Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science Notes
Students should read Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science Notes provided below. These notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and books issued by NCERT, CBSE and KVS. These important revision notes will be really useful for students to understand the important topics given in the chapter How do the Organisms Reproduce in Class 10 Science. We have provided class 10 science notes for all chapters.
Revision Notes Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science
Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce is an important chapter in Class 10 Science. The following notes will help you to understand and easily learn all important points to help you score more marks.



1. Advantages of Vegetative Propagation: It allows quicker and easy propagation/exact copy of the parent/ seedless plant propagation.
2. Disadvantages of Vegetative Propagation: Vegetative propagation doesn’tfavourmuch variation and evolution of new species.
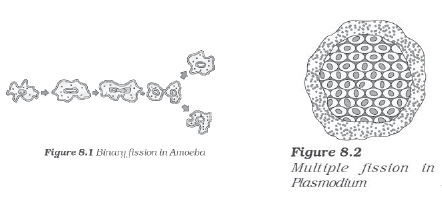
3. Regeneration is the ability of an organism to regenerate the lost part.(e.g.:arm regeneration in star fishes) .Sometimes, an organism can be made from its fragmented body parts.e.g. Planaria.
4. Flower is the reproductive part of the plant .A complete flower has four whorls-sepals, petals, stamens and carpels.
5. Unisexual flowers and bisexual flowers

6. Pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from anther lobe to the stigma of the flower.
7. Post pollination changes in plants: Growth of pollen tube/motion of male gametes towards the ovule/ fertilization
8.Fertilized ovule develops in to seed and ovary develops into fruit
9.Unisexual and bisexual organisms

10. The fusion of male and female gamete is called fertilization.
11 Parts and functions

12. On reaching puberty,one egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.The release of egg by theovaryiscalled ovulation, which takes place at 12-16 th day of menstrual cycle.During that time,if sexual contact takes place,sperm fuses with the egg producing zygote which get implanted in the uterus.
13. Itis through placenta glucose and oxygen are given to the developing embryo and waste materials are removed from embryo and given to the mother’s blood.
14 Common birth control measures
(1) Physicalbarriermethodslikecondoms and vaginal diaphragm
(2) chemical methods like oral or vaginal pills
(3) surgical methods like tubectomy in females and vasectomy in males
(4) IUCD – Copper T
15 STD are sexually transmitted diseases spread through sexual contact with the infected Person.Common bacterial STDs are syphilis and gonorrhoea.AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) and warts are examples of viral STDs.
IMPORTANT DIAGRAMS



Important Questions How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science
Very Short Answer type Questions :
Question. Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
Answer: Buds arise from the notches in the leaf margins of Bryophyllum.
Question. What happens when a Planaria gets cut into two pieces?
Answer: Each piece regenerates into new organism, planaria.
Question. What happens when a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length?
Answer: A mature spirogyra filament breaks into smaller fragments and each fragment grows into a new plant.
This process of reproduction is called fragmentation.
Question. Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilisation?
Answer : Zygote is located inside the ovule which is present in the ovary.
Question. Give an example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers.
Answer : An example of unisexual flower is Papaya, water melon (write any one) and of bisexual flower is Hibiscus, mustard (write any one).
Question. “Cell division is a type of reproduction in unicellular organism”. Justify.
Answer : Cell division is a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms because by means of cell division the unicellular organisms produce daughter cells which develop into new
organisms.
Question. Name a unicellular organism which reproduces by multiple fission.
Answer : Plasmodium is a unicellular organism which reproduce by multiple fission.
Question. Name one organism which reproduces by:
(a) multiple fission
(b) binary fission
Answer :
| Types of fission | Name of Organism | |
| 1. | Multiple fission | Plasmodium, yeast |
| 2. | Binary fission | Amoeba, Paramecium |
Question. Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
Answer : Leaf
Question. Name the life process of an organism which helps in the growth of its population.
Answer: Reproduction
Question. Name the causative agent of the disease ‘kala-azar’ and its mode of asexual reproduction.
Answer: Leishmania causes ‘kala-azar’. It reproduces by binary fission in a definite orientation.
Question. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name a STDs which damages the immune system of human body.
