DK Goel Solutions Chapter 1 Financial Statements of Companies
Read below DK Goel Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 1 Financial Statements of Companies. These solutions have been designed based on the latest Class 12 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
In this chapter, students will understand the different types of financial statements of a company. it is important for the students to get a detailed understanding of different types of statements that are prepared at the end of the accounting period based on which the overall financial position of a company is understood. these financial statements are being used by people who run the company as well as various other stakeholders. students should understand this chapter very carefully as this will help them in long run.
The chapter contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful for Class 12 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career. These solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 12 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Financial Statements of Companies DK Goel Class 12 Accountancy Solutions
Short Answer Questions
Question 1
Solution 1

Point for Students:-
As per Section 2(41) of the Companies Act, 2013, all companies are required to have a uniform financial year which shall be a period from 1st April to 31st March every year. Only companies which are a holding or subsidiary of a foreign company required to follow different financial year for the purpose of consolidation of its accounts outside India may apply to the Tribunal for a different financial year.
Question 2.
Solution 2

Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes.
Question 3.
Solution 3

Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 4.
Solution 4
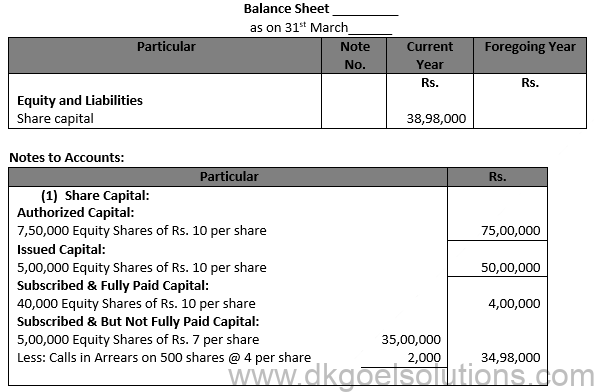
Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes.
Question 5.
Solution 5

Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 6.
Solution 6
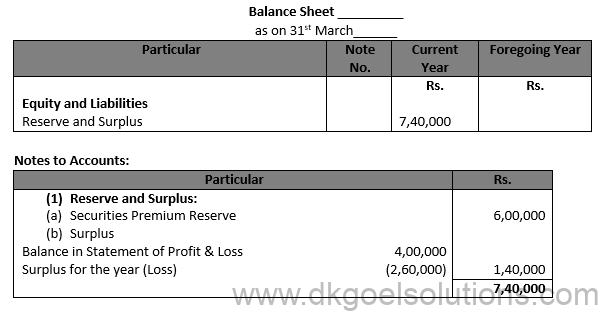
Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 7
Solution 7


Point for Students:-
As per Section 2(41) of the Companies Act, 2013, all companies are required to have a uniform financial year which shall be a period from 1st April to 31st March every year. Only companies which are a holding or subsidiary of a foreign company required to follow different financial year for the purpose of consolidation of its accounts outside India may apply to the Tribunal for a different financial year.
Question 8
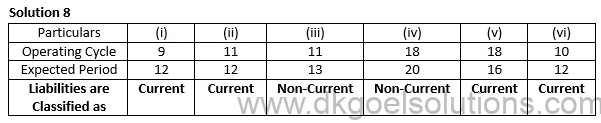
Point of Student:-
As per Schedule-III: “An operating cycle is the time between the acquisition of assets for processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. Where the normal operating cycle cannot be identified, it is assumed to have duration of 12 months.”
Question 9
Solution 9

