DK Goel Solutions Chapter 9 Company Accounts Redemption of Debentures
Read below DK Goel Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 9 Company Accounts Redemption of Debentures. These solutions have been designed based on the latest Class 12 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
After a certain period of time, there is a requirement that the company should redeem the debentures and pay back the money to the investors. in such a situation whenever the debentures are redeemed there is a requirement to accordingly pass accounting entries in the books so that the current financial position can be displayed.
In this chapter and Redemption of Debentures DK Goel solutions, the students will understand the basics of redemption of debentures as well as the kind of accounting entry which has to be passed when the debentures are redeemed.
The chapter contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful for Class 12 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career. These dk goel class 12 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 12 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Company Accounts Redemption of Debentures DK Goel Class 12 Accountancy Solutions
Short Answer Questions
Q1.
Sol. 1
1.) Use Rs. 10,00,000 to write off the Commission on Underwriting.
2.) Use Balance Rs. 12,00,000 to pay down 9% Redemption Premium Debentures.
Numerical Questions
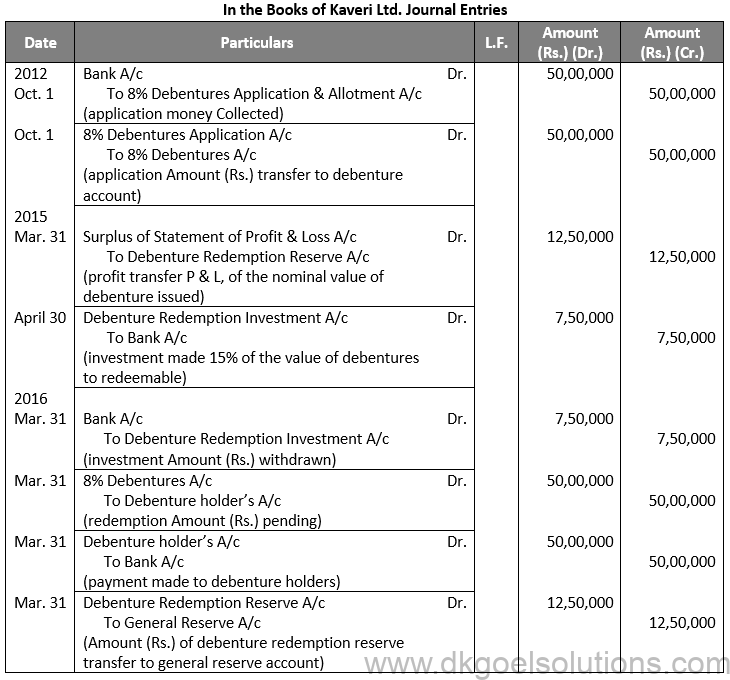
Q1
Sol. 1
Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
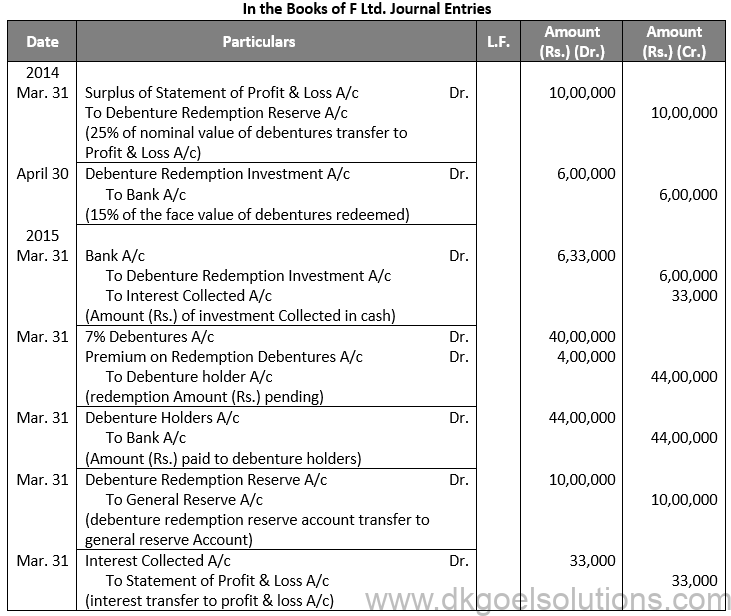
Q2.
Sol. 2
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
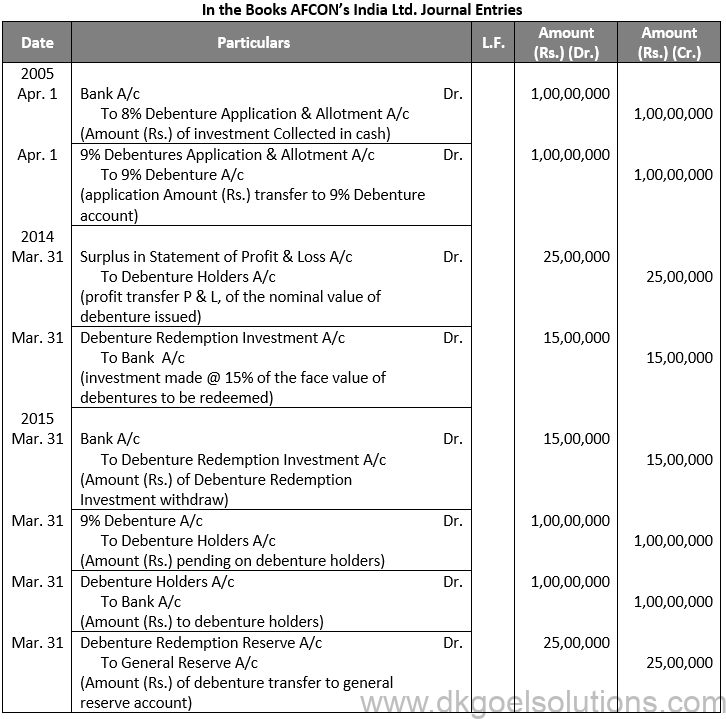
Q3.
Sol. 3

Point for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q4.
Sol. 4
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q5.
The company met the requirements of Companies Act, 2013 regarding Debenture Redemption Reserve & Debenture Redemption investments & redeemed the debentures.
Ignoring interest on investments, pass necessary Journal entries for the above transactions in the books of company.
Sol. 5

