Exam Question for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Biology teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Biology and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Biology exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes are very important and should be revised daily.
Exam Question Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes
Read the following passage and answer any four questions from 46 to 50 given below:
The DNA, which is transferred from one organism into another by joining it with the vehicle DNA is called passenger or foreign DNA. Generally three types of passenger DNAs are used. These are complementary DNA (cDNA), synthetic DNA (sDNA) and random DNA. Complementary DNA (cDNA) is synthesized on RNA template (usually mRNA) with the help of reverse transcriptase. Synthetic DNA (sDNA) is synthesized on DNA template or without a template. Random DNA are small fragments formed by breaking a chromosome of an organism in the presence of restriction endonucleases.
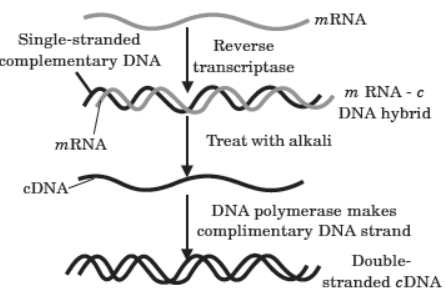
Question. During cDNA formation, what would happen if DNA formed by reverse transcriptase is not treated with the alkali?
(a) cDNA will not be digested
(b) mRNA will not be digested
(c) Hydrogen bonds will not form between base pairs
(d) mRNA will not be formed.
Answer : B
Question. DNA synthesised without a template is referred to as
(a) complementary DNA
(b) random DNA
(c) synthetic DNA
(d) Z-DNA.
Answer : C
Question. Enzyme that helps in the formation of double stranded cDNA is
(a) DNA synthetase
(b) ligase
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) helicase.
Answer : C
Question. Reverse transcriptase enzyme was discovered by
(a) Temin and Baltimore
(b) Cohen and Boyer
(c) Arber and Nathan
(d) Paul Berg.
Answer : A
Question. DNA polymerase can be obtained form
(a) retrovirus
(b) Agrobacterium
(c) tobacco mosaic virus
(d) Thermus aquaticus.
Answer : D
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 51-60, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA to produce sticky ends or blunt ends.
Reason : Stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in specific regions of DNA sequence.
Reason : DNA fingerprinting is the basis ofpa ternity testing.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Bacteriophage vectors are more advantageous than plasmid vectors.
Reason : Bacteriophage vectors can be easily detected at the time of cloning experiments.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Soil inhabiting bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is called a natural plant genetic engineer.
Reason : Agrobacterium tumefaciens produce crown galls in several dicot plants.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Type I restriction endonucleases are not used in recombinant DNA technology.
Reason : Type I restriction endonucleases recognise specific sites within the DNA but do not cut these sites.
Answer : A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the material used as matrix in gelelectrophoresis and mention its role.
Answer : Most commonly used matrix in DNA gel electrophoresis is agarose. It provides sieving effect for separation of DNA fragments according to their size.
Question. What is the role of sterile air bubbles in the sparged stirred-tank bioreactor?
Answer : The sterile air bubbles in the sparged stirred-tank bioreactor increases the surface area for oxygen transfer.
Question. State what happens when an alien gene is ligated at SalI site of pBR322 plasmid.
Answer : When an alien gene is ligated at SalI site of pBR322, the gene tetR becomes non functional and plasmid loses its tetracycline resistance. Hence, the cell possessing such recombinant pBR322 will not be able to grow on tetracycline.
Question. Who is considered as the “father of genetic engineering”?
Answer : Genetic engineering was started by Paul Berg (1972) when he was able to introduce a gene of SV-40 into a bacterium. He is often considered as “father of genetic engineering”.
Question. Why do DNA fragments move towards the anode during gel-electrophoresis?
Answer : DNA is a negatively charged molecule hence during gel electrophoresis it moves towards anode (positive electrode) under the influence of electrical field.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Write the role of ‘ori’ and ‘restriction’ site in a cloning vector pBR322.