Point for Students:-
There is distinction between ‘Reserves’ and ‘Provision’. Reserves means accumulated profits and it is created to strengthen the financial position of the Company and to meet unforeseen liabilities and losses.
‘Provision’ is an amount provided for any known liability whose amount as yet is uncertain. Provision is made to meet a specific liability of which the amount cannot be determined with substantial accuracy. Provision is also made for known losses such as ‘Provision for Depreciation’.
Question 10
Solution 10 Both will be classified under ‘Shareholder’s Funds’.
Question 11 A (new)
Solution A 11 (new) (i) Outstanding Salary shows in Current Liabilities under Other Current Liabilities.
(ii) Bank Balance shows in Current Assets under Cash and Cash Equivalents.
(iii) Unpaid Matured Deposits shows in Current Liabilities under Other Current Liabilities.
(iv) Preliminary Expenses not shown in balance sheet.
(v) Bills Payable shows in Current Liabilities under Trade Payables.
Question 11 B (new)
Solution 11 i) Patents and Trade Marks shows in Non-current assets under fixed assets (intangible assets).
(ii) Income Received in Advance shows in Current liabilities under Other current Liabilities.
(iii) Debentures issued by the Company shows in Non-Current Liabilities under Long-term Borrowing.
(iv) Stores and Spare-parts shows in Current Assets under Inventories.
(v) Motor Vehicles show in Non-Current Assets under Fixed Assets (Tangible Assets).
(vi) Forfeited Shares Account shows in Shareholder’s Fund added to Subscribed Capital.
(vii) Government Securities shows in Non-Current Assets under Non-Current Investments.
(viii) Uncalled Liabilities on Partly paid shares shows in Commitments in notes to accounts.
Question 11
Solution 11 The sub-headings under which Current Liabilities shall be classified in a Company’s Balance Sheet are:
i. Short term Borrowing
ii. Trade Payable
iii. Other Current Liability
iv. Short Term Provision
Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 12 (new)
Solution 12 (new)
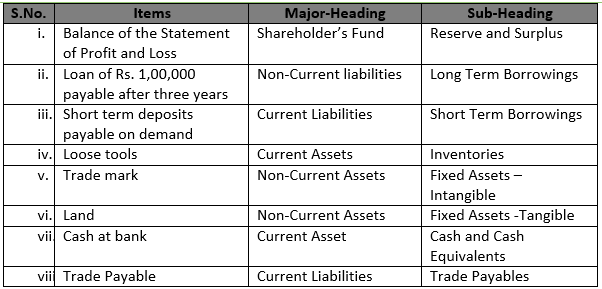
Question 12
Solution 12 (i) Items:- Unclaimed Dividend
Major-Heading:- Current liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
(ii) Items:- Proposed dividend
Major-Heading:- Contingent Liabilities in notes to accounts
(iii) Items:- Security Premium Reserve
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
(iv) Items:- Share forfeited Account
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund added to ’Subscribed Capital
(v) Items:- Public Deposits
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long -Term Liabilities
(vi) Items:- Debentures
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long Term provision
(vii) Items:- Bills discounted but not matured
Major-Heading:- Contingent Liabilities in notes to accounts
Question 13 (new)
Solution 13 (new)

Question 13
Solution 13 (i) Items:- Shares options outstanding Account
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
(ii) Items:- Excess Application money due for refund
Major-Heading:- Current liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
(iii) Items:- GST payable
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
(iv) Items:- Debenture redemption
Major-Heading:- Reserve Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
(v) Items:- Premium Payable on Redemption of debentures
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Long -Term Liabilities
(vi) Items:- Provision for Gratuity
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long Term provision
(vii) Items:- Outstanding Expenses
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
Question 14 (new)
Solution 14 (new)
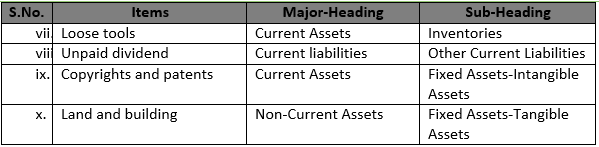
Question 14
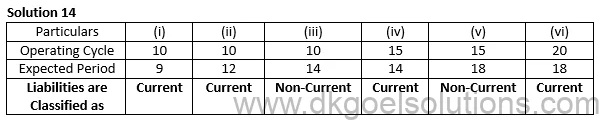
Point of Student:-
As per Schedule-III: “An operating cycle is the time between the acquisition of assets for processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. Where the normal operating cycle cannot be identified, it is assumed to have duration of 12 months.”
Question 15 (new)
Solution 15 (new)

Question 15.

Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes.
Question 16 (new)
Solution 16 (new)
Question 16.
Solution 16. Sub-Headings Under Current Assets: Current Investment
Inventories
Trade receivables
Cash and cash equivalents
Short-term loans and advances
Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 17 A (new)
Solution 17 A (new)

Question 17 B (new)
Solution 17 B (new)

Question 17.
Solution 17
Point for Students:-
As per Section 2(41) of the Companies Act, 2013, all companies are required to have a uniform financial year which shall be a period from 1st April to 31st March every year. Only companies which are a holding or subsidiary of a foreign company required to follow different financial year for the purpose of consolidation of its accounts outside India may apply to the Tribunal for a different financial year.
Question 18 (new)
Solution 18 (new)

Question 18
Solution 18
Revenue from Operations:
Sales
Revenue from services rendered
Other Income:
Interest on Loans given,
Divided income,
Sale of miscellaneous items
Refund of income tax.
Question 19 (new)
Solution 19 (new)
Question 19
Solution 19
i. Revenue from Operations:
ii Revenue from serviced rendered
iii. Interest on loan given
vi. Dividend income
Other Income:
Refund on income tax
Sale of miscellaneous items
Question 20 (new)
Solution 20 (new)

Question 20

Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes.
Question 20 (new)
Solution 21 (new)

Question 21
Solution 21

Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 22 (new)
Solution 22 (new)

Question 22
Solution 22

Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 23 (new)
Solution 23 (new)
Question 23
Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes
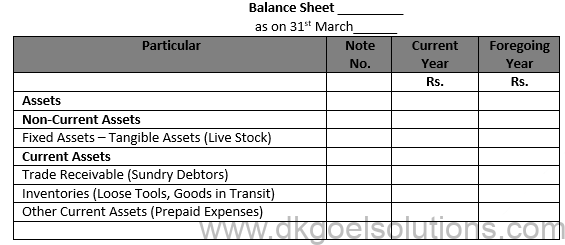
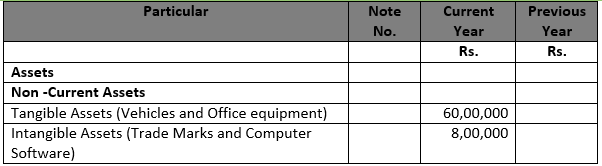
Question 24 (new) Show the following items in a company’s Balance Sheet as at 31st, March,2017:
Particular Rs.
i. Deferred Tax Assets 2,00,000
ii. Loose Tools 1,20,000
iii. Goods in Transit 5,00,000
iv. Prepaid Expenses 15,000
v. Interest Accrued on investments 10,000
Solution 24 (new)

Question 24

Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 25 (new)
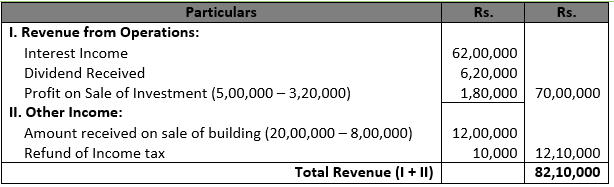
Solution 25 (new) Revenue from Operations: Sales and Revenue from services rendered
Other Income: Interest on Loans given, Divided income, Sale of miscellaneous items and Refund of income tax.
Question 25
Solution 25
Employee Benefit Expenses:
i. Salaries
ii. Medical Expenses
iv. Gratuity paid
vi. Contribution on provident fund.
Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to the past periods and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. The financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 26 (new)
Solution 26 (new) Revenue from Operations: Revenue from serviced rendered, Interest on loan given, and Dividend income
Other Income: Refund on income tax and Sale of miscellaneous items.
Question 26

Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes.
Question 27 (new)
Solution 27 (new)

Question 27
Solution 27
The following items shown in the Notes of Accounts on Finance Costs:
i. Interest paid in bank overdraft
ii. Interest paid on borrowings
iii. Deposit on issue of debentures written off
iv. Interest paid on term loan
Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to the past periods and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. The financial statement shows profitability through the Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through the Balance Sheet.
Question 28 (new)
Solution 28 (new)
Question 28
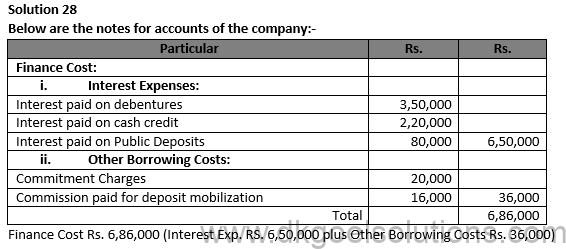
Point for Students:-
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, ‘Financial Statements’ in relation to a Company, include the following:
(i) A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year.
(ii) A statement of profit and loss for the financial year.
(iii) Cash flow statement for the financial year.
(iv) A statement of changes in equity, if applicable.
(v) Explanatory notes.
Question 29 (new)
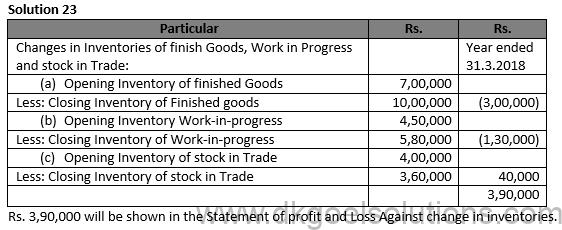
Solution 29 (new) Cost of Material Consumed: Rs.
Opening Inventory: Materials 4,20,000
Add: Material Purchased 20,00,000
24,20,000
Less: Closing Inventory of Material 3,80,000
20,40,000
Question 29
Solution 29 Below are the items will be shown in the notes of accounts on ‘other expense’:-
i. Consumptions of loose tools
iv. Courier expenses
v. Carriage outwards
vi. Discount allowed
vii. Bank Charges
viii. Rent for Warehouse
Question 30 (new)
Solution 30 (new)

