DK Goel Solutions Chapter 8 Company Accounts Issue of Debentures
Read below DK Goel Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 8 Company Accounts Issue of Debentures. These solutions have been designed based on the latest Class 12 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
DK Goel Class 12 Accountancy Company Accounts Issue of Debentures, One of the ways of raising capital is by issuing debentures to the public. This helps the companies in various types of financial needs including the expansion of the business. the students should understand what are debentures and why are they issued by various companies. In this chapter, the students will understand the basics of the issue of debentures and also the related accounting entries which have to be passed whenever the company issues fresh debentures in the market.
The chapter contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful for Class 12 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career. These solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 12 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Company Accounts Issue of Debentures DK Goel Class 12 Accountancy Solutions
Short Answer Questions
Q1.
Sol.1 Debentures may be issued either at par, at premium or at a discount.
Issue of Debentures at Par:-
Keshav Ltd. issued 4,000, 10% Debentures of Rs. 100 each at par
Journal Entries

Issue of Debentures at Premium:-
Keshav Ltd. issued 4,000, 10% Debentures of Rs. 100 each at a premium of 10%.
Journal Entries

Issue of Debentures at Discount:-
Keshav Ltd. issued 4,000, 10% Debentures of Rs. 100 each at a discount of 10%.

The debentures are said to have been sold at a discount because the business offers debentures at a premium that is lee than their face or nominal value. A capital loss is a discount or loss on debenture issuance. It may be charged down by debiting the benefit or loss statement or the securities premium balance account.
Journal Entries

Q2.
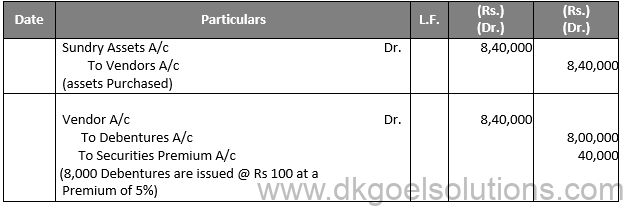
Sol.2 A business buys some properties from the seller and instead of paying the seller in cash, the company may opt to offer debentures to the seller in lieu of purchases. Such a dilemma of debentures to manufacturers for consideration other than cash is known as the question of debentures for debentures.
Assets A/c Dr.
To Vendors’ A/c
(assets purchases)
Vendor’s A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(issue of debenture to vendor at par)
Vendor’s A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
To Securities Premium Reserve A/c
(issue of debenture to vendor at premium)
Vendor’s A/c Dr.
Discount of issue of debenture A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(issue of debenture to vendor at discount)
Q3.
Sol.3 In addition to the principal protection, anytime a corporation takes a loan from a bank or any other party, the company will have to issue debentures as a subsidiary or secondary security. In addition to main security, collateral security means secondary security. In the company’s account books, there are two ways of dealing with such debentures:—
- First Method:- No entry in the company’s accounts must be transferred in this manner, since the debentures are not officially released, but rather provided as collateral protection. As for the taking of a loan entry as passed only:—
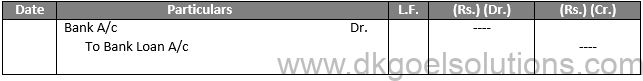
2 Second Method:- In this process, with the entry for taking the loan, the entry for issuing debentures as collateral protection is also registered.
Journal Entries
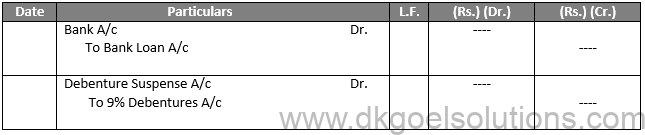
Q4.
Sol.4
(a) When the interest is pending:-
If a corporation pays half-yearly interest on debentures on 30 June and 31 December, while preparing the balance sheet on 31 March 2019, if the interest stays outstanding for the term ended 31 December 2018, it will be referred to as ‘interest accumulated and awaiting.’
(b) When the interest is paid:-
If a corporation pays half-yearly interest on debentures on 30 June and 31 December, when preparing the balance sheet on 31 March 2018, the interest will be considered ‘Interest accumulated but not outstanding’ for the period from 1 January 2018 to 31 March 2018.
i) When interest is pending:
Journal Entries

ii) When interest is paid to the debenture holders:
Journal Entries
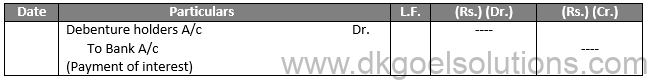
ii) On transfer of debenture interest to statement of profit and loss:
Journal Entries