Answer: Diseases that spread through the sexual contact are called STDs AIDS damages the body’s immune system.
Question. If a women is using copper-T, will it help in protecting against sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer: No, it can only prevent unwanted pregnancy. It will not be able to prevent contact of body fluids.
Question. Give the respective scientific term used for studying.
(i) The mechanism by which variation are created and inherited and
(ii) The development of new type of organism from the existing ones.
Answer: (i) Heredity, (ii) Evolution.
Question. Name the type of cells which undergo regeneration.
Answer: Specialised cells called regenerative cells which can make large number of new cells.
Question. Regeneration is not possible in all types of animals. Why?
Answer: Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells which are present in few animals which can reproduce by regeneration.
Question. List two unisexual flowers.
Answer: Watermelon, Cucumber and Willows
Question. List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
Answer: (i) Special cell division involved in the process of gametes formation is the cause of variations.
(ii) Genetic material comes from two parents, which brings variations in offsprings.
Question. List two functions performed by testis in human beings.
Answer: (i) Testis produces sperms.
(ii) It produces testosterone hormone.
Question. Name the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
Answer: Sepals and petals are not directly involved in reproduction.
Question. What is the role of scrotum?
Answer: Scrotum regulates the temperature of testes and maintains it at 35°C, two degree below the body temperature, so as to protect sperms from high temperature.
Question. How can the chromosomes be identified?
Answer: Chromosomes can be seen as thread like structure having specific shape when cell is dividing by which they can be identified.
Question. How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer: In binary fission cell divides into two cells whereas in multiple fission a cell divide into many daughter cells.
Question. Organisms have a varied body design. Name the property which gives the basic difference in body design.
Answer: Errors in DNA copying.
Question. Differentiate between germination and fertilisation.
Answer: Germination: Involves development of embryo into a seedling.
Fertilisation: It involves fusion of male with female gametes.
Question. Name the method by which hydra reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Answer: Hydra reproduces by budding. It is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Short Answer type Questions :
Question. From the Internet, gather information about the chromosome numbers of five animals and five plants. Correlate the number with the size of the organism and answer the following questions:
(A) Do larger organisms have more number of chromosomes/cells?
(B) Can organisms with fewer chromosomes reproduce more easily than organisms
with more number of chromosomes?
(C) The more the number of chromosomes/cells the greater the DNA content. Justify.
Answer : This table shows the number of chromosomes present in some important animals and plants:
Question. Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms? Give one reason.
Answer : Unicellular organisms reproduce by asexual reproduction, which is a simple division of parent cell into two daughter cells. Now, these two daughter cells grow into mature organisms.
Hence, cell division can be considered as themo de of reproduction in single celled organisms as it results in the production of more individuals of the organism.
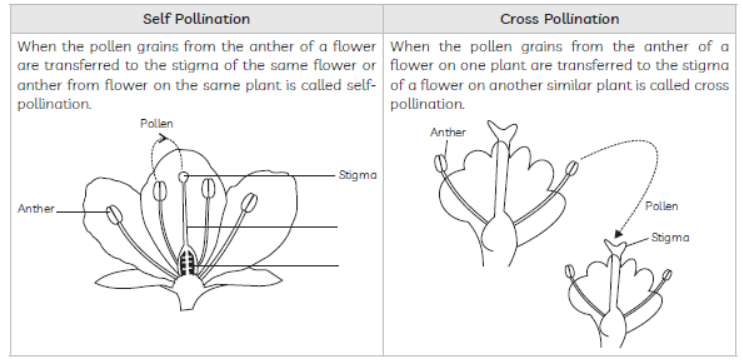
54. Define the term pollination. Differentiate between self pollination and cross pollination.
What is the significance of pollination?
Answer : Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anthero of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called.
Pollination: It is done by various agents like wind, water, insects like bees and butterflies, birds etc.
Pollination can occur in two ways:
(i) self pollination
(ii) cross Pollination
Difference between self pollination and cross pollination.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? Write the names of any two plants grown by this method.
Answer : Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual reproduction in some higher plants in which a new plant develops from the vegetative parts of a plant such as root, stem or leaf.
Two plants grown by this method are:
(1) Dahlia, sweet potato from roots.
(2) Ginger, potato, onion are grown from stem.