Rs. 3,90,000 will be shown in the Statement of profit and Loss Against change in inventories.
Question 30
Solution 30 (i) Items:- Loss processing charges
Major-Heading:- Finance Costs
(ii) Items:- Sale of products
Major-Heading:-Revenue from Operations
(iii) Items:- Leave encashment expenses
Major-Heading:-Employee Benefit Expenses
(iv) Items:- Courier expenses
Major-Heading:-Other Expenses
(v) Items:- Computer software amortized
Major-Heading:-Depreciation and amortization exp.
(vi) Items:- Interest on cash credit
Major-Heading:-Finance costs
(vii) Items:- Materials purchased
Major-Heading:-Cost of Materials Consumed
Question 31 (new)
Solution 31 (new)

Question 31
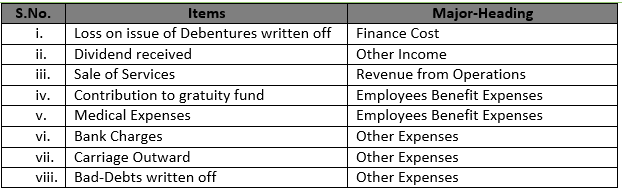
Solution 31 (i) Item:- Loss on issue of debentures written off
Major Head:- Finance Costs
(ii) Item:- Dividend received
Major Head:- Other Income
(iii) Item:- Sale of services
Major Head:- Revenue from Operations
(iv) Item:- Contribution of gratuity fund
Major Head:- Employee Benefit Expenses
(v) Item:- Medical expenses
Major Head:- Employee Benefit Expenses
(vi) Item:- Bank charges
Major Head:- Other Expenses
(vii) Item:- Carriage outwards
Major Head:- Other Expenses
(viii) Item:- Bad-Debts written off
Major Head:- Other Expenses
Question 32 (new)
Solution 32 (new) Employee Benefit Expenses:
i. Salaries
ii. Medical Expenses
iv. Gratuity paid
vi Contribution on provident fund.
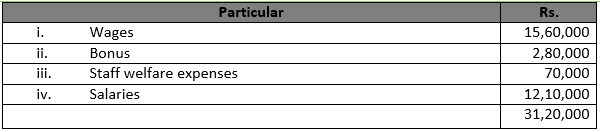
Question 32
Solution 32 (i) Items:- Commission paid for deposit mobilization
Major-Heading:- Finance Costs
(ii) Items:- Dividend received
Major-Heading:- Revenue from Operations
(iii) Items:-Refund of income tax
Major-Heading:-Other Income
(iv) Items:-Lease rent
Major-Heading:-Other Expenses
(v) Items:-Gain on sale of investments
Major-Heading:-Revenue from Operations
(vi) Items:-Expenses on employee’s stock option scheme
Major-Heading:-Employee Benefit Expenses
(vii) Items:-Audit fee
Major-Heading:-Other Expenses
(viii) Items:-Premium payable on redemption of debentures written off
Major-Heading:-Finance Costs
Question 33 A (new)
Solution 33 A (new)
Question 33 (A)
Solution 33 (A)
1. Outstanding salary: Current Liabilities under other Current Liabilities
2. Bank balance: Current Assets under cash and cash Equivalents.
3. Unpaid matured deposits: Current Liabilities under Other Current Liabilities.
4. Preliminary expenses: Not Shown in Balance Sheet since they are written off in the same year.
5. Bills payable: Current Liabilities under Trade payables
6. Sale of services: Revenue from Operations.
7. Goodwill written off: Depreciation and Amortization Expenses.
8. Medical Expenses: Employee Benefit Expenses.
Point for Students:-
Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents. They are expressed in terms of money. Financial statement shows profitability through Statement of Profit and Loss and financial position through Balance Sheet.
Question 33 (B)
Solution 33 (B) i. Patents and Trade Marks
Major- Heading: Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading: Fixed Assets- Intangible Assets
ii. Income Received in Advance
