DK Goel Solutions Chapter 11 Books of Original Entry – Cash Book
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 Books of Original Entry Cash Book. These solutions have been prepared based on the latest Class 11 DK Goel Accountancy book issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
In this chapter of DK Goel Accounting Solutions Class 11, explain various concepts relating to cash books, what they mean, and their importance. It also provides basic steps on how to prepare cash books.
The chapter also includes lot of good quality problems or questions which can be very helpful to understand the concepts for Class 11 students of Accountancy and will also help build a strong foundation.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 11 Accountancy
Books of Original Entry – Cash Book DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy Solutions
Students can refer below for solutions for all questions given in your DK Goel Accountancy Textbook for Class 11 in Chapter 11
Short Answer Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11
Question 1:
Solution 1: For any type of transactions, it is useful to keep a different book, one to record cash transactions, another to record credit purchases of goods, and still another to record credit sales of goods.
All these books ( DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 )are referred to as initial entry books or main entry books or subsidiary books – it is a special type of Journal, a Journal sub-division.
Question 2:
Solution 2: Original entries are recorded in the below books:-
- Cash Book
- Purchases Book
- Sales Book
- Purchases Return Book
- Sales Return Book
- Bills Receivable Book
- Bills Payable Book
- Journal Proper
Question 3:
Solution 3: (a) Only monetary transactions are reported in the Cash Book, since this book documents only cash or bank-related transactions. The cash book almost still reflects a debit balance.
Since cash transfers cannot surpass cash receipts, the cash column in the cash book cannot display a credit balance. If the overall cash receipt is equal to the total bill, it will display zero balance at most.
(b) As cash Book is a book in which all transactions relating to cash receipts and cash transfers are registered, Cash Book is both Journal and Ledger. At the start of the cycle, it begins with cash or bank accounts.
Question 4:
Solution 4: As an original book and a ledger, the Cash book plays both roles. The Cash Book serves the dual purpose of the original entry or both books and the Ledger.
If we create a cash book, there is no need to create a separate cash account. A transaction is recorded in a cash book or cash account only if there is either cash inflow or cash outflow. The cash book therefore has a dual purpose.
Question 5:
Solution 5: Some transactions are reported in a Two-Column Cash Book that refers to both cash and money, i.e. the balance of one will drop and, owing to such transactions, the other will increase.
Certain transactions are entered on all sides of the Cash Book. Against such entries, the letter ‘C’ is written in the L.F. column to indicate that these are contra transactions and are not posted into the Ledger Account.
(a) Cash deposited into the Bank 10,000
(b) Cash withdrawn from Bank for Office Use 1,000
Question 6:
Solution 6: The three advantages of Sub-Division of Journal are:-
(i) Division of work by capacity.
(ii) Ease of posting.
(iii) Save Time
Question 7:
Solution 7:
(i) Deposit of Cash into Bank:-
In the aforementioned trade, a cash account and a bank account are also influenced by the account. It is also contra-entry since all accounts are influenced concurrently by cash and bank.
Bank a/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
(ii) Withdrawal of money from bank for office use:-