(3) Bryophyllum grown from leaf.
(4) Grapes grown by cutting.
(5) Guava grown by layering.
(6) Lemon grown by Grafting
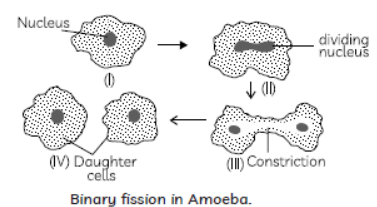
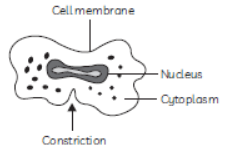
Question. A student is given a permanent slide showing binary fission in Amoeba. Write two steps to focus the slide under microscope. Draw diagram and label the parts.
Answer : Steps to focus the slide under microscope:
(i) Move the stage down to its lowest position.
(ii) Place the glass slide onto the stage.
(iii) Select the lowest power objective lens.
(iv) Turn the focus know slowly until the cells are not seen.
(v) There is a proper management of light.
(A) Number of chromosomes is not related to the size of an organisms. In the given table, we can see that even though a Kingfisher is smaller in size than a dog, the number of chromosomes is more in a Kingfisher.
(B) Ease of reproduction is not dependent on the number of chromosomes present. It depends on other factors like availability of water, nutrients, suitable mate and favorable environment.
(C) Yes, since the maJor component of chromosome is DNA, Chromosomes are made up of DNA. If chromosomes are more, this implies DNA will be more.
Question. Explain the process of budding in yeast by drawing labelled diagrams of different stages of the process in a correct sequence.
Answer : Diagram showing budding in yeast:

Question. Answer the following:
(A) Rahul observes bread mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread rather than on a dry slice of bread. Explain the observation briefly.
(B) Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water, but multiply in sugar solution. Give reason.
Answer : (A) The spores of bread mould need favourable conditions like moist surface to germinate.
Moisture is an important factor for the growth of hyphae of bread mould that contains spores. Therefore, moistened bread slice offers both moisture and nutrients to the bread mould, hence it grows profusely.
Dry slice of bread offers nutrients, but not moisture hence, hyphae fail to grow.
(b) The sugar solution provides the yeast with a food source and energy for sustaining all life activities in yeasts. So they can respire and therefore multiply. The water contains no food source, and thus does not provide energy to the yeast cells to multiply.
Question. Is the chromosome number of zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
Answer : Yes, zygote, embryonic cell and adult of a particular organism always have constant chromosome number.
Sexual reproduction includes gamete formation through meiosis and fertilization. Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes to half in male and female gametes. This reduced chromosome number is then restored to normal during fertilization of male and female gametes. This is how; constant chromosome number is maintained in sexually reproducing
organisms. Growth and development of zygote into embryonic cell and then into adult one takes place by mitosis (equatorial cell division) which produce the daughter cells carrying same chromosome number as that of parent cell.
Question. In a tobacco plant, the male gametes have 24 chromosomes. What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete? What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote?
Answer : Male and female gametes of a species have the same number of chromosomes. Hence, the number of chromosome in the female gamete of tobacco plants is 24. Zygote is formed by the fusion of male and female gametes, so it will have 48 chromosomes.
The number of chromosomes in the female gamete is 24.
The number of chromosomes in zygote is 48.
60. Give an example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers.
Answer : An example of unisexual flower is Papaya, water melon (write any one) and of bisexual flower is Hibiscus, mustard (write any one).
Question. List any four modes of asexual reproduction.
Answer : The four modes of asexual reproduction are:
(1) Fission
(2) Fragmentation
Question. Answer the following:
(a) What is a clone? Why do offspring formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity?
(b) Explain how offspring and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes?
Answer : (a) The new organisms or offsprings produced by one parent through asexual reproduction are called clones. The clones possess exact copies of the DNA or genes of their parents and hence show remarkable similarity Mto the parent or one another. Asexual reproduction does not involve gamete formation by meiosis and fertilization of male and female gametes; the offspring are genetically similar to the single parent.
(b) Sexual reproduction includes gamete formation through meiosis and fertilization.
The gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the amount of DNA or half the number of chromosomes as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell zygote will have the normal amount of
DNA.
