Notes for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 2 Issue and Redemption of Debentures
Commerce students can refer to the Issue and Redemption of Debentures Notes Class 12 Accountancy given below which is an important chapter in class 12 accountancy book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Accountancy teachers have prepared these notes for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Issue and Redemption of Debentures Notes Class 12 Accountancy
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Issue and Redemption of Debentures which are really useful and have been recommended by Class 12 Accounts teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books for Class 12 Accounts.
Choose the correct answer:
A. Debentures which are transferrable by mere delivery are:
(a) Registered debentures
(b) First Debentures
(c) Bearer debentures
(d) None of these
Answer:
Bearer debentures
B. The following journal entry appears in the books of X Co. Ltd.
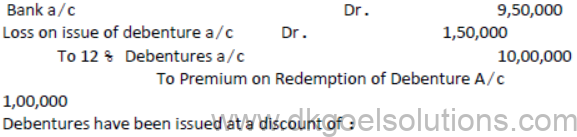
(a) 15 %
(b) 5 %
(c) 10 %
(d) 8 %
Answer:
(b) 5 %
C. X Co. Ltd purchased assets worth Rs 14, 40,000. It issued debentures of Rs 100 each at a discount of 4 percent in full satisfaction of the purchase consideration. The number of debentures issued to vendor is:
(a) 15, 000
(b) 14,400
(c) 16,000
(d) 30,000
Answer:
(a) 15, 000
C. X Co. Ltd purchased assets worth Rs 14, 40,000. It issued debentures of Rs 100 each at a discount of 4 percent in full satisfaction of the purchase consideration. The number of debentures issued to vendor is:
(a) 15, 000
(b) 14,400
(c) 16,000
(d) 30,000
Answer:
(a) 15, 000
D. Convertible debentures cannot be issued at a discount if:
(a) They are to be immediately converted;
(b) They are not to be immediately converted,
(c) None of the above
(d) Both a and b
Answer:
(a) They are to be immediately converted;
E. Discount on issue of debentures is shown under the following head in the Balance sheet :
(a) Statement of profit and Loss,
(b) Other non-Current Assets,
(c) Debentures account
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
F. Debentures can be issued at :
(a) Par
(b) Discount
(c) Premium
(d) All of them
Answer:
(d) All of them
G. Debenture is also named as :
(a) Share
(b) Bond
(c) Equity
(d) Reserve
Answer:
(b) Bond
H. When debentures are issued at a discount and are redeemable at a premium, which of the following accounts is debited at the time of issue:
(a) Debentures account
(b) Premium on redemption of debentures account,
(c) Loss on issue of debentures account
(d) Securities Premium Reserve Account
Answer:
(c) Loss on issue of debentures account
I. When all the debentures are redeemed, balance in the debentures redemption fund account is transferred to :
(a) Capital reserve,
(b) General reserve,
(c) Statement of profits and loss
(d) Any of these
Answer:
(b) General reserve,
Fill in the blanks
a) A……………….. may be defined as subsidiary or secondary or additional security beside the primary security when a company obtains a loan or overdraft from a bank or any other financial Instituiton.
Answer:
collateral security
b) …………………….. is a written instrument acknowledging a debt under the common seal of the company.
Answer:
Debenture
c) ………………. refer to those debentures where a charge is created on the assets of the company for the purpose of payment in case of default. The charge may be fixed or floating.
Answer:
Debenture
d) Debentures which are convertible into equity shares or in any other security either at the option of the company or the debenture holders are called …………….
Answer:
convertible debentures
e) ……….. can be issued at dicount but………… cannot be issued at discount except ESOP.
Answer:
Debentures, Shares
f) …………….. refers to extinguishing or discharging the liability on account of debentures in accordance with the terms of issue.
Answer:
Redemption of debentures
g) The amount credited to the Debenture Redemption Reserve shall not be utilised by the company except for the purpose of ………………..
Answer:
redemption of debentures
h) No DRR is required for debentures issued by …………… regulated by Reserve Bank of India …………….. Companies for both public as well as privately placed debentures.
Answer:
All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs) Banking
Question. Z ltd issued 2000, 10% debentures of Rs 100 each, at par. Debentures payable as follows:
Application Rs.40 Allotment Rs.60
The debentures were fully subscribed and all the amount was duly received. Pass the necessary journal entry.
Solution: [DEBENTURES ISSUED AT PAR]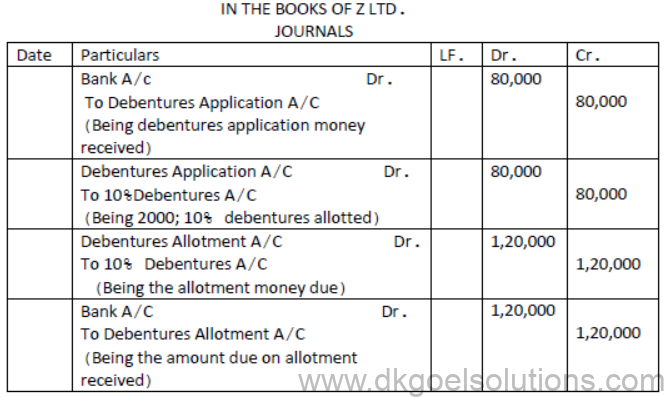
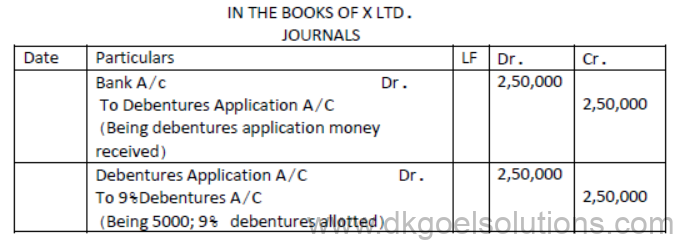
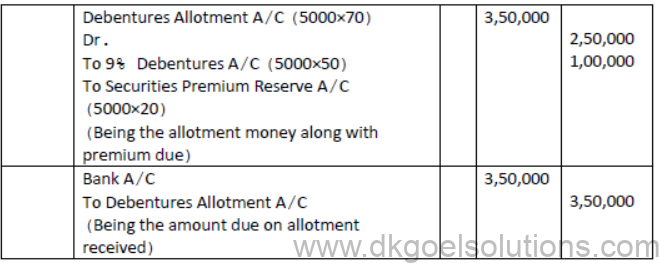
Question. X ltd issued 5000; 9% Debentures of Rs.100 each at a premium of 20% payable:
On Application-Rs.50, On Allotment- Balance
Applications were received for the debentures issued and also the amount due on allotment including premium was received. Pass journal entries for the above.
- Solution:[DEBENTURES ISSUED AT PREMIUM]
Question. Y ltd issued 20,000, 9% Debentures of Rs.100 each at a discount of 4% on 1st April, 2019, payable Rs.30 on application and the balance on allotment. The debentures are redeemable after 5 years. Pass Journal entries for the issue of debentures and writing off discount on issue of debentures.
Solution: [DEBENTURES ISSUED AT A DISCOUNT]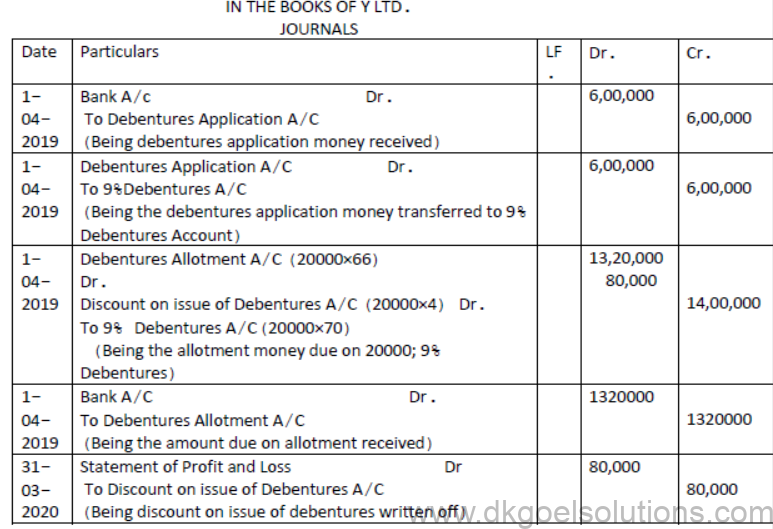
Question. Jyoti ltd. invited applications for 3000;12% Debentures of Rs.100 each at a premium of Rs.50 per Debentures. Full amount was payable on application. Application were received for 4000 debentures. Applications for 1000 debentures were rejected and application money was refunded. Debentures were allotted to the remaining applicants.
Solution:[OVER SUBSCRIPTION]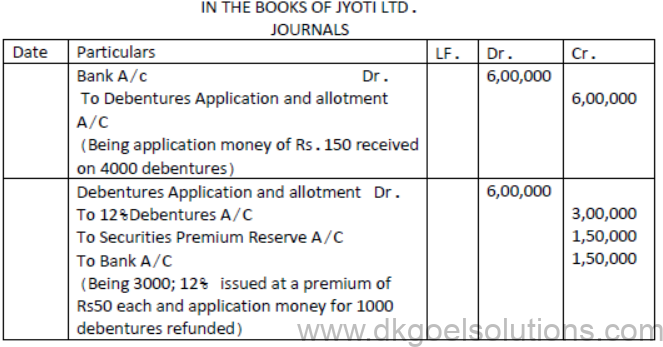
Question. Honey ltd issued 10,000, 9% Debentures of Rs.100 each for subscription, payable Rs.60 on application and balance on allotment. Subscription was received for 9000 debentures. Allotment was made and due amount was received.
Pass necessary journal entries for issue and allotment of debentures.
Solution: [UNDER SUBSCRIPTION]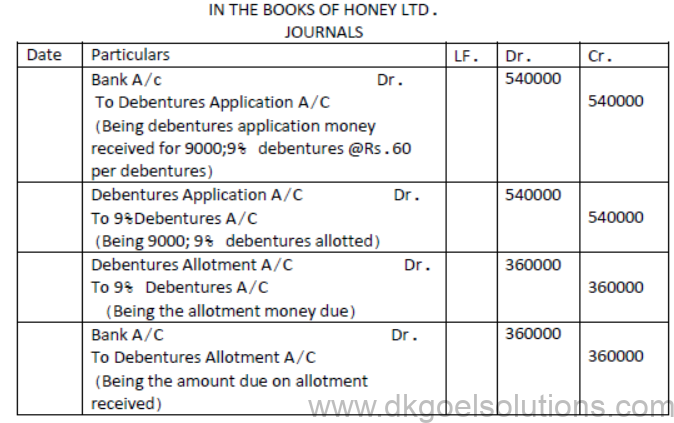
Question. A company purchased assets of Rs.9,90,000 from another firm. Payment was by issuing, 11% Debenture of Rs.100 each. Pass journal entries when debentures have been issued at par.
Solution: [ISSUE OF DEBENTURES FOR CONSIDERATION OTHER THAN CASH]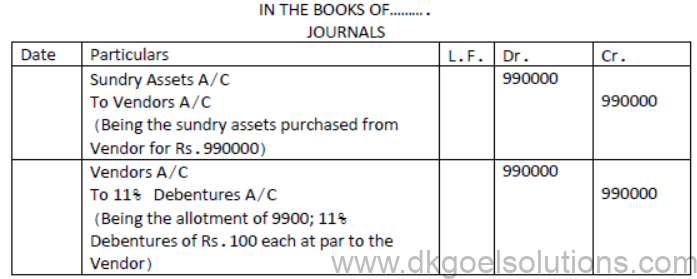
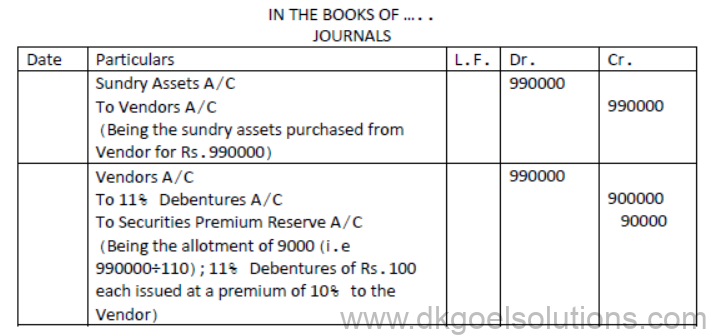
Question. A company purchased assets of Rs.990000 from another firm. Payment was by issuing, 11% Debenture of Rs.100 each. Pass journal entries when debentures have been issued at a premium of 10%.
Solution:
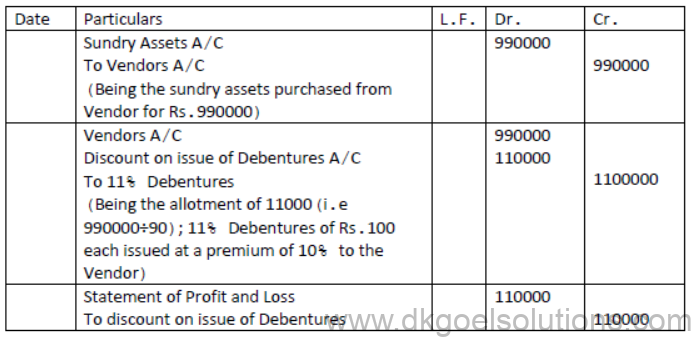
Question. A company purchased assets of Rs.990000 from another firm. Payment was by issuing, 11% Debenture of Rs.100 each. Pass journal entries when debentures have been issued at a discount of 10%.
Solution:
Question. X ltd purchased building for Rs.22,00,000. Half the payment was made by cheque and the balance half by issue of 9% Debentures of Rs.100 each at a premium of 10%. Pass necessary Journal entries.
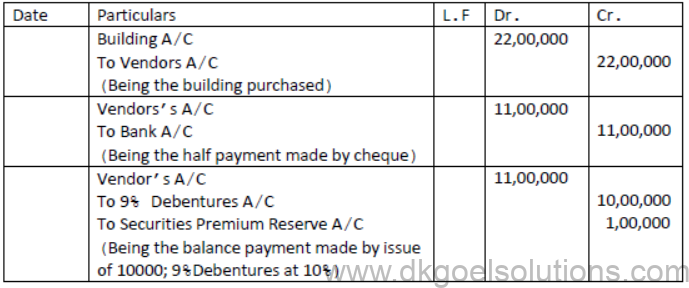
Number of Debentures issued= (2200000-1100000)÷110=10000 Debentures
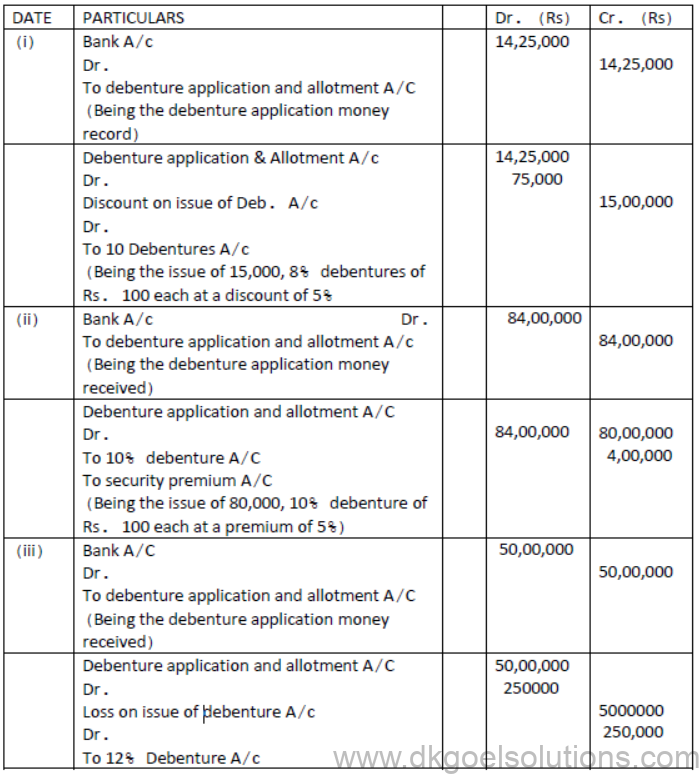
Question. Pass Journal entries to record the following transaction:
(i) A Ltd. issued 15000; 8% Debentures of Rs. 100 each at discount of 5% to be repaid at par at the end of 5 years.
(ii) A Ltd. Issues 10% Debentures of ` 100 each for the total nominal value of Rs. 80,00,000 at a premium of 5% to be redeemed at par.
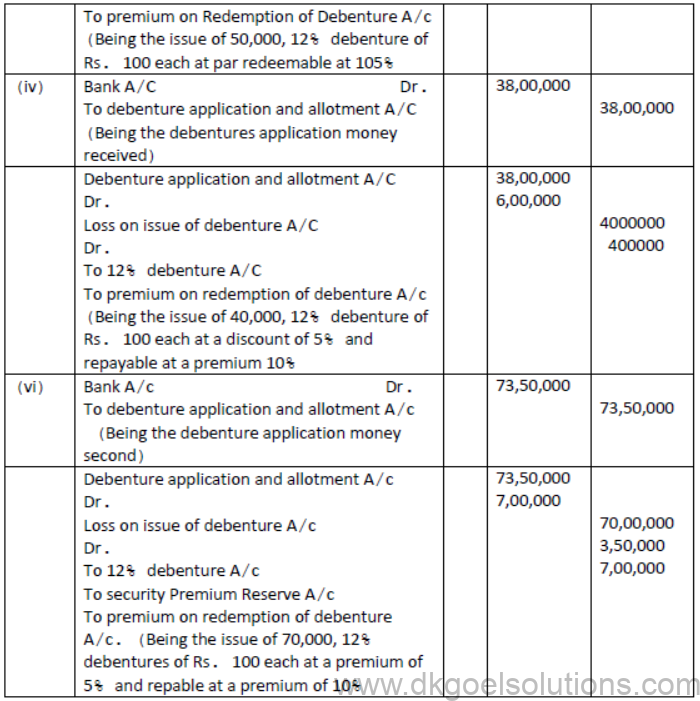
(iii) A Ltd. Issues 50,00,000; 9% Debentures of 100 each at par but redeemable at the end of 10 years at 105%.
(iv) A Ltd. Issued Rs40,00,000, 12% debentures of 100 each at a discount of 5% repayable at a premium of 10% at the end of 5 years.
(v) A Ltd issued 70,000; 12% debentures of 100 each at a premium of 5% repayable at 110% at the end of 10 years.
Solution: [Issue of debentures from terms of Redemption]
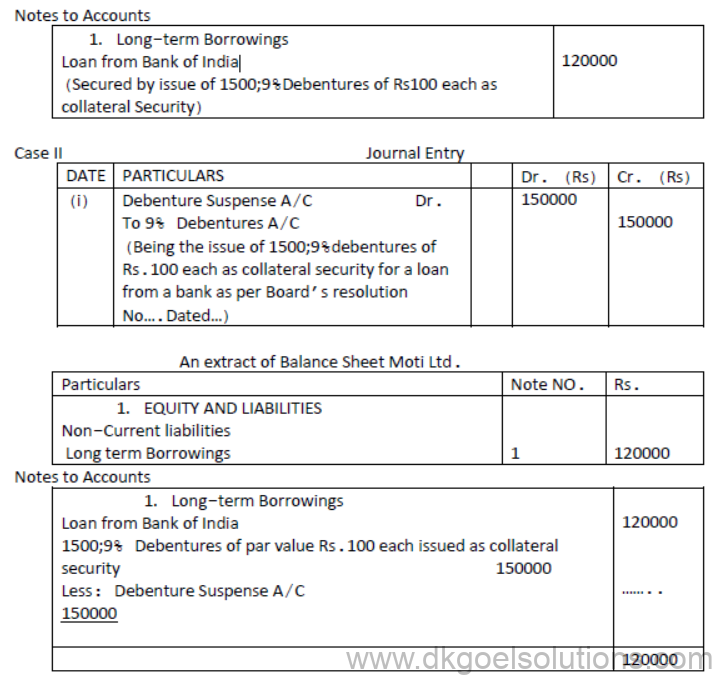
Question. Moti ltd. Obtained loan of Rs.120000 from Bank of India and issued 1500; 9% Debentures of Rs.100 each as collateral security. How will be issues of Debentures shown in the Balance Sheet?
Case I. when journal entry is NOT passed.
Case II. When journal entry is passed.
Solution: [ Debentures as collateral Security]
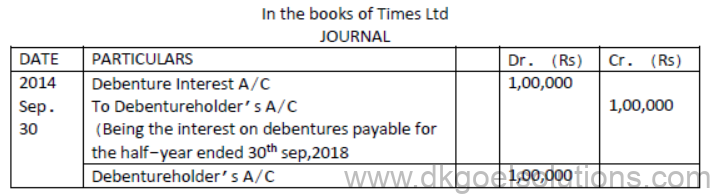
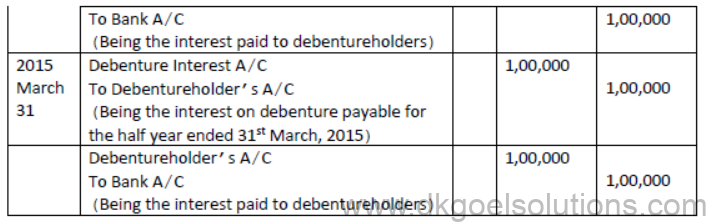
- Question. Times ltd issued 20000; 10% Debentures of Rs.100 each on 1st April 2018. The issue was fully subscribed. According to the terms of issue, interest is payable on half yearly basis. Pass journal entries for the year ended 31st March,2019 (Ignore TDS)
Solution: [ Interest on Debentures]
Question.Rohit Ltd. Has issued 50000, 8% Debentures of Rs.100 each at a discount of 9% on July 1, 2019. The company has balance of Rs.5,00,000 in Securities Premium Reserve. Pass necessary journal entries for issue of debentures and to write off discount/loss on issue of debentures. The debentures are redeemable after 5 years at a premium of 7%.
Solution: [Writing off discount/loss on issue of debentures]
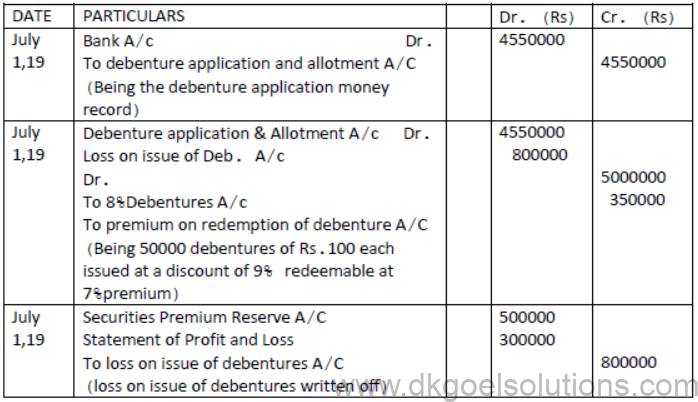
Question. On April 1st 2019 X ltd issued 10,000 ,8% Debentures of Rs.100 each at a premium of 5%, to be redeemable at a premium of 10%, after 5 years. The entire amount was payable on application. The issue was oversubscribed to an extent of 10,000 debentures and the allotment was made proportionately to all the applicants. The securities premium account has not been utilised for any other purpose during the year. Give journal entries for the issue of debentures and writing off loss on issue of debentures.
Solution:
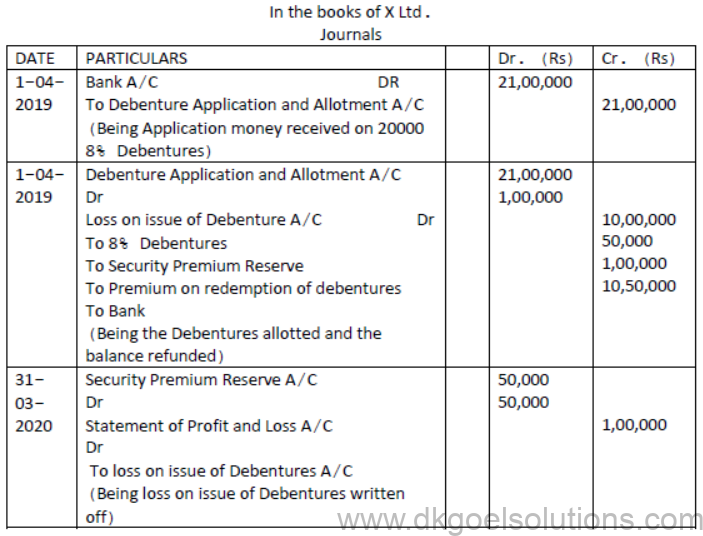
Question.X ltd took over the business of Y Ltd. on 01-04-2020. The details of the agreement regarding the assets and liabilities to be taken over are:
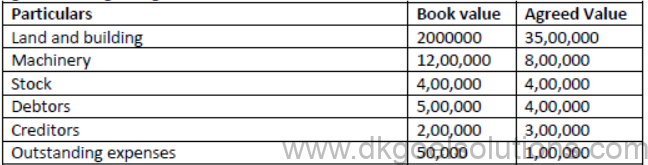
It was decided to pay for purchase consideration as Rs.700,000 through cheque and balance by issue of 2,00,000 9%Debentures of Rs.20 each at a premium of 25%. Journalise.
Solution:

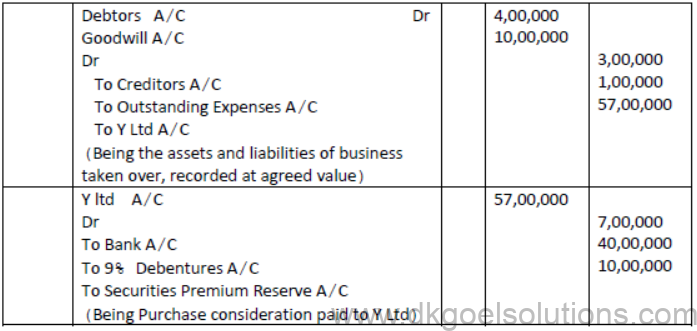
Question.. A ltd. issued 2,000: 9% Debentures of Rs.100 each on the following terms:
Rs.20 on Application: Rs.20 on allotment : Rs.30 on first call: Rs.30 on final call.
The public applied for 2,400 debentures. Applications for 1800 debentures were accepted in full. Applications for 400 Debentures were allotted 200 debentures and applications for 200 debentures were rejected. Pass necessary journal entries.
Solution:
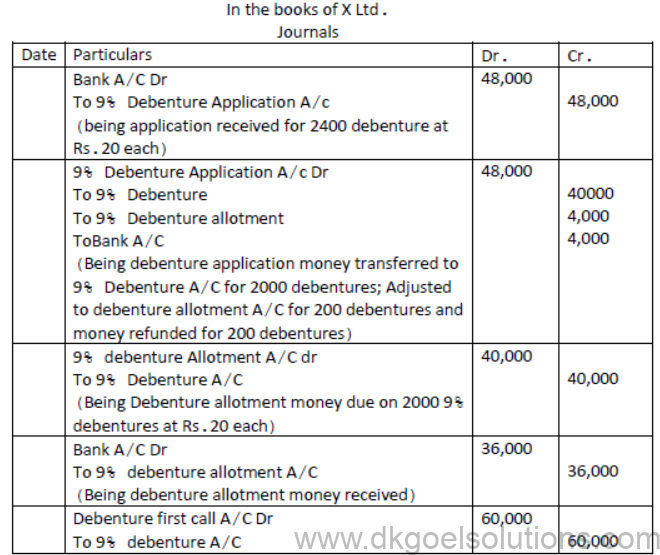
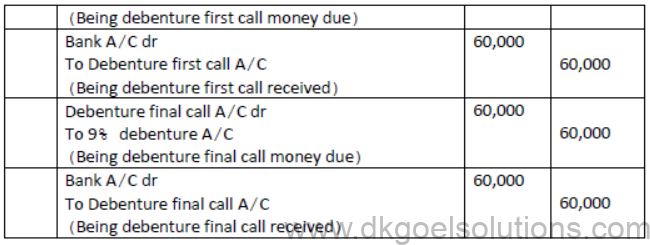
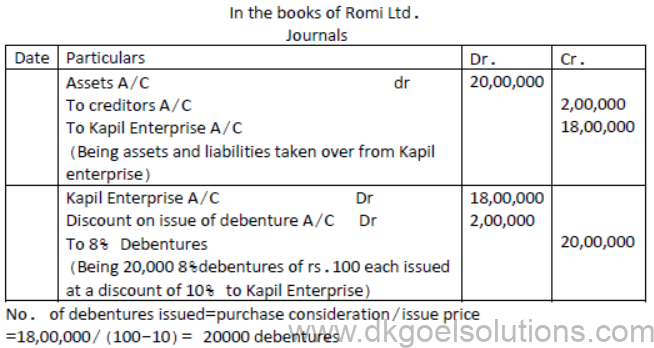
Question. Romi ltd acquired assets of Rs.20 lakhs and took over the creditors of Rs. 2 lakhs from Kapil enterprise. Romi ltd issued 8% debentures of Rs.100 each at a discount of 10% as purchase consideration. Record necessary journal entries in the books of Romi ltd.
Solution:
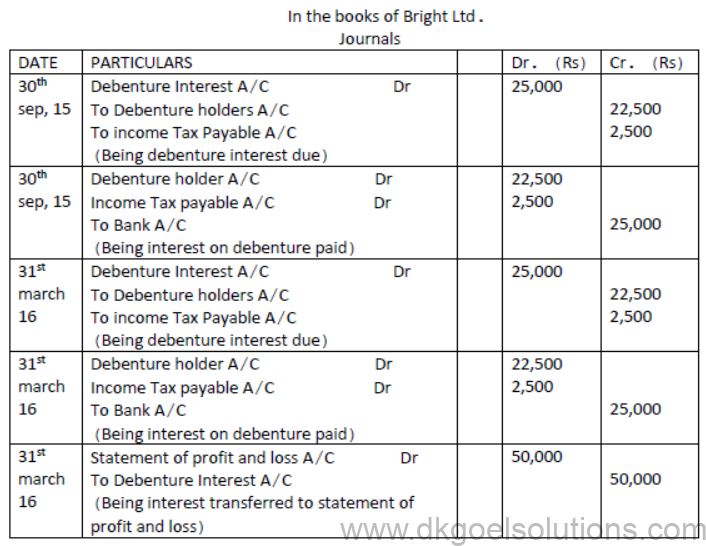
Question. Bright ltd. issued 5000; 10% Debentures of Rs.100 each on 1st April, 2015. The issue was fully subscribed. According to the terms of issue, interest on debenture is payable half yearly on 30th September and 31st March and the tax deducted at source is 10%. Pass necessary journal entries related to the debenture interest for the year ending 31st March 2016 and transfer of interest on debentures of the year to the statement of profit and loss.
Solution:
Notes for Issue and Redemption of Debentures class 12 Accountancy
Accounting For Debentures
Debenture : It is a document issued by a company under its common seal acknowledging the debt and it also contains the terms of repayment of debt and payment of interest at a specified rate.
Section 2 (30) of Companies Act, 2013 defines debenture as “Debenture includes debenture stock, bonds or any other instrument of a company evidencing a debt, whether constituting a charge on the company’s assets or not.”
Debentures are generally freely transferable by the debenture holder. Debenture holders have no rights to vote in the company’s general meetings of shareholders. The interest paid to them is a charge against profit in the company’s financial statements.
TYPESOFDEBENTURES
Convertibilitypoint ofview: There are two types of debentures :
Convertibledebentures, which can be converted into equity shares of the issuing company after a predetermined period of time.
These may be Partly ConvertibleDebentures (PCD): A part of these instruments are converted into Equity shares in the future at notice of the issuer. The issuer decides the ratio for conversion. This is normally decided at the time of subscription.
Fully convertible Debentures (FCD): These are fully convertible into Equity shares at the issuer’s notice. The ratio of conversion is decided by the issuer. Upon conversion the investors enjoy the same status as ordinary shareholders of the company.
Non-convertibleDebentures, which are simply regular debentures, cannot be converted into equity shares. These are debentures without the convertibility feature, these usually carry higher interest rates than their convertible counterparts. On basis of Security, debentures are classified into:
Secured Debentures : These instruments are secured by a charge on the fixed assets of the issuer company. So if issuer fails to pay of either the principal or interest amount, its assets can be sold to repay the liability towards debenture holders.
Unsecured Debentures : These instrument are unsecured in the sense that if the issuer defaults on payment of the interest or principal amount, the investor is treated like other unsecured creditors of the company.
From Redemption point of view
RedeemableDebentures : Redeemable debentures are those which are redeemed or paid off after the termination of fixed term. The amount paid off includes the principal amount and the current year’s interest. The company always has the option of either to redeem a specific number of debentures each year or redeem all the debentures at specified date.
Irredeemable or Perpetual Debentures : Irredeemable debentures are those debentures which do not have any fixed date of redemption. They are redeemed either in the event of winding up or at a very remote period of time. Irredeemable or perpetual debenture holders can never force the company to redeem their debentures.
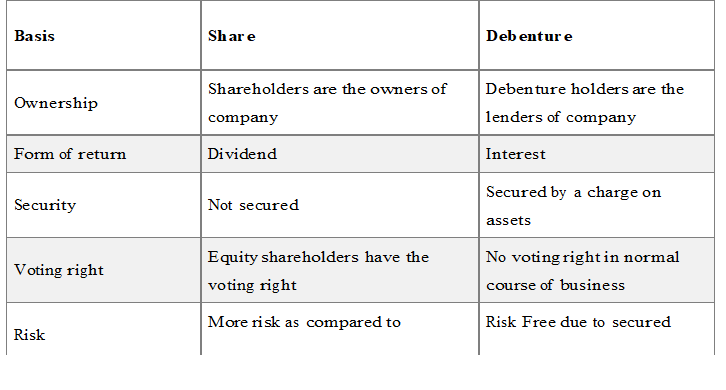
Distinguish Between a Share and Debenture

Issue of Debentures:
Debentures can be issued in following ways:
1. for cash
2. for consideration other than cash
3. As collateral security
Terms of Issue
Debentures can be issued in following ways:
1. Issue of Debentures at Par
2. Issue of Debenture at Premium
3. Issue of Debentures at Discount.
Debenture Payable in Installments
1. First instalment paid along with application is called as application money.
2. Second instalment paid on allotment is called as allotment money.
3. Subsequent instalments paid are called as call money calls can be more than one and called First call, second call or as the case may be.
Issue of Debentures for Cash
(a) When Debentures amount received in lump sum with the application
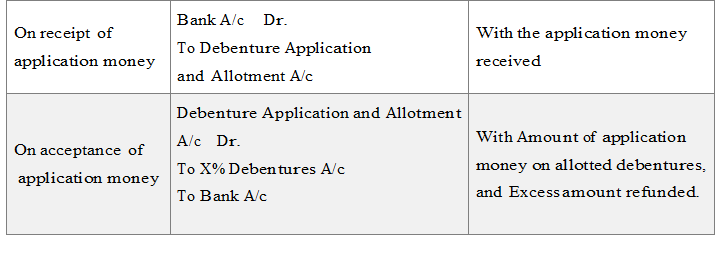
(B) When Debentures amount received in installments.
In this case accounting entries will be same as at the time of issue of shares in instalments with small change in the name of term like-the share capital word replaced with the X% Debentures A/c, and Share word replaced with Debentures e.g. Equity share capital into 8% Debentures, Equity share application into Debentures Application and follows on.
AT Par : means debentures are issued at face value.
Issue of Debentures for Consideration other than Cash
When Debentures are issued for purchased of asset
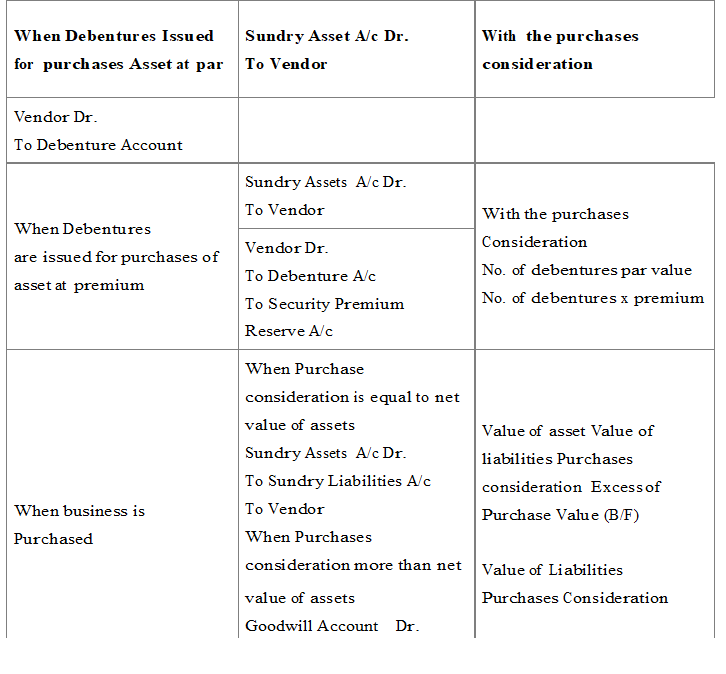
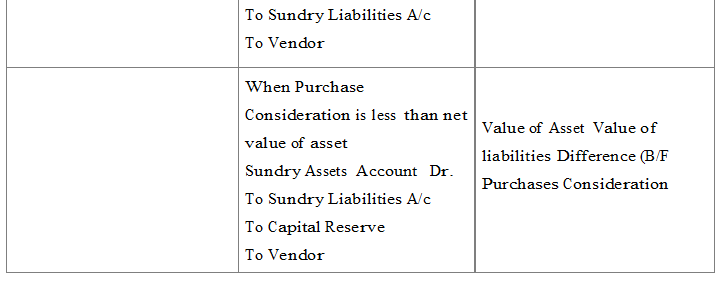
Collateral Security : Collateral security means security provided to lender in addition to the principal security. It is a subsidiary or secondary security. Whenever a company takes loan from bank or from any financial institution it may issue its debentures as secondary security which is in addition to the principal security. Such an issue of debentures is known as ‘issue of debentures as collateral security’. The lender will have a right over such debentures only when company fails to pay the loan amount and the principal security is exhausted. In case the need to exercise the right does not arise debentures will be returned back to the company. No interest is paid on the debentures issued as collateral security because company pays interest on loan.
In the accounting books of the company issue of debentures as collateral security can be credited in two ways :
i. First method : No Journal entry to be made in the books of accounts of the company for debentures issued as collateral security. A note of this fact is given in this case.
ii. Second method : Entry to be made in the books of accounts of the company.
A journal entry is made on the issue of debentures as a collateral security, Debentures Suspense Account is debited because no cash is received for such issue.
Following journal entry will be made
Journal


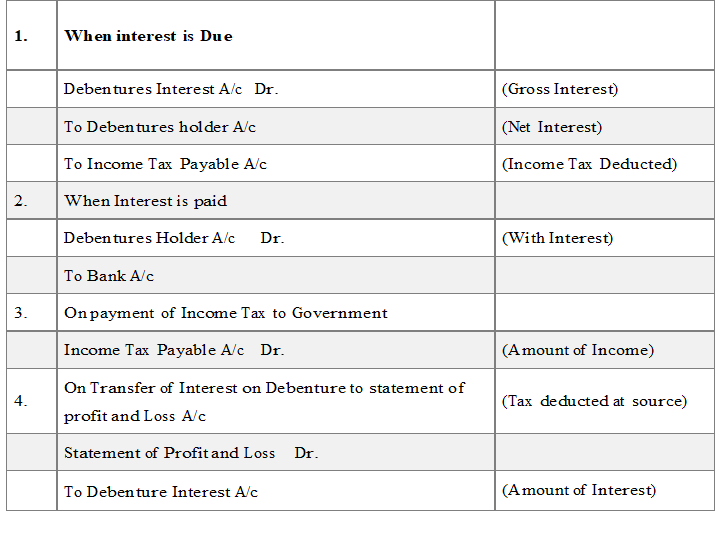
INTEREST ON DEBENTURES
Interest on Debentures is calculated at a fixed rate on its face value and is usually payable half yearly & is paid even company is suffering from loss because it is charge on profit.
Income Tax is deducted from interest before payment to debenture holders. It is called T.D.S. (Tax deducted at source).
JOURNALENTRIES
Company Accounts – Redemption of Debentures
Meaning: Redemption of debentures means repayment of the due amount of debentures holders. Its may be at par or at premium.
Time of Redemption
a. At maturity : When repayment is made at the date of maturity of debentures which is determined at the time of issue of debentures.
b. Before maturity : If articles of association and terms of issue mentioned in prospectus allows, then a company can redeem its debentures before maturity date.
Redemption Methods
1. Redemption in Lump-sum : When redemption is made at the expiry of a specific period, as per the terms of issue.
2. Redemption by draw of lots : In this method a certain proportion of debentures are redeem each, year, the debenture for which repayment is to be made is selected by draw of lots.
3. Redemption by purchases in open market : If articles of association of a company authorize, it may purchases its own debentures from open market e. stock exchange
Advantages of this Method
1. When market price of own debentures is low than the redeemable value is less then the amount payable on maturity.
2. Decrease the amount of interest payable to outsiders.
3. If term of issue is provided that debentures are to be redeemed at premium then such premium can be reduced.
Sometimes company can purchases the debentures at more than the redeemable value due to the following reasons:
1. To maintain the solvency ratio.
2. To utilize the surplus money or funds which are lying idle with the company.
3. When rate of interest on debentures is more than the current market rate of interest on debentures in the industry.
Sources of Redemption of Debentures
1. Proceeds from fresh issue of Share Capital or Debenture holder.
2. From accumulated profit.
3. Proceeds from sale of fixed assets.
4. A company may purchases its own debentures out of its surplus funds. Two terms which are used in the redemption of debentures :
1. Redemption out of capital : When a company has not used its reserve or accumulated profit for redemption of its debentures, it is called redemption out of capital, So company using this method have not transferred its profit to DRR A/c. But as per SEBI guidelines it is necessary for a company to transfer 50% amount of nominal value of debentures to be redeemed in DRR A/c before redemption of debentures commence.
2. Redemption out of profit : Redemption out of profit means that adequate amount of profits are transferred to DRR A/c from Statement of Profit & Loss before the redemption of debenture commences. This reduces the amount available for dividends to shareholders.
3. Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) : Section 71 (4) of the companies Act, 2013 requires the company to create DRR out of the profits available for dividend and the amount created in DRR shall not be utilized for any purpose except redemption. Rule 18 (7) of Companies (share capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014 requires the following companies to create DRR of an amount equal to 25% of the value of Debentures:–
i. NBFCs registered with RBI
ii. Financial institutions other than all India Financial Institutions regulated by RBI.
iii. Housing finance companies registered with National Housing Bank. DRR is required for publicly three classes of companies, not for privately placed.
iv. Any other company (whether listed or unlisted), DRR to be created for both public and private placed debenture.
As per rule 18 (7) (c), every company required to create / Maintain DRR shall invest or deposit before 30th April specified. Securities a sum which shall not be less than 15% of the amount of debentures, maturing for payment during the year ending 31st March of the next year.
Exemptionto create DRR:–
i. All India Financial Institutions regulated by RBI.
ii. Banking Companies.
Note: 1. It is assumed that company has invested 15% of redeemable amount an April 30 and incashed it as per Companies Act, 2013.
2. It is assumed that company has created debenture Redemption Reserve @25% of the redeemable debenture and transferred it to General Reserve after redemption of all the debentures.
Redemption Method 3 : Redemption of debentures by the purchase of own debentures in the open market. According to the Companies Act, a company can redeem its debentures in full or in part by purchasing its own debentures in the open market (Stock exchange) provided the company is authorised to do so by its Articles of Association.
Suitability of this Method
1. When interest rate on own debentures is higher than the market interest rate.
2. When own debentures are quoted at a discount in the open market, a company can earn profit on redemption as debentures are available at below its nominal value in the market, otherwise normal redemption may be at par or at premium.
Debenture Redemption Reserve: Creation of Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) is necessary if debentures have been purchased for cancellation. Unless otherwise stated in question, it is assumed that the company has adequate balance in DRR before initiating the process of purchase of debentures for cancellation.
Accounting Treatment
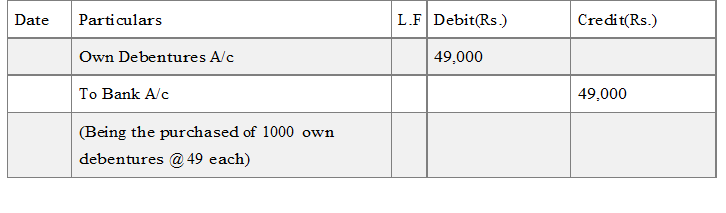
(A) When Debentures are purchased from the open market for immediate cancellation :
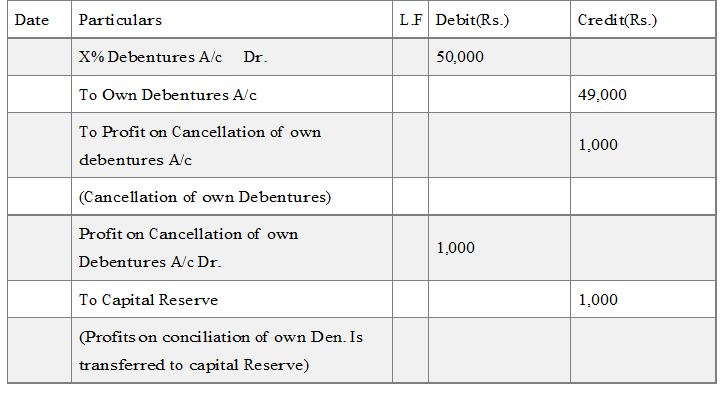
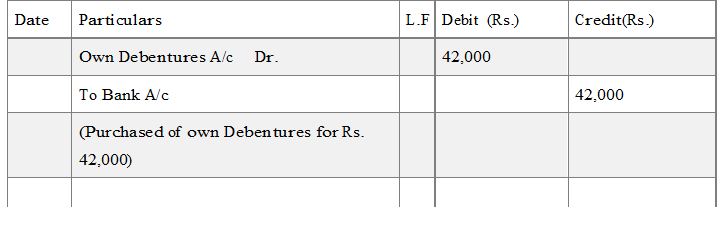
(i) When own debentures are purchased : e.g. if a company purchase 1,000 of its own debentures of 50 each at 49 (including all purchase exp.) in the open market for immediate cancellation
(ii) For Cancellation of own Debentures:
There may be three case – (a) when own debentures are purchased at nominal price – the entry passed is for cancellation :
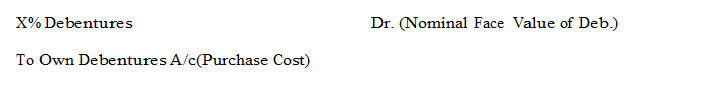
(B) When own debentures are purchased at price below Nominal value of Debentures : the entry pass is for cancellation:
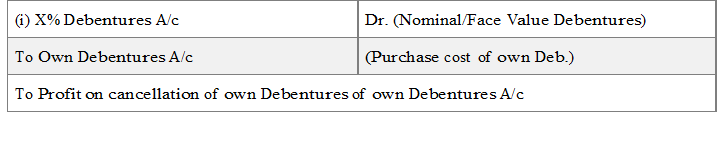
Hint: (Profit on Cancellation is the Excess of nominal value over purchase cost of own debentures cancelled)
Profit on cancellation of own Debentures is a capital profit and therefore, is transferred to capital Reserve (or it may be used to write off discount / Loss on issue of debentures) the entry is:
To writing off Capital losses.]
(ii) Profit on Cancellation of own Debentures A/c or
To Capital Losses (if any) A/c
To Capital Reserve A/c
In above example the entries for cancellation of debentures will be:
Journal
(C) When own debentures are purchased at a price above its face value. E.g. Debentures of the face value of Rs. 40,000 ate purchased in the open market at Rs. 42,000, the entry will be
Journal
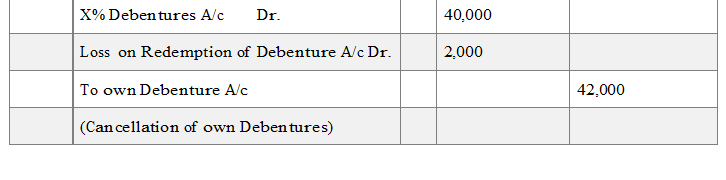
‘Loss on Redemption of Debentures’ is a capital loss and is therefore written off against capital profit or in the absence of capital profit is written off from statement of profit and loss.
(B) Purchase of own Debentures from open market for investment purpose : e.g. if a company purchase it 9% debentures of 50,000 at 49,000 as investment the entry will be:
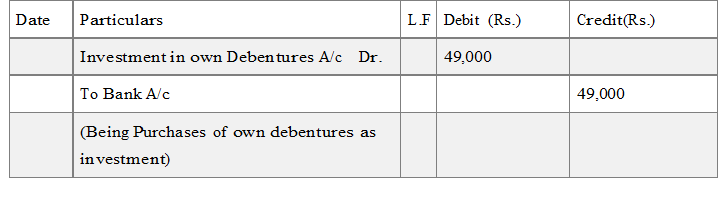
It should be noted that in the above entry an account named “Investment in own debentures A/c” is debited with purchase cost instead of “own debentures A/c” because own debentures have been purchased as an assets. “Investment in own debenture” will appear on the assets side under Non-Current Investment or current investment depending upon the time of Cancellation/Redemption or resell time.
Advantages : Reasons for Purchase of own Debentures as Investment :
i. Debentures are available in open market at a price below its nominal value.
ii. These debentures can be resold at profit in the market OR can be cancelled if the market price of such debentures further goes down.
iii. Interest payment on such debentures is saved which would otherwise be paid to debenture holders.
Resell these debenture in the market : the journal entries will be :
Bank A/c Dr.
(Net amount realised from own Deb.)
Loss on sale of own Debentures A/c*Dr. (Excess of cost over sale price) To Investment in own Debentures A/c (cost of own debentures)
To Profit on sale of own Debentures A/c*(Excess of sale price over cost)
Note : *There will be one entries from two above Profit or Loss as the case. Loss or Profit on sale of own debentures will be transferred to Statement of profit and loss at the end of accounting year.
Profit on sale of own Debentures A/c Dr.
To Statement of Profit and Loss
B (II) On Cancellation of Debentures at a later date :
(a) X% Debentures A/c Dr.
Loss on cancellation of own Debentures A/c Dr..
To Investment in own Debentures A/c
To Profit on cancellation of own Debentures A/c
(b) Profit on cancellation of own Debentures A/c Dr.
To Capital Reserve A/c
Treatment of Interest on Own Debentures : when a Company purchase it own debentures for investment and has not cancelled them upto the interest payment due date. The company will pay interest only to outside debentures holders and interest on own debentures held by the company is retained by the company entries will be:
(i) When interest becomes due on Debentures :

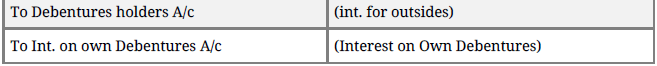
(ii) On Payment of interest to outsider debentures holders:
Debentures holders
A/c Dr.
(iii) Transfer of Int. to statement of P/L at the end of accounting year:
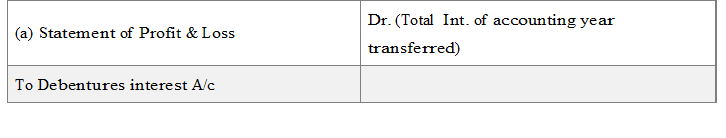
Transfer of Interest on Own debentures to statement of Profit & Loss
Interest on own debentures A/c Dr.
To Statement of Profit & Loss

Also Download : Question Papers for Class 12 Accountancy
and refer to Chapter 8: Redemption of Debentures
Chapter 9: Issue of Debentures
