DK Goel Solutions Chapter 16 Depreciation
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 16 Depreciation. These answers have been developed based on the latest Class 11 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
This chapter of DK Goel accountancy stresses the concepts depreciation with value-based problems. As you are aware that depreciation is charged on all types of assets except land.
Therefore its very important to understand the concepts and accounting process for depreciation so that you can solve all related questions easily. The chapter (DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 16) also contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful to understand the concepts for Class 11 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 16 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 11 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Depreciation DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy Solutions
Students can refer below for solutions for all questions given in your DK Goel Accountancy Textbook for Class 11 in Chapter 16
Short Answer Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 16 Depreciation
Question 1:
Solution 1: Depreciation may be characterized as a persistent and constant decrease in an asset’s quality, quantity or worth.
The two explanations for offering depreciation are below:—
1.) To calculate the actual benefit or loss from the profit & loss account.
2.) For the balance sheet to reflect the real financial condition.
Question 2:
Solution 2: The benefits of using the Straight Line Approach are below:
1.) Simplicity
2.) Properties can be written off entirely
3.) Initial expense perception and up-to-date depreciation
4.) Equity of the Burden of Depreciation
Question 3:
Solution 3: The merits in using the written down value form are below:—
1.) Quick to measure
2.) Equivalent fee against revenue
3.) In later years, no undue burden
4.) Wealth balance is never written down to zero
Question 4:
Solution 4: Here are the Instalment Reduction Process demerits:—
1.) The commodity cannot be written off entirely.
2.) Interest Factor Exclusion
Question 5:
Solution 5: Straight Line Method
1.) Per year, the same amount of depreciation is paid.
2.) Depreciation paid in excess to the initial asset value.
3.) The valuation of an asset can be reduced to zero by this approach.
4.) The Income Tax authorities do not approve this process.
Written Down Value Method
1.) Year by year, depreciation will be declining.
2.) The diminished value is paid for depreciation.
3.) By the WDV method, the asset’s value cannot be negative.
4.) This system is licensed by the tax authorities for taxes.
Question 6:
Solution 6: The original cost approach is known as the straight line method. Depreciation is paid at a fixed percentage of the initial cost of the commodity in this process. The depreciation rate remains the same as the year and the process is also known as ‘Equal Instalments Method’ and ‘Set Instalment Method’ as well. Under this procedure, the deprecation number is determined using the following formula:—
Yearly Depreciation =(Cost of Assets-Scrap Value)/(Estimated life of Asset)
For Example:- A machinery purchased is Rs. 1,00,000 and its scrap value is Rs. 10,000 its estimated life of 10 years, the depreciation will be:-
Annual Depreciation = (Cost of Assets-Scrap Value)/(Estimated life of Asset)
=(1,00,000 – 10,000)/10
=Rs.9,000
Rate of Depreciation =(Amount of Depreciation)/(Total Cost of Asset)×100
=9,000/1,00,000×100
=9%
Question 7:
Solution 7: It is necessary to open a new account called a “asset disposal account” if any of the asset is sold or disposed of. It offers a straightforward and full view of all the activities involved with the selling of an asset and illustrates the benefit and loss from the sale of the asset.
(i) transfer the book value of asset to Asset disposal account:-
Asset Disposal A/c Dr.
To Asset A/c
(ii) Sale of Asset:-
Bank A/c Dr.
To Asset Disposal A/c
(iii) Profit on sale of asset
Asset Disposal A/c Dr.
To Profit on sale of asset A/c
Or
Loss on sale of asset
Loss on sale of asset A/c Dr.
To Asset Disposal A/c
Practical Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 16 Depreciation
Question 1:
Solution 1:

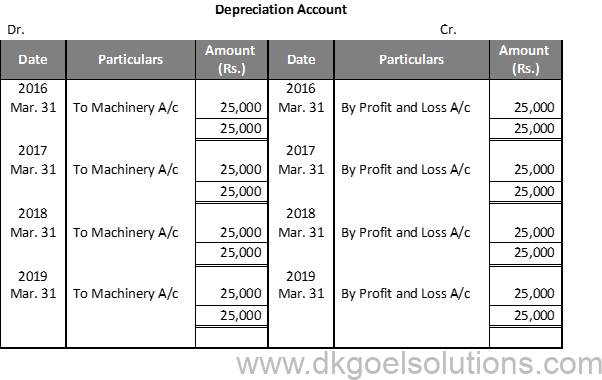
Working Note:-
1.) Total cost of Machinery = Rs. 1,90,000 + Rs. 10,000 = Rs. 2,00,000
2.) Yearly Depreciation = (Cost of Assets-Scrap Value)/(Estimated life of Asset)
=(2,00,000 -50,000)/6
=Rs.25,000
Rate of Depreciation =(Amount of Depreciation)/(Total Cost of Asset)×100
=25,000/2,00,000×100
=12.5%
Question 2:
Solution 2:
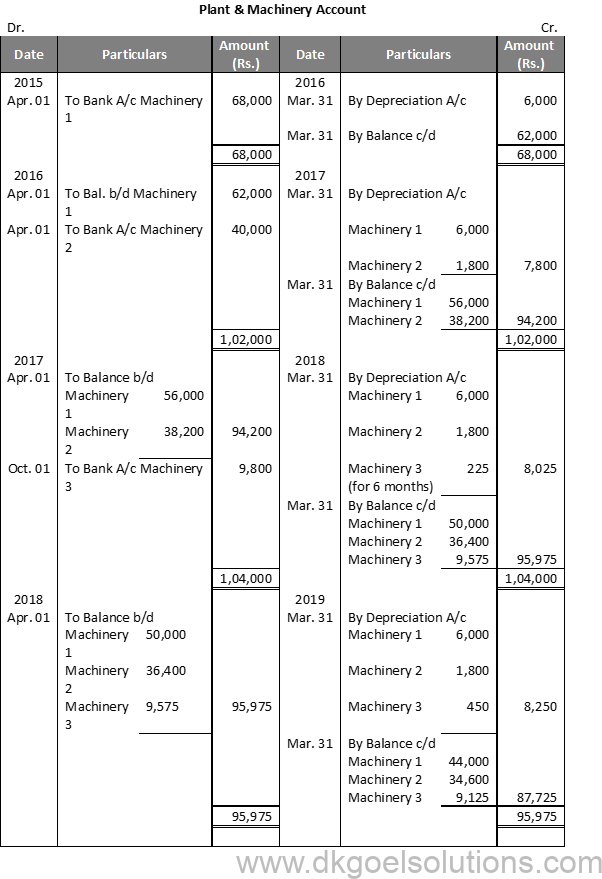
Working Note:-
1.) Annual Depreciation on Machinery 1 = (Cost of Assets-Scrap Value)/(Estimated life of Asset)
=(68,000 – 8,000)/10
=Rs.6,000
2.) Annual Depreciation on Machinery 2 = (Cost of Assets-Scrap Value)/(Estimated life of Asset)
=(40,000 – 4,000)/20
=Rs.1,800
3.) Annual Depreciation on Machinery 3 = (Cost of Assets-Scrap Value)/(Estimated life of Asset)
=(9,800 – 800)/20
=Rs.450
Six month Depreciation = 450 × 6/12 = 225
Question 3:
Solution 3:

Working Note:-
Calculation of Value of machinery
Value of machinery = Rs. 8,000 + Rs. 3,500
Value of machinery = Rs. 11,500
Calculation of Profit and Loss:-
Price of Machinery on dated Apr. 01, 2018 = 8,337
Less: Depreciation for 6 months = 11,500 × 10/100×6/12 = 575
Value of Machinery on dated Sept. 30, 2018
= 8,337 – 575
= 7,762
Less: Sale Value = 6,500
Loss on Sale of Machinery = 1,262
Question 4:
Solution 4

Question 5:
Solution 5:

Working Note:-
Calculation of profit and loss:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Jan. 01, 2018 2,25,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 6,250
Value of Machinery on July 01, 2018 28,750
Less: Sale Value 1,43,000
Loss on Sale Machinery 75,750
Question 6:
Solution 6:

Working Note:-
Calculation of profit and loss:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 48,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 8,000
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2017 40,000
Less: Sale Value 23,000
Loss on Sale Machinery 17,000
Question 7:
Solution 7:
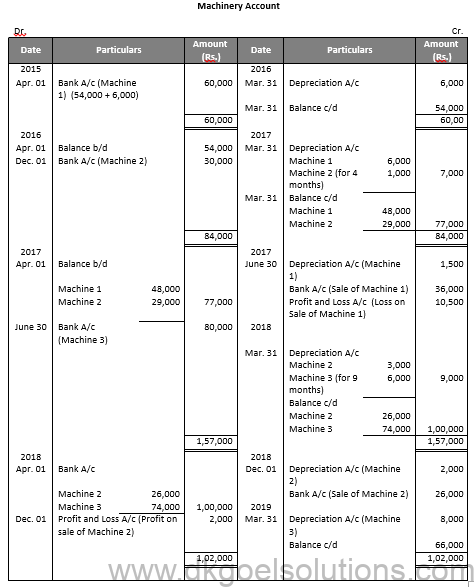
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of Profit or Loss on Sale on Machinery 1st
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 48,000
Less: Depreciation for 3 months 1,500
Value of Machinery on June 30, 2017 46,500
Less: Sale Value 36,000
Loss on Sale 10,500
2.) Calculation of Profit or Loss on Sale on Machinery 2nd
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 26,000
Less: Depreciation for 8 months 2,000
Value of Machinery on Dec. 01, 2018 24,000
Less: Sale Value 26,000
Profit on Sale 2,000
Question 8:
Solution 8:
Machinery Account

Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of Profit and Loss on sale of Machinery 1st:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2019 15,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 1,000
Value of Machinery Sept. 30, 2019 14,000
Less: Sale Value 8,200
Loss on Sale 5,800
Question 9:
Solution 9:

Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and loss:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2019 16,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 1,500
Value of Machinery on Jan.01, 2020 14,500
Less: Sale Value 6,000
Loss on Sale of Machinery 8,500
Question 10:
Solution 10:
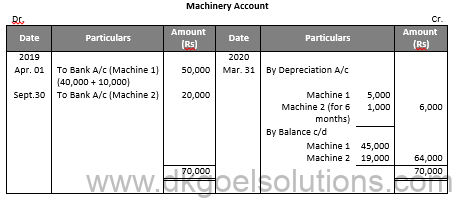
Question 11:
Solution 11:
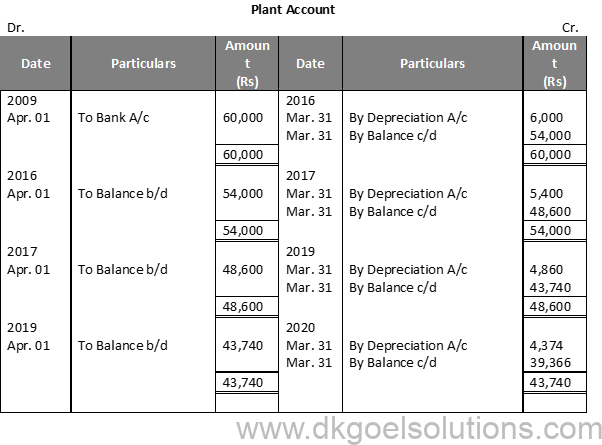
Question 12:
Solution 12:
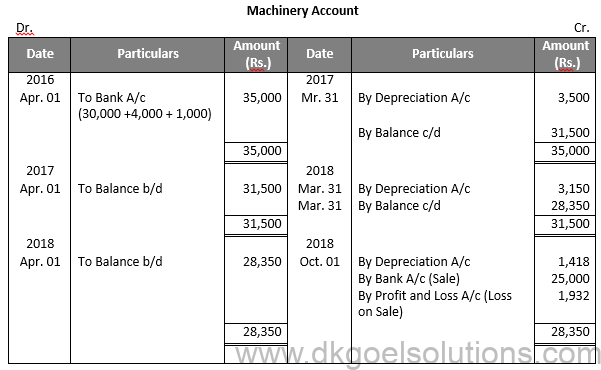
Working Note:-
Total Value of Machinery = 30,000 + 4,000 + 1,000 = 35,000
Calculation of Profit and loss:-
Particulars Amount (Rs.)
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 28,350
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 1,418
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2018 26,932
Less: Sale Value 25,000
Loss on Sale of Machinery 1,932
Question 13:
Solution 13:
Machinery Account
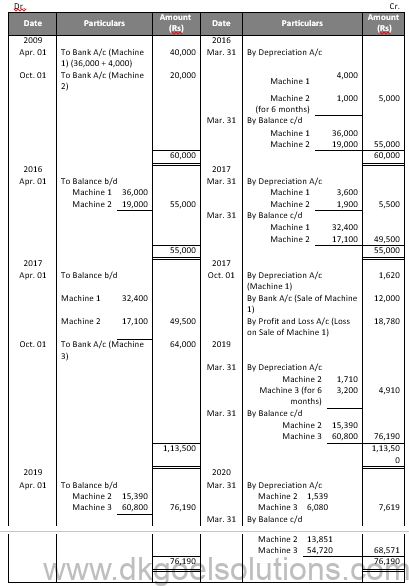
Question 14:
Solution 14:

Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Machinery:-
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 39,312
Less: Depreciation for 12 months 5,897
Value of Machinery on Mar. 31, 2019 33,415
Less: Loss on Sale (given) 5,000
Sale Value (Balancing Figure) 28,415
Question 15:
Solution 15:
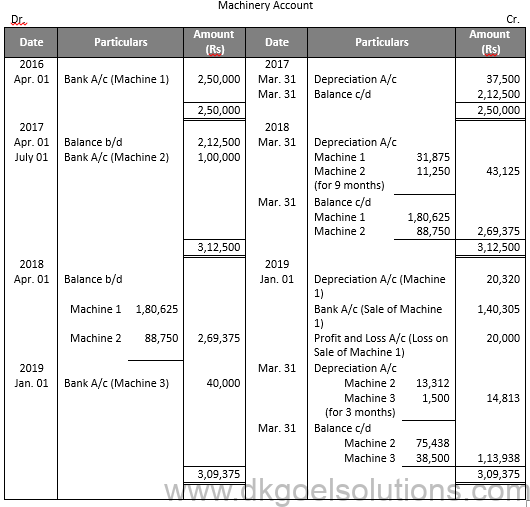
Working Note:-
Value of Machine 1
= Rs. 2,40,000 + Rs. 4,000 + Rs.6,000
= Rs. 2,50,000
Value of Machine 2
= Rs. 75,000 + Rs. 25,000
= Rs. 1,00,000
Point in mind:-
(i) In order to calculate the right benefit or loss, the profit for each year will only be calculated after all the costs of receiving profits have been compensated for. The reduction in the valuation of real assets or depreciation represents the cost of collecting income in the financial year on the basis of the usage of fixed assets. To assess right benefit or loss, depreciation is neither optional nor mandatory.
(ii) Giving a real and realistic understanding of the financial situation: depreciation, if not paid, will result in a higher valuation of the properties. As a consequence of this, an accurate and realistic view of the financial situation will not be reflected in the position statement or balance sheet.
Question 16:
Solution 16:
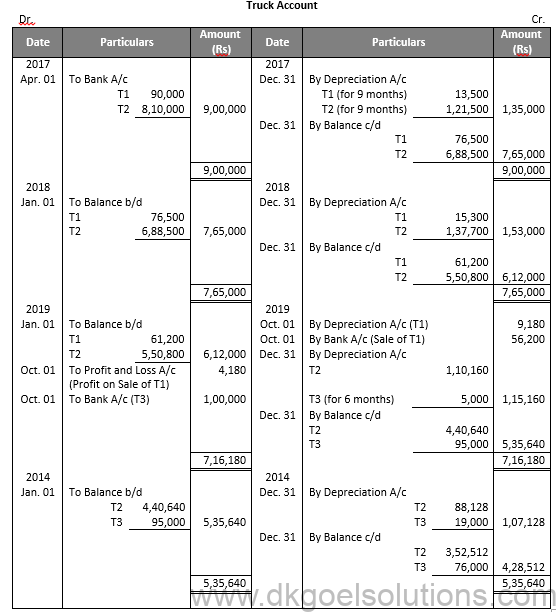
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of T1:-
Value of Truck on Jan. 01, 2019 61,200
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 9,180
Value of Truck on Oct. 01, 2019 52,020
Less: Sale Value 56,200
Profit on Sale 4,180
Question 17:
Solution 17:
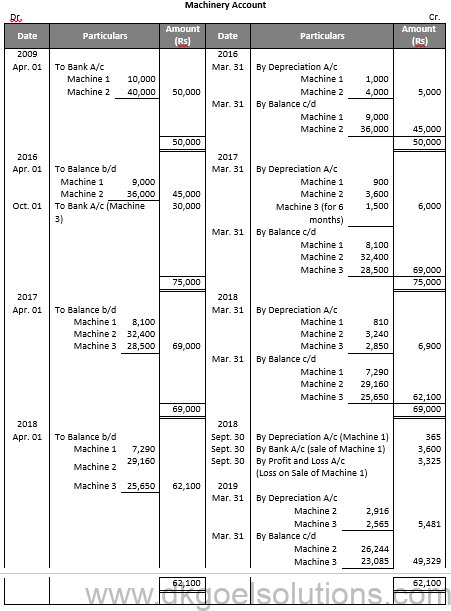
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of T1:-
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 7,290
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 365
Value of Machinery on Sept.30, 2018 6,925
Less: Sale Value 3,600
Loss on Sale of machinery 3,325
Question 18:
Solution 18:

Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and loss on Sale of assets:-
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 8,325
Less: Sale Value 3,000
Loss on Sale 5,325
Question 19:
Solution 19:
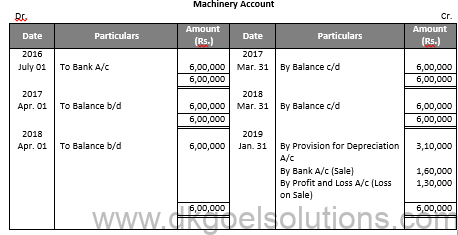
Working Note:-
Value of Machinery
= Rs. 5,70,000 + Rs. 30,000
= Rs. 6,00,000
Question 20:
Solution 20:
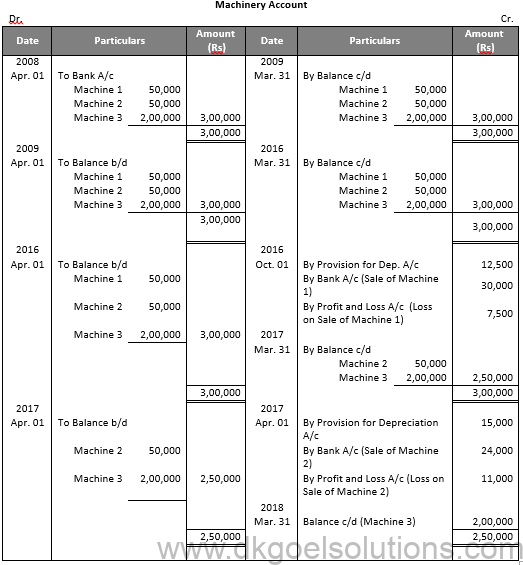
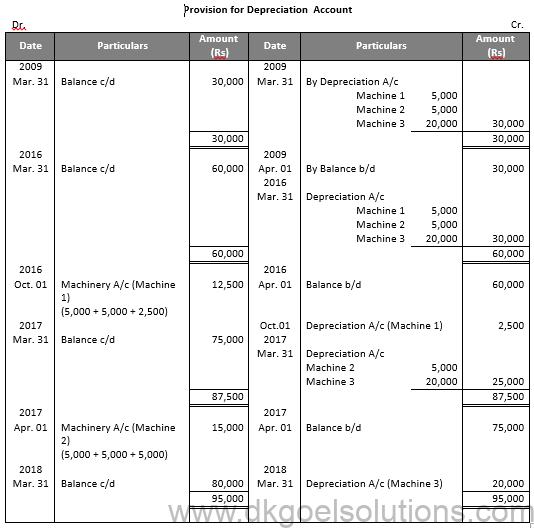
Working Note:-
Value of Machinery 1
= Rs. 5,000 + Rs. 5,000 + Rs. 2,500
= Rs. 12,500
Value of Machinery 2
= Rs. 5,000 + Rs. 5,000 + Rs. 5,000
= Rs. 15,000
Calculation of Profit and loss on sale of machinery 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2008 50,000
Less: Depreciation 5,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2009 45,000
Less: Depreciation 5,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2016 40,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 2,500
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2016 37,500
Less: Sale Value 30,000
Loss on Sale 7,500
Calculation of Profit and loss on sale of machinery 2:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2008 50,000
Less: Depreciation 5,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2009 45,000
Less: Depreciation 5,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2016 40,000
Less: Depreciation 5,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 35,000
Less: Sale Value 24,000
Loss on Sale 11,000
Question 21:
Solution 21:
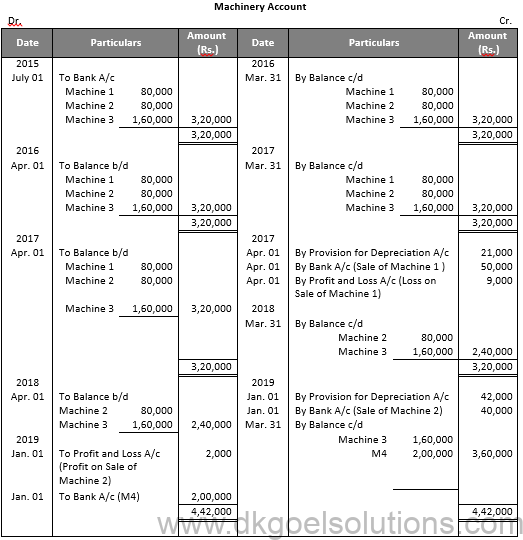
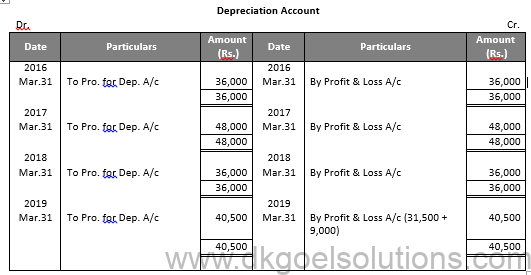
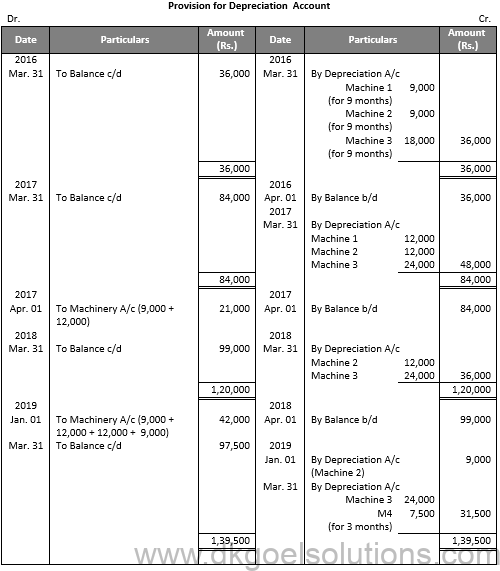
Working Note:-
Profit and loss on Sale of Machinery 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on July 01, 2015 80,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 9,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2016 71,000
Less: Depreciation 12,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 59,000
Less: Sale Value 50,000
Loss on Sale 9,000
Profit and loss on Sale of Machinery 2:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on July 01, 2015 80,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 9,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2016 71,000