Working Note:-
Computation of Transfer Amount:-
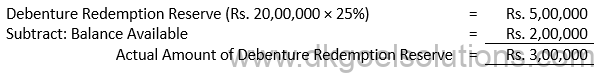
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q6.
Sol. 6
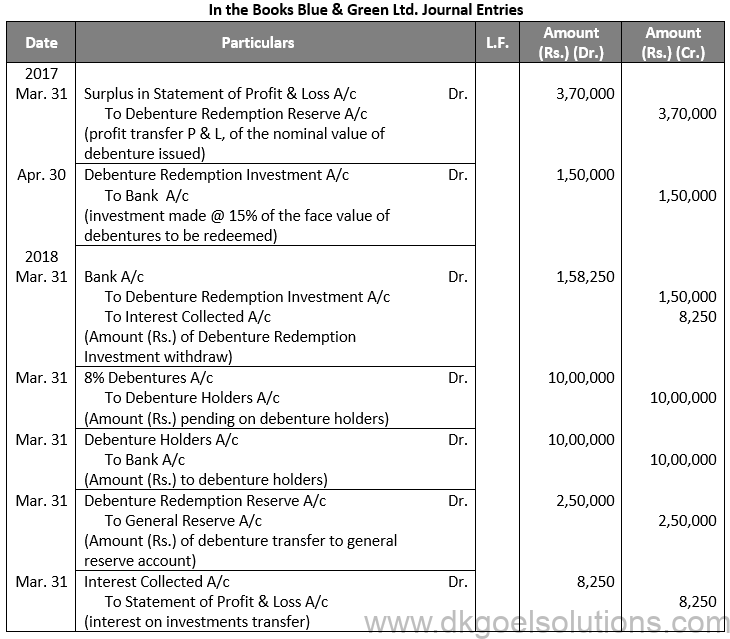
Working Note:-
Computation of Transfer Amount:-
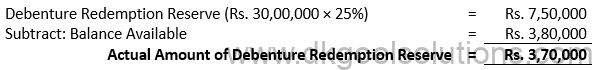
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation. It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q7.
Sol. 7

Working Note:-
Computation of Transfer Amount (Rs.):-

Point for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q8.
Sol. 8
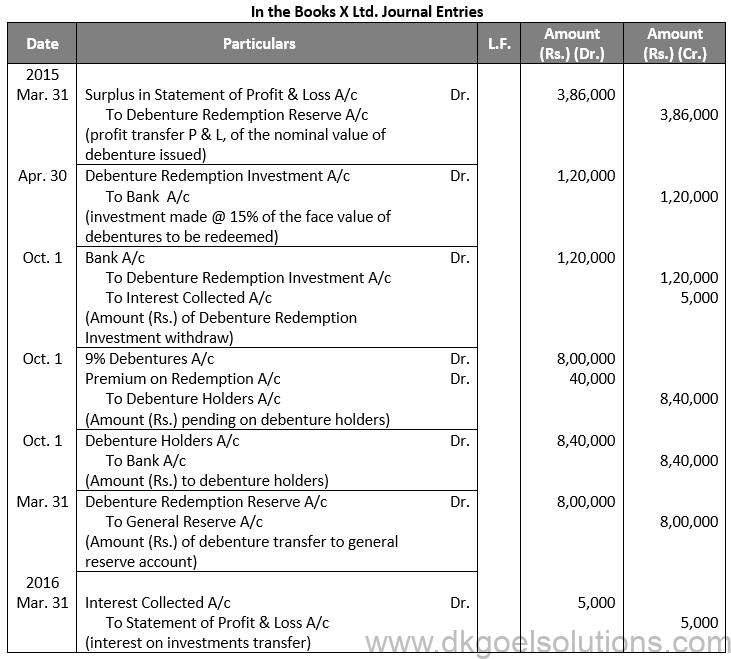
Working Note:-
Computation of Transfer Amount (Rs.):-
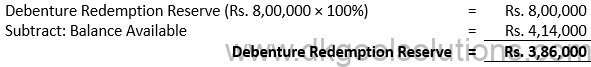
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q9.
Sol. 9
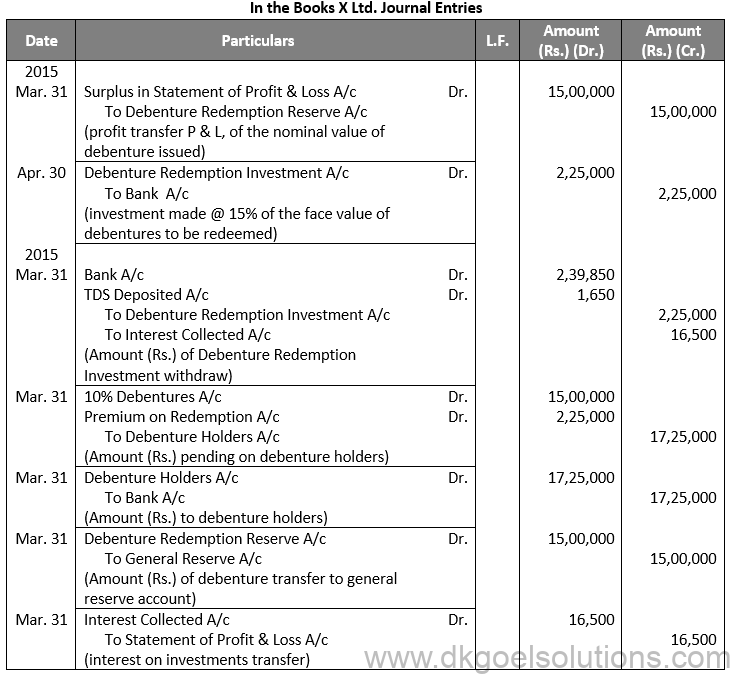
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q10.
Sol. 10
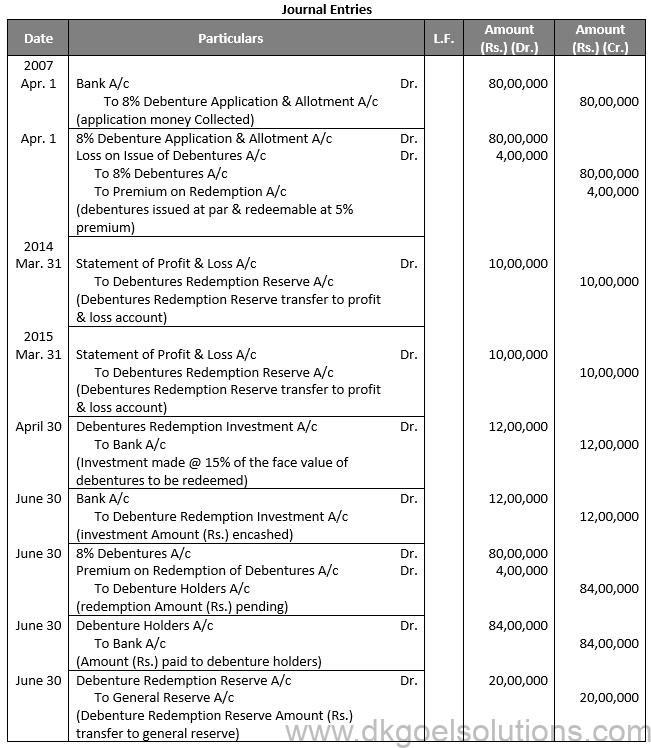
Point for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q11.
Sol. 11
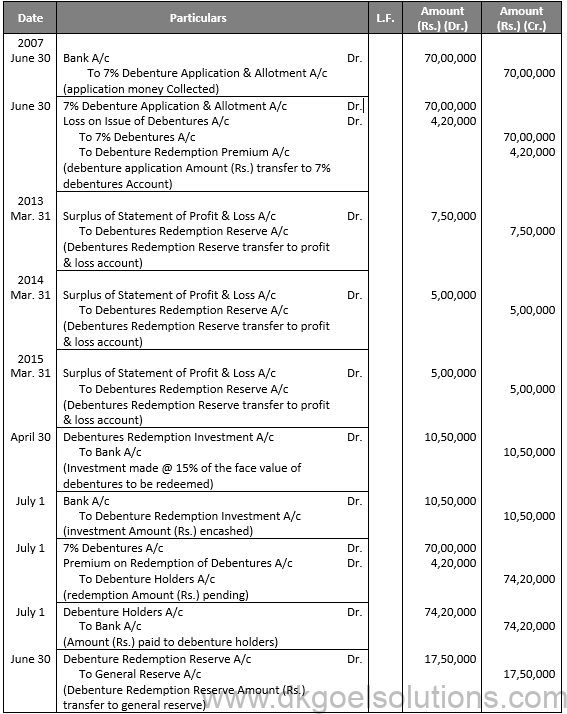
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q12.
Sol. 12