Q5.
Sol.5
The debentures are sold with the express condition that, at the point of their maturity, the corporation will pay a premium. While this premium will be charged at the time of eventual repayment, the Company reports those losses at the time of issue by debiting an account called “Loss on issuance of debentures A/c” since it is a known loss.
Example:- If a debenture of Rs. 100 is issued at Rs. 100 and is redeemable at Rs. 105, the following entries will be passed:
Entries For Issue:
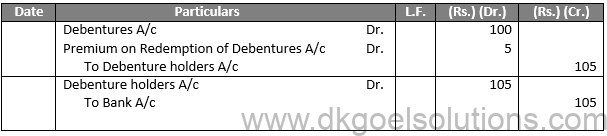
Q5.
Sol.5 The debentures are sold with the express condition that, at the point of their maturity, the corporation will pay a premium. While this premium will be charged at the time of eventual repayment, the Company reports those losses at the time of issue by debiting an account called “Loss on issuance of debentures A/c” since it is a known loss.
Example:- If a debenture of Rs. 100 is issued at Rs. 100 and is redeemable at Rs. 105, the following entries will be passed:
Entries For Issue:
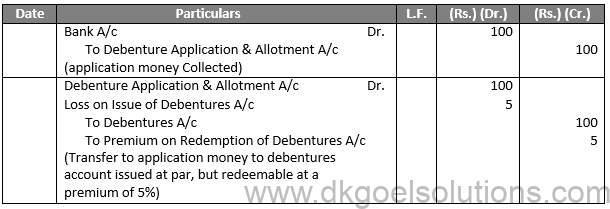
Entries For Redemption:
Journal Entries
Q6.
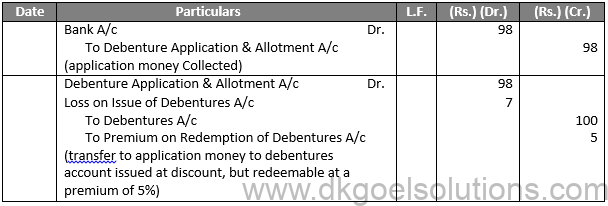
Sol.6
If a debenture of Rs. 100 is issued at Rs. 98 and is redeemable at Rs. 105 the following entries will be passed:-
Entries For Issue:
Journal Entries
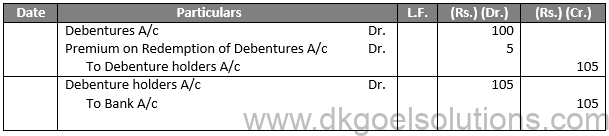
Entries For Redemption:
Journal Entries
Q7.
Sol.7
Oversubscription of debentures suggests that the firm has collected more debenture applications than it has published. In such a case, any of the following three options or combinations can be assigned by the company:
Rejecting excess queries, First Option.
Second Option, distribution partial or pro-rata.
A mixture of the above two options is the third alternative.
Q8.
Sol.8
Journal Entries
Q9.
Sol.9
Journal Entries

Q10.
Sol.10
Journal Entries
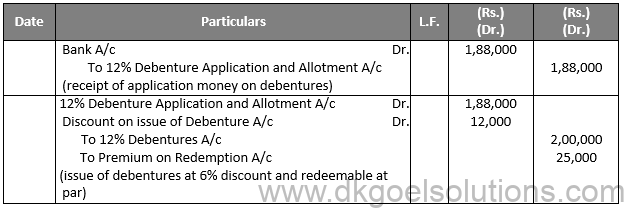
Q11.
Sol.11
In the Books of K K Ltd. Journal Entries