Less: Depreciation 12,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 59,000
Less: Depreciation 12,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 47,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 9,000
Value of Machinery on Jan. 01, 2019 38,000
Less: Sale Value 40,000
Profit on Sale 2,000
Question 22:
Solution 22:
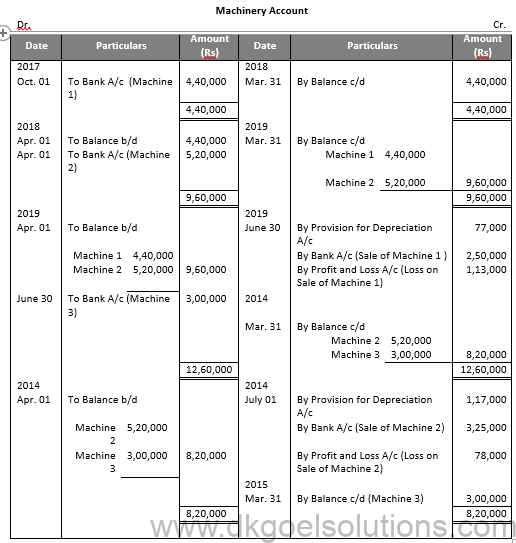
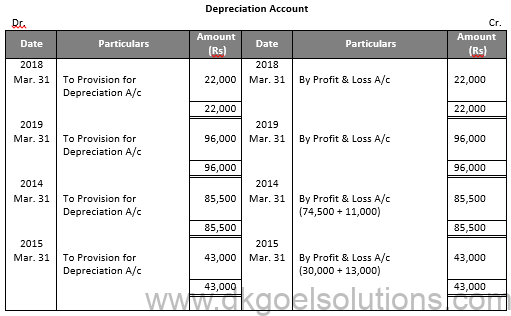
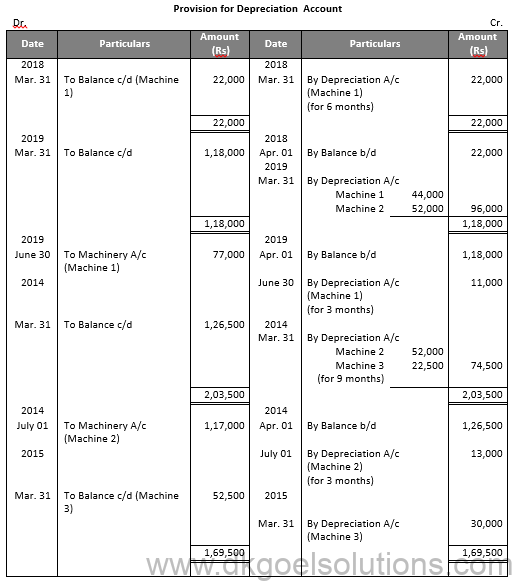
Working Note:-
Value of Machinery 1
= Rs. 22,000 + Rs. 44,000 + Rs. 11,000
= Rs. 77,000
Value of Machinery 2
= Rs. 52,000 + Rs. 52,000 + Rs. 13,000
= Rs. 1,17,000
Profit and Loss on Sale of Machinery 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2017 4,40,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 22,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 4,18,000
Less: Depreciation 44,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2019 3,74,000
Less: Depreciation for 3 months 11,000
Value of Machinery on June 30, 2019 3,63,000
Less: Sale Value 2,50,000
Loss on Sale 1,13,000
Profit and Loss on Sale of Machinery 2:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 5, 20,000
Less: Depreciation 52,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2019 4, 68,000
Less: Depreciation 52,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2014 4, 16,000
Less: Depreciation for 3 months 13,000
Value of Machinery on June 30, 2014 4,03,000
Less: Sale Value 3,25,000
Loss on Sale 78,000
Question 23:
Solution 23:
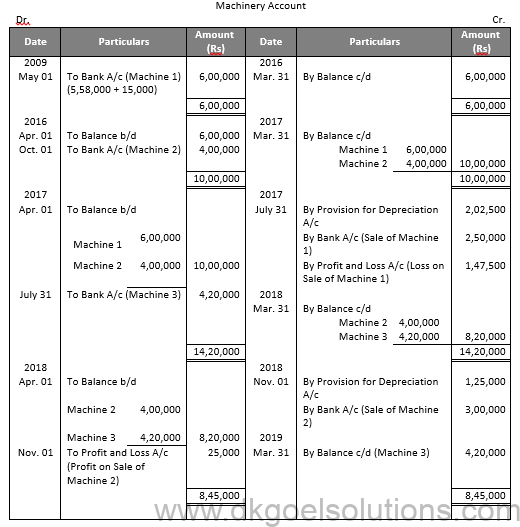
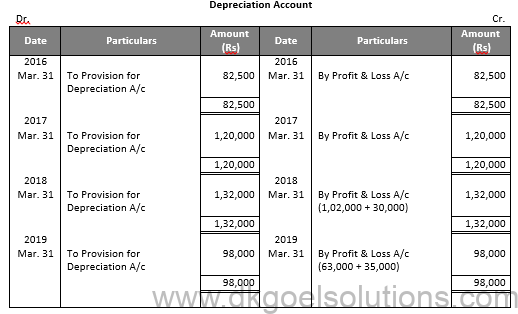
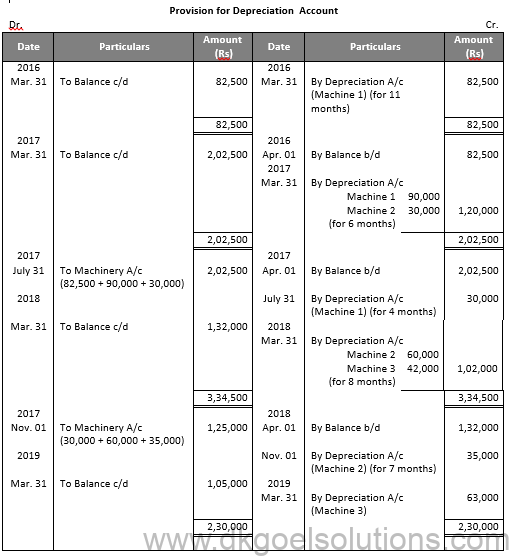
Question 24:
Solution 24:
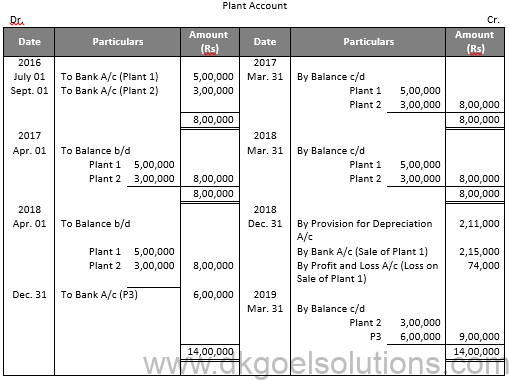
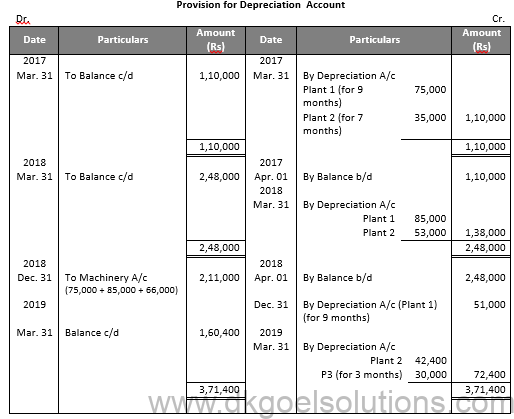
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Machinery 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Plant on July 01, 2016 5,00,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 75,000
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2017 4,25,000
Less: Depreciation 85,000
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2018 3,40,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 51,000
Value of Plant on Dec. 31, 2018 2,89,000
Less: Sale Value 2,15,000
Loss on Sale 74,000
Question 25:
Solution 25:

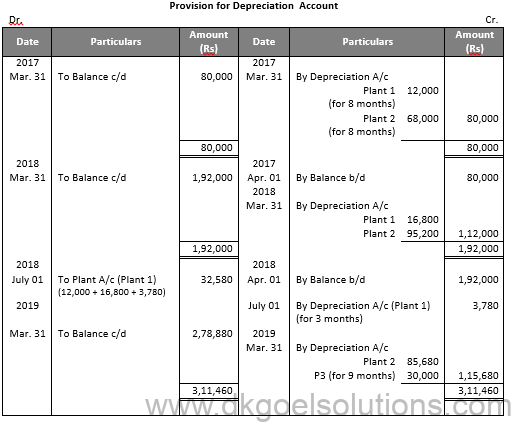
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Plant and Machinery 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Plant on Aug. 01, 2016 1,80,000
Less: Depreciation for 8 months 12,000
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2017 1,68.000
Less: Depreciation 16,800
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2018 1,51,200
Less: Depreciation for 3 months 3,780
Value of Plant on July 01, 2018 1,47,420
Less: Sale Value 1,00,000
Loss on Sale 47,420
Question 26:
Solution 26:


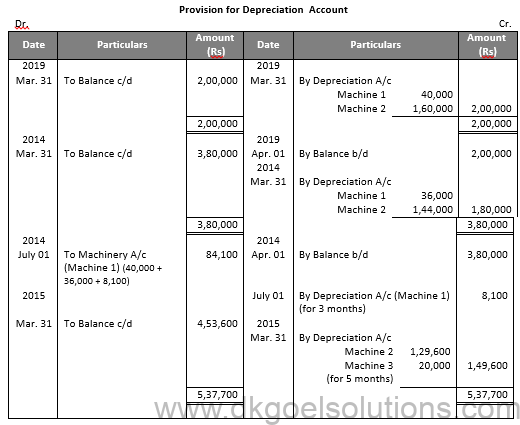
Question 27:
Solution 27:

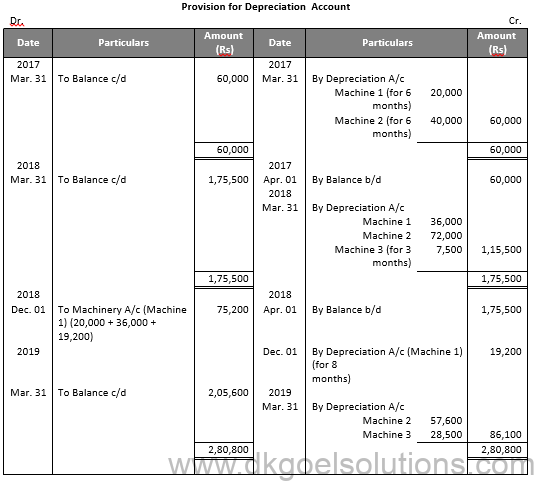
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on sales of Machinery 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2016 2,00,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 20,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 1,80,000
Less: Depreciation 36,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 1,44,000
Less: Depreciation for 8 months 19,200
Value of Machinery on Dec. 01, 2018 1,24,800
Less: Sale Value 80,000
Loss on Sale 44,800
Question 28:
Solution 28:
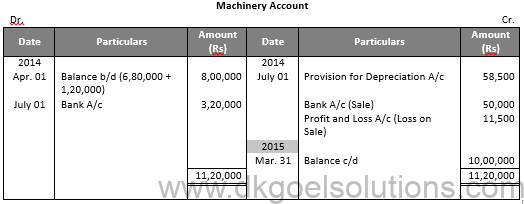
Working Note:-
Value of Machinery
= Rs. 6,80,000 + Rs. 1,20,000
= Rs. 8,00,000
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of machinery:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 1,20,000
Less: Depreciation for 3 Years 3 months 58,500
Value of Machinery July 01, 2014 61,500
Less: Sale Value 50,000
Loss on Sale 11,500
Calculation of Depreciation:-
Rs. 6,80,000 × 15% = Rs. 1,02,000
Rs. 1,20,000 × 15% × 3/12 = Rs. 4,500
Rs. 1,20000 × 15% × 9/12 = Rs. 36,000
Question 29:
Solution 29:
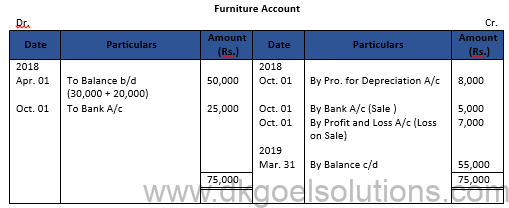

