DK Goel Solutions Chapter 20 Capital and Revenue
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 20 Capital and Revenue. These answers have been developed based on the latest Class 11 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for current year and the questions given in each chapter.
This chapter provides in-depth information about capital expenditure, revenue expenditure, and the contradiction between them. Students should be able to understand the basic concepts of both Capital account and revenue accounts only then they will be able to pass correct accounting entries in the books.
The chapter contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful for Class 11 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 20 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 11 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Capital and Revenue DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy Solutions
Students can refer below for solutions for all questions given in your DK Goel Accountancy Textbook for Class 11 in Chapter 20
Very Short Answer Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 20
Question 1:
Solution 1:
Any expense made to purchase or increase the value of a fixed asset is treated as expenditure in the form of cash.
Question 2:
Solution 2:
The examples of capital expenditures are:-
1.) Purchases of Land and Building
2.) Purchases of Plant and Machinery
Question 3:
Solution 3:
Any investment received during the current year is referred to as tax expenditure. For instance:- Expenditures incurred for the day-to-day operation of the company, such as production expenses, office expenses, sales expenses, etc.
Question 4:
Solution 4:
Question 5:
Solution 5:
Question 6:
Solution 6:
Wages paid on machine installation are a capital expenditure because it will be treated as a machine cost.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1:
Solution 1:
Any expense made to purchase or increase the value of a fixed asset is treated as expenditure in the form of cash. For instance:- Land and building acquisition, plant and machinery acquisitions. Whereas the gain of any investment that is collected during the financial year itself is considered a tax expenditure. For instance:- Expenditures incurred for the day-to-day operation of the company, such as production expenses, office expenses, sales expenses, etc.
Question 2:
Solution 2:
Any expense made to purchase or increase the value of a fixed asset is treated as expenditure in the form of cash. As such, furniture is also written in assets, the money spent on the purchases of property and renovation, plant and machinery.
Examples are as follows:-
(1) Investment resulting in the procurement of a fixed asset, such as land, renovation, factory, motor vehicles, trademarks, etc. Such an asset will be used for a number of years in the sector.
2.) Spending in connection with the purchasing or development of a fixed asset, such as salaries paid to employees for the construction of machinery, carriages paying for the procurement of plants and machinery, overhauling of second-hand machinery, etc.
Any investment received during the current year is referred to as tax expenditure. As such, all sales losses are debited into the record of trade and benefit and loss. Such spending does not translate to an improvement in the company’s profits, but only leads to sustaining the current earning potential.
Examples are as follows:-
1.) Costs paid on day-to-day corporate activities, such as processing costs, office expenses, sales expenses, etc.
2.) Costs for ordinary repairing and maintenance of fixed properties, house whitewashing, etc.
Question 3:
Solution 3:

Question 4:
Solution 4: (a) Preliminary Expenses : Deferred Revenue Expenditure
(b) Purchases of Furniture : Capital Expenditure
(c) Payment of Salary : Revenue Expenditure
(d) Expenses paid for construction of building : Capital Expenditure
Practical Questions:
Question 1:
Solution 1:

Question 2:
Solution 2:

Question 3:
Solution 3:
(a) Rs. 20,000 which is increase the output of the firm, so it is capital expenditure.
Rs. 5,000 is related to repairs as it is done on regular basis, so it is revenue expenditure.
(b) Repairs of Rs. 40,000 is done on regular basis, as it is a Revenue Expenditure.
Rs. 1,60,000 is done on improvements which will give future benefits, so its capital expenditure.
(c) Compensation and remuneration to employees are done in normal course of business, so it is Revenue expenditure.
(d) Any expenses incurred on bringing the asset into operation will be capitalized so it is a Capital expenditure.
(e) Compensation and remuneration to employees are done in normal course of business so Revenue expenditure.
(f) Benefit will be derived over a number of years, so it is a Deferred revenue expenditure.
Question 4:
Solution 4:
(a) As this transaction related to normal business transaction so it is Revenue receipts.
(b) As it is a capital gain which arose by selling of machinery so it is Capital receipt.
(c) As it is received in normal course of business over exchange of goods so it is a Revenue receipt.
(d) As it will improve the financial position of the company of the company so it is a Capital receipt.
(e) As it will enhance the productivity of the company it is a Capital receipt.
(f) As it is received regularly from the government it is a Revenue receipt.
(g) As it is received for construction and will it will result in increasing the earning capacity of the firm so it is a Capital receipt.

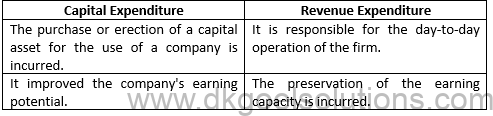
Capital expenditures highlight the funds utilized by a firm to purchase, improve and maintain long-term assets to elevate the credibility of the firm. Capital expenditures include the purchase of several items required for improving the business performance, including new equipment or machinery, software, business vehicles, and much more.
Revenue expenditures refer to some short-term expenses required to meet some ongoing operational charges. In simple words, the revenue expenditure is the summation of all the expenses incurred during the production of the goods and services. For instance, the funds incurred by a company in a day-to-day project are the revenue expenditure.
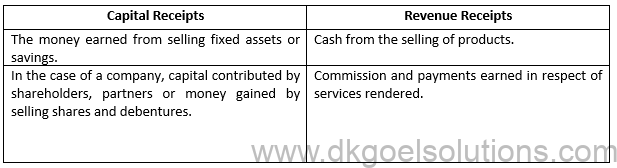
Capital receipts are one of the integral components of accounting. It is a receipt that increases the liabilities of a company, thereby reducing the financial assets. Cash receipts are forms of cash flow within a business generating liabilities. They are generally non-recurrent in nature and are placed within the liability section of the balance sheets.
The revenue receipt is the ladder to the financial success of a business. Revenue receipts refer to the note that reflects the funds collected by the companies. This includes the cash from the sale of goods or services and also the commissions earned in exchange for services or products.
Any expense made during the purchase of a fixed asset to improve the functioning or scale up the business is termed as capital expenditure. For example, acquisition of land or plot for setting up a factory, installing new machinery, etc. At the same time, the returns from any investment collected during an accounting year are titled revenue expenditure. For example, sales expenses, production expenses, and more. Typically, a company can enjoy the perks of revenue expenses within a financial year.
Funds invested for installing a machine always come under the capital expenditure section as it is used to elevate the worth of the company in the long term by adding a fixed asset to it.