For example: Human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg also has 23 chromosomes. So when a sperm and an egg fuse together, then the zygote formed will have 46 chromosomes.
Question. Give two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
Answer : Progeny formed as a result of sexual reproduction shows variations because:
(1) Sexual reproduction involves combining of DNA from two different individuals.
(2) The gene combination is different in gametes. The genetic material is exchanged between chromosomes before the formation of zygote, i.e., deoxyribonucleic
acid (DNA) exchange in the chromosome. The combination of two sets of chromo-somes, one set from each parent during zygote formation, leads to variation within a species.
Question. What changes are observed in the uterus if fertilisation does not occur?
Answer : In female, ovary produces one egg every month.
The uterus also prepares itself to receive a fertilised egg. So, the wall of uterus becomes thick and spongy containing lots of blood capillaries. If egg gets fertilised with sperm,then fertilised egg gets attached with uterus wall and gets nourishment from it. In case,egg is not fertilised, then this lining is no longer needed. The inner lining of uterus breaks down
and comes out in the form of blood and mucous through the vagina. This cycle occurs every month and is called menstruation. It usually lasts for about 2 to 8 days.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram to show that particular stage of binary fission in Amoeba in which its nucleus elongates and a constriction appears in its cell membrane.
Answer : Labelled diagram showing the stage in binary fission of amoeba in which its nucleus elongates and a constriction appears in its cell membrane is drawn below:
Question. List two preparations shown every month by the uterus in anticipation of pregnancy in the humans.
Answer: (i) The inner uterine wall becomes thick.
(ii) More blood vessels develop in its lining.
Question. Write the number of immature eggs present in the ovaries of newly born baby girl. Mention what happens to these immature eggs when the girl attains maturity.
Answer: Ovaries contain thousands of immature eggs at the time of birth. Some of these eggs start maturing when girls attain puberty. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
Question. Trace the path of sperms from where they are produced in human body to the exterior.
Answer: Testes → vas deferens → urethra → penis and then opens to outside.
Question. What is the main difference between sperms and eggs of humans? Write the importance of this difference.
Answer: Sperms are motile (movable) and have X or Y chromosomes whereas eggs are non-motile and have X chromosome only.
The sperms can reach to egg for fertilisation because these are motile. Chromosomes in them help in determination of sex of a new born child.
Question. The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same. Justify this statement.
Answer: (i) In sexual reproduction, fusion of male and female gametes takes place, each of their germ cells or gametes contain half the number of chromosomes.
(ii) When male and female gametes fuse at the time of fertilisation it restores the original number of chromosomes of parent.
Question. What is a clone? Why do offsprings formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity?
Answer: Clones are organisms which are exact genetics copies of their parents. Their DNA is exactly identical to their parents, which is the cause of remarkable similarity.
Question. Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Answer: Those organisms which reproduce by regeneration have similar and non-differentiated cells throughout the body, therefore body parts of organism grows into new organism.
In multicellular complex organisms, the cells get differentiated and perform different functions. In such organisms, body parts like skin, muscles, i.e. tissues can be regenerated, but the whole organism cannot be reproduced by regeneration.
Question. Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Answer: (i) Vegetative propagation is used to grow plants in which seeds are not formed or very few seeds are formed, e.g. banana, pineapple, orange.
(ii) It helps to grow plants in conditions where seed germination fails due to change in environment.
(iii) It is a faster, easier and cheaper process.
(iv) The plants produced are genetically similar and good quality or variety can be preserved easily.
Question. List two advantages of growing grapes or banana plants through vegetative propagation.
Answer: (i) Characteristics of parent plants are preserved.
(ii) Since these plants do not have viable seeds, therefore vegetative propagation is advantageous.
Question. List three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow.
Answer: (i) Availability of nutrition (food), (ii) moist place, (iii) warmth, (iv) dark place.
Question. Name the type of asexual reproduction in
(a) Planaria (b) Rhizopus
(c) Spirogyra (d) Hydra
Answer: (a) Regeneration (b) Spore formation
(c) Fragmentation (d) Budding
Question. Leaves of bryophyllum fallen on the ground produces new plants, why?
Answer: Leaves of bryophyllum has adventitious buds or plantlets in the notches along the leaf margin. When buds fall on the soil, they develop into new plant under favourable conditions.