Working Note:-
Computation of Number of Debentures issued

Hence, the 6,000 Debentures @ Rs. 100 each.
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q13.
Sol. 13
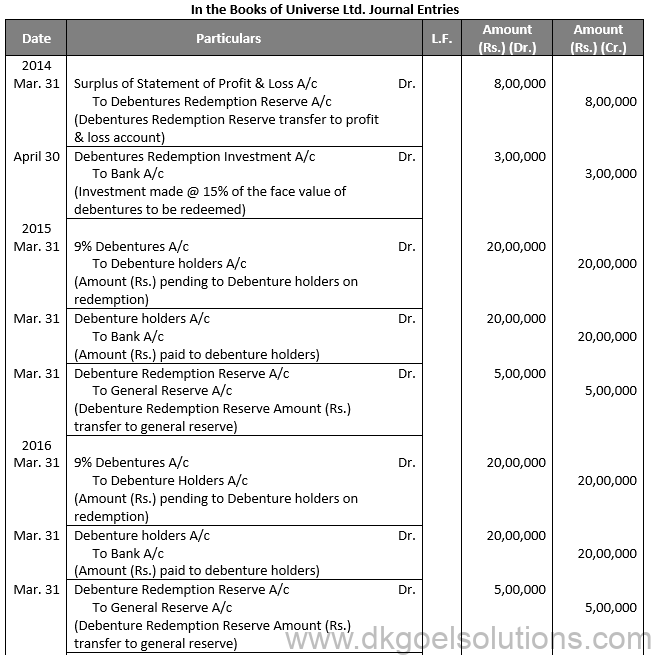
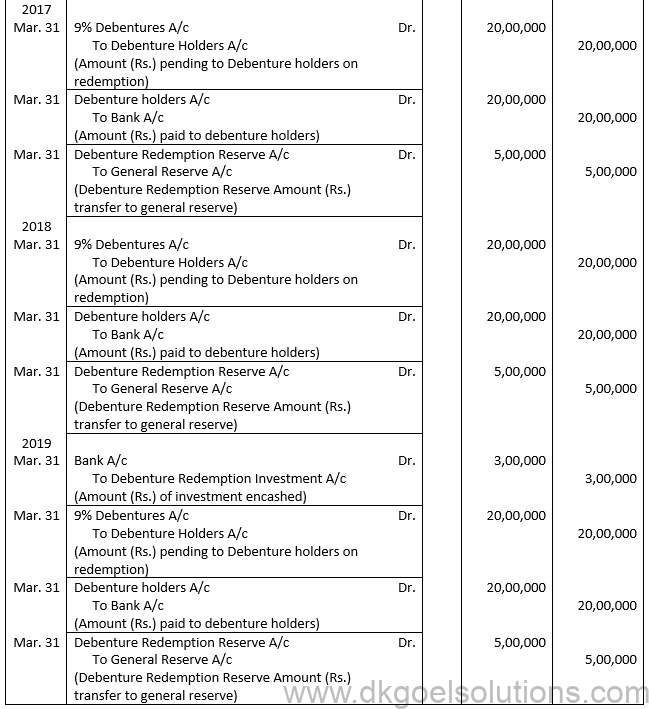
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q14.
Sol. 14
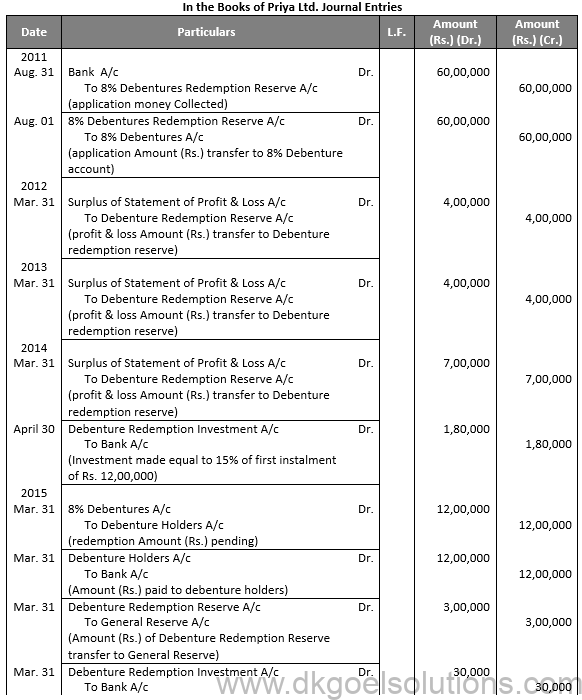
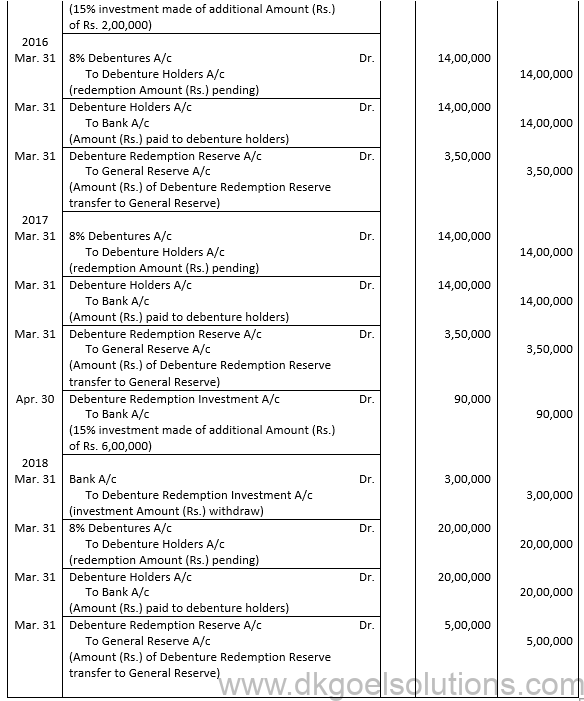
Working Note:-
Computation of Debenture Redemption Reserve Account:-
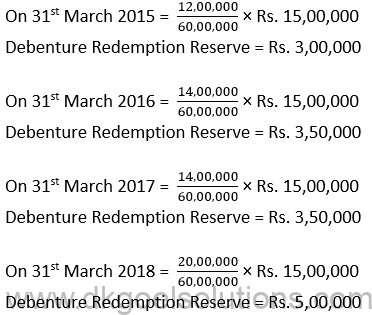
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q15.
Sol. 15
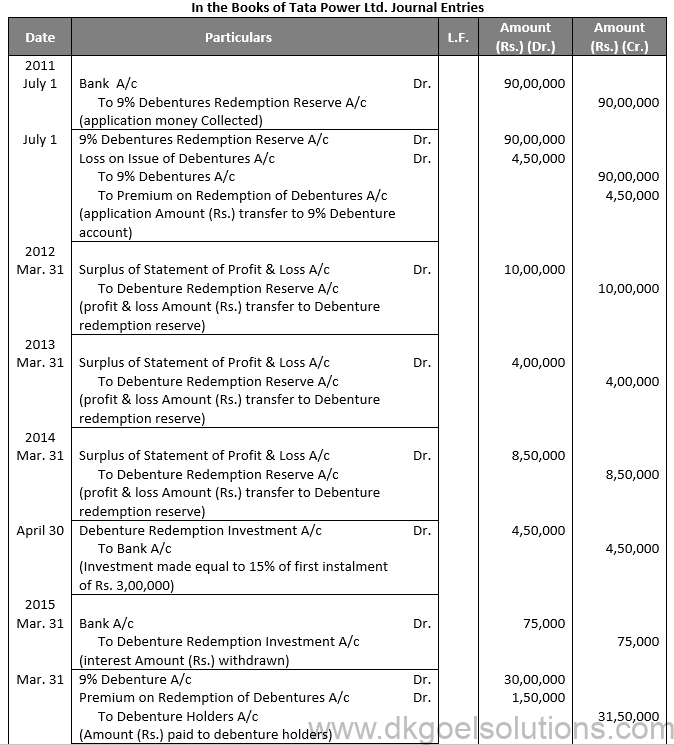