Major- Heading: Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading: Other Current Liabilities
iii. Debentures issued in Advance
Major- Heading: Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading: Long Term Borrowings
iv. Stores and Spare-parts
Major- Heading: Current Assets
Sub-Heading: Inventories
v. Motor vehicles
Major- Heading: Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading: Fixed Assets- Tangible Assets
vi. Forfeited Shares Account
Major- Heading: Shareholder’s Funds; added to ‘Subscribed Capital’
vii. Government Securities
Major- Heading: Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading: Non-Current Investments
viii. Uncalled Liabilities on Partly paid shares.
Major- Heading: Commitment (to be shown in Notes to Accounts)
Question 34 (new)
Solution 34 (new) Finance Cost:
i. Interest paid in bank overdraft
ii. Interest paid on borrowings
iii. Deposit on issue of debentures written off
iv. Interest paid on term loan
Question 34
Solution 34 i) Balance of the Statement of Profit and Loss
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
ii) Loan of Rs. 1,00,000 payable after three years
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
iii) Short term deposits payable on demand
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short Term Borrowings
iv) Loose tools
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
v) Trade mark
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets – Intangible
vi) Land
ajor-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets -Tangible
vii) Cash at bank
Major-Heading:- Current Asset
Sub-Heading:- Cash and Cash Equivalents
viii) Trade Payable
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Trade Payables
Question 35 (new)
Solution 35
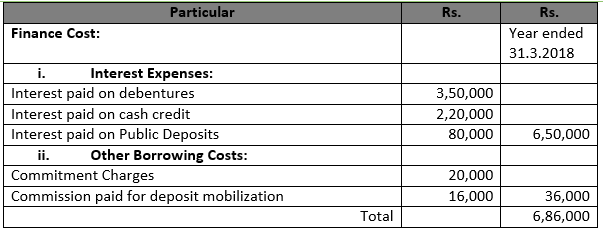
Finance Cost Rs. 6,86,000 (Interest Exp. RS. 6,50,000 plus Other Borrowing Costs Rs. 36,000)
Question 35
Solution 35 i) Public deposits
Major-Heading:- Non- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long Term Borrowings
ii) Sinking fund
Major-Heading:- Shareholder Funds’
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
iii) Office equipment
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Tangible Assets
iv) Prepaid expenses
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Assets
v) Outstanding salaries
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
vi) Motor car
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Tangible Assets
Question 36 (new)
Solution 36 (new) Other Expenses:
i. Consumptions of loose tools
iv. Courier expenses
v. Carriage outwards
vi. Discount allowed
vii. Bank Charges
viii. Rent for Warehouse
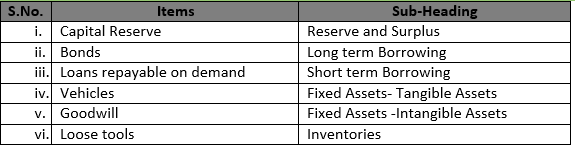
Question 36
Solution 36 i) Loose tools
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
ii) Unpaid dividend
Major-Heading:- Current liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
iii) Copyrights and patents
Major-Heading:-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Intangible Assets
iv) Land and building
Major-Heading:-Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Tangible Assets
Question 37 (new)
Solution 37 (new)

