DK Goel Solutions Chapter 23 Accounts from Incomplete Records
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 23 Accounts from Incomplete Records. These answers have been developed based on the latest Class 11 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for current year and the questions given in each chapter.
This chapter of DK Goel solutions explains how to make accounting books based on any incomplete information that you have. Its also refers to a situation when due to lack of proper accounting related information informal accounts have to be prepared.
The chapter contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful for Class 11 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 23 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 11 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Accounts from Incomplete Records DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy Solutions
Students can refer below for solutions for all questions given in your DK Goel Accountancy Textbook for Class 11 in Chapter 23
Short Answer Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 23
Question 1:
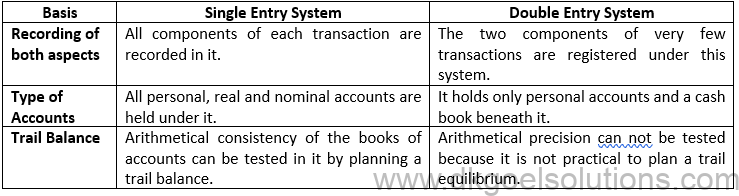
Solution 1: The features of the single entry system are below:—
1.) Management of personal accounts only:- Generally, only personal accounts in the books are prepared under this system and the actual and nominal accounts are overlooked.
2.) Cash Book Maintenance:- In this method, a cash ledger is kept, which typically combines the proprietor’s business as well as private transactions.
3.) Dependency on Original Vouchers:- One has to rely on original vouchers to collect the necessary details.
Question 2:
Solution 2: The explanations for holding documents under the single entry system are below:-
1.) Basic Procedure:- It is a fast and simple method of tracking business transactions since the rules of the double entry system do not require any special expertise.
2.) Less Expensive:- In this plan, only the cash book and some of the ledger accounts are retained. As such, relative to the double entry scheme, the personnel needed to manage the accounts is therefore lower.
3.) Useful for small issues:- This strategy is most effective for small business concerns that have only cash transactions and very little assets and liabilities.
Question 3:
Solution 3:
The flaws in unfinished documents are below:—
1.) Preparation of Trail Balance not Possible:- The procedure does not document all facets of the transaction. As such, to verify the arithmetical consistency of the books of records, a trail balance cannot be planned. This raises the likelihood of misappropriation and theft.
2.) Inadequate and unscientific method:- Due to the fact that all the components, debit and credit of a transaction are not registered, the system is incomplete and unscientific.
3.) Real benefit or loss will not be determined:- Since nominal accounts are not kept, it is difficult to prepare a trade and profit and loss report and, thus, it is not possible to ascertain with fair certainty the profit gained or loss incurred during a given time.
Question 4:
Solution 4:
Question 5:
Solution 5:
Despite the documents being missing, at the end of a given time, the businessman would like to know the trade reports also the financial status of his company. This is achieved by using one of the following two techniques:—
1.) Statement of affairs method or capital comparison method or Net worth method.
2.) Conversion into double entry method.
Question 6:
Solution 6:
According to this approach, by measuring the capital at the end and the capital at the beginning of the accounting cycle, earnings are calculated. If the capital is higher than that at the outset (with the necessary adjustments) at the conclusion of the accounting period, the differential is regarded as benefit.
Question 7:
Solution 7:
Question 8:
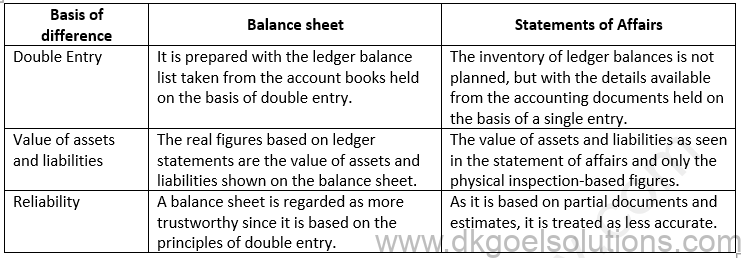
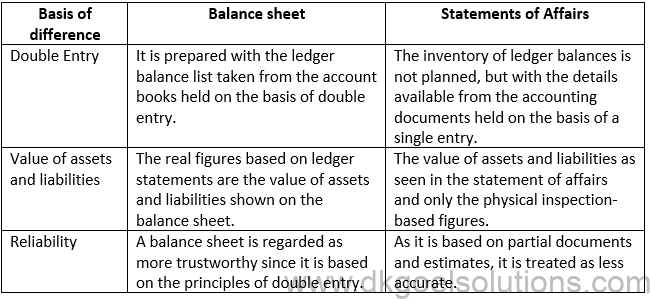
Solution 8: Statement of Affairs not called a balance sheet because;-
Question 9:
Solution 9:
Drawings are added to the closing capital on the basis that the closing capital would have expanded by this sum if the drawings had not been made. Similarly, extra money is excluded from the closing capital if the sum is deducted logically.
Question 10:
Solution 10:
It is necessary to measure the capital at the beginning of the year and again at the end of the year in order to assess benefit according to this process. Capital is determined by planning a ‘opening statement of affairs’ at the beginning and, equally, capital is calculated by preparing a ‘closing statement of affairs’ at the end.
Question 11:
Solution 11:
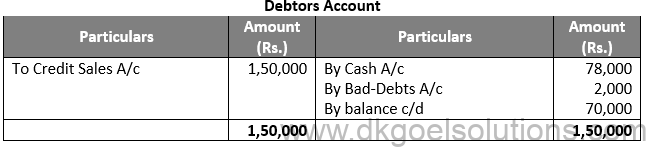
Question 12:
Solution 12:

Question 13:
Solution 13:
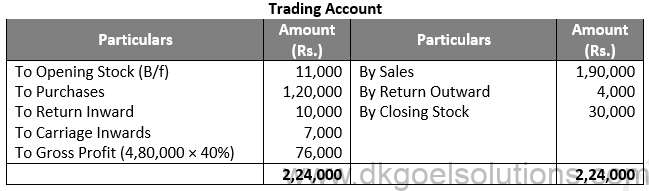
Question 14:
Solution 14:
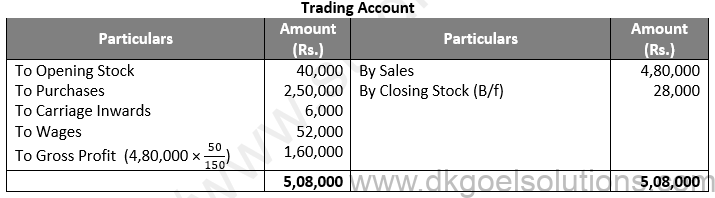
Question 15:
Solution 15:

Question 16:
Solution 16:
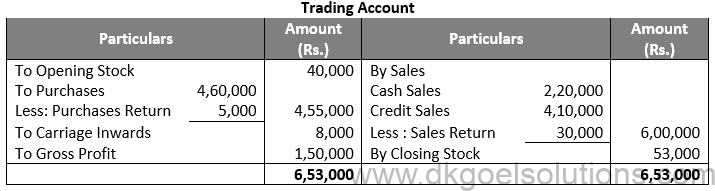
Practical Questions
Question 1:
Solution 1:
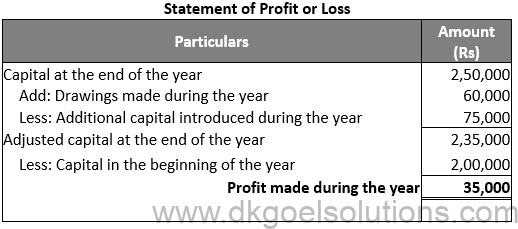
Point in mind:-
Gross Profit = Closing Capital + Drawings – Additional Capital – Opening Capital
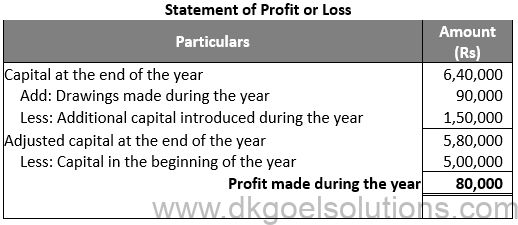
Question 2:
Solution 2:

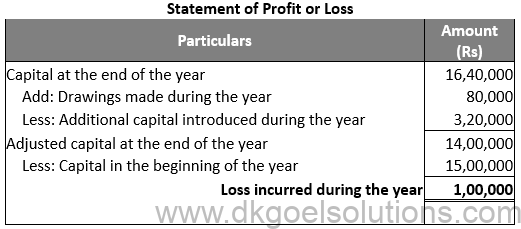
Question 3:
Solution 3:

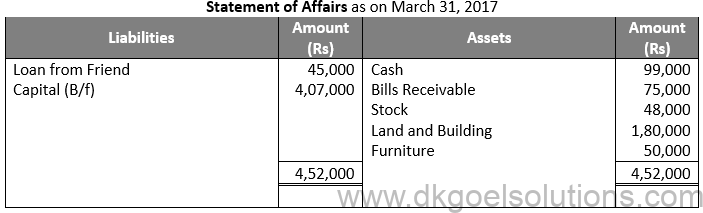
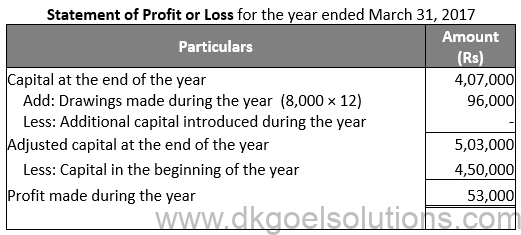
Question 4:
Solution 4:
Question 5: (A)
Solution 5 (A): Statement of Profit or Loss for the year ended December 3, 2005

Question 5 (B)
Solution 5 (B) Profit = Closing Capital + Drawings – Additional Capital – Opening Capital
Closing Capital = Opening Capital + Additional Capital + Profits – Drawings
Closing Capital = 90,000 + 40,000 + 25,000 – 17,000
Closing Capital = Rs 1,38,000
Question 6:
Solution 6: Statement of Profit or Loss for the year ended March 31, 2014
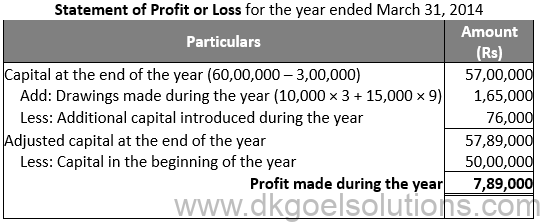
Working Note:-
Investment value = Rs. 80,000
Loss on investment = Rs. 80,000 × 5% = Rs. 4,000
Selling value of investment = Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 4,000 = Rs. 76,000
Question 7:
Solution 7

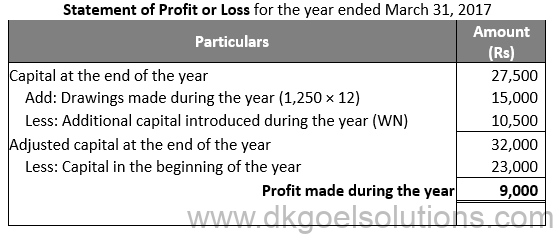
Working Note:-
Investment value = Rs. 10,000
Profit on investment = Rs. 10,000 × 5% = Rs. 500
Selling value of investment = Rs. 10,000 + Rs. 500 = Rs. 10,500
Question 8: .
Solution 8:

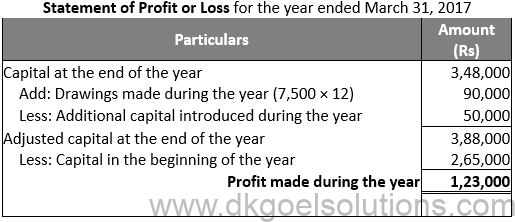
Question 9:
Solution 9:
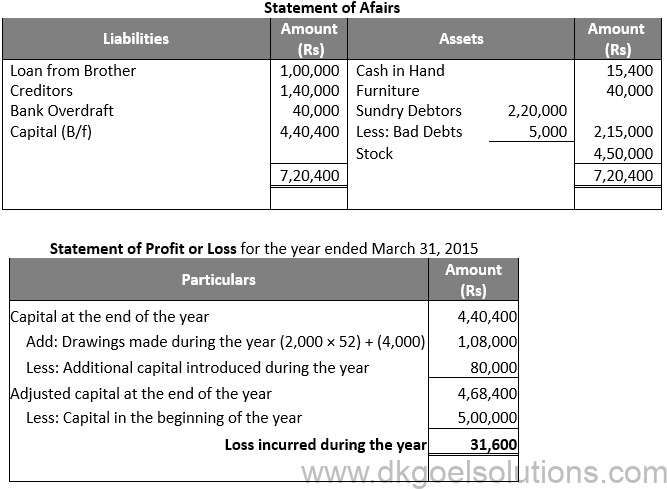
Question 10:
Solution 10:

Working Note:-
Calculation of Drawings:-
Cash withdrawn = Rs. 8,000 × 12
Cash withdrawn = Rs. 96,000
Income tax paid = Rs. 20,000
Personal Loan instalment = Rs. 15,000 × 12
Personal Loan instalment = Rs. 1,80,000
Total Drawings = Rs. 96,000 + Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 1,80,000
Total Drawings = Rs. 2,96,000
Calculation of Additional Capital:-
Value of Shares = Rs. 1,00,000
Profit = Rs. 20,000
Sale value = Rs. 1,20,000
Additional Capital = 1,20,000/2
Additional Capital = Rs. 60,000
Question 11:
Solution 11:

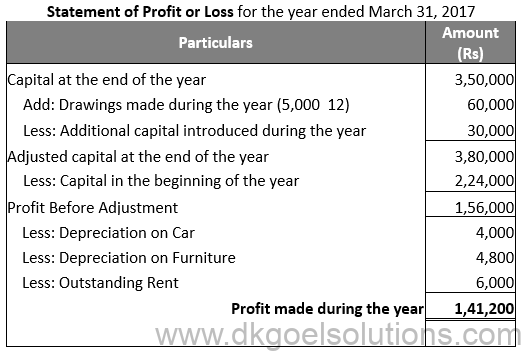
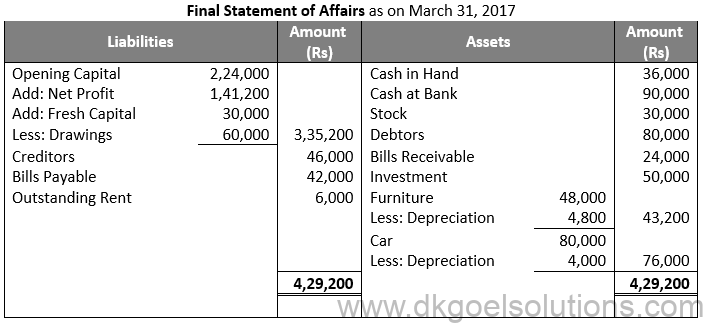
Question 12:
Solution 12:


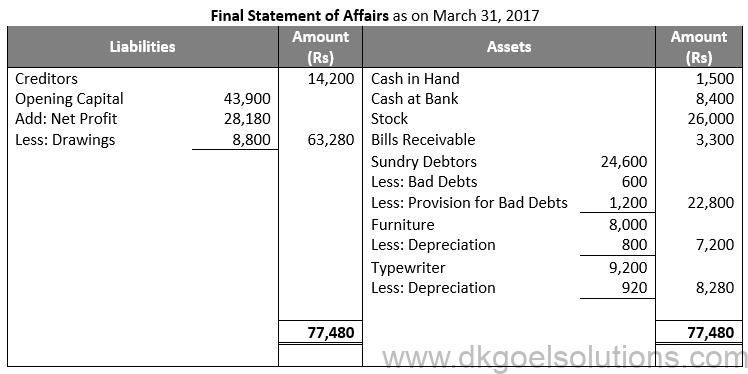
Question 13:
Solution 13:
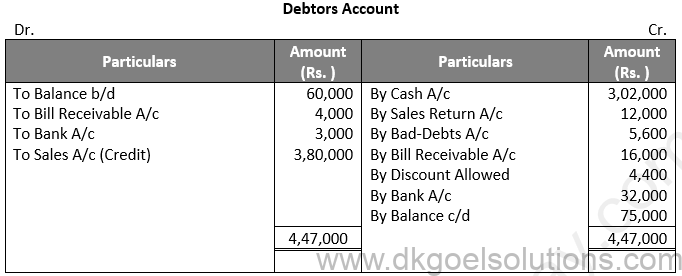
Working Note:-
Calculation of Total Sales:-
Total Cash = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
Total Cash = Rs. 1,05,000 + Rs. 3,80,00 = Rs. 4,85,000
Question 14:
Solution 14:
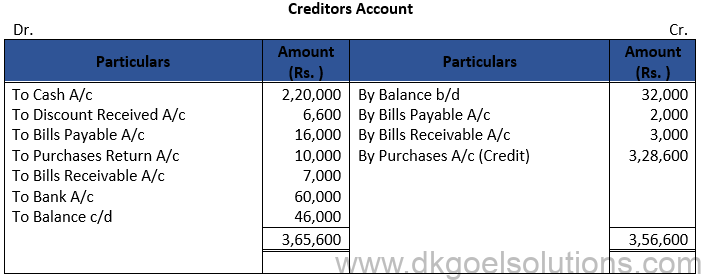
Question 15:
Solution 15:

Working Note:-

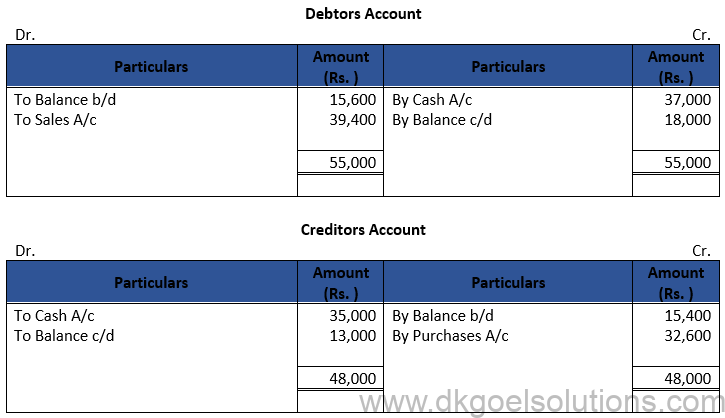
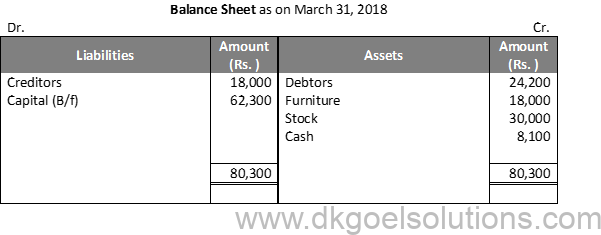
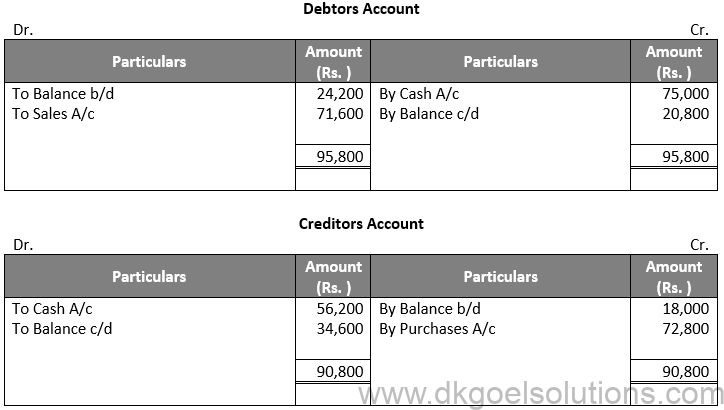
Question 16:
Solution 16:
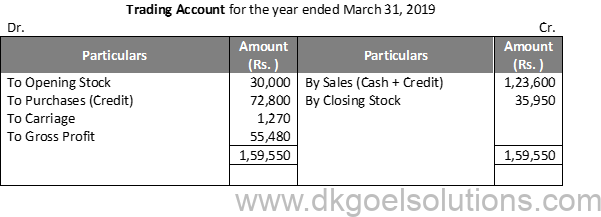
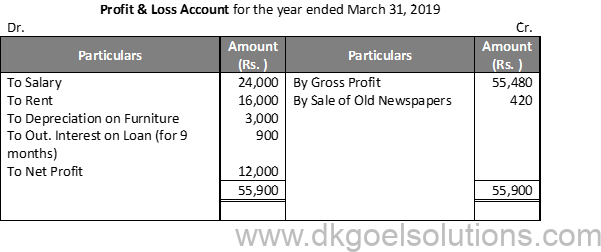
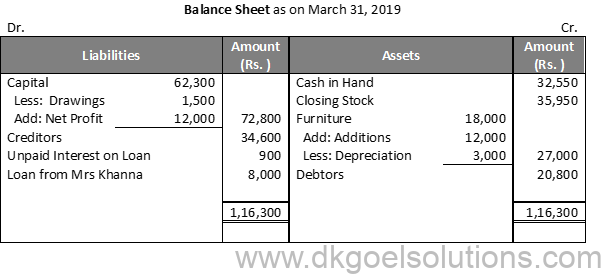
Working Note:-
Question 17:
Solution 17:

Working Note:-

Question 18:
Solution 18:
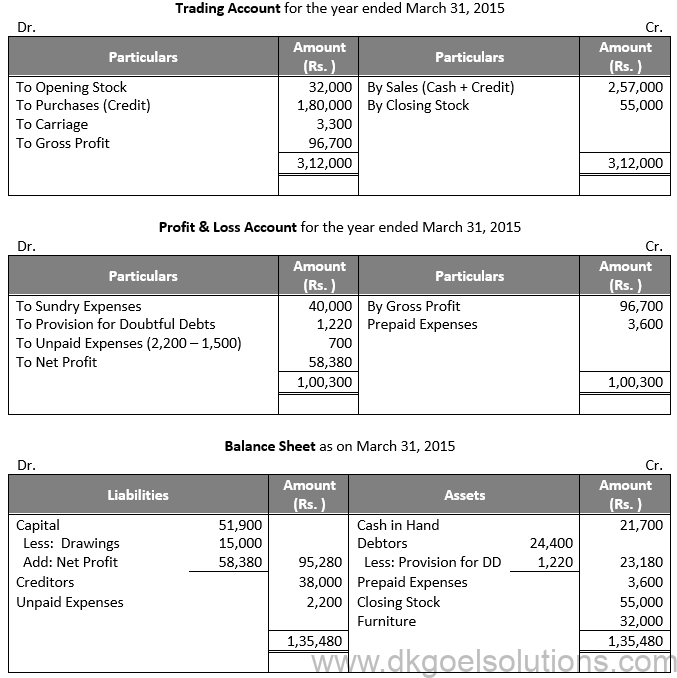
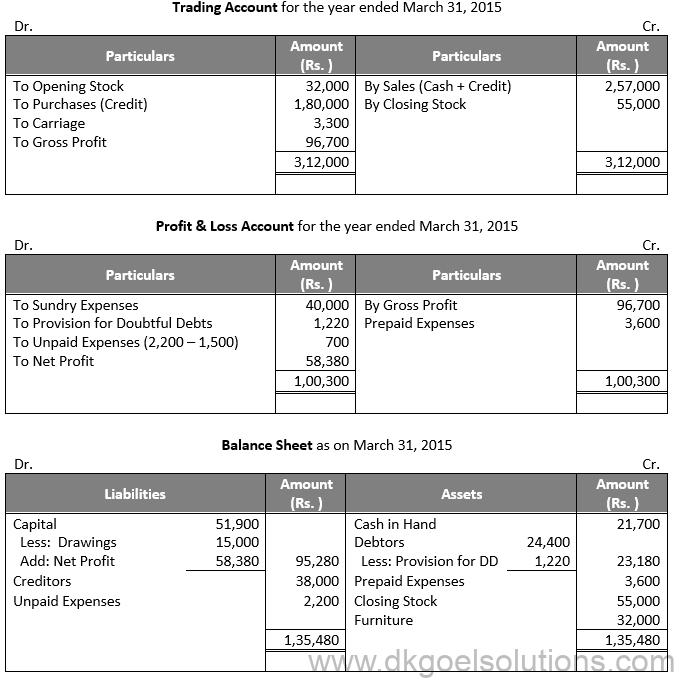
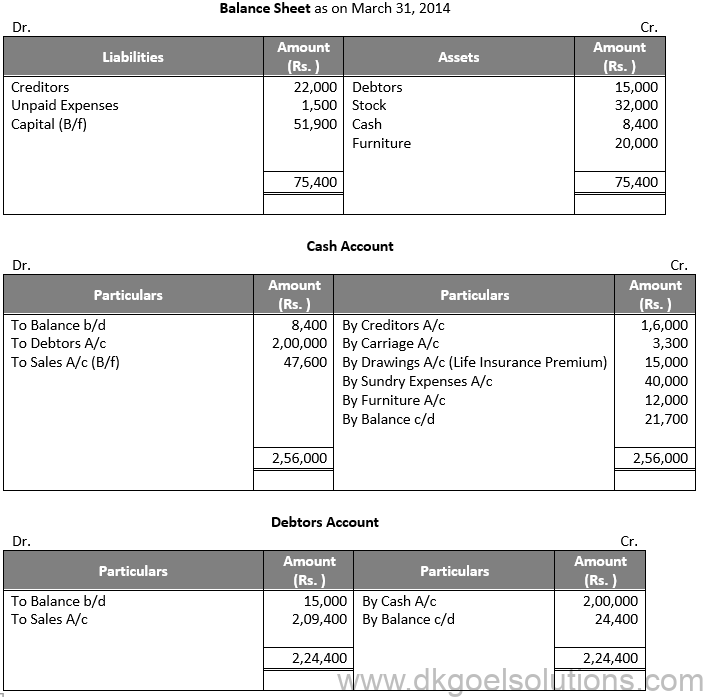
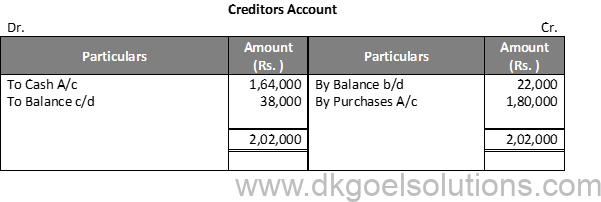
Working Note:-
Question 19:
Solution 19:
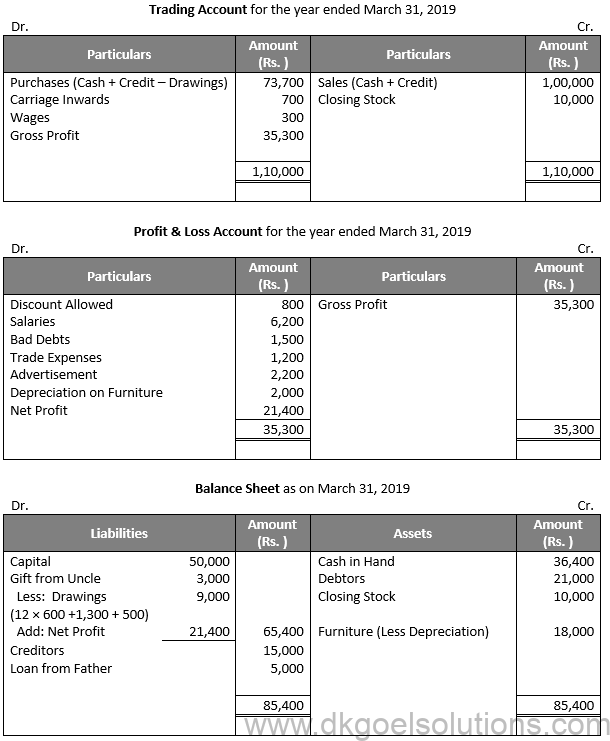
Working Note:-
Question 20:
Solution 20:
Rate of Gross Profit (on cost) = 25%
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = Rs. 1,20,000 × 20%
Gross Profit = Rs .24,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Net Sales – Gross Profit
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 1,20,000 – Rs. 24,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 96,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
Closing Stock = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Cost of Goods Sold
Closing Stock = Rs. 16,000 + Rs. 93,000 + Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 96,000
Closing Stock = Rs. 33,000
Question 21:
Solution 21:
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 40%
Gross Profit = 40% × (2,05,000 – 5,000)
Gross Profit = 80,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Net Sales –Gross Profit
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 2,00,000 – Rs. 80,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 1,20,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
1,20,000 = Opening Stock + (Rs. 1,24,000 – Rs. 4,000) + Rs. 8,000 – Rs. 36,000
Opening Stock = Rs. 1,20,000 – Rs. 1,20,000 – Rs. 8,000 + Rs. 36,000
Opening Stock = Rs. 28,000
Question 22:
Solution 22:
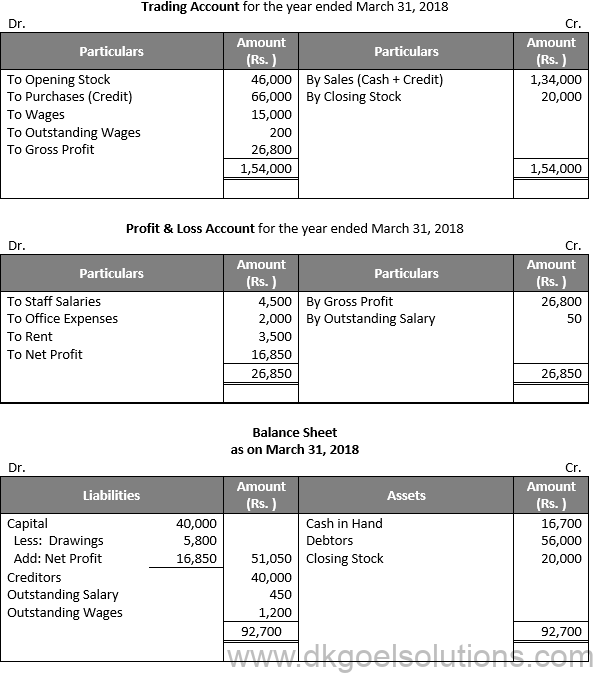
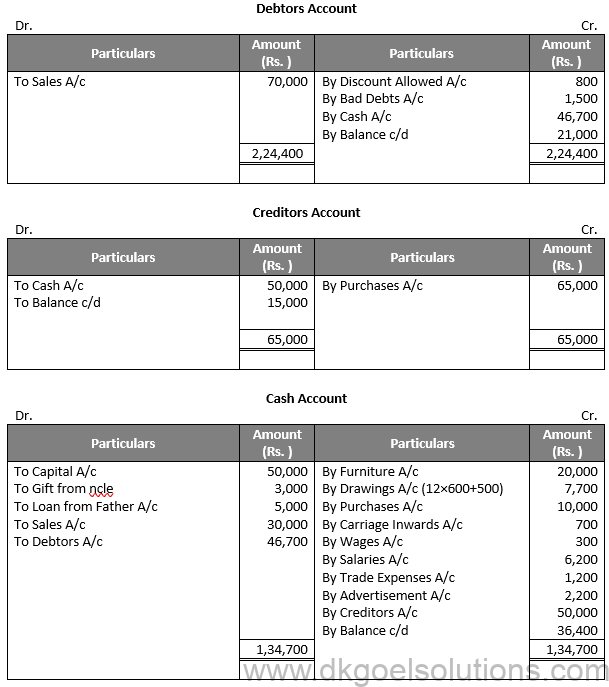
Working Note:-