Answer : Origin of replication (ori) site in cloning vector pBR322 is a sequence from where replication starts. Any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within host cell. Restriction site within the markers tetR and ampR genes permit an easy selection for cells transformed or the recombinant pBR322.
Question. Differentiate between rDNA and cDNA.
Answer : Differences between rDNA and cDNA are as follows:

Question. What are the two main discoveries that led to the built of genetic engineering ?
Answer : Genetic engineering is the technique to form recombinant DNA and then to introduce recombinant DNA into appropriate host. Two main discoveries which led to genetic engineering are : (i) Discovery of plasmid by William Hays and Joshua Lederberg in 1952.
(ii) Discovery of restriction endonuclease by Arber in 1962.
Question. A recombinant DNA is formed when sticky ends of vector DNA and foreign DNA join.
Explain how the sticky ends are formed and get joined.
Answer : When restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, between the same two bases on the opposite strands, it leaves single stranded portions at the ends. This forms overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand. They are called sticky as they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. The stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. Why is it essential to maintain sterile condition in biotechnological processes?
Answer : Sterile condition enable growth of only the desired microbe/ eukaryotic cell in large quantities for the biotechnological products like antibiotics, enzymes, etc.
Question. Explain any two methods of vectorless gene transfer.
Answer : Vectorless gene transfer is a method to introduce recombinant DNA into recipient cells of host without involving carrier molecule. Two methods of vectorless gene transfer are:
(i) Microinjection : It is the introduction of foreign gene into plant cell or animal cell by using microneedles or micropipettes.
(ii) Electroporation : In this method, electrical impulses induce transient pores in the plant cell membrane through which the DNA molecules are incorporated into the plant cells.
Question. State the role of UV-light and ethidium bromide during gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments.
Answer : DNA fragments can be seen only after staining. Ethidium bromide is used to stain DNA fragments followed by exposure to UV radiation. This gives bright orange colour to DNA
fragments which helps to view separated DNA fragments.
Question. Name the natural source of agarose. Mentionone role of agarose in biotechnology.
Answer : Agarose is commonly used as matrix in agarose gel electrophoresis. It is extracted from sea weeds. In recombinant DNA technology, agarose is used to separate DNA fragments according to their sizes.
Question. Why are genes encoding resistance to antibiotics considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector? Explain with the help of one example.
Answer : Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics are considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector because they help in selecting transformant cell from non-transformant ones. The genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as tetracycline, ampicillin, kanamycin or chloramphenicol, etc. are useful selectable markers for E. coli. The common E. coli cells are not resistant to any of these antibiotics. Plasmid pBR322 has two antibiotic resistance genes – ampicillin resistance (ampR) and tetracycline resistance (tetR) which are considered useful for selectable markers. The presence of restriction sites within the markers tetR and ampR permits an easy selection for cells transformed with the recombinant pBR322. For example, insertion of the DNA fragment into the plasmid using enzyme PstI or PvuI places the DNA insert within the gene ampR. This makes ampR nonfunctional. Bacterial cells containing such a recombinant pBR322 will be unable to grow in the presence of ampicillin, but will grow on tetracycline.
Question. How and why is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus employed in recombinant DNA technology ? Explain.
Answer : Taq DNA polymerase isolated from thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus synthesises the DNA region from gene of interest between the primers, using dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates) and Mg2+. The primers are extended towards each other so that the DNA segment lying between the two primers is copied. It is stable even at high temperatures. Taq polymerase is heat stable enzyme and is able to withstand high temperature induced denaturation of DNA during PCR. Hence it is preferred in PCR reactions.