Numerical Questions:-
Q1.
Sol.1
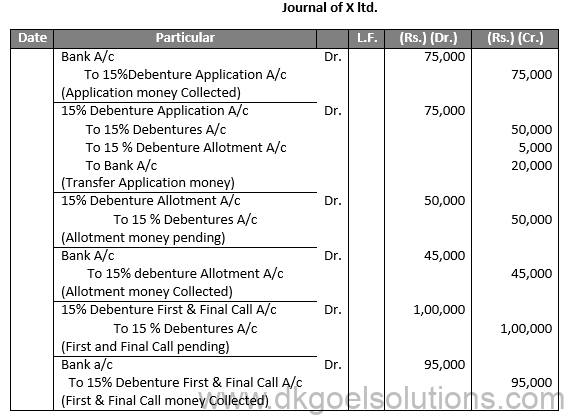
Q2.
Sol.2
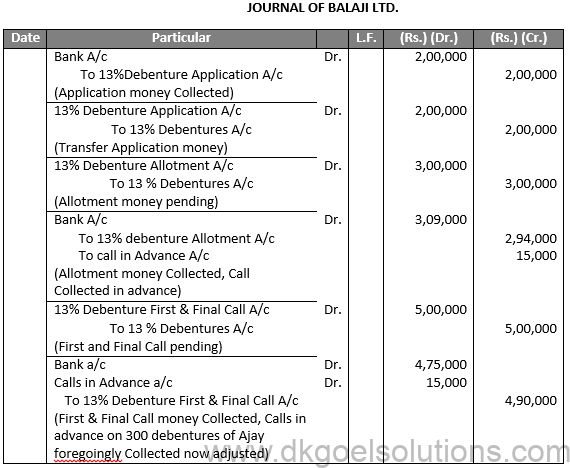
Q3.
Sol.3
JOURNAL OF KAMAL LTD.
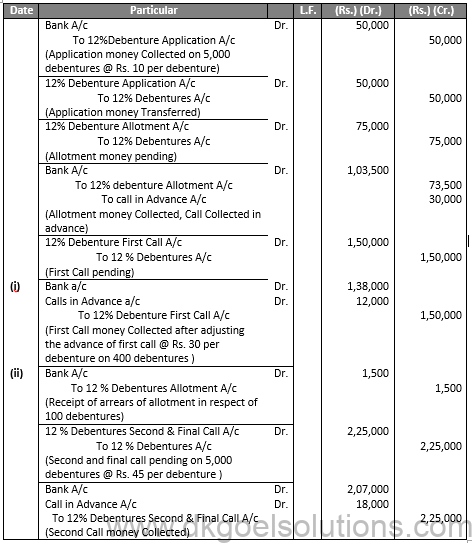
Q4.
Sol.4
JOURNAL OF SUNFLOWER LTD
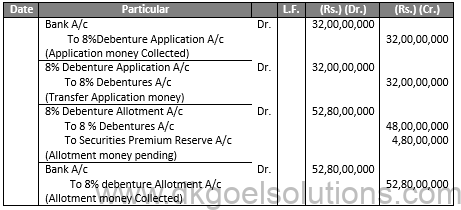
Q5.
Sol.5
JOURNAL OF BALAJI LTD.
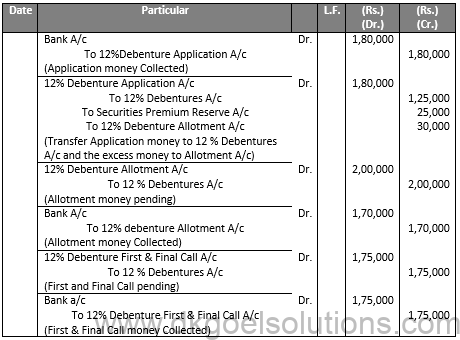
Q6.
Sol.6
JOURNAL OF Nav Lakshmi LTD.
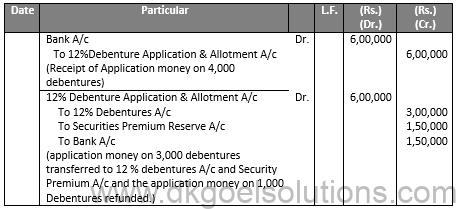
Q7.
Sol.7
JOURNAL OF R LTD.

BALANCE SHEET As at ………. (at the end of first year)
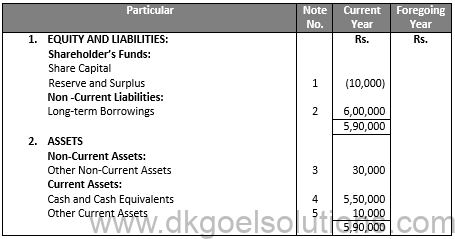
Notes to Accounts:

Q8.
Sol.8
JOURNAL OF Nav Lakshmi LTD.
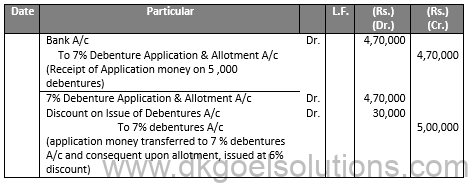
Q9.
Sol.9
JOURNAL OF X LTD.

Working note:
(1) 11,000 debentures of Rs. 100 each at 5% discount
10,45,000/95 = 11,000 Debentures.
(2) 9,500 debentures of Rs. 100 each at 10% premium,
10,45,000/110 = 9,500 Debentures
Q10.
Sol.10
JOURNAL OF GOLDEN LTD.
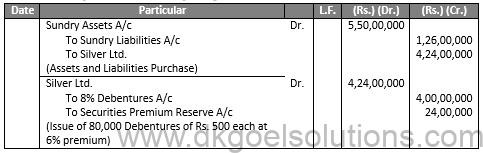
Q11.
Sol.11
JOURNAL OF GOLDEN LTD.

Q12.
Sol.12
JOURNAL OF GOLDEN LTD.
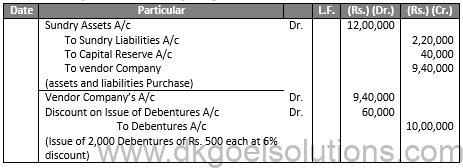
Q13.
Sol.13
JOURNAL OF GOLDEN LTD.
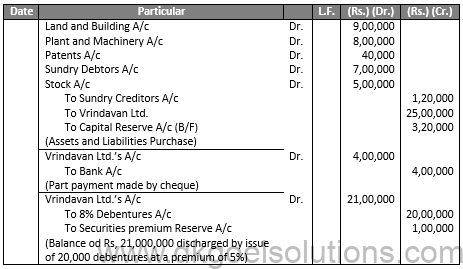
Q14.
Sol.14
JOURNAL OF Y LTD.

Q15.
Sol.15
JOURNAL OF Y LTD.
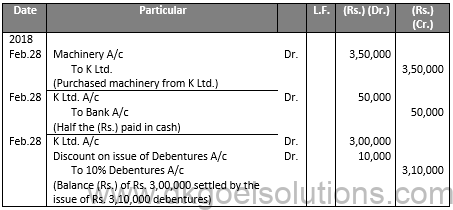
Q16.
Sol.16
JOURNAL OF X LTD
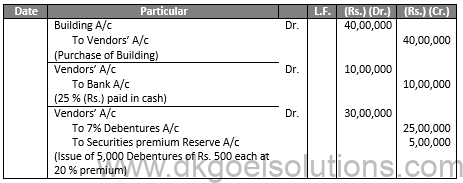
Q17.
Sol.17
JOURNAL OF X LTD.

Q18.
Sol.18
JOURNAL OF STAR TEXTILES LTD.
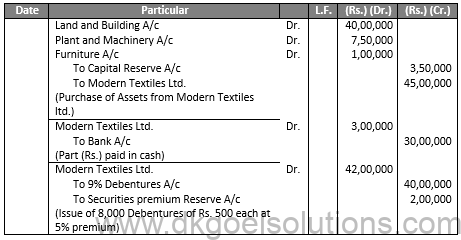
Q19.
Sol.19
JOURNAL OF X LTD
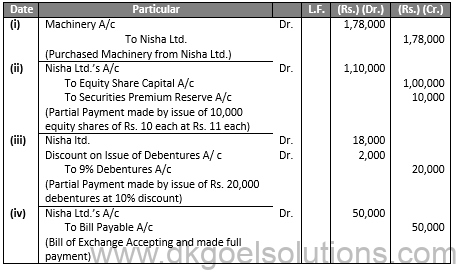
Working Note:-
Purchase consideration: Rs.
(i) 10,000 equity Shares @Rs. 11 each 1,10,000
(ii) 200 Debentures @Rs. 90 each 18,000
(iii) Bill of Exchange 50,000
1,78,000
Q20.
Sol.20
Case (i) When Debenture are not to recorded as collateral security.
JOURNAL OF X LTD.
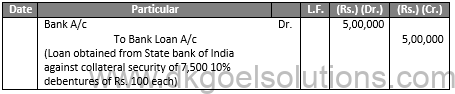
JOURNAL OF X LTD.

Q21.
Sol.21
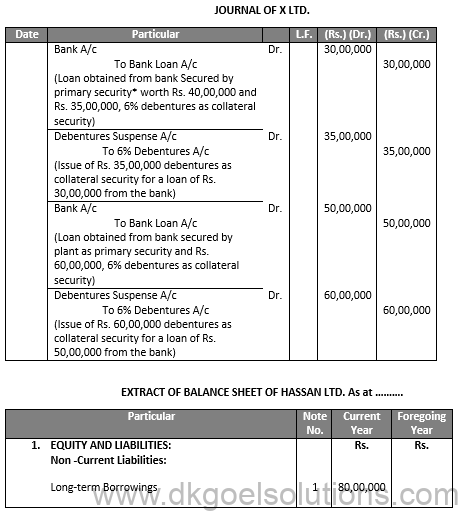
Notes to Accounts:

Q22.
Sol.22
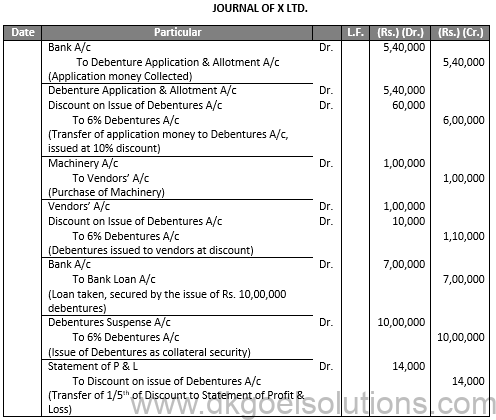
BALANCE SHEET
As at ……….
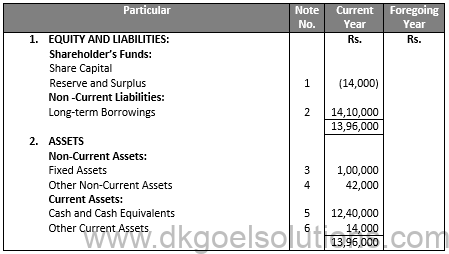
Notes to Accounts:
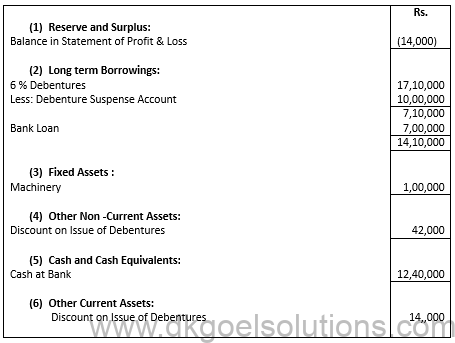
Q23.
Sol.23
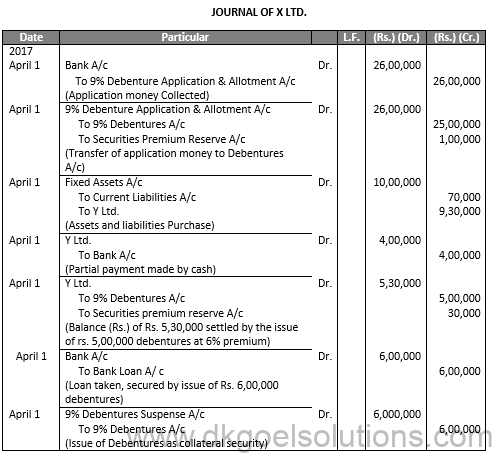
BALANCE SHEET
As at ……….
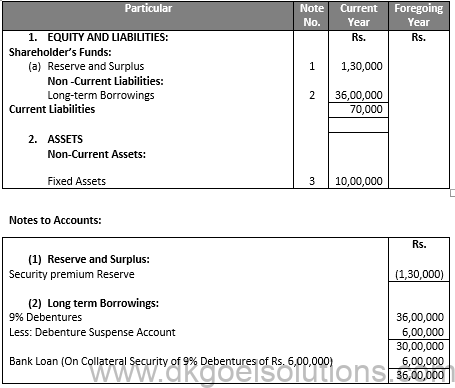
Q24.
Sol.24
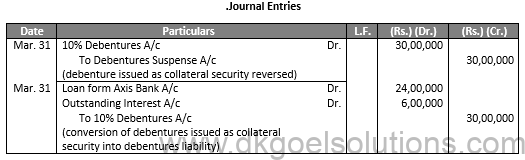
Q25.
Sol.25
Journal Entries
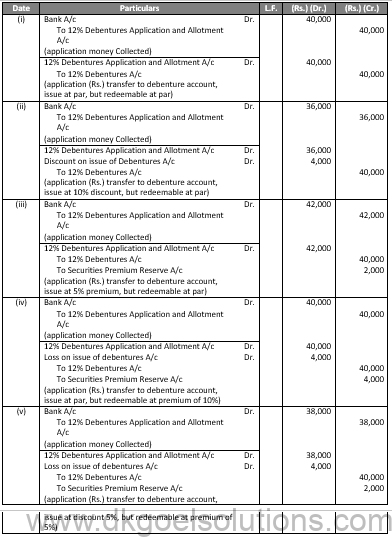
Q26.
Sol.26
(a)

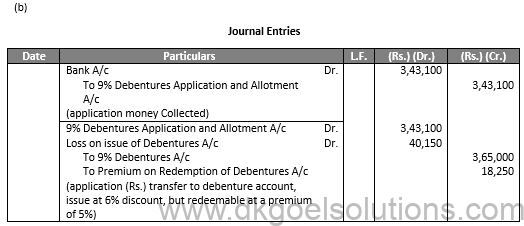
Working Note:-
Calculation of Loss on Issue of Debentures:-
Loss on Issue of Debentures (Rs.)
6% discount on Issue of Debentures (365 × Rs. 60) = Rs. 21,900
5% Premium on Redemption (365 × Rs. 50) = Rs. 18,250
Rs. 40,150
Q27.
Sol.27

Q28.
Sol.28
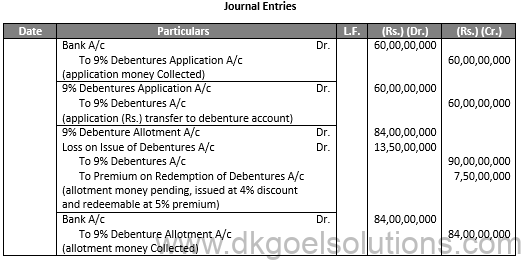
Q29.
Sol.29

Q30.
Sol.30
In the books of K.K. Ltd.
Journal Entries
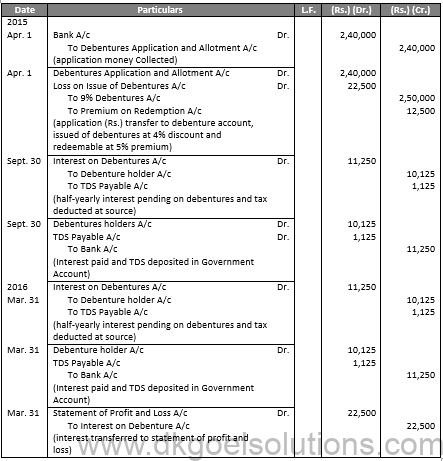
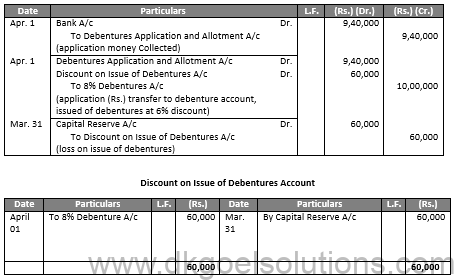
Q31.
Sol.31
Q32.
Sol.32
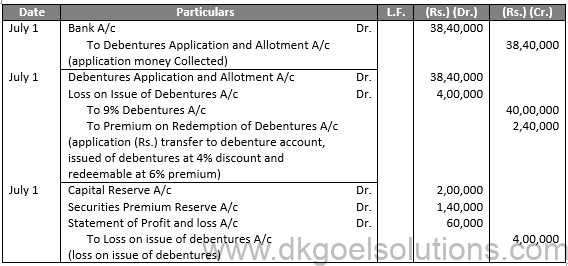
Q33.
Sol.33
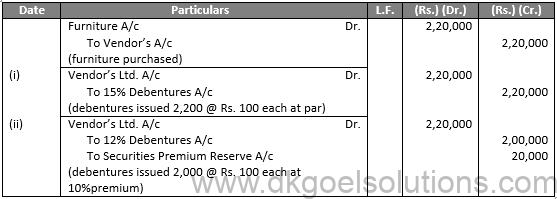
Working Note:-
Number of Debenture issued = (Purchases Consideration)/(Price of a Shares)
Number of Debenture issued = 2,20,000/110
Number of Debenture issued = 2,000
Q34.
Sol.34