Working Note:-
Computation of Debenture Redemption Reserve Account:-
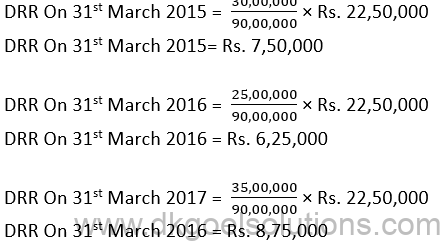
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q16.
Sol. 16
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q17.
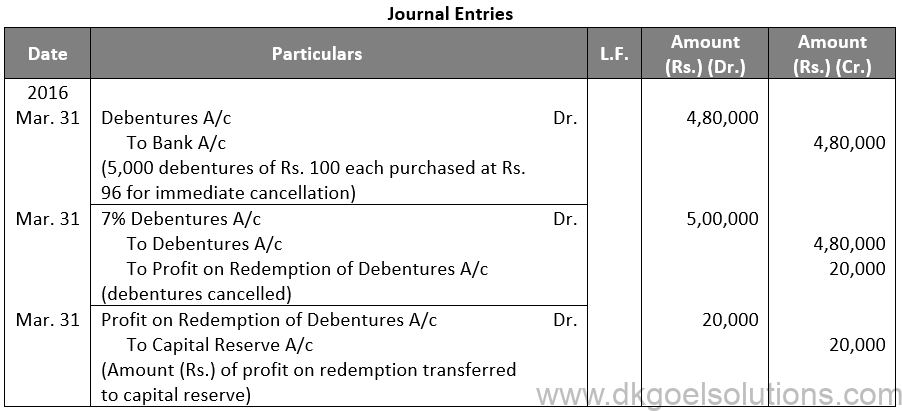
Sol. 17
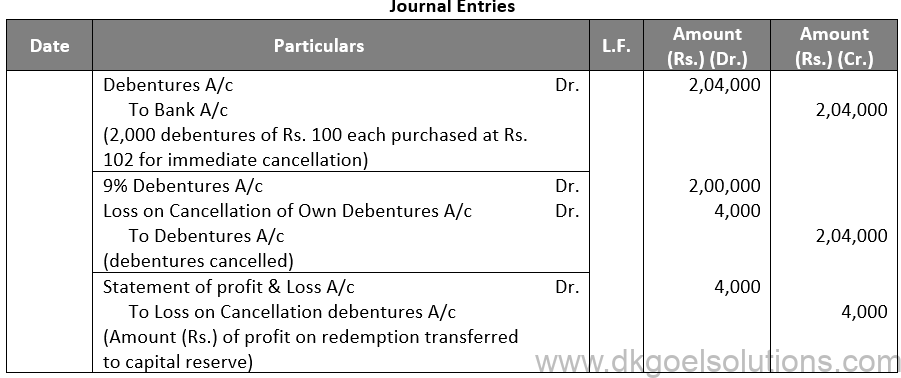
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q18.
Sol. 18 (i)
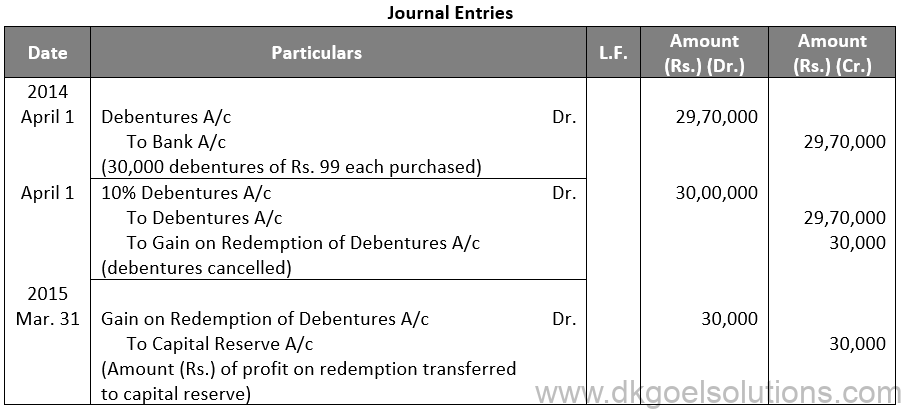
(ii)
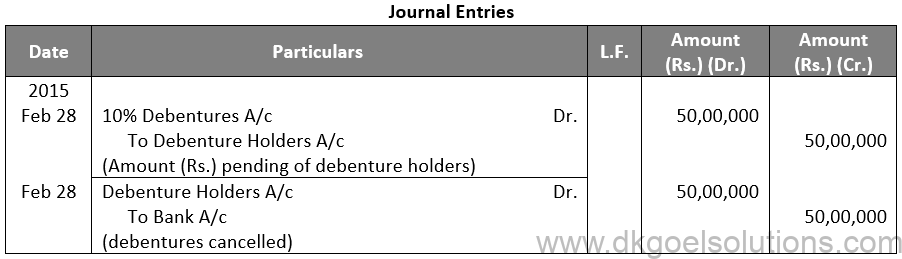
(iii)
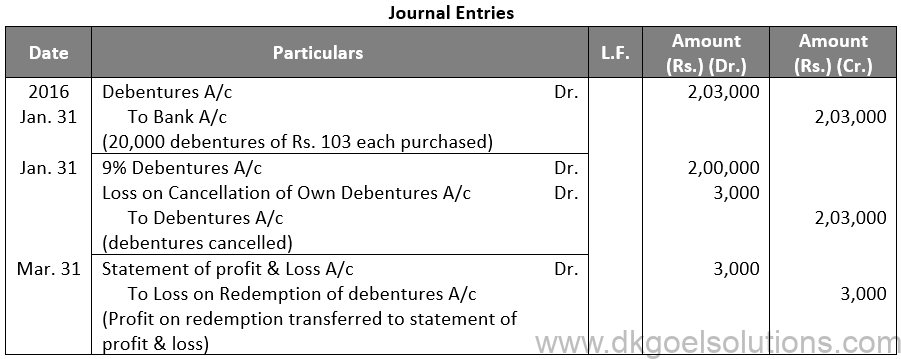
Points for Students:- When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q19.
Sol. 19

Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q20.
Sol. 20
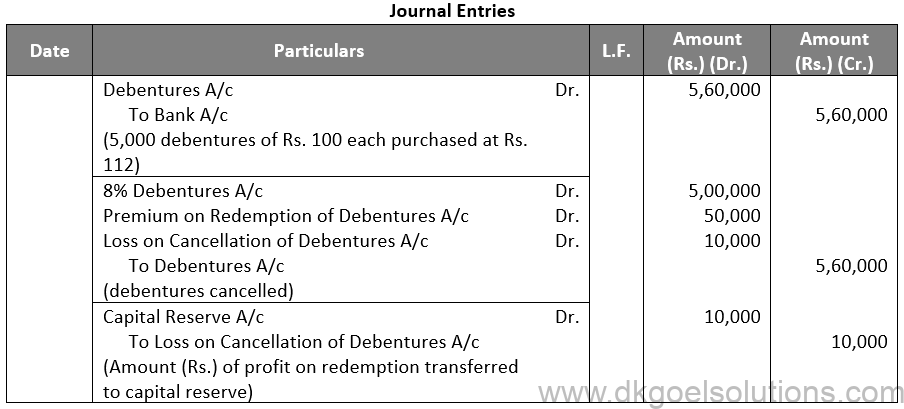
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation. It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q21.
Sol. 21
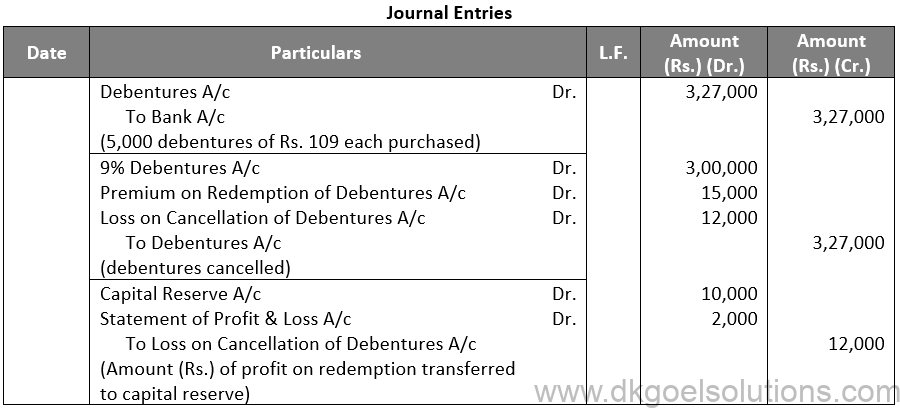
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q22.
Sol. 22

Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q23.
Sol. 23

Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q24.
Sol. 24
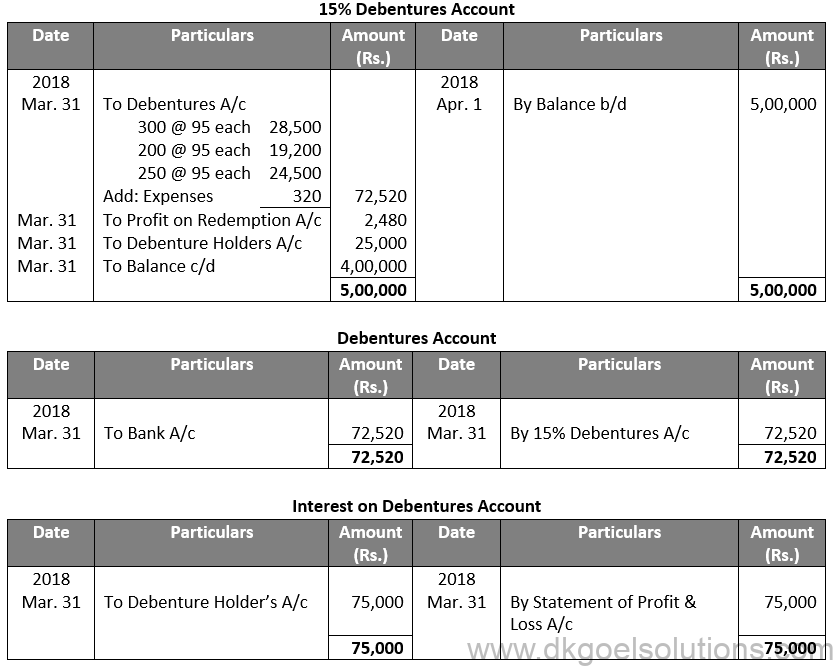
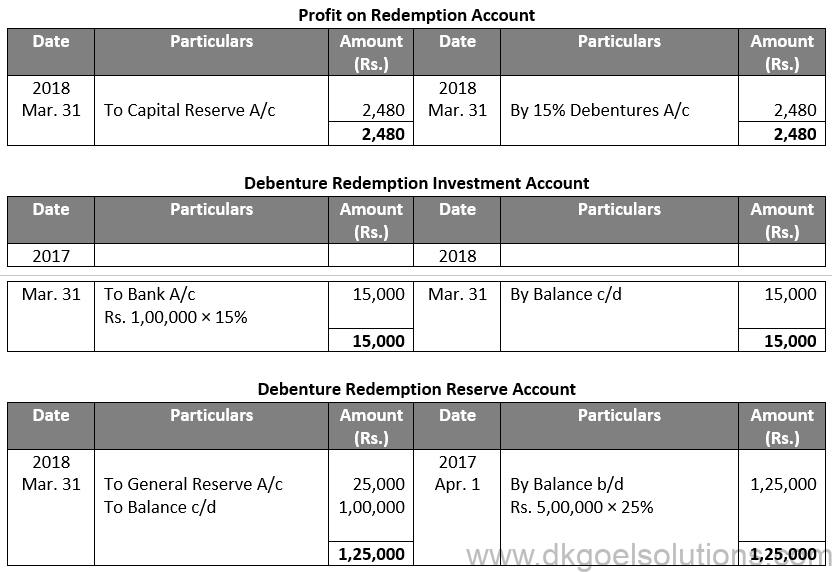
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q25.
Sol. 25 On 31st March, 2018 the company purchased for cancellation debentures of the face value of Rs. 3,00,000 at Rs. 90 per debenture & of Rs. 2,00,000 at Rs. 95 per debenture. Journalise the above transactions & show how the profit on redemption would be treated.Sol. 25