Question. Name the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and Nthe parental identity is lost. Write the first step from where such a type of reproduction begins. Draw first two stages of this reproduction.
Answer: Binary fission, e.g. Fission in Amoeba Elongation of cell and its nucleus is the first step.
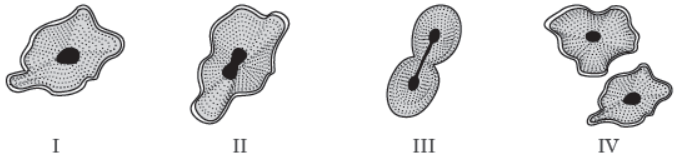
Question. Draw in sequence (showing the four stages), the process of binary fission in Amoeba.
Answer: Sequence (showing the four stages), the process of binary fission in Amoeba.
Question. What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism? Explain briefly. Name an organism which exhibits this type of reproduction.
Answer: The process in which parent cell divides into several small and equal sized daughter cells, which grows into a new organism is called multiple fission.
The nucleus of a cell divides into large number of nuclei and cytoplasm separates, forming a membrane around it. All this occurs within a protective covering. Plasmodium exhibits multiple fission.
Question. Explain the term ‘Regeneration’ as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Answer: Regeneration is the ability to produce an organism from their body parts. Many fully differentiated organisms show ability to reproduce by regeneration. In hydra, if the body is cut into two or three pieces, the lower part will develop head while the upper part will develop rest of the body. If its cells are separated, hydra will reform its structure by regeneration.
Question. In the context of reproduction of species state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each.
Answer:

Question. What happens when
(i) Planaria gets cut into two pieces
(ii) A mature spirogyra filament attains considerable length
(iii) On maturation sporangia burst
Answer: (i) Each piece will regenerate into complete organism. Cells at the location of the site of cut or wound, forms a small ball of cells that will differentiate into new tissues and regenerate the missing parts of the cut piece of the planaria.
(ii) When spirogyra attains considerable length, it breaks into smaller fragments and each fragment grows into a new plant.
(iii) On maturation, sporangial wall breaks and spores are dispersed to grow into new individual. These spores are very light and easily dispersed by wind.
Question. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? OR
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer: Reproduction involves producing same kind of species from parents. The genetic information is passed to the offspring by DNA present in each cell. This DNA, which is replicated (copied) is responsible for the resemblance of parents with offsprings with same traits. New traits are passed on due to difference in copying, new variations may occur and new species may evolve.
Question. What is the role of seminal vesicles and prostate gland? OR
Write the functions of secretions of prostate gland and seminal vesicles in humans.
Answer: Seminal vesicle: It holds the liquid that mixes with sperm to form semen.
Prostate gland: It secretes fluid adding upto the semen and contains enzymes and other substances.
It also provides nutrition to the sperms, in the form of fructose and calcium. It protects sperms.
Long Answer type Question :
Question. (a) Identify the organism A, B and mode of asexual reproduction exhibited by them.
(b) How will an organism be benefitted if it reproduces through spores?
(c) Mention the two asexual methods by which hydra can reproduce. Explain briefly any one such method.
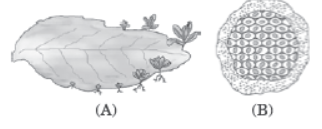
Answer: (a) ‘A’ is Bryophyllum–Vegetative propagation; ‘B’ is Plasmodium–Multiple fission
(b) Spores are covered with thick walls which protect them until they come into contact with a moist surface.
(c) Budding and regeneration
Budding: In this process hydra (or any other organism like yeast) use regenerative cells for reproduction. A bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division which develop into new individuals.
(a) Stem—Potato, Onion, Ginger (b) Roots—Banana, Asparagus
(c) Leaves—Bryophyllum
Question. (i) Describe the various steps involved in the process of binary fission with the help of a diagram.
(ii) Why do multicellular organisms use complex way of reproduction?
Answer: (i)
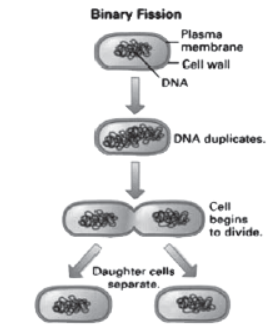
(ii) Multicellular organisms cannot reproduce by cell because they are not simple random collection of cells.