Working Note:-
Number of Debenture issued = (Purchases Consideration)/(Price of a Shares)
Number of Debenture issued = 1,35,000/90
Number of Debenture issued = 1,500
Q35.
Sol.35
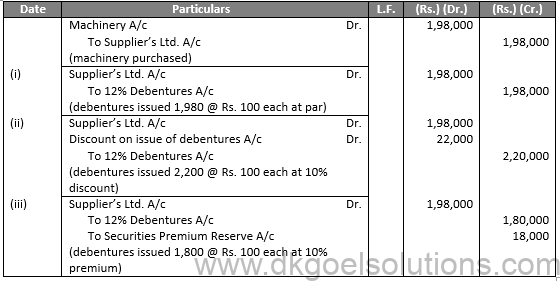
Working Note:-
Number of Debenture issued = (Purchases Consideration)/(Price of a Shares)
Number of Debenture issued = 1,98,000/1100 = 1,800
Q36.
Sol.36
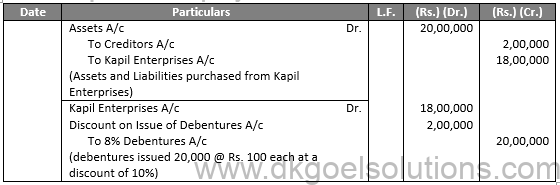
Working Note:-
Number of Debenture issued = (Purchases Consideration)/(Price of a Shares)
Number of Debenture issued = 18,00,000/90 = 20,000
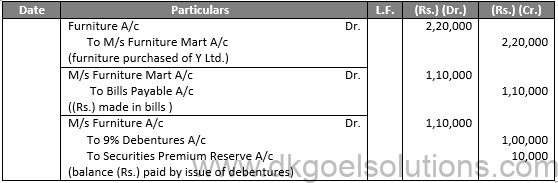
Q37.
Sol.37
Q38.
Sol.38

Q39.
Sol.39

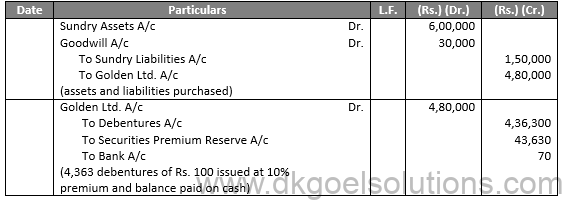
Q40.
Sol.40
Journal Entries
Q41.
Sol.41
In the Books of X Ltd.
Journal Entries
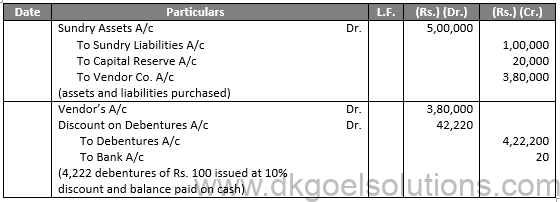
Q42.
Sol.42
In the Books of Oberoi Ltd.
Cash Book

Q43.
Sol.43

Q44.
Sol.44
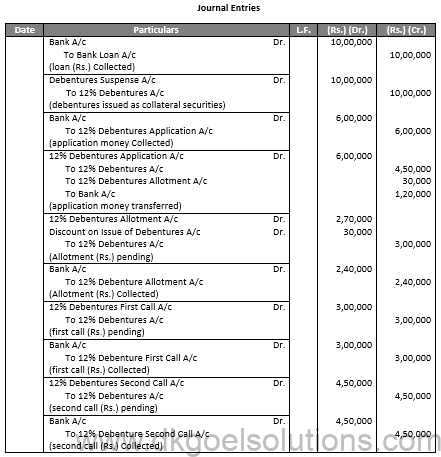

Q45.
Sol.45
(i)

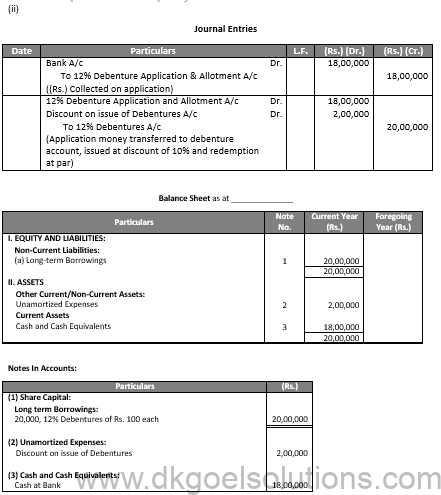
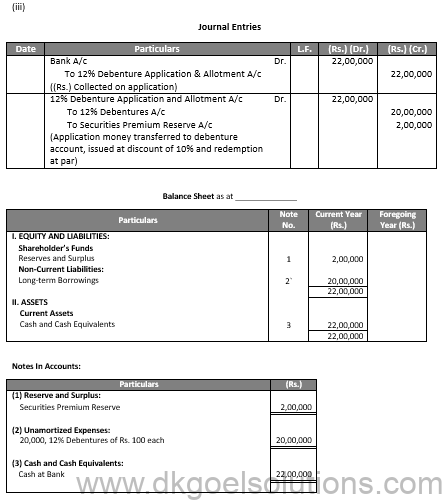

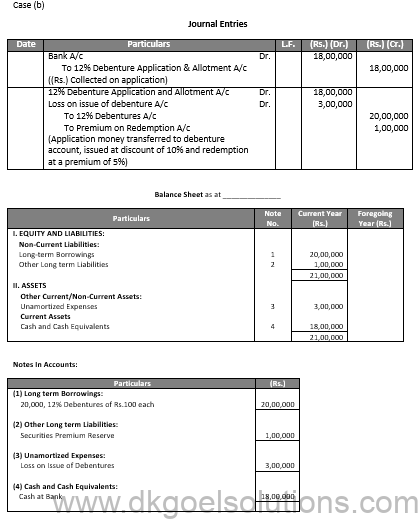
Q46.
Sol.46

Q47.
Sol.47
Journal Entries

Q48.
Sol.48
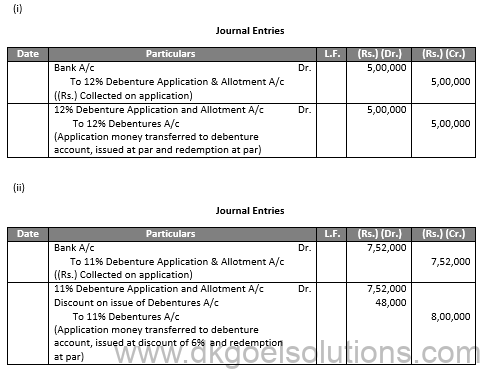
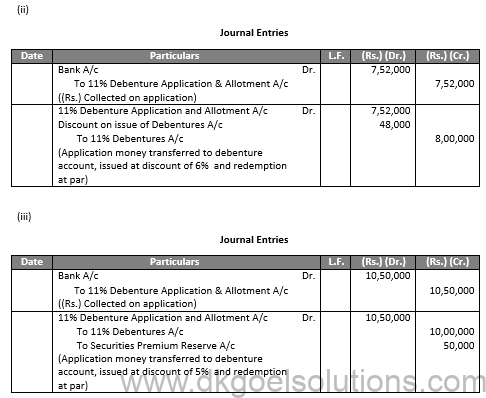
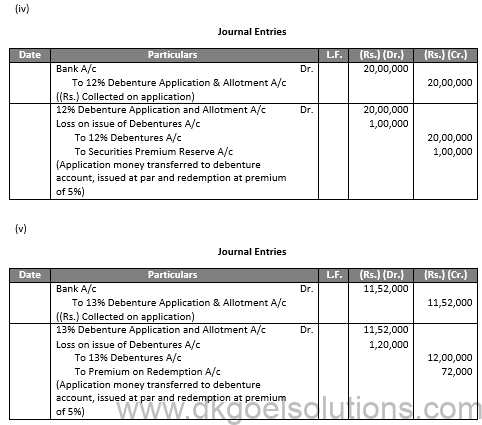
Q49.
Sol.49

Q50.
Sol.50
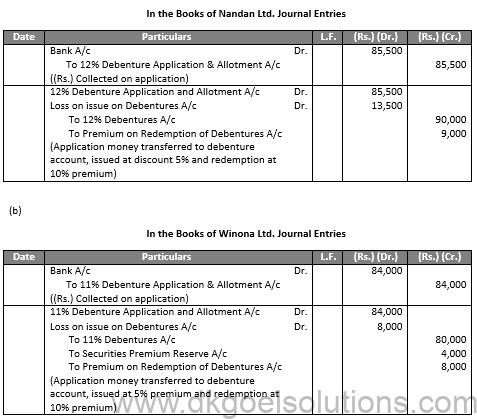
Q51.
Sol.51
Journal Entries

Q52.
Sol.52
(i)
In the Books of A Ltd. Journal Entries
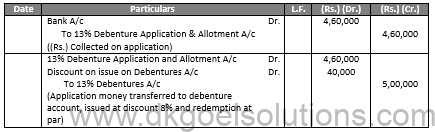
Balance Sheet as at A Ltd.
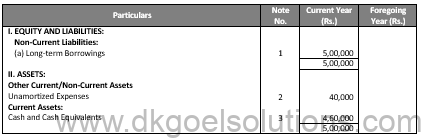
Notes In Accounts:

(ii)
In the Books of A Ltd. Journal Entries
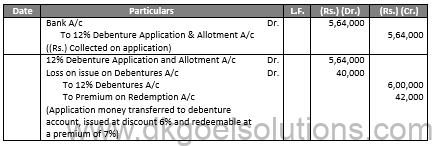
Balance Sheet as at B Ltd.
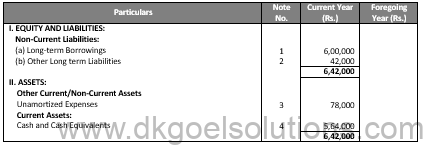
Notes In Accounts:

(iii)
In the Books of C Ltd. Journal Entries
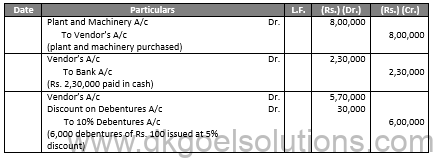
Balance Sheet as at C Ltd.
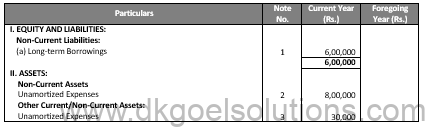
Notes In Accounts:
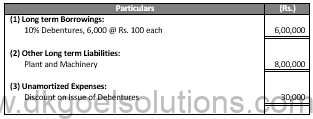
(iv)
In the Books of D Ltd. Journal Entries

Balance Sheet as at D Ltd.

Notes In Accounts:

In the Books of E Ltd. Journal Entries
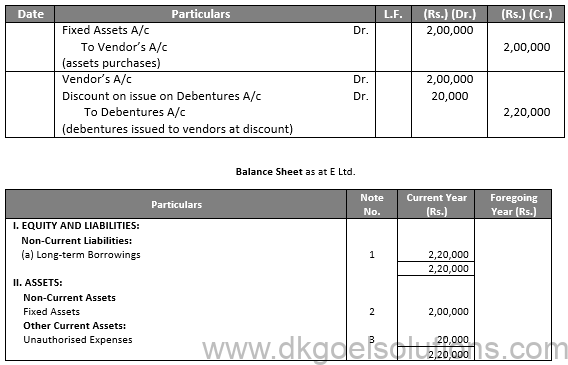
Notes In Accounts:

Q53.
Sol.53
In the Books of Z Ltd. Journal Entries
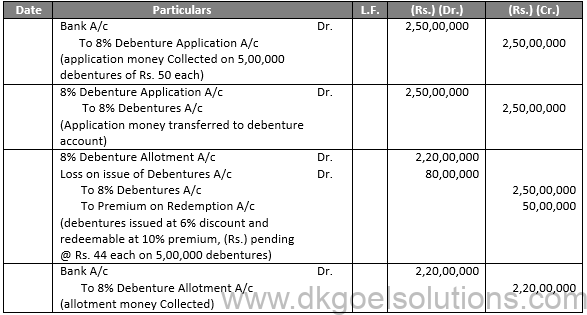

A company purchases their own debentures from the market with the sole motive of either for investments or cancellation. As per the Companies Act, a firm is permitted to purchase its own debenture from the open market only if the firm is authorized by its Articles of Association. This process is termed as the purchase of own debentures.
Debentures can be picked up by a company from the open market for the purpose of cancellation. When its debentures are purchased by the company, its “Own Debenture Account” will get debited for the cash paid. When the companies do not require a specific debenture, they can easily cancel the purchased debenture after some legal procedures.
Convertible debentures can be defined as debentures in which the firm needs an interest-bearing loan. Once the pre-defined time ends, it can be turned into equity shares. Therefore, convertible debentures are those debentures that avail their holders with the option to convert them into equity shares or other securities after a specified time.
Here are the main points of the SEBI Guidelines for the Debenture Redemption Reserve –
● All companies which issue debentures with a maturity of 18 months or more must mandatorily create DRR.
● DRR creation is only applicable to non-convertible debentures.
● After the 10% redemption of the debenture, the company can withdraw freely.
● Before starting the redemption of the debenture, an amount of 50% of the debenture must be transferred to DRR.
When a company owes a loan from any financial institution, they present debentures as collateral security. However, the lender to whom the debentures are offered and not obliged to pay the interest for these debentures.
Debentures can be classified primarily into two types based on security issues; they are –
Secured Debentures
Unsecured Debentures
Also refer to TS Grewal Solutions for Class 12