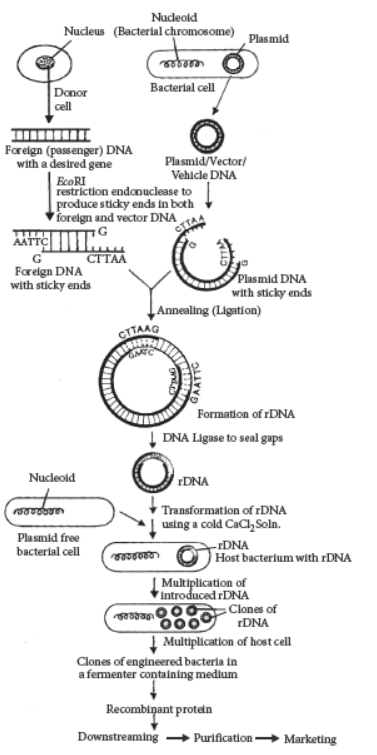
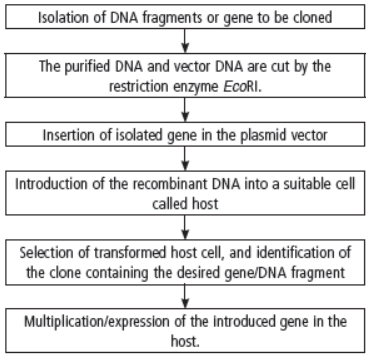
Question. Prepare a flow chart in formation of recombinant DNA by the action of restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoRI.
Answer :
Question. Refer to the given figure and answer the following questions.
(a) Identify the labelled part A and mention its function.
(b) What does B and C represent?
(c) Briefly describe the process shown in the given figure.
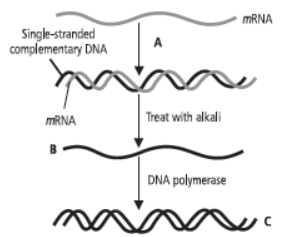
Answer : (a) Labelled part A represents the enzyme reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcriptase is used to synthesise DNA or complementary DNA by using mRNA as template.
(b) The labelled part B represents the separated singlestranded complementary DNA after the RNA-DNA complex is treated with alkaline phosphatase enzyme. The labelled part C is the newly formed double-stranded cDNA.
(c) This diagram represents the synthesis of complementary DNA or cDNA from RNA. With the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase, an RNA-DNA complex is formed from RNA (usually mRNA) where RNA acts as the template. The mRNA in the RNA-DNA complex is digested in the presence of alkaline phosphatase enzyme. A cDNA is formed on the separated single-stranded DNA template with the help of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some experiments, explain the process of the following :
(a) Cutting of desired gene at specific locations.
(b) Synthesis of multiple copies of the desired gene.
Answer : (a) Desirable DNA sequences are cut by the use of enzyme restriction endonuclease. The restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, between the same two bases on the opposite strands, it leaves single stranded portions at the ends. This forms overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand. They are called sticky as they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. The stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
(b) The three steps involved in each cycle of PCR are :
(i) Denaturation
(ii) Annealing
(iii) Extension PCR is based on the principle that a DNA molecule, when subjected to high temperature, splits into two strands due to denaturation. These single stranded DNA molecules are then converted to original double stranded molecules, in the presence of enzyme DNA polymerase. A double stranded molecule of DNA is duplicated in this way and multiple copies of original DNA sequence can be generated by repeating the process several times. Such repeated amplification is achieved by the use of thermostable DNA polymerase (isolated from Thermus aquaticus), which remain active during the high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA.
Question. (a) Mention the role of vectors in recombinant DNA technology. Given any two examples.
(b) With the help of diagrammatic representation only, show the steps of recombinant DNA technology.
Answer : (a) The cloning vectors are DNA molecules that can carry a foreign DNA segment and replicate inside the host cell. These are plasmids, cosmids, phagemids, yeast artificial chromosome (YAC), bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), transposons and virus. Cloning vector carry rDNA and they generally have high copy number, they can produce multiple number of required gene.
(b) Diagram showing various steps of recombinant DNA technology is given below: