Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Notes
Students should read Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Notes provided below. These notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and books issued by NCERT, CBSE and KVS. These important revision notes will be really useful for students to understand the important topics given in the chapter Metals and Non-Metals in Class 10 Science. We have provided class 10 science notes for all chapters.
Revision Notes Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals is an important chapter in Class 10 Science. The following notes will help you to understand and easily learn all important points to help you score more marks.
IMPORTANT TERMS & CONCEPTS
1. Metals:
1.Those elements which can lose electrons easily and form positive ions.
2. They are mostly solids, possess high density.
3. They have high melting and boiling points.
4.They have metallic luster and they are sonorous, i.e., produce metallic sound.
5. They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
6.they are usually malleable and ductile, e.g., gold, silver, copper, tin, lead, iron, mercury, cobalt, nickel, aluminum, sodium, potassium are metals.
2. Properties of metal:
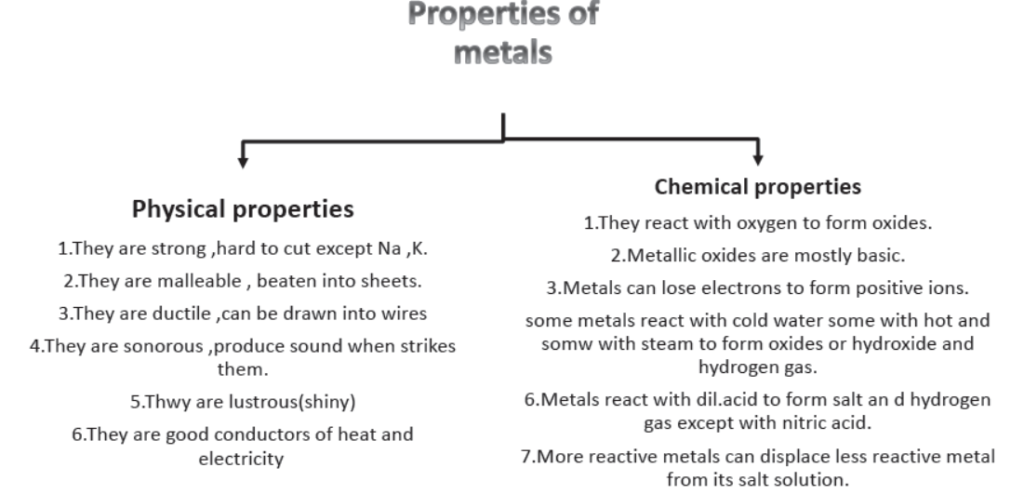
3. Hardness: Most of the metals are hard. If you try to cut them with knife, it will not be possible in most of the metals.
Some of the metals like sodium, potassium are soft metals and can be cut with knife.
4. Malleability: The ability of a metal due to which it can be beaten into sheets is called malleability. Iron, copper, zinc, aluminium. Magnesium is available in the form of sheets. Aluminium, steel, copper, brass, bronze are used in making utensils.
Brass and bronze are also used for making statues. Bronze is used for making medals. Aluminium and silver metals are converted in foils. Aluminium foils are used for packaging whereas silver foils are used in decorating sweets.
5. Ductility: It is the ability of metal due to which it can be drawn into wires. Copper, aluminium, iron can be drawn into wires. Silver, gold and platinum are highly ductile metals. 1 gram 6. Effect of Tapping (Sonorous): When metals are struck with hard substance, they produce sound, i.e., they are sonorous. Brass and bronze are highly sonorous. They are used in making bells and gongs.
7. Electrical Conductance: It is the property due to which electric current can pass through the metal. It is due to presence of free electrons or mobile electrons, e.g., copper, silver, gold, aluminium are good conductors of electricity.
Silver is best conductor of electricity followed by copper, gold, aluminium and tungsten. Mercury and lead have low electrical conductivity due to high resistance.
8. Thermal Conductivity: It is the property due to which metals can conduct heat e.g., copper, silver, aluminium, gold, and iron are good conductors of heat.
9. Metallic Lustre: Most of the metals have shiny surface i.e., they show metallic lustre e.g., Au, Ag, Pt are lustrous.
10. Exceptions if classification of metals and non-metals is done on the basis of physical properties:
I. All metals are hard except sodium, potassium, lithium. They can be cut even with knife. Osmium (Os) is hardest metal. Lithium is lightest metal.
II. All metals are solids except mercury. Cesium, francium, germanium and gallium are low melting solids; Gallium becomes liquid if kept on palm. But gallium has very high boiling point which makes it useful for high temperature thermometers.
III. Iodine is a non-metal but has metallic lustre. Diamond (an allotrope of carbon) is highly lustrous.
IV. Non-metals have low melting and boiling points but diamond, graphite, boron and silicon have high melting and boiling points.
V. Metals have high melting and boiling points. Tungsten has highest melting point whereas sodium, potassium have low melting and boiling points.
VI. Non-metals are bad conductors of heat and electricity, but graphite is a non-metal which is good conductor of heat and electricity.of gold can be drawn into 2 km long wire.

11. Properties of metals :
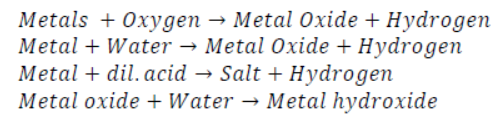
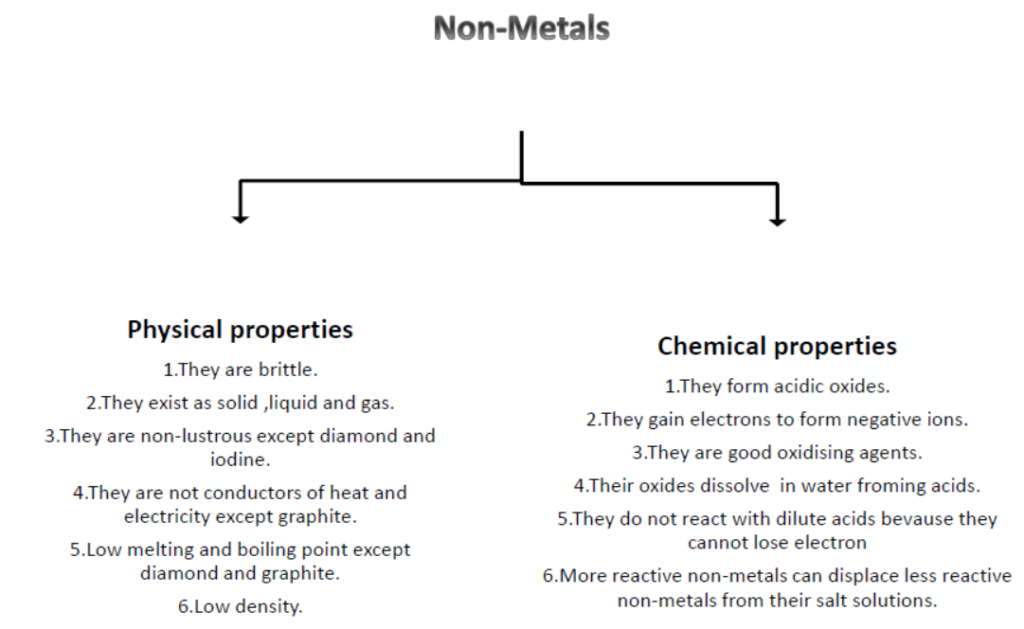
Properties of Non-Metals:

Note: NO , CO ,N2O ,are neutral oxides formed by non-metals with oxygen .
12. Alkalies: Those bases, which are soluble in water, are called alkalies. For example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 etc. They turn phenolphthalein pink and turn red litmus blue.
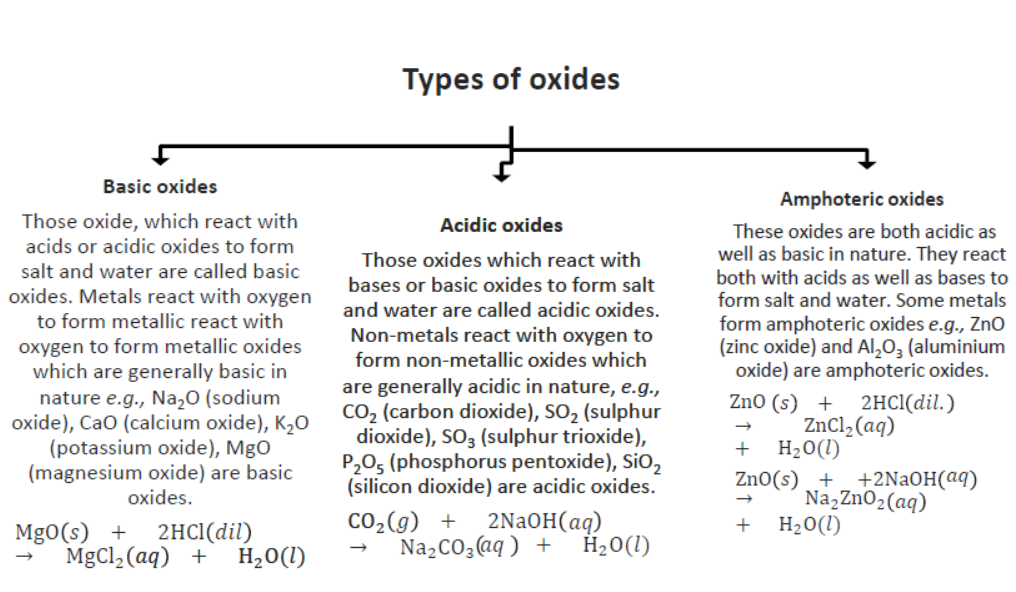
Note: Neutral Oxides: These oxides are neither acidic nor basic in nature. They neither react with acids nor with bases. Some non-metals form neutral oxides. Carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxide (NO), and Nitrous oxide (N2O) is examples of neutral oxides.
13. Reaction of Metal Oxides with Acid: Metal oxides react with acid to form salt and water because most of the metal oxides are basic or amphoteric in nature. Amphoteric oxides react with both acids as well as bases.

14. Reactivity of Metals: All the metals do not react with the same rate. Some react very fast, some react moderately whereas others react very slowly e.g., sodium, potassium react with oxygen at room temperature vigorously to form oxide. They can catch fire in the presence of moist air. These metals are kept in kerosene oil or benzene so as to protect them from formation of oxide and hydroxide in open air.
At room temperature, metals like Al, Z, Cu, Mg, Sn, Pb form oxide layer on their surface and become dull.
This oxide layer makes aluminium passive and does not allow it to react further with H2O, O2 and even conc.
HNO3. Copper is less reactive and forms black coloured oxide and gives green coloured flame with blue tip in burner. Magnesium burns with dazzling light forming MgO. Silver, gold and platinum do not react with oxygen. Mercury forms red coloured oxide, HgO.
Reactivity Series of Metals: The series of metals in decreasing order of reactivity is called reactivity or activity series of metals. The metals at the top are most reactive whereas metals at the bottom are less reactive. The following is the activity series of metals. The metals above hydrogen are more reactive than hydrogen. They can displace hydrogen from dilute acids and water. Metals below hydrogen are less reactive than hydrogen and cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids and water.
Activity Series:
1. More reactive metals can lose electrons most easily.
2. More reactive metals from stable compound
3. More reactive metals are difficult to extract from its one and exist as compounds.
4. Least reactive metals are found in nature in free stale ., eg .copper ,silver ,gold

15. Reaction of Metals with Water: Some metals like Na, K, and Ca react with cold water vigorously to form hydroxide and liberate hydrogen gas. Some metals like Mg, Zn, Al, react with hot water to form oxide and hydroxides and hydrogen gas. Some metals like Fe reacts with steam to form Fe3O4 and H2(g).some metals like Cu, Ag, Au, Hg, Pb and
Pt do not react with water at all because they are less reactive than hydrogen. Let us perform the following experiment.
16. Reaction of Metals with Acids: Metals react with dilute acids to form salt and hydrogen gas. The metal replaces hydrogen of the acid to form salt.
17. Aqua Regia: It is a mixture of conc. HCl (hydrochloric acid) and conc. HNO3 (nitric acid) in the ratio of 3:1. It can dissolve gold and platinum. Gold and platinum do not react with conc. HCl. They do not react even with conc. HNO3.
They dissolve in aqua regia. Aqua regia is a strong oxidizing agent due to the formation of NOCl (nitrosyl chloride) and chlorine produced by the reaction of two acids. Aqua regia (Latin word for royal water) is a highly corrosive and fuming liquid. Therefore, it should be kept away from eyes and skin.
Note: Noble metals like gold and platinum are soluble in aqua regia (royal water) .
18. Reaction of Metals with solution of Other Metal Salts: More reactive metal can displace less reactive metal from their salt solution. These reactions are called displacement reactions.
19. Reason for difference in Reactivity of Metals: We have observed with the help of experiments that some metals are less reactive whereas other metals are more reactive. Let us find out the reason why some metals are more reactive whereas other metals are less reactive.
Metals are those elements which can lose electrons easily. The reactivity of metal depends upon how easily metal can lose electrons and from positively charged ion. Metals have 1 to 3 electrons whereas non-metals 4 to 8 electrons in their outermost shell. Hydrogen and helium have one and two electrons respectively but still they are non-metals because they cannot lose electrons easily. Boron has three valence electrons but still it is a non-metal.
20. Electronic Configuration of Elements and Classification as Metals and Non-metals.
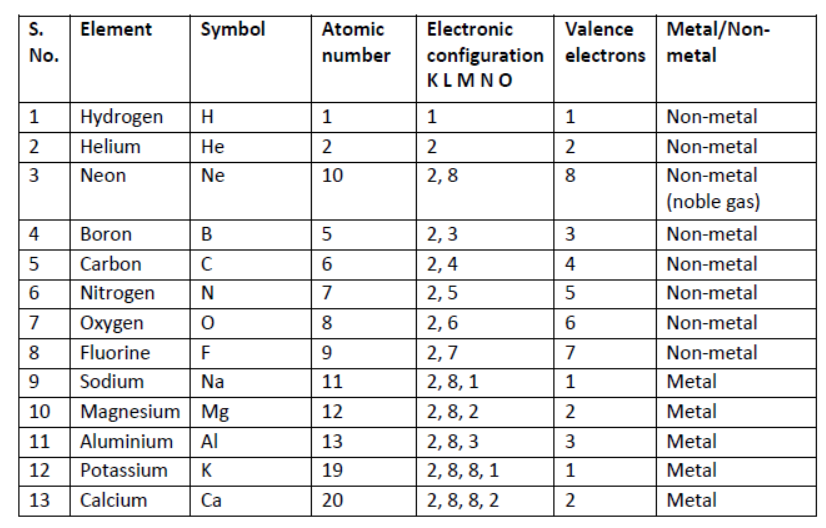
21. Reason for Metals for Losing Electrons: In the electronic configuration of elements, you have observed that noble gases have 8 electrons in their outermost shell and they are quite stable excepts helium which has two valence electrons, it is also quite stable. It means all metals will try to lose electrons to acquire nearest noble gas configuration, e.g.,

22. Reason for Non-metals for Gaining Electrons: Non-metals can gain electrons to form negative ions so as to acquire stable noble gas configuration, i.e., 8 electrons in its outermost orbit.

23. Octet: A stable group of eight electrons in the outermost orbit of the atom.
24. Ionic bond: The bond which is formed by loss and gain of electrons is called ionic or electrovalent bond.


30. Properties of Ionic Compounds:
I. Ionic compounds are solids, e.g., NaCl, KCl, CuSO4, K2SO4, NaNO3 are solids.
II. Ionic compounds are somewhat hard and brittle. It is due to strong force of attraction between them.
III. Ionic compounds have closed packed structures, e.g., NaCl has face centred cubic structure.
IV. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points. It is because of strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions; therefore, high energy is required to break the metallic bonds between ions.
V. Ionic or electrovalent compounds are soluble in water because they form ions in aqueous solution.
31. Corrosion:
It is process in which metal react with substances present in atmosphere to form surface compounds, e.g.,
• silver metal turns black due to the formation of Ag2S.
• Copper forms a greenish layer of CuCo3, Cu(OH)2 on its surface.
• Iron forms reddish brown coating of hydrated ferric oxide, Fe2O3, xH2O.
32. Prevention of Corrosion:
I. Iron articles are painted so as to prevent them from rusting.
II. Oiling and greasing of machine parts prevent rusting.
III. Galvanisation. The process of coating iron articles with zinc which is more reactive than iron is called galvanisation.
IV. The iron tanks are connected with magnesium wire so as to protect them from rusting.
V. Iron articles are electroplated by chromium or other more reactive metals so as to protect them from rusting.
33. Amalgam: When a metal is alloyed with mercury, it is called amalgam.
34. Purpose of Making Alloy:
I. Alloys do not get corroded or get corroded to very less extent.
II. They are harder and stronger than pure metals, e.g., gold mixed with copper is harder than pure gold.
III. They have fewer conductances than pure metals, e.g., copper is good conductor of heat and electricity whereas and bronze are not good conductors.
IV. Some alloys have lower melting point than pure metals, e.g., solder is an alloy of lead and tin which has lower melting point than each of the metals. It is used for soldering of metals.
36. Preparation of Alloy: They are prepared by first melting the main metal, and then dissolving the other elements in it in definite proportion. It is then cooled to room temperature.
37.

38. 24 Carat Gold: Pure gold is 24 carat. It is 100% pure gold. It is very soft; therefore, ornaments cannot be made from it.
39. Occurrence of Metals: The main source of metals is earth’s crust. Some metals are also present in sea water in the form of their salts.
40. Mineral: The natural materials in which metals occure in the form of their compounds are called minerals.
They are mostly found in earth’s crust. Some minerals are also found in sea water, e.g., NaCl (sodium chloride), feldspar, mica, kaolin, etc.
41. Ores: They are minerals from which metals are extracted profitably, e.g., hematite (Fe2O3) is an ore of iron, and bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O) is an ore of aluminium.

12. Alkalies: Those bases, which are soluble in water, are called alkalies. For example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 etc. They turn phenolphthalein pink and turn red litmus blue.
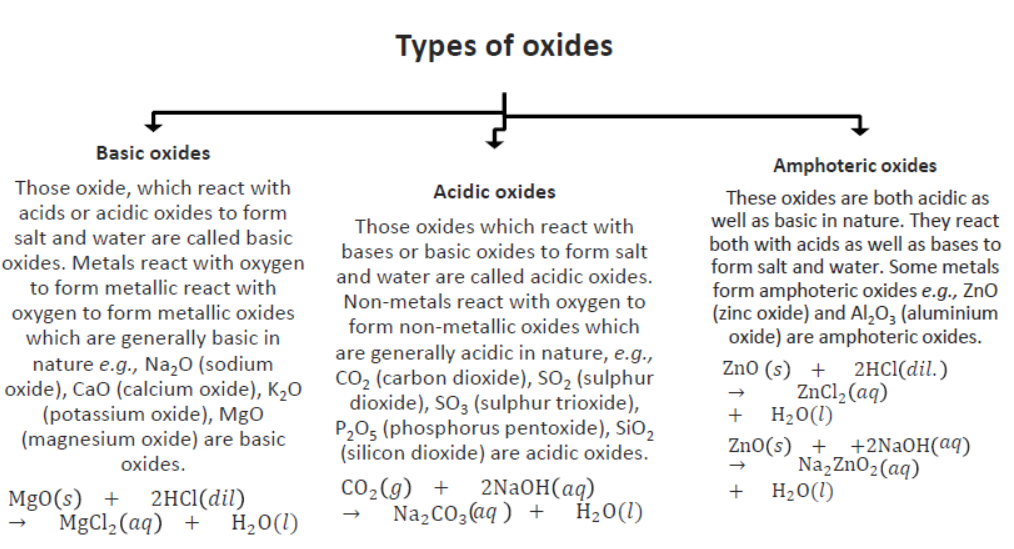
Note: Neutral Oxides: These oxides are neither acidic nor basic in nature. They neither react with acids nor with bases. Some non-metals form neutral oxides. Carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxide (NO), and Nitrous oxide (N2O) is examples of neutral oxides.
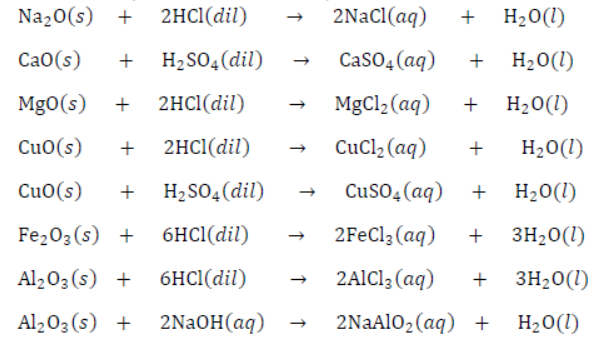
13. Reaction of Metal Oxides with Acid: Metal oxides react with acid to form salt and water because most of the metal oxides are basic or amphoteric in nature. Amphoteric oxides react with both acids as well as bases.
14. Reactivity of Metals: All the metals do not react with the same rate. Some react very fast, some react moderately whereas others react very slowly e.g., sodium, potassium react with oxygen at room temperature vigorously to form oxide. They can catch fire in the presence of moist air. These metals are kept in kerosene oil or benzene so as to protect them from formation of oxide and hydroxide in open air.
II. Calcination: It is a process of heating ore in the absence of air so as to remove moisture and volatile impurities and to convert carbonate ores into oxide, e.g.,
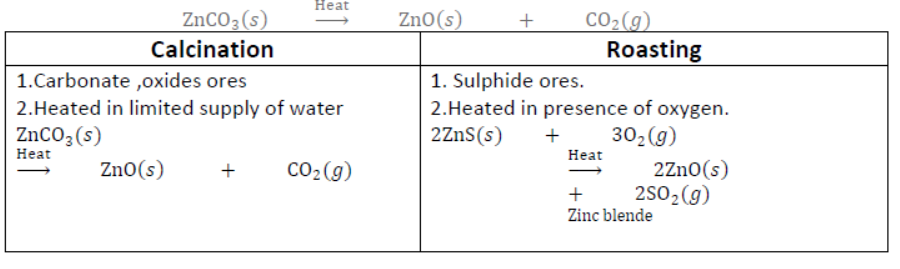
III. By heating metal oxides with reducing agent: Some metals are obtained by heating their oxides with suitable reducing agent. When metal oxide is heated with reducing agent like carbon, free metal is obtained.