In the aforementioned trade, a cash account and a bank account are also influenced by the account. It is also contra-entry since all accounts are influenced concurrently by cash and bank.
Cash a/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
(iii) Deposit of cheque (received from other) into Bank:-
On the debit side “To Cheque-in-hand a/c” and on credit side “By Debtors a/c” with the same amount recorded.
Cheque-in-hand A/c
To Debtors A/c
(iv) Dishonour of cheque deposited into Bank:-
On the credit side “By Debtor a/c” and amount will be credited into the bank account.
Debtor a/c Dr
To Bank a/c
Question 8:
Solution 8
(i) Similarities of Cash Book with Journal:-
- The transactions in the cash book are documented from source records for the first time, much like a report.
- Transactions in the cashbook are reported date-wise, i.e. in a chronological order, when and when they are put, much like a document.
- Much as a log, cash book transfers are often posted in the ledger to the related accounts.
- A cash book also includes a ledger folio column, much like a journal.
(ii) Similarities of cash book with ledger:-
- The sort of cash book closely resembles the account of a ledger. Having similar columns, it has two evenly separated sides. The left side (receipt side) is the debit side and the credit side is the right side and the credit side is the right side (payment side).
- The cash book itself often functions as a cash account and as such, when a cash book is held, the cash account is not opened in the ledger. The cash book, however, is indeed a part of the ledger.
- In a cash book, much like a ledger account, the words ‘To’ and ‘By’ are sometimes used.
- Much like a ledger account, it is balanced.
Question 9:
Solution 9: Contra entries indicate entries on both sides of the cash book that are registered. When depositing or withdrawing money from the bank, these entries are made.
The two accounts, the cash account and the bank account, are influenced by Contra entries. In the Cash Book, these two accounts appear together only so that the result of entries is fulfilled in the Cash Book and there is no need to post them in the ledger.
Question 10:
Solution 10: Cash book is a journalised Ledger, it is a log because it first documents cash and bank transfers in it and a ledger since it often fits the function of a cash account. No distinct cash account is opened in the ledger when a cash book is prepared.
Question 11:
Solution 11:
| Cash Book | Cash Account |
| The Cash Book is a prime entry book that documents cash and bank transfers in a linear order, i.e. when they occur.In the debit side of the cash ledger, cash refunds are registered as well as cash transfers on the credit side. | A cash account is a ledger account that is used to document the company’s day-to-day cash transactions.Cash receipts are recoded and or other side cash transfers are reported on the debit side of the account. |
Question 12:
Solution 12: The book used for the purpose of tracking expenses containing minor sums is the Petty Cash Book. In addition to minor expenditures, principal cash receipts are reported.
The Petty Cash Book is prepared by the Petty Cashier which is the Petty Cash Account. In addition to large payments, it is retained as in a company, it is important to make a variety of minor payments, such as conveyance, stationary, cartage, etc.
Question 13:
Solution 13:
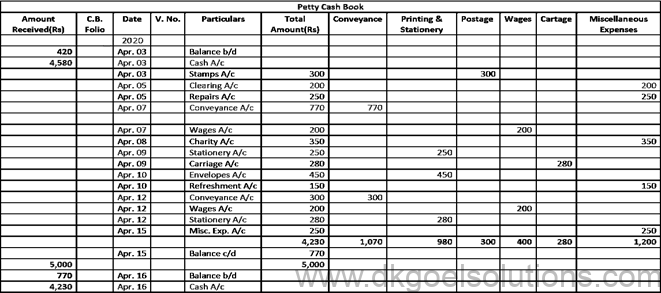
Question 14:
Solution 14: The Petty Cash imprint scheme is discussed below. Under this method, the amount needed for minor expenditures for a certain time is determined (say for a week, a fortnight or a month). At the beginning of an era, the amount so calculated is issued to the petty cashier and the amount charged by him during the period is repaid.
Numerical Question DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 :-
Question 1:
Solution 1:

Point in Mind:- The Cash Book Balancing is done like every other account. The debit column is often bigger than the credit column.
Question 2:
Solution 2:
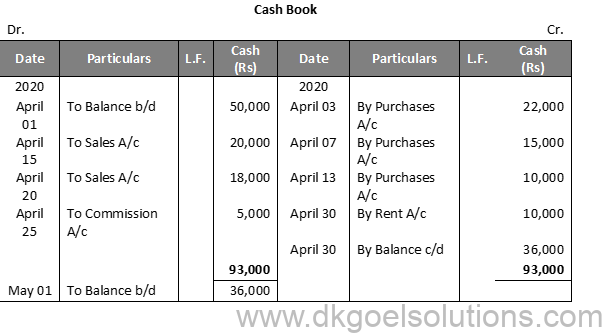
Point in mind:-
Only currency transfers are reported in the cash book. There is no recording of credit transfers. The debit side is still higher than the credit, since the cash available is never surpassed by transfers.
Question 3:
Solution 3:

Question 4:
Solution 4:

Question 5:
Solution 5:

Question 6:
Solution 6:
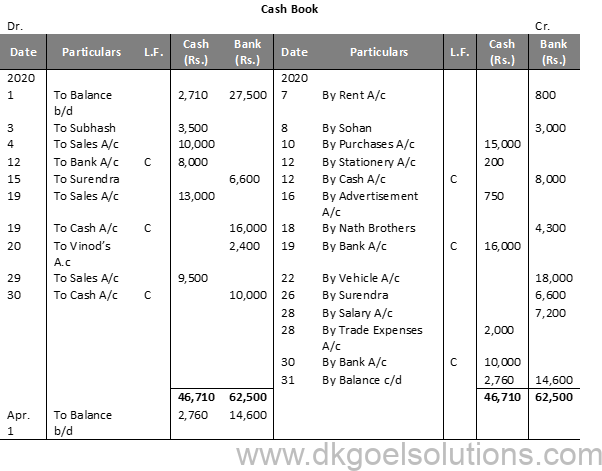
Question 7:
Solution 7:
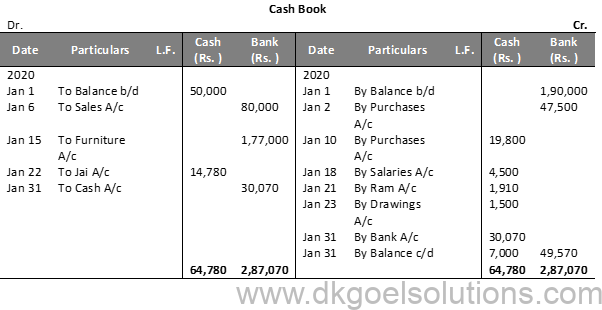
Question 8 (A):
Solution 8(A):
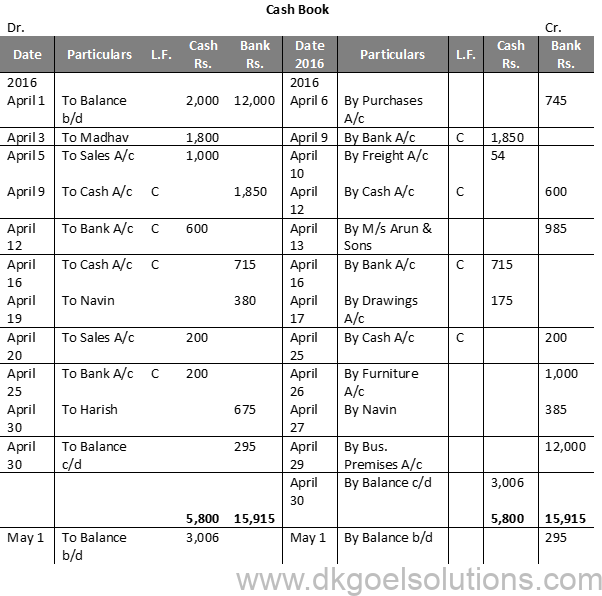
Question 8 (B):
Solution 8 (B):