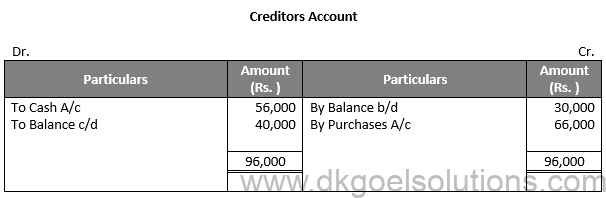
Rate of Gross Profit (on cost) = 25%
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = 20% of (30,000 + 1,04,000)
Gross Profit = 26,800
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Net Sales – Gross Profit
Cost of Goods Sold = 1,34,000 – 26,800
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 1,07,200
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
1,07,200 = Opening Stock + 66,000 + (15,000 + 200) – 20,000
Opening Stock = 1,07,200 – 66,000 – 15,200 + 20,000
Opening Stock = Rs. 46,000
Question 23:
Solution 23:

Working Note:-

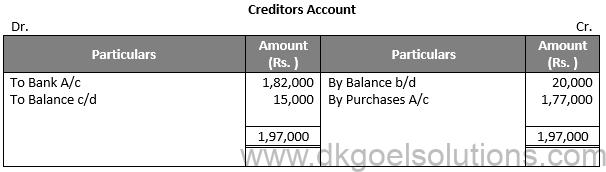
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = 20% × Rs. 2,32,000
Gross Profit = Rs. 46,400
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Gross Profit – Net Sales
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 2,32,000 – Rs. 46,400
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 1,85,600
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
1,85,600 = 34,000 + 1,77,000 – Closing Stock
Closing Stock = 34,000 + 1,77,000 – 1,85,600 = Rs. 25,400
Question 24:
Solution 24:
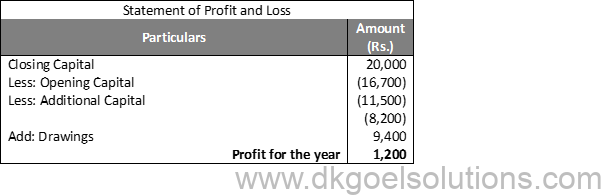
Question 25:
Solution 25:
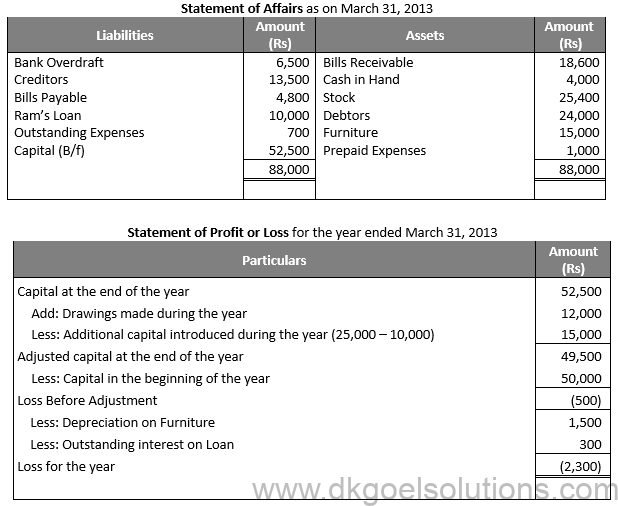
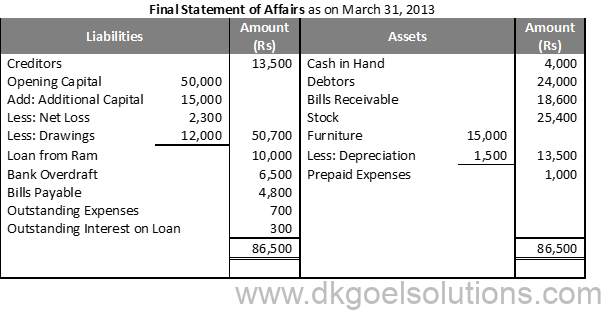
Question 26:
Solution 26:

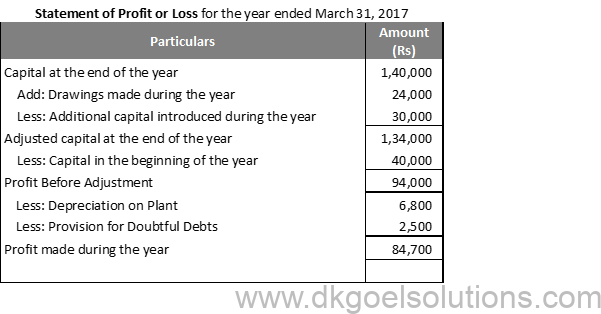

Question 27:
Solution 27:


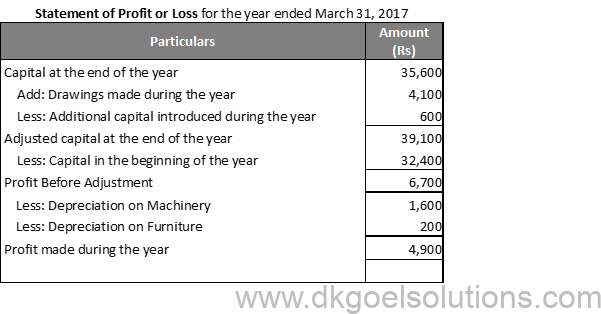
Question 28:
Solution 28:
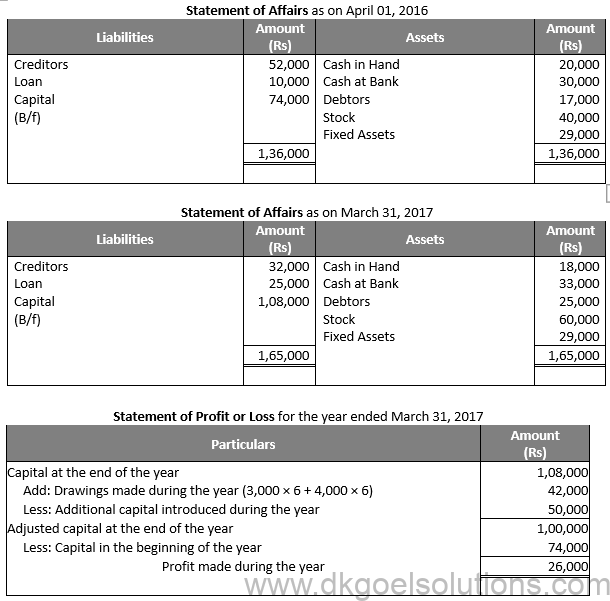
Question 29:
Solution 29:
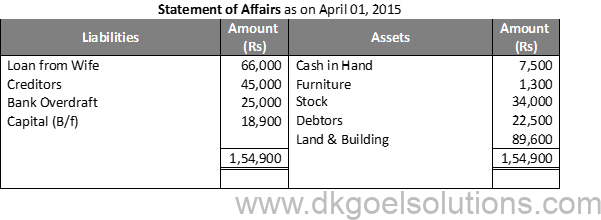
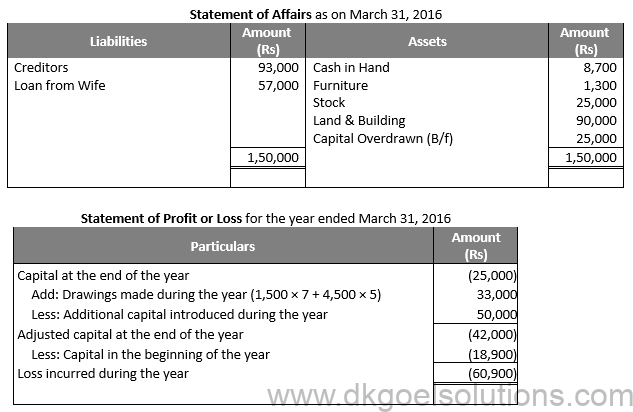
Question 30:
Solution 30:
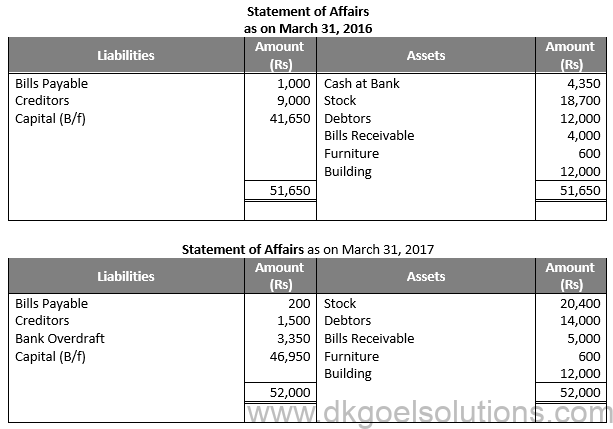
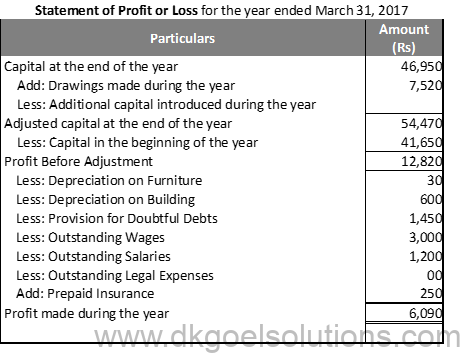
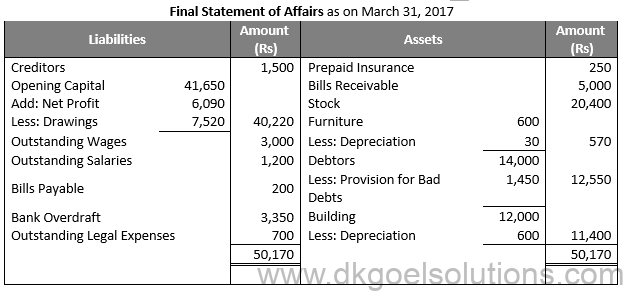
Question 31:
Solution 31:
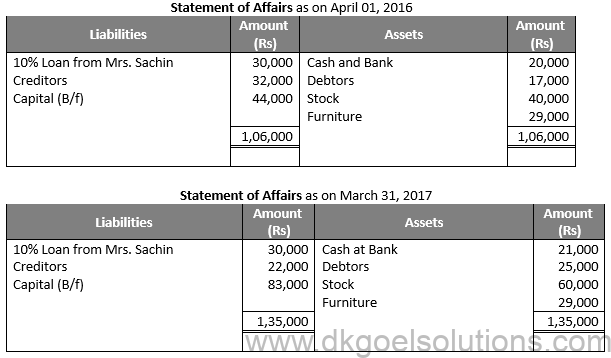


Question 32:
Solution 32:
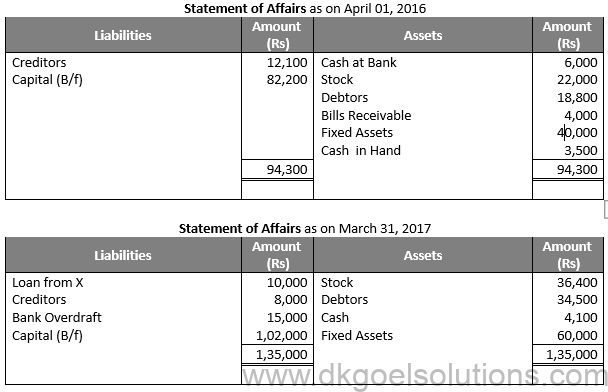
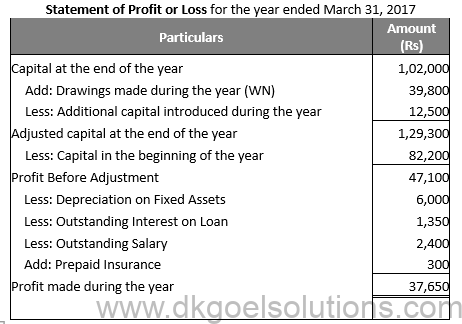
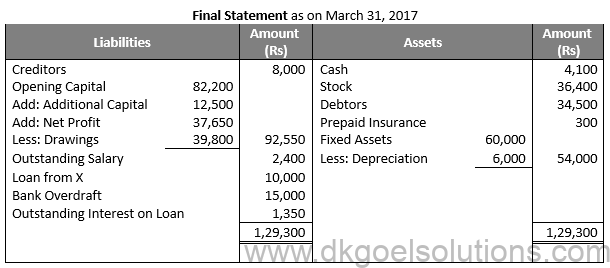
Working Note:-
Amount of Drawings:-
Cash Withdrawn = Rs 18,000
Loan to Brother = Rs 8,000
Rent = Rs 10,800
Electricity Charges = Rs 3,000
Total Drawings = Rs 18,000 + Rs 8,000 + Rs 10,800 + Rs 3,000
Total Drawings = Rs 39,800
Question 33:
Solution 33:
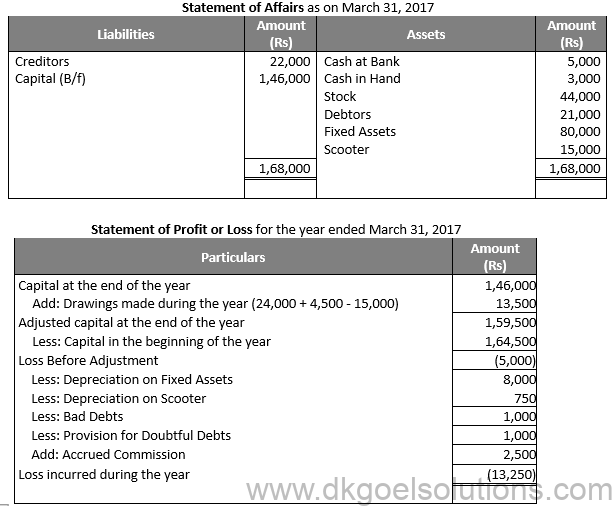