Question 37. Classify the following items under Major Head and Sub- Head in the Balance Sheet of a company as per schedule III part I of the companies Act, 2013/
i. Capital Work in Progress
ii. Provision for Warranties
iii. Income received in advance
iv. Capital Advances
v. Capital Reserve
vi. Bank Overdraft
Solution 37 i) Capital Work in Progress
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets
ii) Provision for Warranties
Major-Heading:- Non-Current liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long Term Provision
iii) Income received in advance
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
iv) Capital Advances
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Long Term Loan and Advances
v) Capital Reserve
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Find
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
vi) Bank Overdraft
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short Term Borrowings
Question 38 (new)
Solution 38 (new)
Question 38.
Solution 38 i) Capital Reserve
Sub-Heading:- Reserve and Surplus
ii) Bonds
Sub-Heading:- Long term Borrowing
iii) Loans repayable on demand
Sub-Heading:- Short term borrowing
iv) Vehicles
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets- Tangible Assets
v) Goodwill
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets -Intangible Assets
vi) Loose tools
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
Question 38 A (new)
Solution 39 A (new)

Question 39 (A)
Solution 39 (A) i) Computer Software
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Intangible Assets
ii) Bills Receivable
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Trade Receivables
iii) Interest Accrued and Due on Debentures
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
iv) Interest Accrued on Investments
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Assets
v) Calls in Arrears
Major-Heading:- Deducted from Subscribed but not fully paid Capital under the head ‘Shareholder’s Funds’
vi) Discount on Issue of Debentures written off
Major-Heading:- Financial Costs
vii) Fees received for arranging loans
Major-Heading:- Other Incomes
viii) Telephone and Internet Exp.
Major-Heading:- Other Expenses
Question 39 (B)
Solution 39 (B) (i) Authorized Capital
Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund under Share Capital to be shown only in the notes to Accounts
(ii) Share Forfeiture Account
Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund Added to ‘Subscribed Capital’
(iii) Capital Reserve
Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund under reserve and Surplus
(iv) Secured Debentures
Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities under Long Term Borrowing
(v) Provision for Tax
Heading:- Current Liabilities Under Short Term Provision
(vi) Trade Payable written back
Heading:- Other Income
(vii) Loan Processing Charges
Heading:- Finance Costs
Question 40 (new)
Solution 40 (new) These five items shown under Reserve and Surplus are:
i. Capital Reserves;
ii. Securities Premium Reserve;
iii. Debenture Redemption Reserve;
iv. Revaluation Reserve;
v. Capital Redemption Reserve
Question 40
Solution 40 i) Mining Rights
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Intangible Assets
ii) Debtors
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Trade Receivables
iii) Interest on Calls in Advance
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
iv) Working in progress
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
v) Mortgage Loan
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long-term Borrowings
vi) Bonds
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long term Borrowings
Question 41 (new)
Solution 41 (new)
Question 41
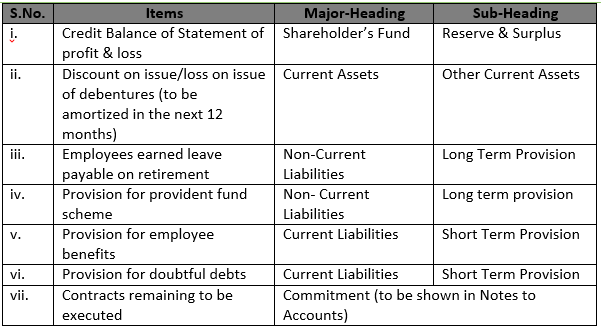
Solution 41 i) Credit Balance of Statement of profit & loss
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserve & Surplus
ii) Discount on issue/loss on issue of debentures (to be amortized in the next 12 months)
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Assets
iii) Employees earned leave payable on retirement
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long Term Provision
iv) Provision for provident fund scheme
Major-Heading:- Non- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long term provision
v) Provision for employee benefits
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short Term Provision
vi) Provision for doubtful debts
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short Term Provision
vii) Contracts remaining to be executed
Major-Heading:- Commitment (it is shown in Notes to Accounts)
Question 42 (new)
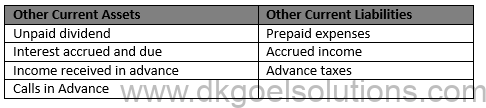
Solution 42 (new) Other Current Assets Other Current Liabilities
Unpaid dividend Prepaid expenses
Interest accrued and due Accrued income
Income received in advance Advance taxes
Calls in Advance
Question 42.
Solution 42 i) Stores and spares
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
ii) Debentures due for redemption
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
iii) Live stock
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Tangible Assets
iv) Intellectual property rights
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Intangible Assets
v) Advance from customers
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
vi) Advance to suppliers
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Assets
vii) Commission received in Advance
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other Current Liabilities
Question 43 (new)
Solution 43 (new)