Working Note:-
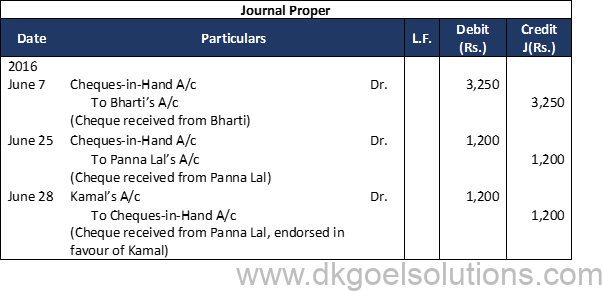
Question 9:
Solution 9:
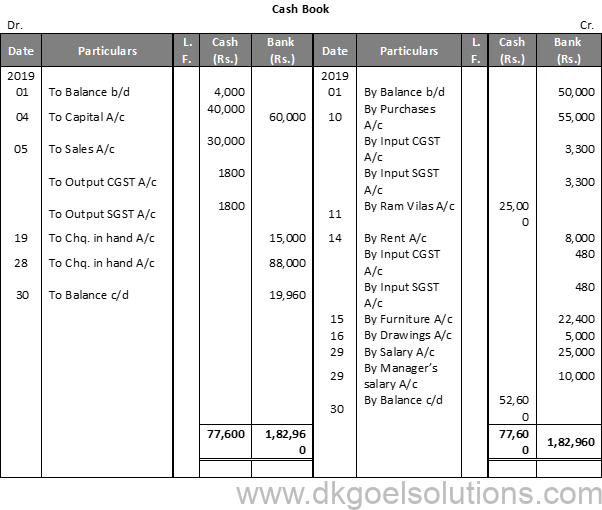
Working Note:- On 20th April, Entry for Credit sales of Rs. 80,000 plus CGST and SGST @ 6% each will he recorded in journal.
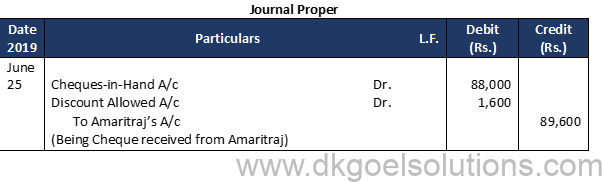
Question 10 (A):
Solution 10 (A):
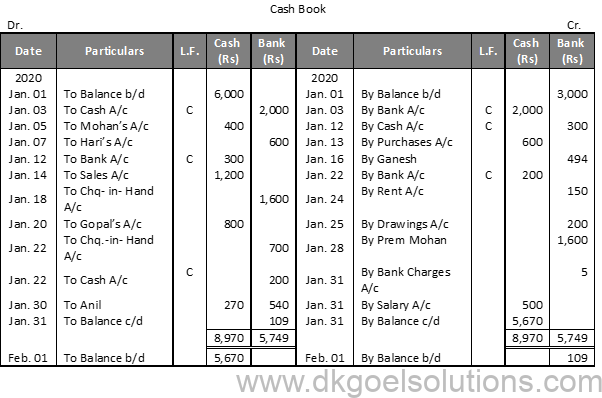
Working Note:- 1. Cheque received from Prem Mohan on 9th and from Gopal on 20th will be recorded through Journal. These will be recorded in the Cash Book on the dates of their deposit into the Bank.
Question 10 (B):
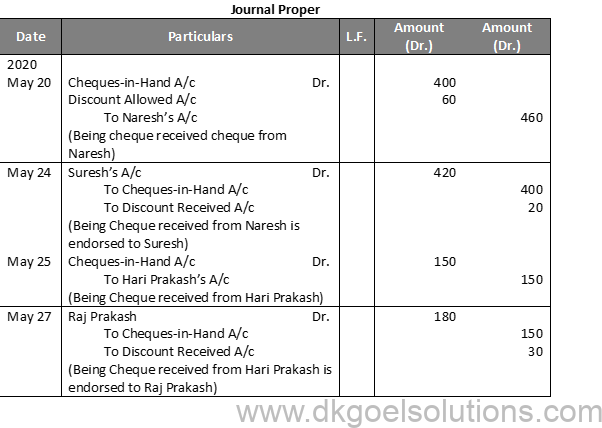
Solution 10 (B):

Working Note:-
Question 11 (A):
Solution 11 (A):
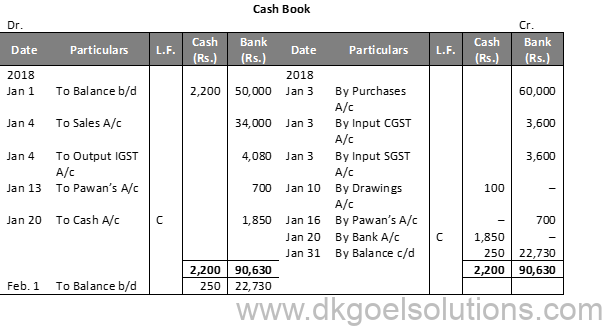
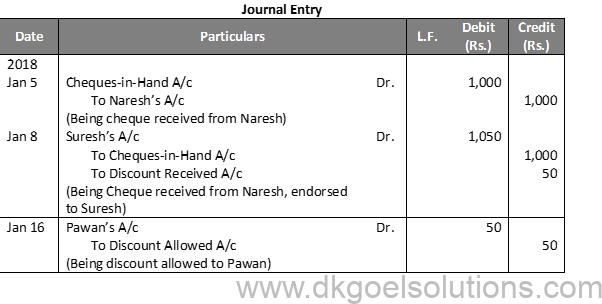
Working Note:-
Question 11 (B):
Solution 11 (B):
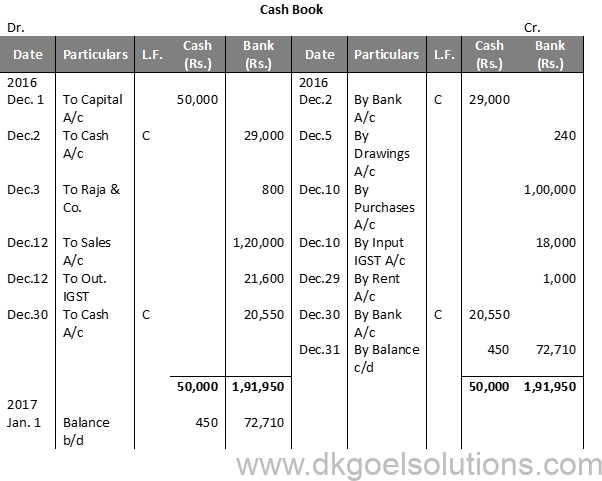
Working Note:-

Calculation of Cash deposit into the Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Bal.
Cash deposit into bank = 50,000 – 29,000 + 450
Cash deposit into bank = 50,000 – 29,450
Cash deposit into bank = 20,550
Question 12:
Solution 12:
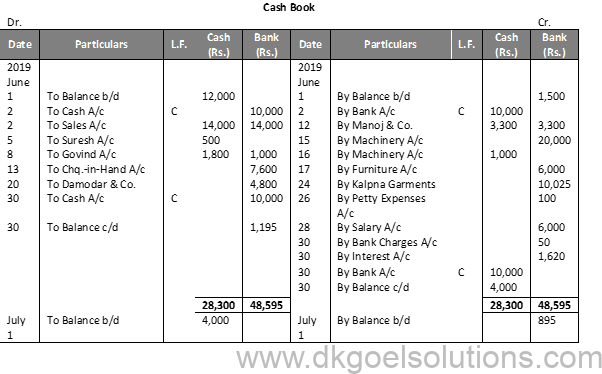
Working Note:-
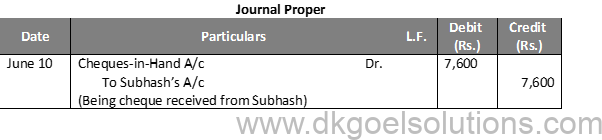
Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Balance
Cash deposit into bank = 28,300 – 14,300 + 4,000
Cash deposit into bank = 28,300 – 18,300
Cash deposit into bank = 10,000
Question 13 (A):
Solution 13 (A):
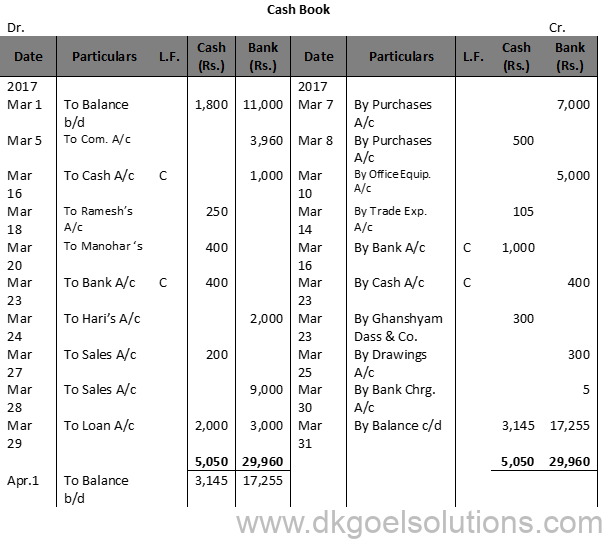
Question 13 (B):
Solution 13 (B):
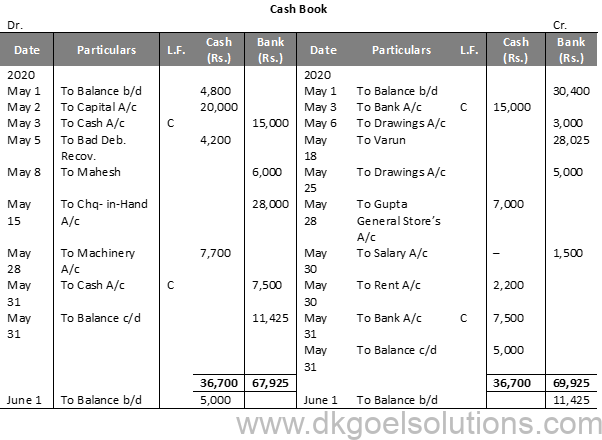
Working Note:-
May 6th : Life Insurance Premium is treated as Drawings.
May 12th : Entry for receipt of cheque will be recorded in Journal Proper.
May 15th : To cheque in hand a/c Rs. 28,000 in bank column
May 18th : by Varun Rs. 28,025 in Bank Column, Entry for discount withdrawn Rs. 2,000 will be passed through Journal Proper.

Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side -Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Balance
Cash deposit into bank = 36,700 – 24,200 + 5,000
Cash deposit into bank = 36,700 – 29,200
Cash deposit into bank = 7,500
Question 14:
Solution 14:
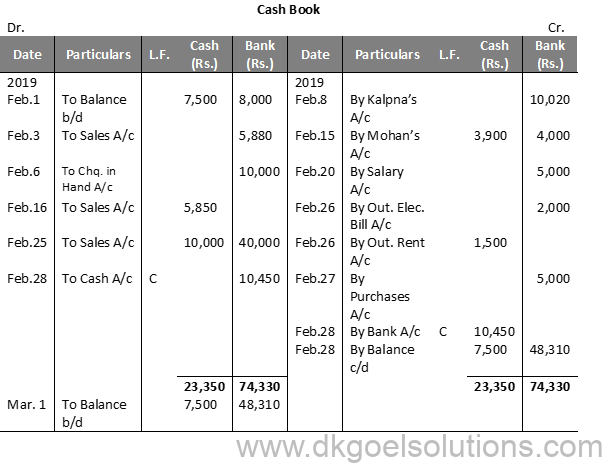
Working Note:-

Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Debit side – Total of Cash Col. of Credit side + Cash Bal.
Cash deposit into bank = 23,350—5,400-+-7,500
Cash deposit into bank = 23,350 – 12,900
Cash deposit into bank = 10,450
Question 15::
Solution 15:
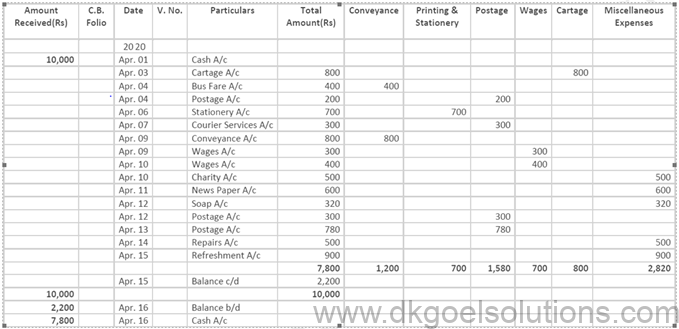
Point in mind DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11:–
Petty Cash Book is the book that is used for the purpose of recording expenses involving petty amounts. Besides petty expenses, receipts from main cash are recorded. Petty Cash Book is prepared by Petty Cashier and acts as the Petty Cash Account.
Question 16:
Solution 16:

Working Note:- The imprest system of Petty Cash is explained below. Under this system, an estimate is made of amount required for petty expenses for a certain period (say for a week, a fortnight or a month).
Question 17:
Solution 17:

Point in mind:- Petty Cash Book is the book which is used for the purpose of recording expenses involving petty amounts. Besides petty expenses, receipts from main cash are recorded. Petty Cash Book is prepared by Petty Cashier and acts as the Petty Cash Account.
Question 18:
Solution 18:

Working Note:-

Question 19:
Solution 19:
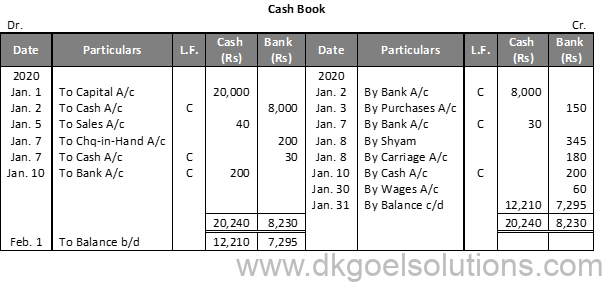
Question 20:
Solution 20:
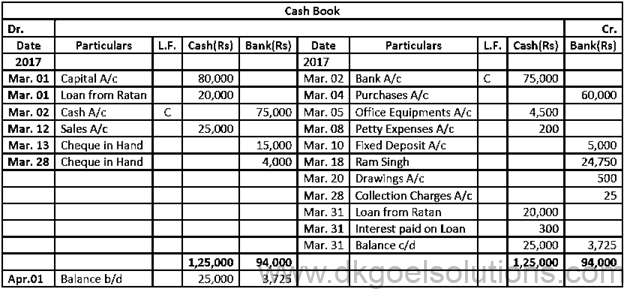
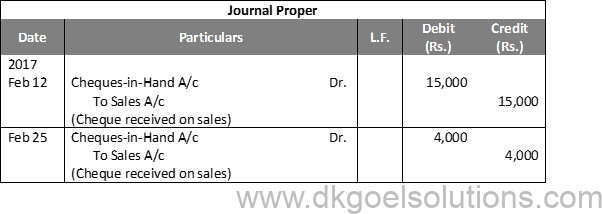
Working Note:-
Calculation of interest on loan:-
Time for loan = 1 Month
Rate on Interest = 18%
Interest on Loan = Rs. 20,000 × 1/12 × 18/100
Interest on Loan = Rs. 300
Question 21:
Solution 21:
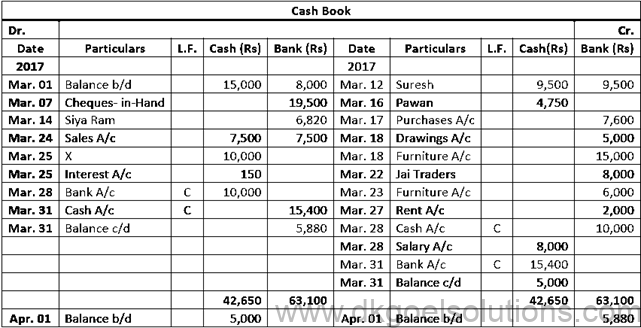
Working Note:-

Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Bal.
Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 22,250 + 5,000
Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 27,250
Cash deposit into bank = 15,400
Question 22:
Solution 22:

Working Note:-
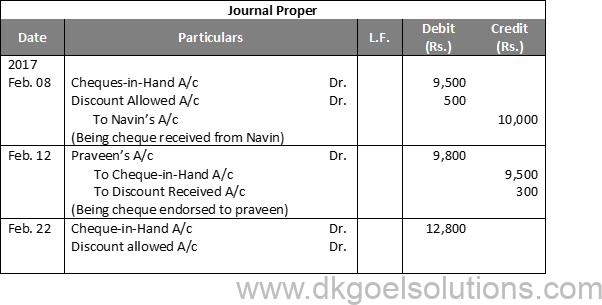
Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side-+-Cash Bal.
Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 22,250 + 5,000
Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 27,250
Cash deposit into bank = 15,400
Question 23:
Solution 23:

Question 24:
Solution 24:
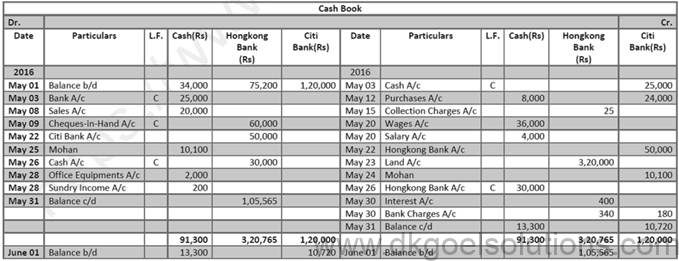
Working Note ( DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 ):-

Question 25:
Solution 25:

Working Note:-
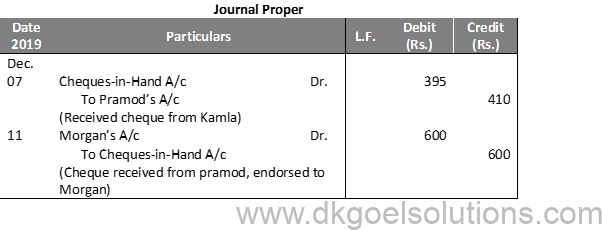
Calculation of Cash deposit into the Bank:-
Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Bal.
Cash deposit into bank = 50,000 – 29,000 + 450
Cash deposit into bank = 50,000 – 29,450
Cash deposit into bank = 20,550
Question 26:
Solution 26:
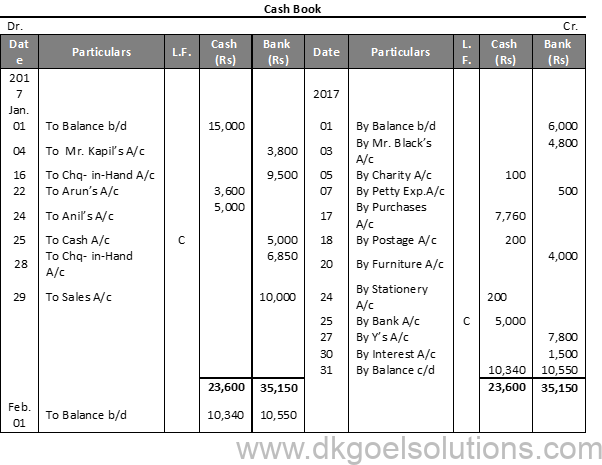
Working Note:-
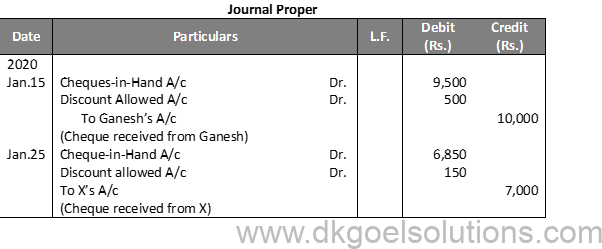
Question 27:
Solution 27:
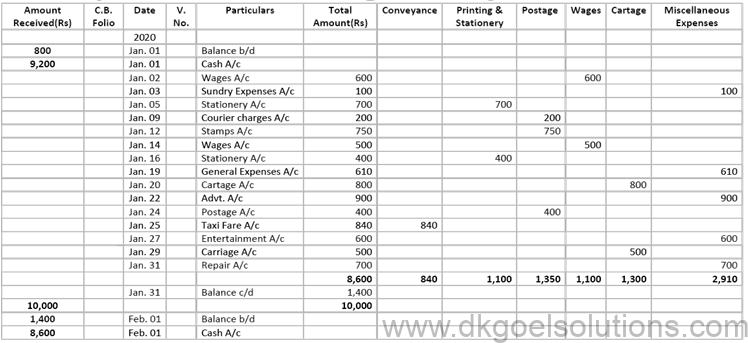
Working Note:-
The imprest system of Petty Cash is explained below. Under this system, an estimate is made of amount required for petty expenses for a certain period (say for a week, a fortnight or a month).
Question 28:
Solution 28:
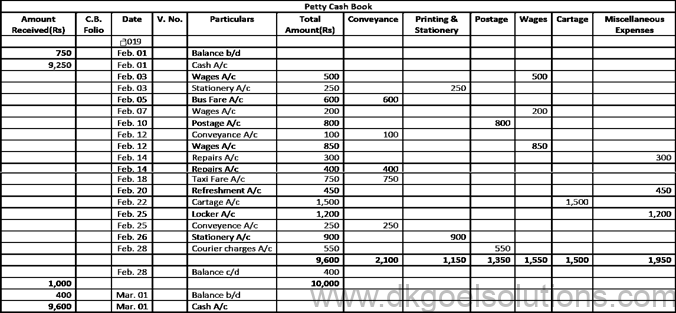
Question 29:
Solution 29;

Working Note:- The Petty Cash imprint scheme is discussed below. Under this method, the amount needed for minor expenditures for a certain time is determined (say for a week, a fortnight or a month). At the beginning of an era, the amount so calculated is issued to the petty cashier and the amount charged by him during the period is repaid.

As explained in DK Goel Solutions class 11 Chapter 11, cash book is a financial record holder which amalgamates all the cash receipts and disbursements, highlighting the financial transactions in cash. After the financial cash transactions are recorded in the cash book, they are added to the ledger. Only the bank-related and cash transactions are added to the cash book, and a cash book always highlights the debit balance.
Cash Book is considered to have dual nature being both journal and ledger, as it records all the business transactions relating to cash payments and cash receipts. It is one of the most crucial accounting books maintained by every company. A cash book is multi-functional as it acts as both ledger and books of original entry. A cashbook eliminates the need for a cash account for all organizations.
Contra Entry is a type of entry that affects both bank accounts and cash. In simple words, it defines any financial transaction involving the transfer of cash from a cash account to another bank account or from a cash account to another cash account, or from a bank account to another bank account.
A cash book is a written record of all the financial transactions relating to cash or banks arranged in a specific sequence. In contrast, a cash account is a form of a ledger account that depicts the day-to-day transactions of an organization.
Petty cash book is one of the popular accounting books utilized to record all the minor expenses. For instance, daily wages, stationery, postage and handling, and much more. These types of cash books are usually designed and handled by petty cashiers.
Here are the notable similarities between Cash Books and Journals –
● Identical to the journal, in the cash book, all the entries are arranged in chronological format according to the date and time of the transaction.
● Similar to the journals, the data from the cash books flows to the ledger.
● Cash Books also includes a ledger folio column, just like journals.