They have specialised cells, organised as tissues which are organised into organs.
Cell-by-cell division would be impractical .
Multicellular organisms require to use more complex ways of reproduction.
Question. (i) Identify A, B, C and D in the given figure. Write their names.
(ii) What is pollination? Explain its significance.
(iii) Explain the processes of fertilisation in flowers. Name the parts of the flower that develop after fertilisation into (a) seed (b) fruit.
Answer: (i) ‘A’ is stigma, ‘B’ is pollen tube, ‘C’ is ovary and ‘D’ is egg cell (female germ cell).

(ii) Pollination is a process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of stamen to the stigma of carpel. It is necessary for fertilisation by sexual reproduction.
(iii) When male gamete and egg fuse together to form zygote, it is called fertilisation.
It takes place in ovule. After that the ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into seed.
Fruit: The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit after ovule has been fertilised.
Question. (i) Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the part where (a) Egg develops, (b) fertilisation takes place, (c) fertilised egg gets implanted.
(ii) Describe in brief the changes that uterus undergoes (a) to receive the zygote (b) if zygote is not formed.
Answer: (i) (a) Egg develops in ovary.
(b) Fertilisation takes place in fallopian tube.
(c) The fertilised egg gets implanted in uterus.
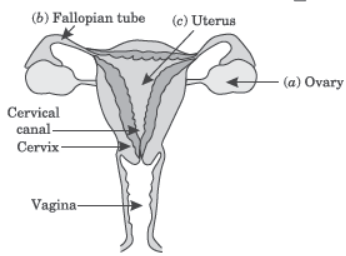
(ii) (a) The inner uterus lining becomes thick to receive the zygote and is supplied with blood and nutrients to nourish the embryo.
(b) The inner uterus lining breaks and released in the form of blood and mucus through vagina.
Question. (a) Name the organ that produces sperms as well as secretes a hormone in human males. Name the hormone it secretes and write its functions.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs.
(c) Explain how the developing embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Answer: (a) The organ that produces sperms as well as secretes male hormone is testis. The hormone secreted by it is testosterone. Its important functions are as follows:
It stimulates sperm production.
It stimulates the development of secondary sexual characters in males like growth of beard hairs, low pitch voice, etc. It involves in the development, maturation and functioning of the male accessory sex organs like vas deferens and seminal vesicles
(b) In human female reproductive system, the process of fertilisation takes place in one of the fallopian tubes.
(c) The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta.
Placenta is a vascular membranous organ that connects the developing foetus to the uterine wall of the mother. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. The placenta draws nutrients and oxygen, which it supplies to the foetus, from the maternal circulation. In turn, the placenta receives carbon dioxide and wastes of foetal metabolism and discharges them into the maternal circulation for disposal.
Question. Trace the changes that take place in a flower from gamete formation to fruit formation.
Answer: [Diagram drawn and annotated with the following points will also be considered]
– Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains.

• The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
• The pollen needs to be transferred from the stamen to the stigma.
• If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination./ On the other hand, if the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as crosspollination.
After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ-cells which are in the ovary. For this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary/Figure
• The male germ-cell produced by pollen grain fuses with the female gamete present in the ovule.
• This fusion of the germ-cells or fertilisation gives the zygote.
• After fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
• The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
• Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
Question. List four points of significance of reproductive health in society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years.
Answer: Significance of reproductive health in society are:
(i) Prevent STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease)
(ii) Advantages of small family
(iii) Less mortality among new borns
(iv) Reduces cases of maternal mortality
Two areas of Improvement are:
(i) Family planning. (ii) Decrease in STD cases.
Question. Identify the following methods and give one example of each:
(a) Process in which reproduction takes place by breaking up of parent into several fragments.
(b) Process of dividing of organisms into many cells simultaneously.
(c) Process of reproduction by formation of bud on the parent body.
(d) Process of reproduction by formation of spores.
(e) Process used by multi-cellular organisms to reproduce by cutting into many pieces and each piece forms a new individual.
Answer: (a) Fragmentation, Spirogyra
(b) Multiple fission, Plasmodium
(c) Budding, Yeast/Hydra
(d) Spore formation, Rhizopus
(e) Regeneration, Planaria
Question. Explain what happens when:
(a) Testosterone is released in males. (b) Pollen grains falls on the stigma of flowers.
(c) Egg fuses with sperm cell. (d) Planaria is cut into many pieces.
(e) Buds are formed on notches of the bryophyllum leaf.
Answer: (a) (i) Formation of sperms and change in appearance.
(ii) Thick hair growth on face stet and pubic region and change in voice.
(b) A tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to the ovary.
(c) Zygote is formed i.e. fertilisation takes place.
(d) Each piece grows into new organism.
(e) Buds may fall on the soil and change into new organism.
Question. (i) Describe the role of prostate gland, seminal vesicle and testes in the human male reproductive system.
(ii) How is the surgical removal of unwanted pregnancies misused?
(iii) Explain the role of oral contraceptive pills in preventing conception.
Answer: (i) Prostate glands and seminal vesicle add their secretions so that the sperms are in a fluid state and it makes their transport easier and also provides nutrition to sperms. Testes secrete testosterone hormone which brings about changes in the appearance in the boys at the time of puberty.
(ii) Female foeticides/illegal sex selected abortion of female child.
(iii) Interfere in release of egg and eggs are not released.
Question. (a) List three different categories of contraception methods.
(b) Why has Government of India prohibited prenatal sex determination by law? State its benefits in the long run.
(c) Unsafe sexual act can lead to various infections. Name two bacterial and two viral infections caused due to unsafe sex.
Answer: (a) (i) Barrier method, (ii) Oral pills, (iii) Use of copper-T, (iv) Vasectomy in males, tubectomy in females.
(b) • It is because female foeticide is increasing.
• It leads to unbalanced sex ratio i,e , more males , less females.
On long run, it will help in maintaining healthier (equal) sex ratio.
It will save mothers from illegal medical termination of pregnancy and health issues.
(c) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are bacterial infections.
Warts and HIV-AIDS are viral infections.
Question. What is binary fission in organisms? With the help of suitable diagrams, describe the mode of reproduction in amoeba.
Answer: Binary fission is a fission in which two daughter cells are formed of nearly equal size after replicating the genetic material of a single cell. Single-celled organisms like amoeba undergoes binary fission.

Question. Write two causes of human population explosion. Explain with the help of a suitable examples how this explosion can be checked.
Answer: Two causes of human population explosion are:
(i) Reduced mortality rate due to better medical facilities.
(ii) Desire for male child.
(iii) Less awareness of birth control methods.
(iv) Illiteracy and poverty.
Methods to check population explosion are:
(i) By using contraception methods.
(ii) Awareness among people of the advantage of small family.
Question. (a) (i) Write full form of DNA.
(ii) State the role of DNA in the cell nucleus.
(iii) What will be the effect if the information of the DNA is changed?
(b) Explain the importance of DNA copying in reproduction.
Answer: (b) (i) Deoxy Ribonucleic Acid
(ii) It helps in synthesis of protein and transfer of genetic characteristics.
(iii) Proteins will be changed.
(b) Body designs are similar due to DNA copying.
DNA cell nucleus carry information for synthesis of protein.
If DNA copying will not take place then body design will change.
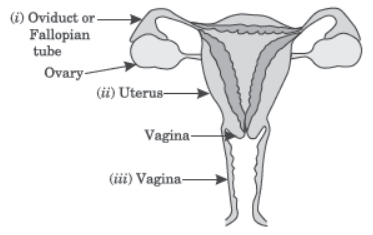
Question. (a) Draw the diagram of female reproductive system and match and mark the part (s):
(i) Where block is created surgically to prevent fertilisation.
(ii) Where CuT is inserted. (iii) Inside which condom can be placed.
(b) Why do more and more people prefer to use condoms? What is the principle behind use of condoms?
Answer: (a) (i) Fallopian Tube/Oviduct
(ii) Uterus
(iii) Vagina
(b) People prefer use of condoms as it prevents STDs/gives privacy to the user. Condoms help create a mechanical barrier preventing meeting of sperms and ovum.