Question 43
Solution 43
i) Plant and Machinery
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
ii) Building
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
iii) Equity Share Capital (Authorized)
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
iv) Equity shares of Rs, 100 per share Rs. 70 called and paid up
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
v) 10% Debentures
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
vi) Furniture and Fixtures
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
vii) Long term bank loan (secured)
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Question 44 (new)
Solution 44 (new) Rs. 45,00,000 as Long term Borrowings
Rs. 15,00,000 as Other Current Liabilities
Question 44
Solution 44 These five items shown under Reserve and Surplus are:
i. Capital Reserves;
ii. Capital Redemption Reserve
iii. Securities Premium Reserve;
iv. Debenture Redemption Reserve;
v. Revaluation Reserve;
Point for Students:-
Share Options Outstanding Account: It is a form of employee compensation wherein employees are offered an option to apply and get allotment of Company’s shares at a future date at a specified price which is usually sufficiently below the market price of the share.
Question 45 (new)
Solution 45 (new)

Question 45
Solution 45 i) Preliminary Expenses
Major-Heading:- Not shown in the Balance Sheet as these expenses are written off in the same year.
ii) Discount on Issue of Debentures
Major-Heading:- Current/Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Other Current/Non-Current Assets
iii) 10% debentures
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long Term Borrowing
iv) Stock -in -trade
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
v) Cash at Bank
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Cash and Cash Equivalents
vi) Bills Receivable
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Trade Receivables
vii) Goodwill
Major-Heading:- Non- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Intangible Assets
viii) Loose Tools
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
ix) Horses and Carts
Major-Heading:- Non- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Tangible Assets
x) Motor Truck
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets-Tangible Assets
xi) Provision for Taxation
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short Term Provisions
xii) Sundry Creditors
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Trade Payables
Question 46

Point for Students:-
As per Section 2(41) of the Companies Act, 2013, all companies are required to have a uniform financial year which shall be a period from 1st April to 31st March every year. Only companies which are a holding or subsidiary of a foreign company required to follow different financial year for the purpose of consolidation of its accounts outside India may apply to the Tribunal for a different financial year.
Question 47

Point for Students:-
There is distinction between ‘Reserves’ and ‘Provision’. Reserves means accumulated profits and it is created to strengthen the financial position of the Company and to meet unforeseen liabilities and losses.
‘Provision’ is an amount provided for any known liability whose amount as yet is uncertain. Provision is made to meet a specific liability of which the amount cannot be determined with substantial accuracy. Provision is also made for known losses such as ‘Provision for Depreciation’.
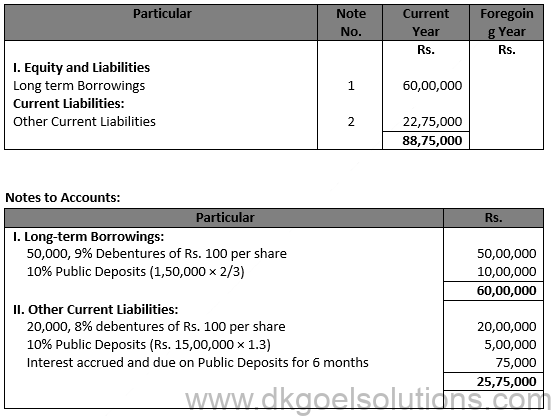
Question 48 Show the following items in a company’s Balance Sheet as at 31st, March,2017:

Question 49
Solution 49 Long Term Borrowings RS. 60,00,000 Other Current liabilities Rs. 25,75,000.
Point for Students:-
There is distinction between ‘Reserves’ and ‘Provision’. Reserves means accumulated profits and it is created to strengthen the financial position of the Company and to meet unforeseen liabilities and losses.
‘Provision’ is an amount provided for any known liability whose amount as yet is uncertain. Provision is made to meet a specific liability of which the amount cannot be determined with substantial accuracy. Provision is also made for known losses such as ‘Provision for Depreciation’.
Question 50
Solution 50 i) Consumption of Loose Tools
Major-Heading:- Other Expenses
ii) Sale of Services
Major-Heading:- Revenue from Operations
iii) Trade Marks written off
Major-Heading:- Depreciation and Amortization Exp.
iv) Trade Payable written off
Major-Heading:- Other Income
v) Canteen Expenses
Major-Heading:- Employee Benefit Expenses
vi) Purchase of Stock in Trade
Major-Heading:- Purchase of stock in Trade
vii) Courier Charges
Major-Heading:- Other Expenses
viii) Revenue from Project Consultancy
Major-Heading:- Other Income
ix) Computer Hiring Charges
Major-Heading:- Other Expenses
x) Commitment Charges
Major-Heading:- Finance Cost
Question 51
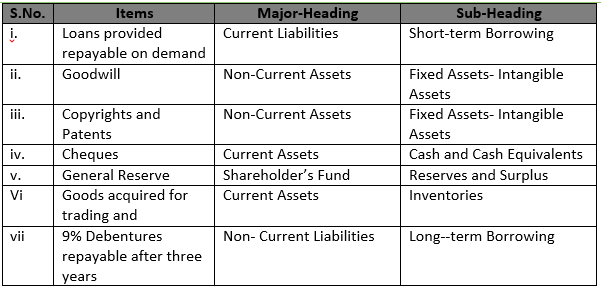
Solution 51 i) Loans provided repayable on demand
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short-term Borrowing
ii) Goodwill
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets- Intangible Assets
iii) Copyrights and Patents
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets- Intangible Assets
iv) Cheques
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Cash and Cash Equivalents
v) General Reserve
Major-Heading:- Shareholder’s Fund
Sub-Heading:- Reserves and Surplus
vi) Goods acquired for trading and
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Inventories
vii) 9% Debentures repayable after three years
Major-Heading:- Non- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long–term Borrowing
Question 52
Solution 52
Point for Students:-
There is distinction between ‘Reserves’ and ‘Provision’. Reserves means accumulated profits and it is created to strengthen the financial position of the Company and to meet unforeseen liabilities and losses.
‘Provision’ is an amount provided for any known liability whose amount as yet is uncertain. Provision is made to meet a specific liability of which the amount cannot be determined with substantial accuracy. Provision is also made for known losses such as ‘Provision for Depreciation’.
Question 53
Solution 53 i) Bank overdraft
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Short-term Borrowing
ii) Draft in hand
Major-Heading:- Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Cash and Cash Equivalents
iii) Trade Marks
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Assets
Sub-Heading:- Fixed Assets- Intangible Assets
iv) Long-Term Provision
Major-Heading:- Non-Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Long -term provision
v) Calls in Advance
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other current Liabilities
vi) Interest on Calls in Advance
Major-Heading:- Current Liabilities
Sub-Heading:- Other current liabilit

The company’s financial statement is basically the output of the accounting process and generally designed after the company’s accounting period. The financial statements reveal the company’s financial position and allow them to have a clear picture of the end products of their financial decisions.
The financial statements of the companies primarily constitute of four fundamental components, which are –
● Balance Sheet or Position Statement of the company
● A statement of profit and loss of the company during the accounting period.
● Notes to Accounts.
● Cash Flow Statement.
A balance sheet is an official statement that depicts clear information about the assets, liabilities, and equities of a company. It is basically a document that depicts the financial position of the company at a specific time span. The balance sheet is a key element of the financial statement of a company, and it gives an in-depth picture of the company’s financial status.
Here are some of the limitations of the financial statements –
● Financial Statements only present the quantitative data of the transactions. It does not highlight any qualitative aspect of the transaction like size, quality, or capabilities.
● Financial Statements portray the pre-defined price of the products or services. It fails to quote any modifications in the price. Thereby giving no data about the current price.
● Financial Statements are designed by humans. Therefore, it may contain errors.
Here is the sole objective of the financial statements –
● The financial statement is one of the most reliable sources for companies to understand their financial positions. It periodically supplies the companies with updated financial data.
● It portrays all details about the financial status of the companies, including profitability, liquidity, etc.
● Financial Statements evaluate the estimated earning capacity of the companies.
Financial Statements are extremely fruitful for the shareholders as it allows them to understand the profit-making capacity of the firm. It supplies them with the most accurate information to grasp the company’s financial status, helping them make better business decisions.
Also refer to TS Grewal Solutions for Class 12