Aluminium, magnesium, calcium, sodium can also be used as reducing agents.

51. Extraction of Metals Towards the Top of the Activity Series:
Electrolytic Reduction: Most reactive metals like sodium, potassium, calcium, aluminium cannot be obtained by chemical reduction. They are obtained by electrolysis of fused (molten) compounds. Sodium, calcium and magnesium are obtained by electrolysis of their fused chlorides. Aluminium is obtained by electrolysis of molten bauxite. Metals are obtained at cathode whereas non-metals are obtained at anode.
Electrolysis of molten NaCl is shown as follows with the help of chemical reactions.

52. Thermite Process (Aluminothermy): It is a process in which molten oxides are treated with aluminium powder. It is highly exothermic reaction. The molten metal obtained is used for welding of railway tracks or cracked machine parts, e.g., aluminium is heated with Fe2O3 (haematite) to get molten iron and aluminium oxide.

This process is also used for extraction of metals like iron and chromium.
53. Refining: It is a process of converting impure metal into pure metal by different processes depending on the nature of metals. In other words, it is a process of purification of metal. There are many ways of refining the metals.
54. Electrolytic Refining: This method is widely used as method of purification of metals like zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), aluminium (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), gold (Au). In this process, impure metal is used as anode, a strip of pure metal is used as cathode and soluble salt of metal is used as an electrolyte. On passing electric current through the electrolyte, cations move towards cathode, gain electrons and pure metal gets deposited on cathode. In electrolytic refining of copper, the impurities left behind at anode called anode mud contains valuable metals such as gold and silver which can be recovered in the native state.
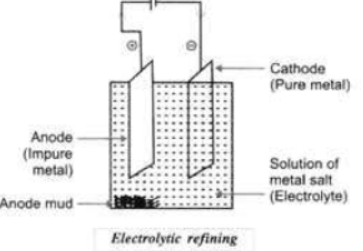
55. Blister Copper: The impure copper having spots or blisters due to the evolution of sulphur dioxide is known as blister copper.
56. Metalloids: Those elements which have characteristic of both metals and non-metals are called metalloids.
Examples of metalloids are germanium, silicon, tellurium and antimony.
57. Reducing Agent: The element which can lose electrons easily is called reducing agent. Metals are reducing agents. The substances which gain oxygen or electronegative element or lose hydrogen or electropositive element are also called reducing agents.
58. Flux: The substance which reacts with gangue to form a fusible mass which can easily be removed, e.g., CaO (calcium oxide) is used as flux so as to remove SiO2 (silica) as gangue.

59. Slag: The fusible mass formed by the reaction of flux and gangue is known as slag.
Slag is lighter than molten metal, hence floats over molten metal and can be easily removed. It prevents metal from oxidation.
LONG ANSWER
Question. Explain the following:
(A) Sodium chloride is an ionic compound which does not conduct electricity in solid state, whereas it does conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
(B) Reactivity of aluminium decreases if it is dipped in nitric acid.
(C) Metals like calcium and magnesium are never found in their free state in nature [Diksha]
Answer : (A) We know that solid sodium chloride is made up of ions but it does not conduct electricity. This is because of the fact that the sodium ions and chloride ions are held together in fixed positions in the sodium chloride crystal. They cannot move freely. When sodium chloride is dissolved in water to make aqueous solution, it becomes a good conductor of electricity. On dissolving in water, the sodium chloride crystal breaks, sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl–) become free to move and as a result conduct electricity.
(B) A layer of aluminium oxide is formed on the metal when aluminium is dipped in nitric acid. This happens because nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. The layer of aluminium oxide acts as a barrier to prevent further reaction of aluminium. As a result, the reactivity of aluminium decreases.
(C) Metals like calcium and magnesium are never found in free state in nature because these metals are very reactive and readily combine with other elements to form a compound.
Question. Explain the following:
Reactivity of Al decreases if it is dipped in HNO3.
Answer : When aluminium (Al) is dipped in nitric acid (HNO3), a layer of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) is formed over the metal surface. This happens because nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent.
The layer of aluminium oxide prevents further reaction of aluminium. This is the reason why the reactivity of aluminium decreases.
Question. (A) (i) Write two properties of gold which make it the most suitable metal for ornaments.
(ii) Name two metals which are the best conductors of heat.
(iii) Name two metals which melt when you keep them on your palm.
(B) Explain the formation of ionic compound CaO with electron-dot structure. Atomic numbers of calcium and oxygen are 20 and 8 respectively.
Answer : (A) (i) Two properties of gold which makes it the most suitable metal for ornaments are:
(a) Gold is an unreactive metal and therefore does not lose its shine easily.
(b) Gold is a highly malleable metal.
(c) Gold is the most ductile metal which makes it the best choice for making ornaments.
(ii) The two best conductors of heat are silver and copper.
(iii) Gallium and caesium are two metals which melt if kept in our palms as they have very low melting points.
(B) Atomic number of calcium = 20 Electronic configuration = (2, 8, 8, 2) Atomic number of oxygen = 8 Electronic configuration = (2, 6) Calcium atom loses 2 valence electrons to form Ca2+ ion and oxygen atom gains 2 electrons to form O2– ion. This way both attain their nearest inert gas configuration. The formation of ionic compound CaO is shown below;
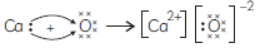
Calcium atom oxygen atom calcium ion oxide ion.
Question. Of the three metals X, Y and Z, X reacts with cold water, Y with hot water and Z with steam only. Identify X, Y and Z and also arrange them in increasing order of reactivity.
Answer : X is alkali metal, Na or K.
Y is alkaline earth metal, Mg or Ca.
Z is Fe.
X reacts with cold water, so it must be very reactive like alkali metals, like sodium. Sodium reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
Y metal can react with hot water, so it must be a little less reactive than X i.e., alkaline Earth metal. So, Y can be magnesium (Mg) which reacts with hot water to form magnesium
hydroxide.
Mg + 2H2O → Mg(OH)2 + H2
Z metal which reacts with steam must be iron that forms iron (III) oxide with steam.
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
Hence, the increasing order of reactivity of the given metals is:
Z (Fe) < Y (Mg) < X (Na)
Question. (A) Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(i) Al2O3 + HCl →
(ii) K2O + H2O →
(iii) Fe + H2O →
(B) An element ‘X‘ displaces iron from the aqueous solution of iron sulphate. List your observations if the element ‘X‘ is treated with the aqueous solutions of copper sulphate, zinc sulphate and silver nitrate. Based on the observations arrange X, Zn, Cu and Ag in increasing order of their reactivities
Answer :

Question. Name the following:
(A) Metal that can be cut by knife
(B) Lustrous non-metal
(C) Metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature
(D) Most malleable and ductile metal
(E) Metal that is best conductor of electricity
(F) Non-metal that can exist in different forms
Answer : (A) Metal which can be cut by knife—Sodium
(B) Lustrous non—metal—Iodine
(C) Metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature—mercury
(D) Most Malleable and ductile metal—Gold
(E) Metal that is best conductor of electricity—Silver
(F) Non-metal that can exist in different forms—Carbon
Question. (A) What are amphoteric oxides? Choose the amphoteric oxides from amongst the following oxides: Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, CO2, H2O.
(B) Why is it that non-metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids?
Answer : (A) Those metal oxides which show basic as well as acidic behaviour are known as amphoteric oxides. Amphoteric oxides react with both acids as well as bases to form salts and water. Al2O3, ZnO are amphoteric oxides among the given oxides.
(B) Non-metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids because in order to displace hydrogen ions (H+) of an acid and convert them into hydrogen gas, electrons should be supplied to the hydrogen ions (H+) of the acid. A non-metal is itself an acceptor of electrons. Hence it cannot give electrons to the hydrogen ions of the acid to reduce them to hydrogen gas. As a result, nonmetals are not able to displace hydrogen ions from acids to form hydrogen gas.
Question. Out of three metals P, Q and R, P is less reactive than Q and R is more reactive than P and Q both. Suggest an activity to arrange P, Q and R in order of their decreasing reactivity.
Answer : (A) Take salt solutions, say sulphate solutions, of metals P and Q in separate test tubes.
(B) Put a strip of metal R in both the test tubes.
(C) The solution becomes colourless in both the test tubes which shows that metal R displaces P and Q ions from their solutions.
(D) Next, put a strip of metal P in the test tube containing salt solution of metal Q.
(E) No reaction takes place as P cannot displace Q ions from its solution. The decreasing order of reactivity of given metals is : R > Q > P.
Question. (A) When calcium metal is added to water, the gas evolved does not catch fire but the same gas evolved on adding potassium metal to water catches fire. Explain.
(B) Name a metal for each case:
(i) It displaces hydrogen gas from nitric acid.
(ii) It does not react with any physical state of water.
(iii) It does not react with cold as well as hot water but reacts with steam.
Answer : (A) More heat is evolved during the reaction of potassium metal with water due to which the hydrogen gas formed catches fire. On the other hand, less heat is evolved during the reaction of calcium metal with water, which cannot make the hydrogen gas burn.
(B) (i) Zinc because it is more reactive than hydrogen and can easily displace hydrogen from its compounds like water and acids to form hydrogen gas.
(ii) Copper because it is a highly unreactive metal.
(iii) Iron because it is a very less reactive metal.
(B) (i) When a reactive metal reacts with dilute mineral acid Observations:
(i) The reaction will be violent.
(ii) Evolution of hydrogen gas is seen as bubbles of gas forming in the reaction mixture.
Question. List in tabular from three chemical properties on the basis of which we can differentiate between a metal and a non-metal.
Answer : Chemical properties used to differentiate between metal and non-metals:
| Metals | Non-Metals | |
| 1. | Metals are electropositive in nature as they lose electrons and form positive ions. K → K+ + e– | Non-Metals are electronegative in nature as they accept electrons and form negative ions. S + 2e– → S2– |
| 2. | Metals combine with oxygen to form basic or amphoteric oxides. 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO | Non-metals combine with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides which are covalent compounds. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) |
| 3. | Metal reacts with dil acids such as dil HCl and dil H2SO4 to form salt and H2 gas. Mg(s) + 2HCl → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) | Non-metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids as it cannot supply electrons to H+ ions. |
| 4. | Metals react with water and produce a metal hydroxide or oxide and H2. 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + Heat | Non-metals do not react with water. |
| 5. | Metals react with chlorine to form metal chlorides, which are electrovalent compounds. Ca2+ + 2Cl– → CaCl2 | Non-metals form covalent chlorides which is generally a volatile liquid or a gas. P4(s) + 6Cl2(g) → 4PCl3(g) |
Question. (A) Explain the formation of ionic compound, Al2O3 with electron-dot structure:
(Given: Atomic no. of Al and O are 13 and 8 respectively)
(B) What happens when (Report only observations)
(a) a reactive metal reacts with a dilute mineral acid?
(b) an amphoteric oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide solution?
(c) a metal of low reactivity is dropped in the salt solution of a metal of high reactivity?
(d) a metal carbonate is treated with acid?
Answer : (A) Formation of Ionic compound Al2O3
Atomic number of Al —13
Atomic number of O — 8
Electronic configuration of Al = 2, 8, 3
Electronic configuration of O = 2,
All loses 3 electrons from the valence shell to acquire the nearest noble gas (Neon) configuration and form

Oxygen gains only 2 electrons in the valence shell to acquire the nearest noble gas (Neon) configuration and form O2–
O + 2e– → O2–
2,6 2, 8
Al has to lose 3 electrons and oxygen atom can only 2 electrons, therefore 2 atoms of Al and 3 atoms of oxygen are required :
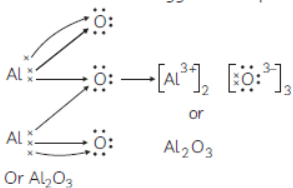
Question. State five uses each of metals and nonmetals.
Answer : Uses of metals:
(A) Lead metal is used in making car batteries.
(B) Zinc is used for galvanizing iron to protect it from rusting.
(C) Iron, copper and aluminium are used to make utensils.
(D) Copper and aluminium metals are used to make electrical wires.
(E) Aluminium is used to make aluminium foil for packaging materials.
Uses of non-metals:
(A) Hydrogen is used in the hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
(B) Carbon is used to make electrodes of electrolytic cells and dry cells.
(C) Nitrogen is used in the manufacture of ammonia, nitric acid and fertilizers.
(D) Sulphur is used for producing sulphuric acid.
(E) Liquid hydrogen is used as rocket fuel.