Working Note:-
Value of Machinery = Rs. 30,000 + Rs. 20,000 = Rs. 50,000
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Machinery:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Furniture on Apr. 01, 2014 20,000
Less: Depreciation for 4 Years @ 10% 8,000
Value of Furniture on Oct. 01, 2018 12,000
Less: Sale Value 5,000
Loss on Sale 7,000
Question 30:
Solution 30:

Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on sale of machinery:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2009 2,00,000
Less: Depreciation for 6 months 10,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2016 1,90,000
Less: Depreciation 19,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 1,71,000
Less: Depreciation 17,100
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01,2018 1,53,900
Less: Sale Value 80,000
Loss on Sale 73,900
Question 31:
Solution 31:
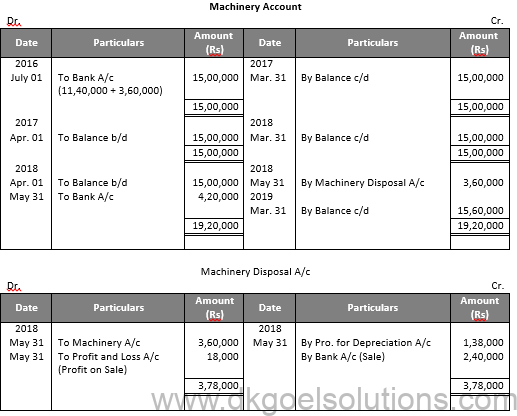
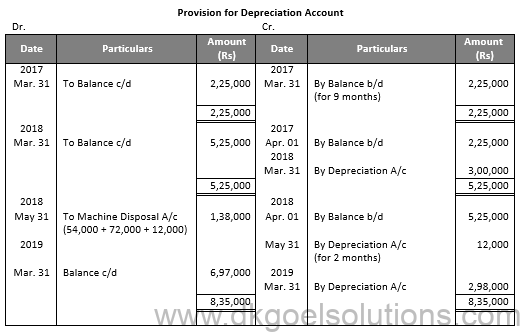
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Machinery:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on July 01, 2016 3,60,000
Less: Depreciation for 9 months 54,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 3,06,000
Less: Depreciation 72,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 2,34,000
Less: Depreciation for 2 months 12,000
Value of Machinery on May 31, 2018 2,22,000
Less: Sale Value 2,40,000
Profit on Sale 18,000
Question 32:
Solution 32:

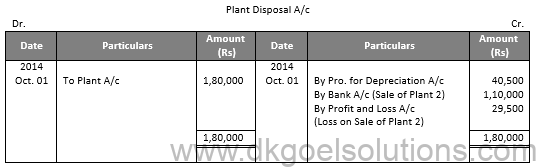
Point in Mind:-
Amount on Annual Depreciation under Fixed Instalment Method:-
= (Amount to be Depreciated)/(Number of year of life of Machine)
= (Cost Price-Scrap Value)/(Number of year of life of Machine)
Question 33:
Solution 33:
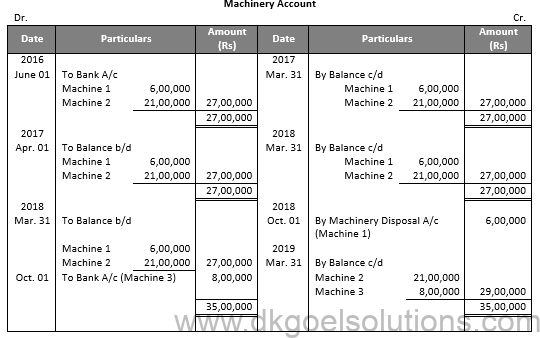
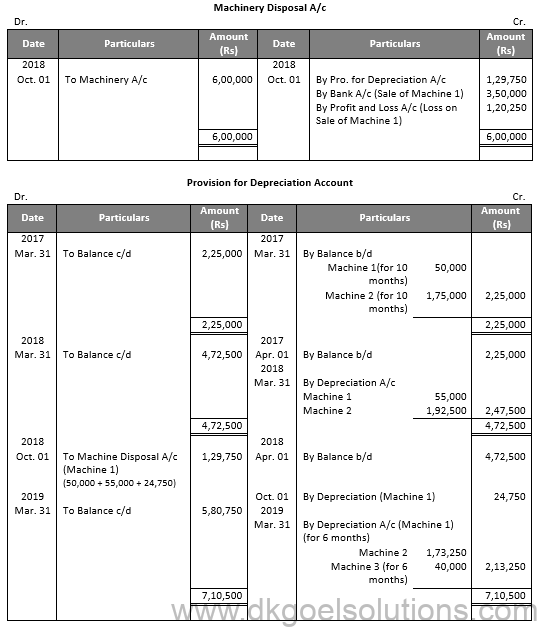
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and loss on Sale of machinery:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Machinery on June 01, 2016 6,00,000
Less: Depreciation @ 10% for 10 months 50,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2017 5,50,000
Less: Depreciation @ 10% 55,000
Value of Machinery on Apr. 01, 2018 4,95,000
Less: Depreciation @ 10% for 6 months 24,750
Value of Machinery on Oct. 01, 2018 4, 70,250
Less: Sale Value 3,50,000
Loss on Sale Machinery 1,20,250
Point in Mind:-
Amount on Annual Depreciation under Straight Line Method:-
= (Amount to be Depreciated)/(Number of year of life of Machine)
Question 34:
Solution 34:

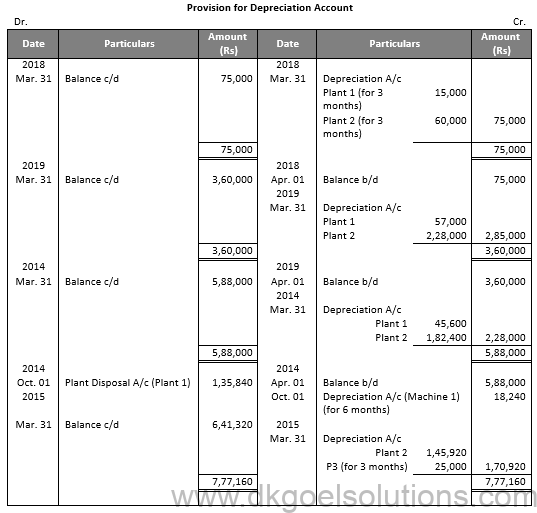
Working Note:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Plant on Jan. 01, 2018 3,00,000
Less: Depreciation for 3 months 15,000
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2018 2,85,000
Less: Depreciation 57,000
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2019 2,28,000
Less: Depreciation 45,600
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2014 1,82,400
Less: Depreciation for 3 months 18,240
Value of Plant on Oct. 01, 2014 1,64,160
Less: Sale Value 1,75,000
Profit on Sale 10,840
Question 35:
Solution 35:

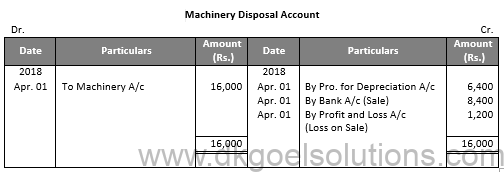
Working Note:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Furniture on Apr. 01, 2014 16,000
Less: Depreciation for 4 years @ 10% p.a. 6,400
Value of Furniture on Apr. 01, 2018 9, 600
Less: Sale Value 8,400
Loss on Sale of Furniture 1,200
Question 36:
Solution 36:
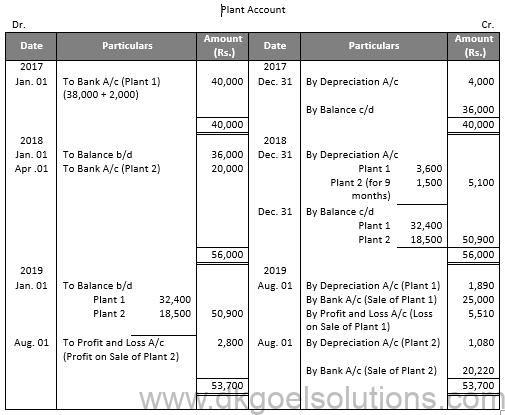
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Plant 1:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2019 32,400
Less: Depreciation for 7 months 1,890
Value of Plant on Aug. 01, 2019 30,510
Less: Sale Value 25,000
Loss on Sale 5,510
Calculation of Profit and Loss on Sale of Plant 2:-
Particulars Amount
Value of Plant on Apr. 01, 2019 18,500
Less: Depreciation for 7 months 1,080
Value of Plant on Aug. 01, 2019 17,420
Add: Profit on Sale 2,800
Sale Value 20,220
Question 37:
Solution 37:
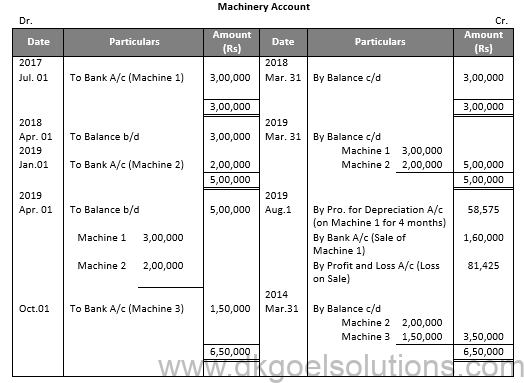

Working Note:- (DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 16 Depreciation)
Calculation of Profit and Loss:-

Question 38:
Solution 38:
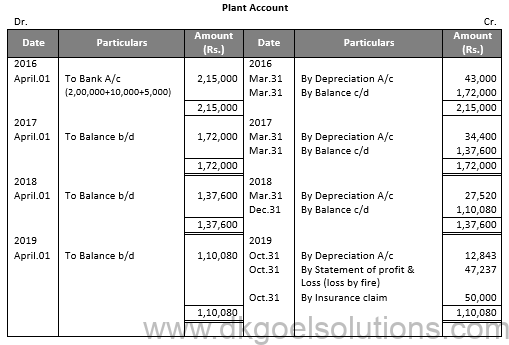
Working Note:-
Calculation of Profit and Loss:-

Point of Knowledge:-
(i) Asset disposition account: in the event of the selling of an asset. For the purposes of measuring benefit or loss on the disposition of an asset, a new account called ‘Asset Disposal Account’ is opened in the ledger. Journal entries for asset purchases or disposition will depend on the depreciation tracking process.
(ii) Written Down Value/Decreasing Balance/Reducing Balance Depreciation Billing Process: In this method, depreciation is paid yearly at a set rate on the decreasing balance or costs less depreciation. A fixed rate on the asset’s written down value is paid as a depreciation of the asset’s estimated useful life per year.

Depreciation can be highlighted as the process of constant decrement of a fixed asset’s value in terms of quality and quantity. For instance, let us say a company owns a car as a fixed asset. With time the car depreciates its original value. Determining the depreciated value of the assets allows businesses to define the actual value of the entire business accurately.
Here the most prominent reasons for providing depreciation –
● Depreciation helps businesses find their actual financial position by accurately calculating the exact figures.
● It assists in keeping track of the true profit and loss of a business.
Here are the ways to calculate depreciation –
● Straight-line Depreciation method
● Sum of the Year’s Digits Depreciation method
● Declining Balance Depreciation method
● Units of Production Depreciation method
Here are the advantages of the straight-line method of providing depreciation –
● It is one of the simplest and convenient methods.
● It gives a brief about the original price of the assets and the depreciated price.
● With this method, the assets can be entirely written off.
The demerits of Reducing Instalment Method of providing depreciation are listed below –
● In this method, it is quite challenging to write all the details of the assets.
● The omission Interest factor plays a significant role in this method.
Whenever an asset is disposed of or sold, a new account titled the asset disposal account is crafted in the ledger. This account clearly depicts the profit or loss on the sale of the fixed asset. The account is also titled Profit on Sale of Asset when the selling price is higher than the assets written value. While the account is termed Loss on Sale of Asset if the sale price is lower than the written price.
Here are the advantages of the written down value method for depreciation –
● Quick and easy to calculate.
● No burden of undue.
● Wealth balance is never recorded as zero.