Question 34:
Solution 34:
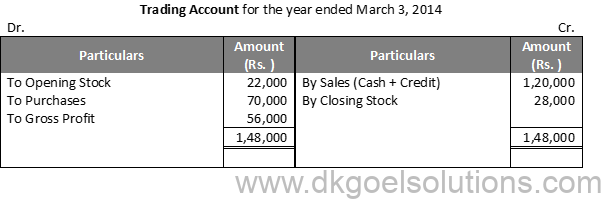
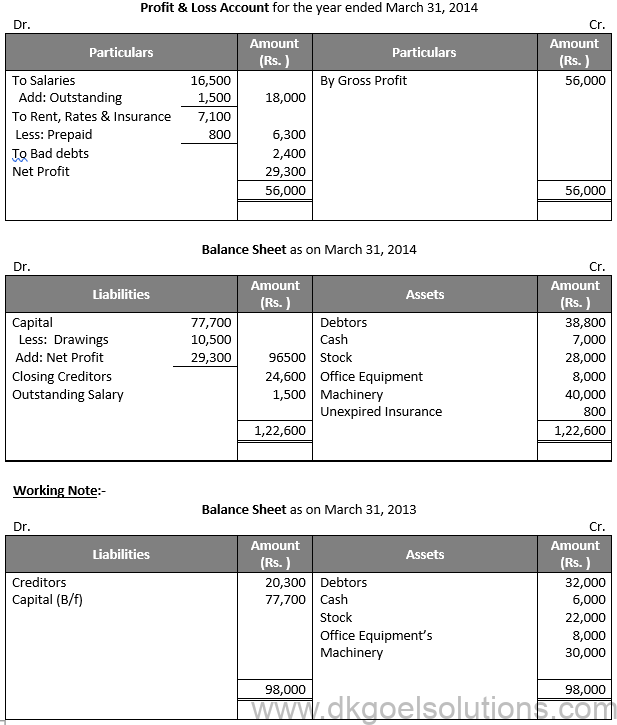

Question 35:
Solution 35:
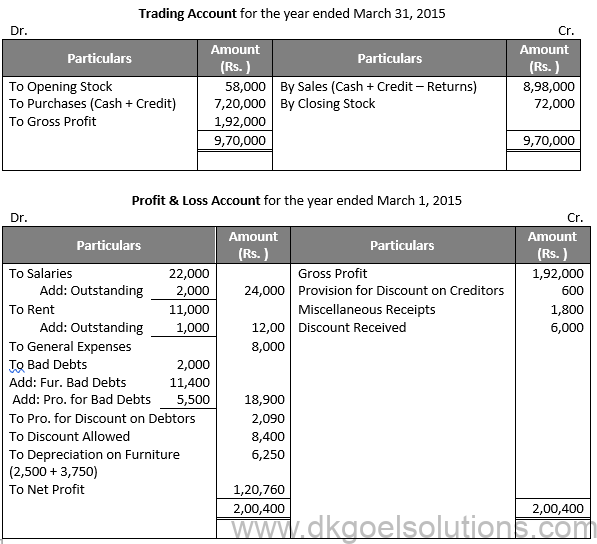
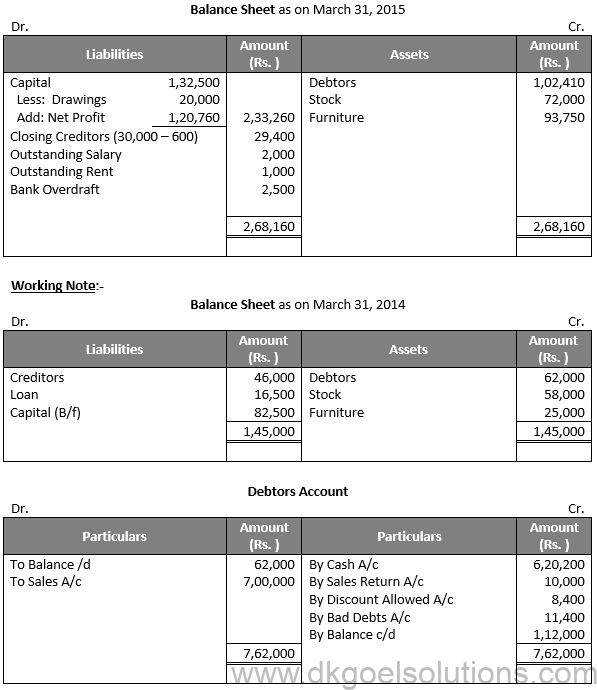
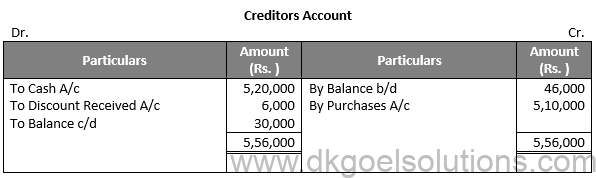
Question 36:
Solution 36:
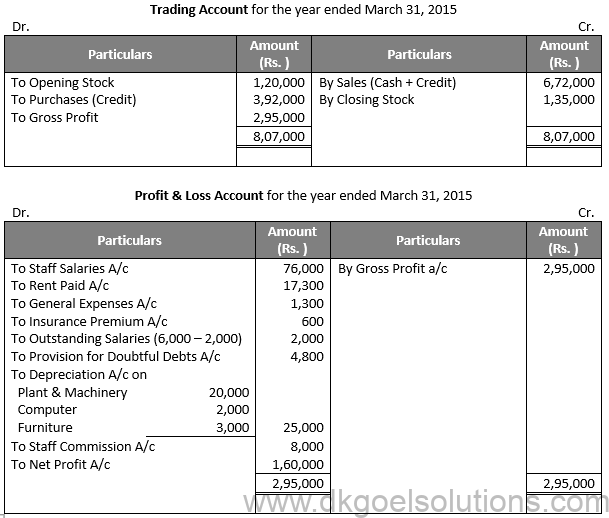

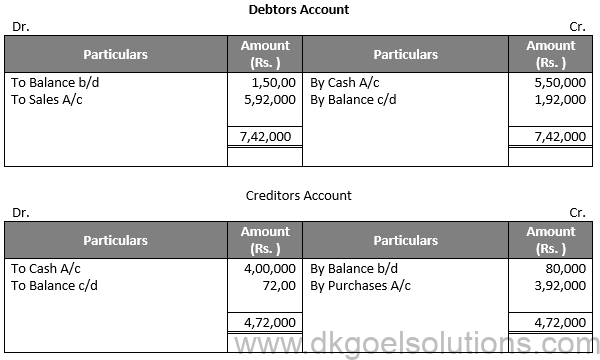
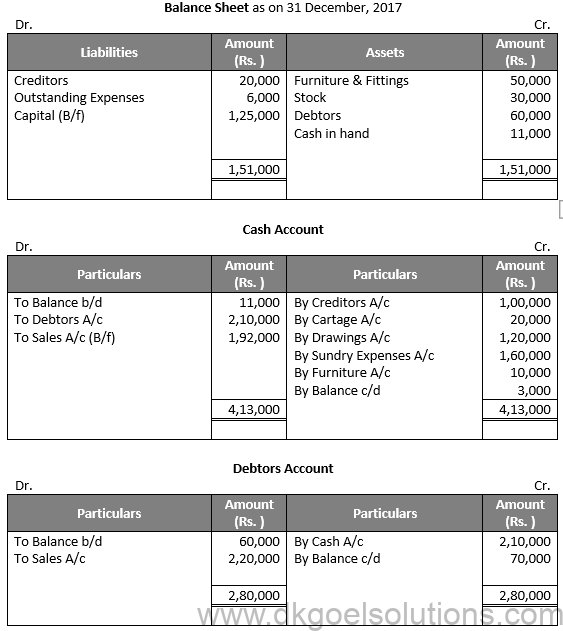
Q37.
Solution 37:
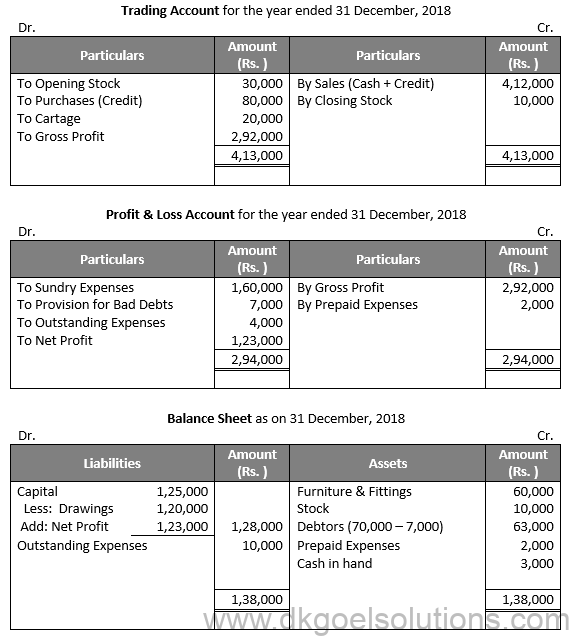
Working Note:-

