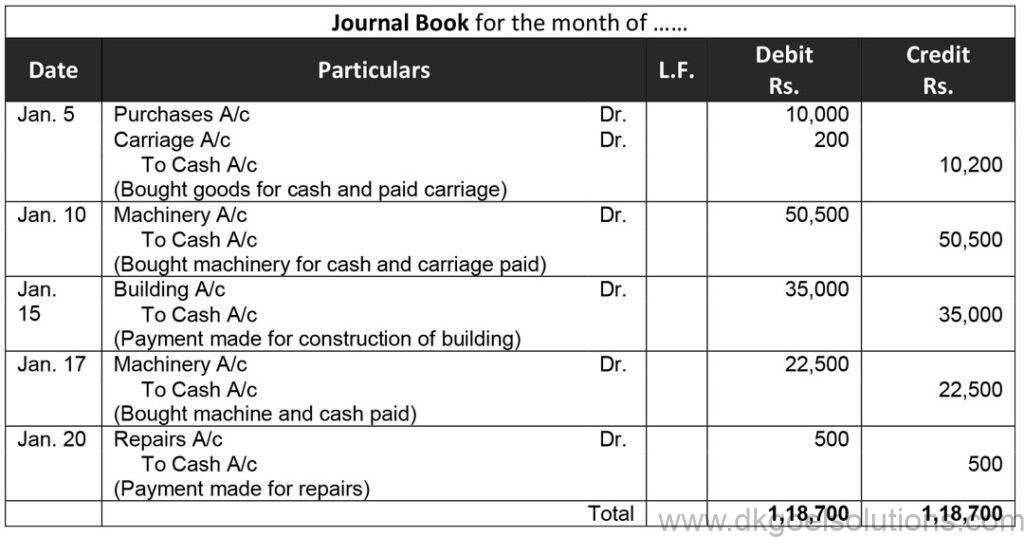
Question 17:
Solution 17:

Question 18:
Solution 18:

Question 19:
Solution 19:

Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 10,000 and Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 10,000 × 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 8,000
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 8,000 × 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 400
Amount Received = Rs. 8,000 – Rs. 400
Amount Received = Rs. 7,600
Question 20:
Solution 20:

Question 21:
Solution 21:

Question 22:
Solution 22:

Question 23:
Solution 23:

Question 24:
Solution 24:

Question 25:
Solution 25:
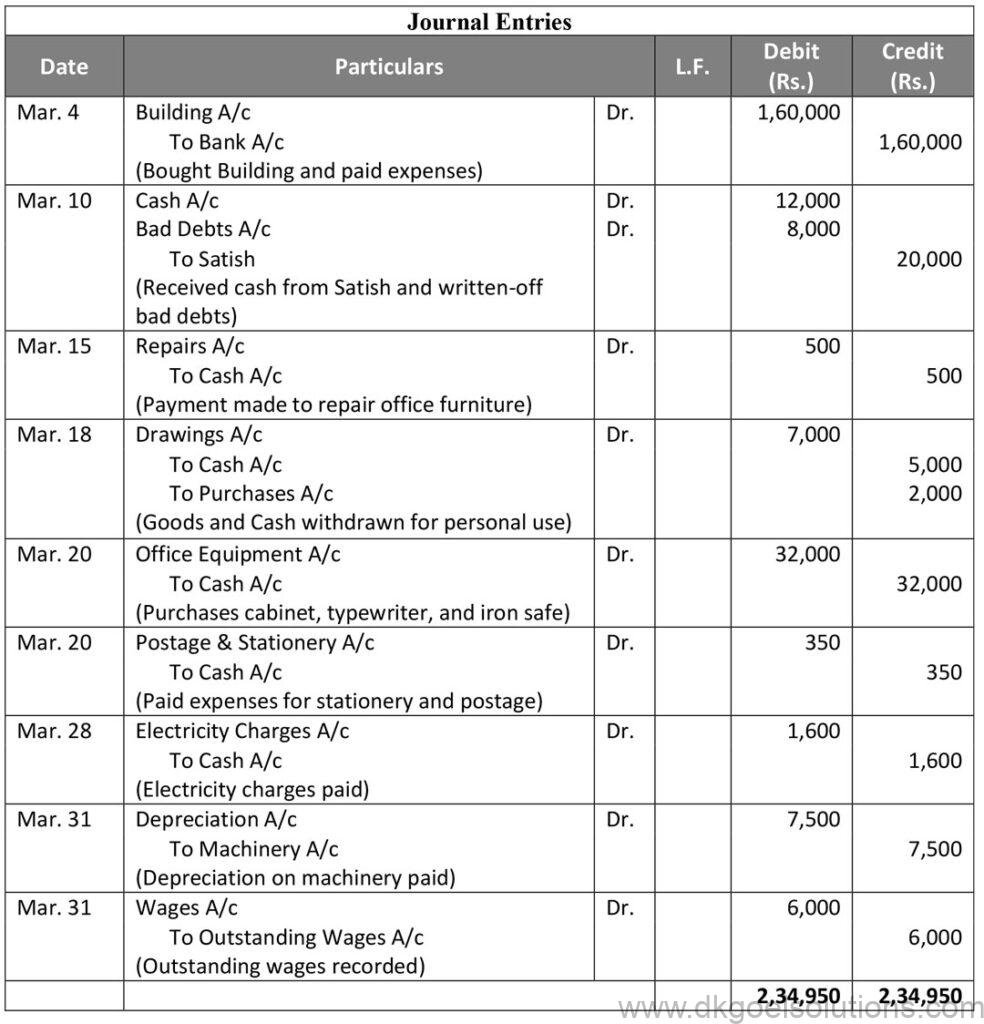
Question 26:
Solution 26:

Question 27:
Solution 27:
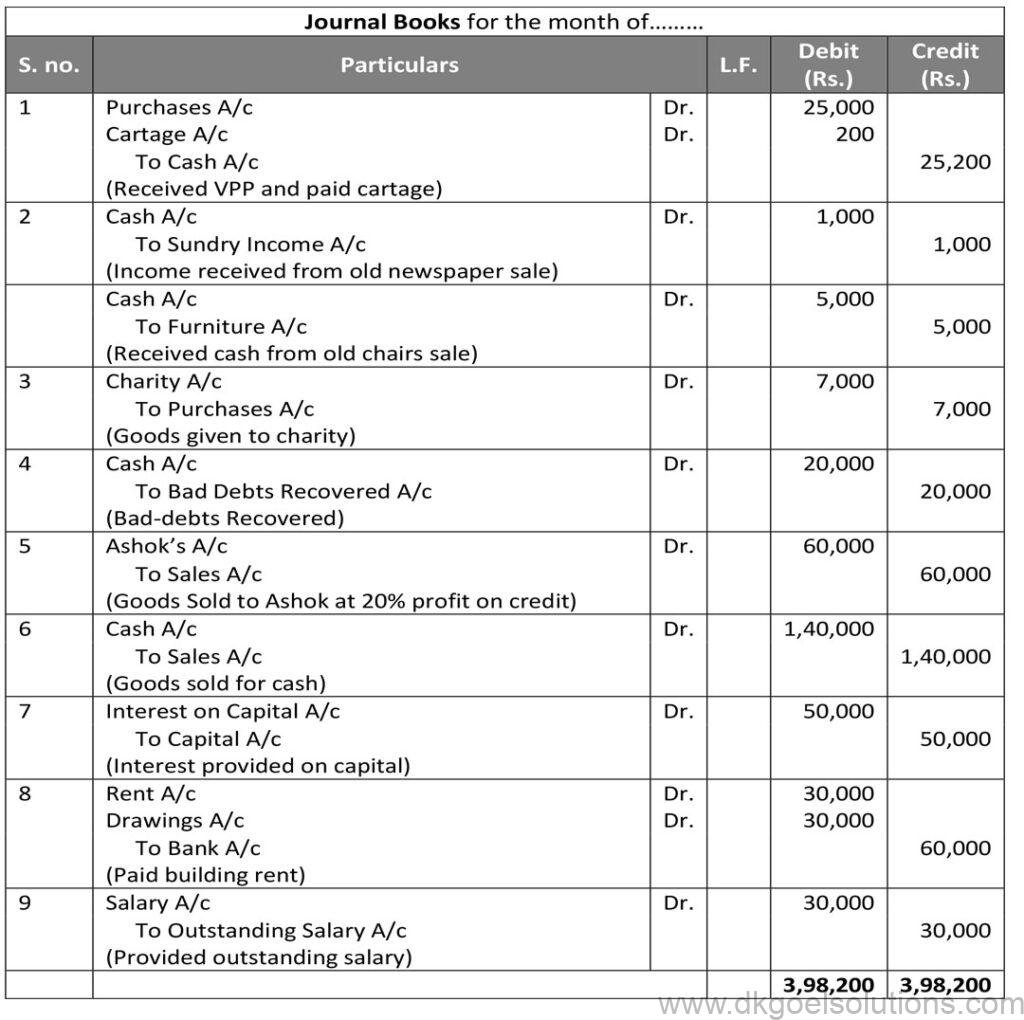
Question 28:
Solution 28:

Question 29:
Solution 29:
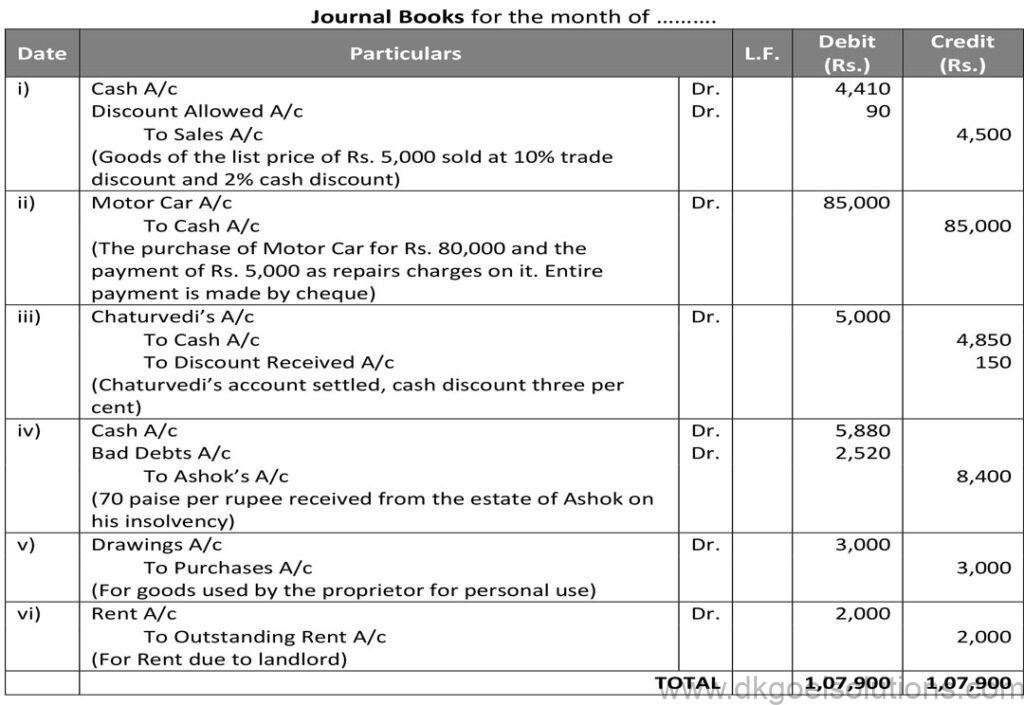
Question 30:
Solution 30:

Question 31:
Solution 31:
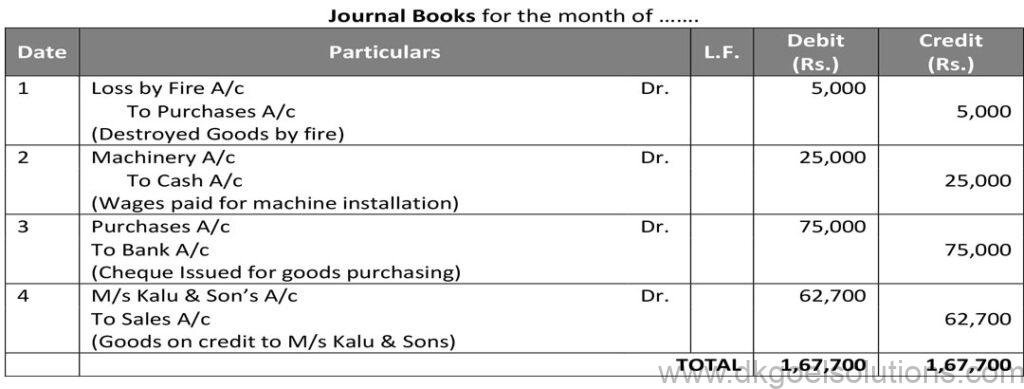
Working Note:-
Calculation selling price of the goods sold to M/s Kalu & Sons
Cost = Rs. 60,000
Profit = Rs. 60,000 × 10%
Profit = Rs. 6,000
List Price = Cost price + Profit
List Price = Rs. 60,000 + Rs. 6,000
List Price = 66,000
Trade discount = 5%
Trade discount = List Price × % of trade discount
Trade discount = Rs. 66,000 × 5%
Trade discount = Rs. 3,300
Sale price = List Price – Trade discount
Sale price = 66,000 – 3,300
Sale price = 62,700
Question 32:
Solution 32:
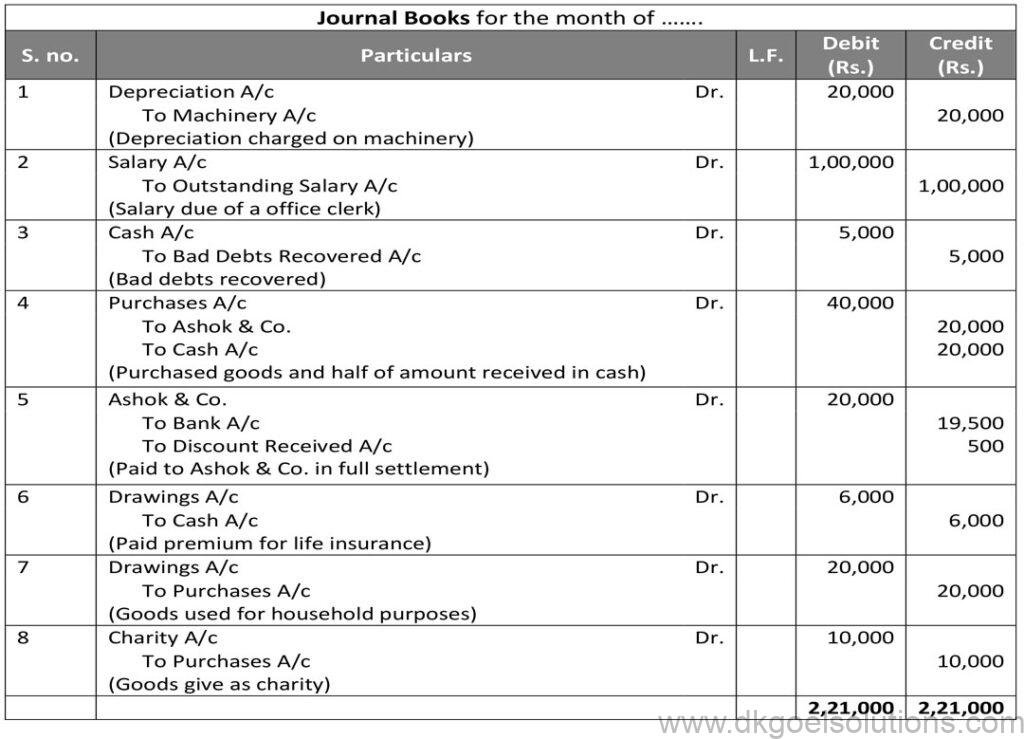
Question 33:
Solution 33:

Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 25,000 and Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 25,000 × 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 25,000 – Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 20,000
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 20,000 × 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,000
Amount Received = Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 1,000
= Rs. 19,000
Question 34:
Solution 34:

Question 35:
Solution 35:
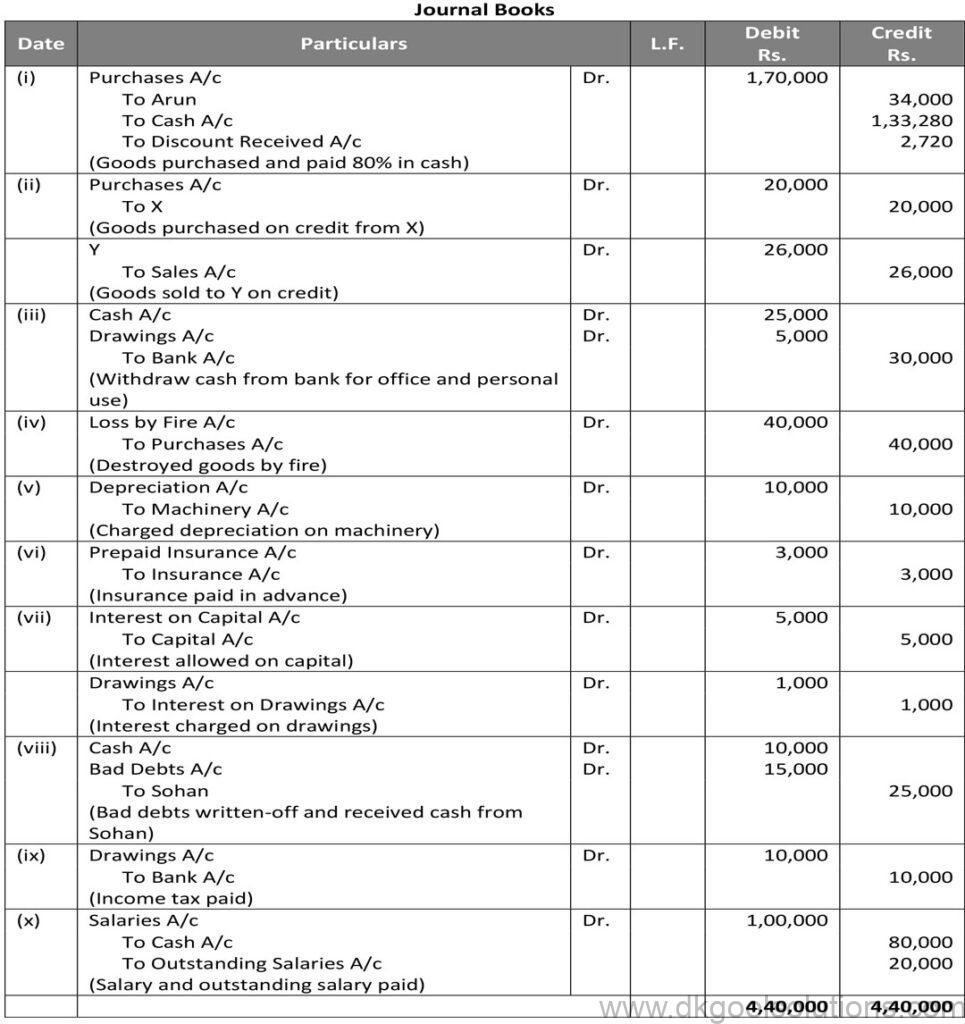
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 2,00,000 and Trade Discount = 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,00,000 × 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 30,000
Sales = Rs. 2,00,000 – Rs. 30,000
Sales = Rs. 1,70,000
Cash Received = 1,70,000 × 80%
Cash Received = Rs. 1,36,000
Cash discount = 2%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,36,000 × 2%
Discount amount = Rs. 2,720
Amount Received = Rs. 1,36,000 – Rs. 2,720
Amount Received = Rs. 1,33,280
Question 36:
Solution 36:

Point in Mind:-
- Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
- Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
Question 37:
Solution 37:
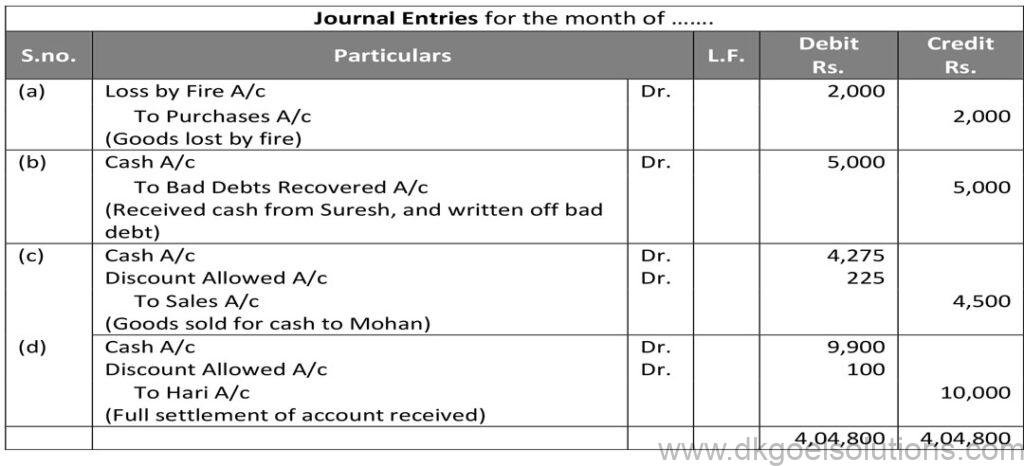
Question 38:
Solution 38:
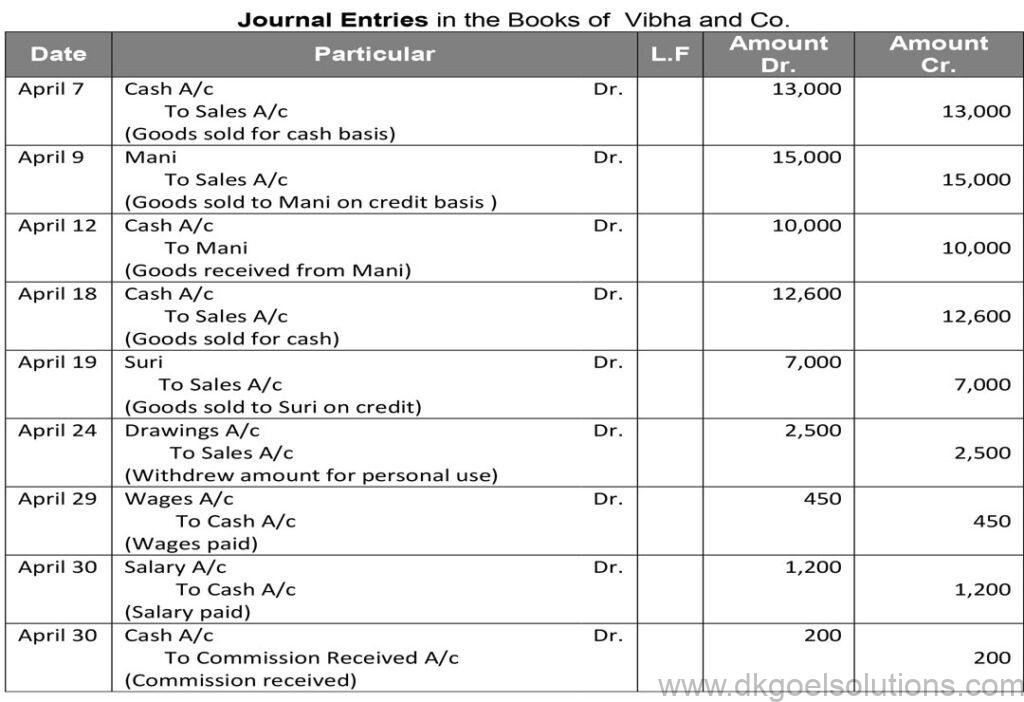
Question 39:
Solution 39:

Point of Knowledge for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9 :-
- Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
- Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.

Journal refers to the original entry book in which all financial transactions are recorded initially. Journals are recorded as soon as a financial transaction occurs to minimize the chances of omission of any transaction details. The journal is also termed the Book of Original Entry as it consists of the original report of the transactions.
Journalizing is a mechanism employing which all business transactions are recorded for a firm’s financial records. A business transaction is first entered in a journal. The journal keeps the firms keep track of all business transactions arranged in chronological order.
The prominent advantages of journals are as follows –
● Journal keeps track of all the financial transactions on a date and time basis, arranged in a proper sequence.
● Journal enlists all the transactions supported with source documents to ensure the authenticity of the transaction.
● With a journal, the business prevents the omission of any transaction as journals efficiently record every financial transaction.
As mentioned in DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 9, the general journal highlights the book of original entries, where business transactions are recorded in raw format, in order of date and time of the events. An account records the details of the transactions firstly on these journals.
The limitations of journals are as follows –
● Whenever the number of transactions of a company becomes large, the journals turn to be bulky and unmanageable.
● As the authority of the journal lies in the hands of an individual account, this prevents multiple system check-ins.
● The journals do not record the cash transactions as they are recorded in the cash books.
Ledger is basically a generalized summary of all the entries in a journal. All business transaction details flow from the journal to the ledgers. The summary from the ledgers helps the companies to efficiently design their financial statements.
Journals are titled the Books of Original Entry because all financial transactions are firstly recorded in the journals.

Nice