Working Note:-
(i) Computation of purchase of debentures:
Purchased Debentures = 3,000 debentures @ Rs. 90 + 2,000 debentures @ Rs. 95
Purchased Debentures = 2,70,000 + 1,90,000
Purchased Debentures = 4,60,000
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q26.
Sol. 26 (i) If debentures are purchased for immediate cancellation:-
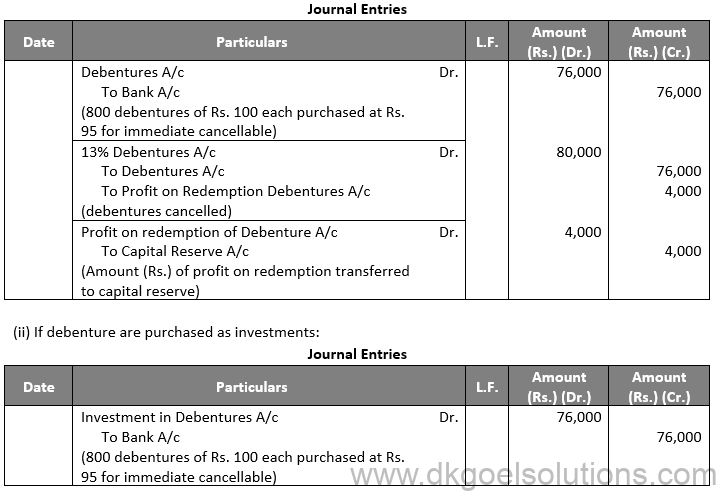
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q27.
Sol. 27

Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital. (3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits
Q28.
Sol. 28
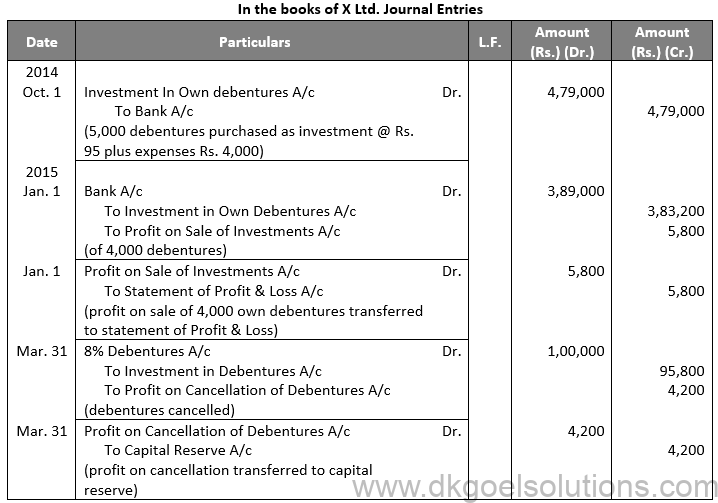
Working Note:-

Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q29.
Sol. 29
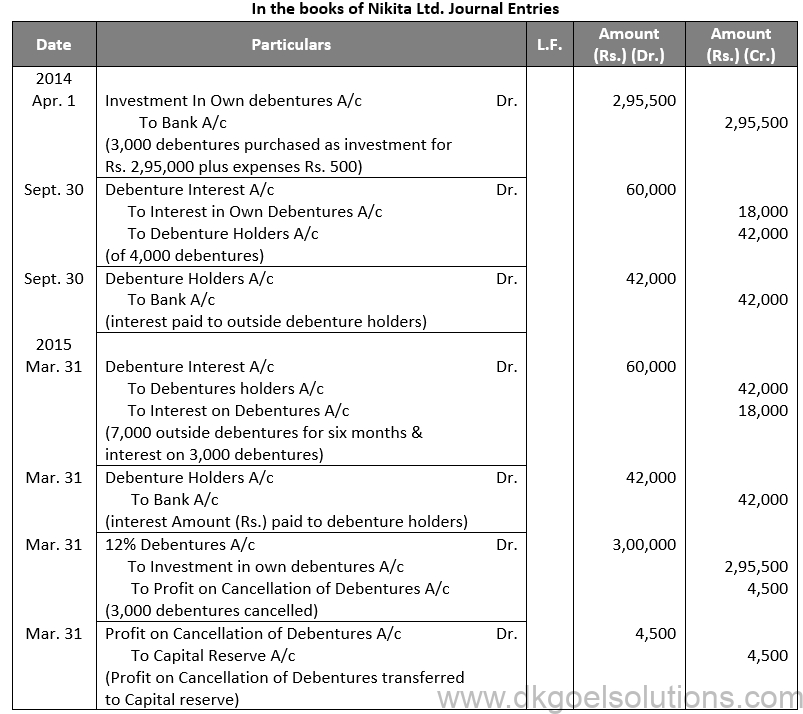
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q30.
Sol. 30
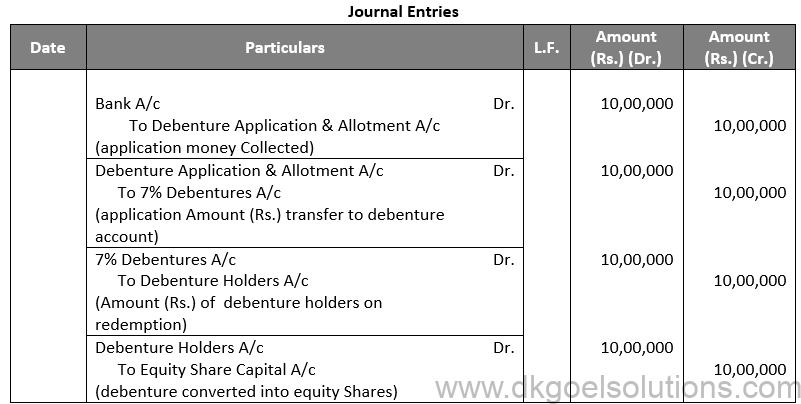
Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q31. (A).
Sol. 31 (A)
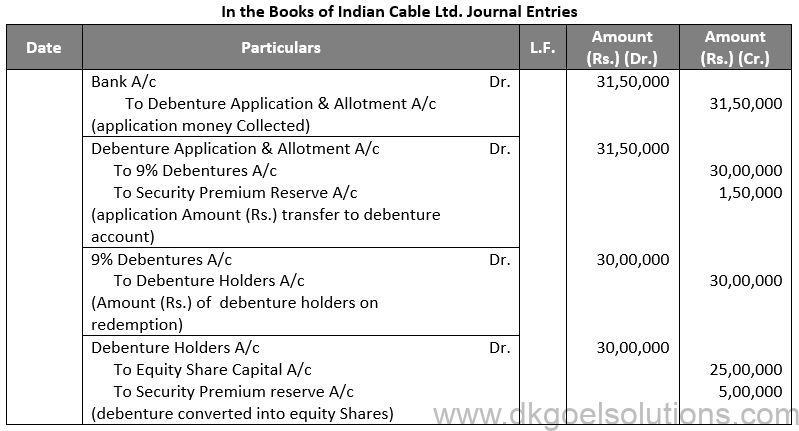
Working Note:-
(i) Equity Shares Converted into Debentures:-
Debentures = Rs. 3,00,000
Equity Share = Rs. 20 + Rs. 4
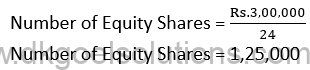
Equity Share Capital = 1,25,000 × Rs. 20
Equity Share Capital = Rs. 25,00,000
Security Premium = 1,25,000 × Rs. 4 Security Premium = Rs. 5,00,000
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q32. (B)
Sol. 32 (B)
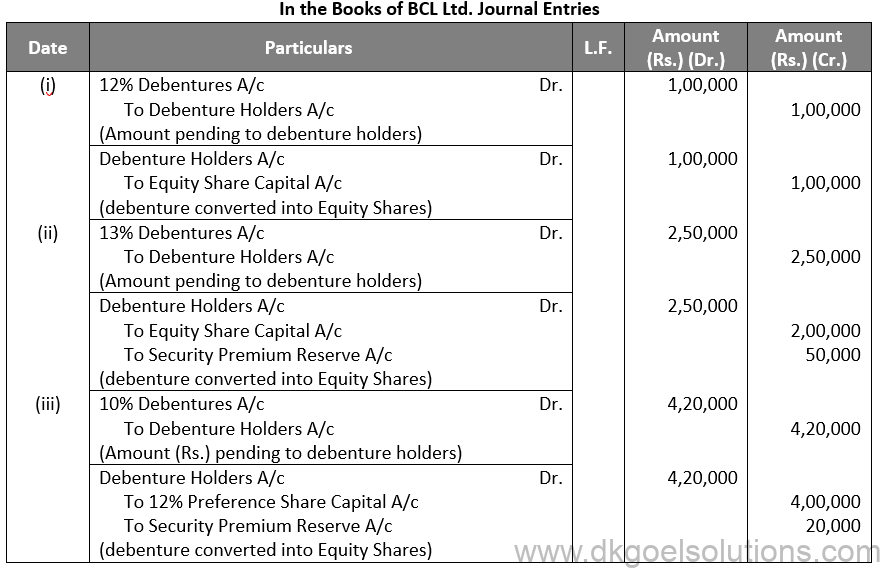
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debenture into Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Debentures = Rs. 2,50,000
Equity Shares = Rs. 10 + Rs. 12.5
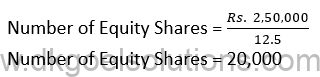
Debentures into Preference Shares:-
Debentures = Rs. 4,20,000
Equity Shares = Rs. 100 + Rs. 5
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q33.
Sol. 33

Q34.
Sol. 34
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q35.
Sol. 35

Working Note:-
(i) Conversion of Debentures into Shares:-
Debentures into Preference Shares:
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 6,30,000
Rate of Preference Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 5
Number of Preference Shares = Rs. 6,30,000 / 105
Number of Preference Shares = 6,000
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
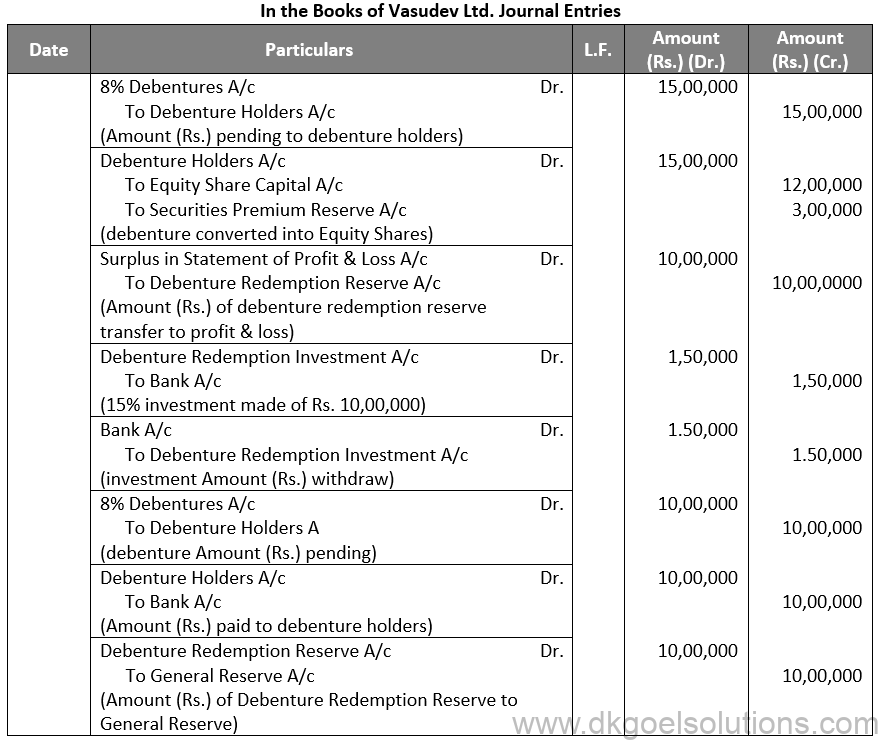
Q36.
Sol. 36
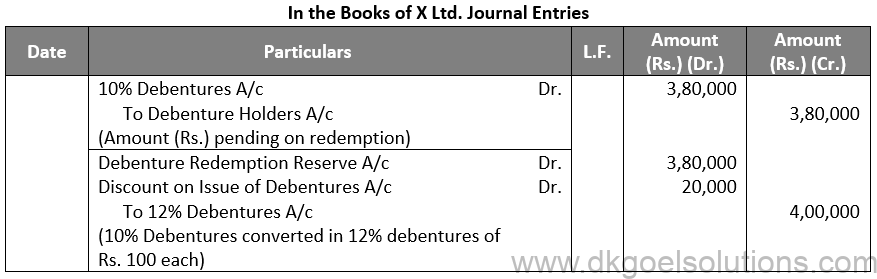
Working Note:-
(i) Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
10% Debentures into 12% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 3,80,000
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 100 – Rs. 5
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 95
Number of 12% Debentures = Rs. 3,80,000 / 95
Number of 12% Debentures = 4,000 Debentures
Points for Students:- Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q37.
Sol. 37