Question 38
Solution 38:
Rate of Gross Profit (on cost) = 25% and Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = 1,00,000 × 20%
Gross Profit = 20,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Net Sales – Gross Profit
Cost of Goods Sold = 1,00,000 – 20,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 80,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
80,000 = 18,000 + 69,000 + 10,000 – Closing Stock
Closing Stock = 18,000 + 69,000 + 10,000 – 80,000 = Rs. 17,000
Question 39:
Solution 39:
Rate of Gross Profit (on cost) = 50% Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 33.33%
Gross Profit = 33.33% × 1,05,000
Gross Profit = 1,05,000 × 33.33/100
Gross Profit = 35,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Net Sales – Gross Profit
Cost of Goods Sold = 1,05,000 – 35,000 = Rs. 70,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
70,000 = Opening Stock + 60,000 + 3,000 – 20,000
Opening Stock = 70,000 – 60,000 – 3,000 + 20,000
Opening Stock = Rs. 27,000
Question 40:
Solution 40:
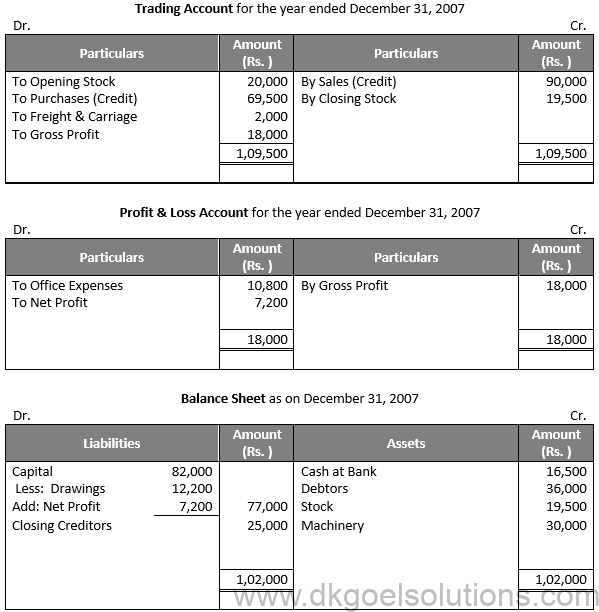
Working Note:-
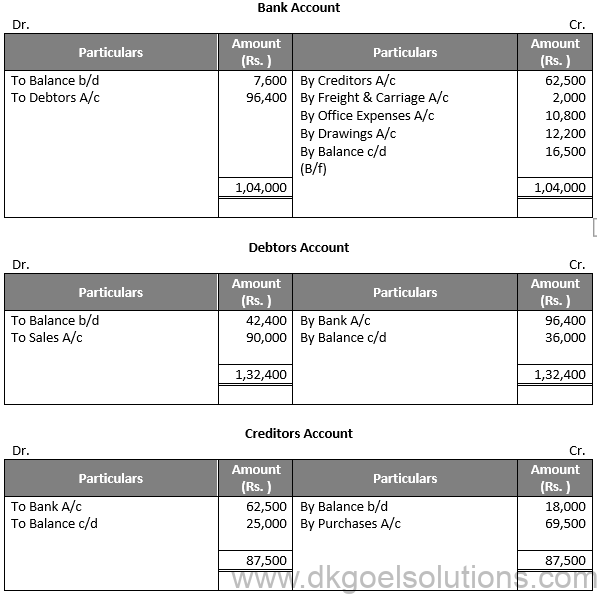
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = 20% × 90,000
Gross Profit = 18,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = Net Sales – Gross Profit
Cost of Goods Sold = 90,000 – 18,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs. 72,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
72,000 = 20,000 + 69,500 + 2,000 – Closing Stock
Closing Stock = 20,000 + 69,500 + 2,000 – 72,000 = Rs. 19,500
Question 41:
Solution 41:

Working Note:-
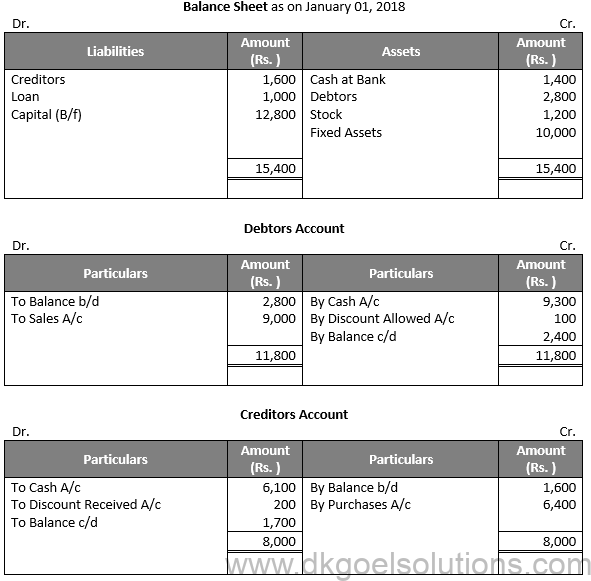

A Single Entry System can be defined as the method of recording financial transactions on only one side. It is one of the oldest and the simplest ways to record the financial activities of a company. However, this method is more or less incomplete as it supplies insufficient details of the transaction due to the lack of a set of prescribed rules. Therefore, the Single Entry System lacks the dual concept, and the recorded transactions are mostly inaccurate.
Here are the essential characteristics of Single Entry System –
Easy & Straightforward – Single Entry System is one of the easiest ways to record transactions. It does not involve any complex procedures.
Lack of Accuracy – The limitation of the Single Entry System prohibits the preparation of accurate accounts. Typically, personal accounts are designed under this system. At the same time, the nominal and actual accounts get overlooked.
Reliability on Original Voucher – Under this system, the accounts need to depend on the original voucher to get hands-on the required details.
Here are the reasons to use the Single Entry System –
Low Investment – This is one of the most economical methods to record the transactions as it comes with limited stationery and processing fees.
Basic procedure – Single Entry System does not involve tons of rules like the double-entry system. Therefore, it is pretty easy to use and does not require any expertise.
Beneficial for small businesses – Single Entry System, if utilized strategically, can be highly beneficial for small businesses.
The fruitfulness of keeping incomplete records are as follows –
It is appropriate for small concerns – This method is the perfect fit for small businesses which primarily transact in cash and maintains little assets and liabilities.
Presents flexibility – It allows modification as per the company’s requirements.
As explained in DK Goel Solutions class 11 Chapter 23, the limitations of incomplete records are as follows –
● It hinders the checking of arithmetic accuracy.
● It is an incomplete method as it does not cover all the details about credit and debit.
A Statement of Affair can be defined as a document that reflects complete details about a company’s liabilities and assets. It is a vital component of the insolvency process as it presents a transparent audit of a company.