Working Note:-
(i) Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
9% Debentures into 11% Debentures:-
Amount Debentures = Rs. 11,50,000
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 100 – Rs. 8
Number of 12% Debentures = Rs. 11,50,000 / 92
Number of 12% Debentures = 12,500 Debentures
Points for Students:- When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption
Q38.
Sol. 38 (i)
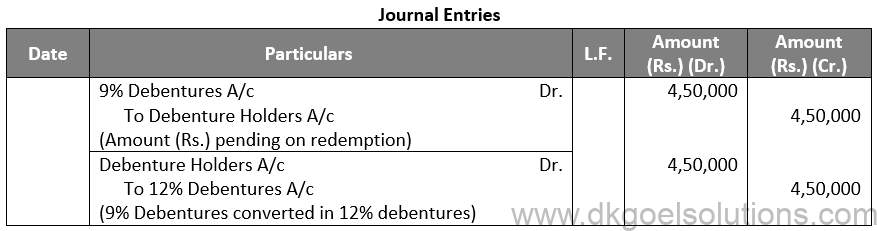
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
9% Debentures into 12% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 100
Number of 12% Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000 / 100
Number of 12% Debentures = 4,500 Debentures
(ii)
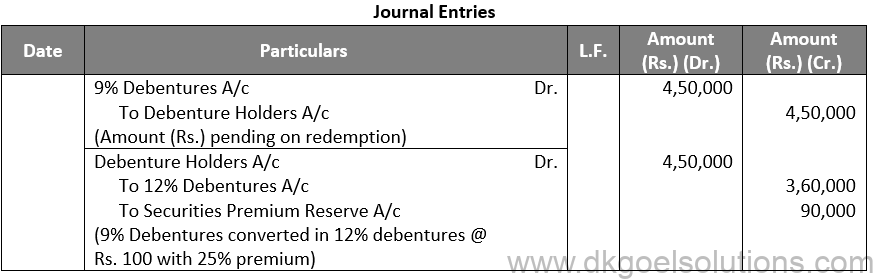
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
9% Debentures into 12% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 125
Number of 12% Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000 / 125
Number of 12% Debentures = 4,500 Debentures
(iii)
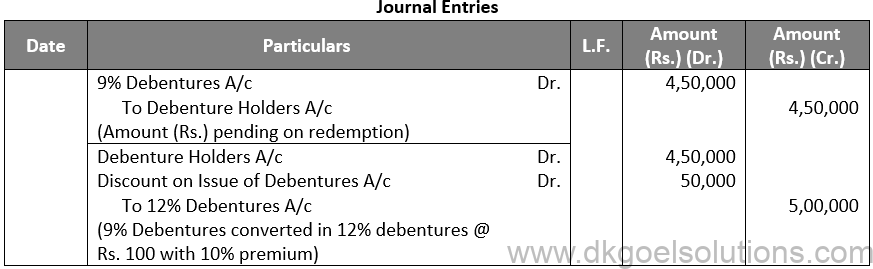
Working Note:-
(i) Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
9% Debentures into 12% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 100 – Rs. 10
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 90
Number of 12% Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000 / 90
Number of 12% Debentures = 5,000 Debentures
(iv)
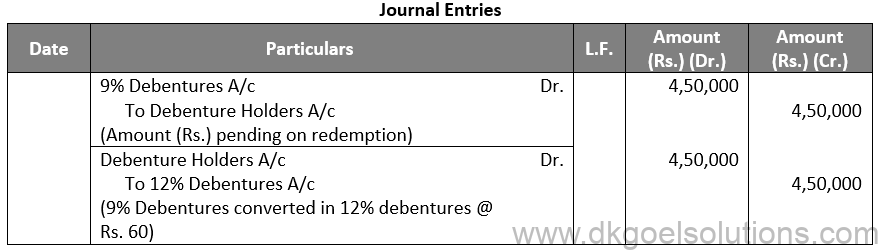
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
9% Debentures into 12% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 100 – Rs. 10
Rate of 12% Debentures = Rs. 90
Number of 12% Debentures = Rs. 4,50,000 / 60
Number of 12% Debentures = 7,500 Debentures
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q39.
Sol. 39

Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
7% Debentures into 9% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 22,00,000
Rate of 9% Debentures = Rs. 100 – Rs. 20
Rate of 9% Debentures = Rs. 80
Number of 9% Debentures = Rs. 22,00,000 / 80
Number of 9% Debentures = 27,500 Debentures
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q40.
Sol. 40

Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
Conversion of 9% Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 19,00,000
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 10 + Rs. 15
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 25
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 19,00,000 / 25
Number of Equity Shares = 76,000 Debentures
Equity Share Capital = Rs. 76,000 × Rs. 10
Equity Share Capital = Rs. 7,60,000
Security Premium Reserve = Rs. 76,000 × Rs. 15
Security Premium Reserve = Rs. 11,40,000
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q41.
Sol. 41
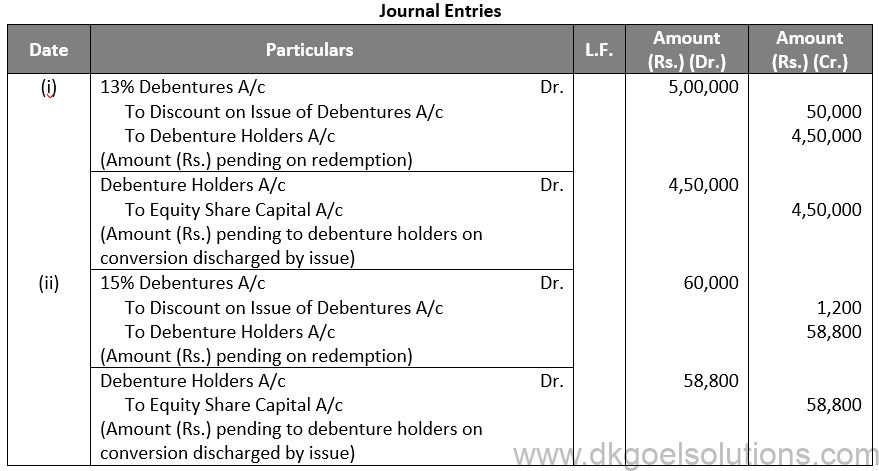
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
7% Debentures into 9% Debentures:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 58,800
Rate of 9% Debentures = Rs. 10 + Rs. 5
Rate of 9% Debentures = Rs. 15
Number of 9% Debentures = Rs. 58,800 / 15
Number of 9% Debentures = 3,920 Debentures
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q42.
Sol. 42

Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q43.
Sol. 43

Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
7% Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 18,800
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 10 + Rs. 2.5
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 12.5
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 18,800 / 12.5
Number of Equity Shares = 1,504 Debentures
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q44.
Sol. 44
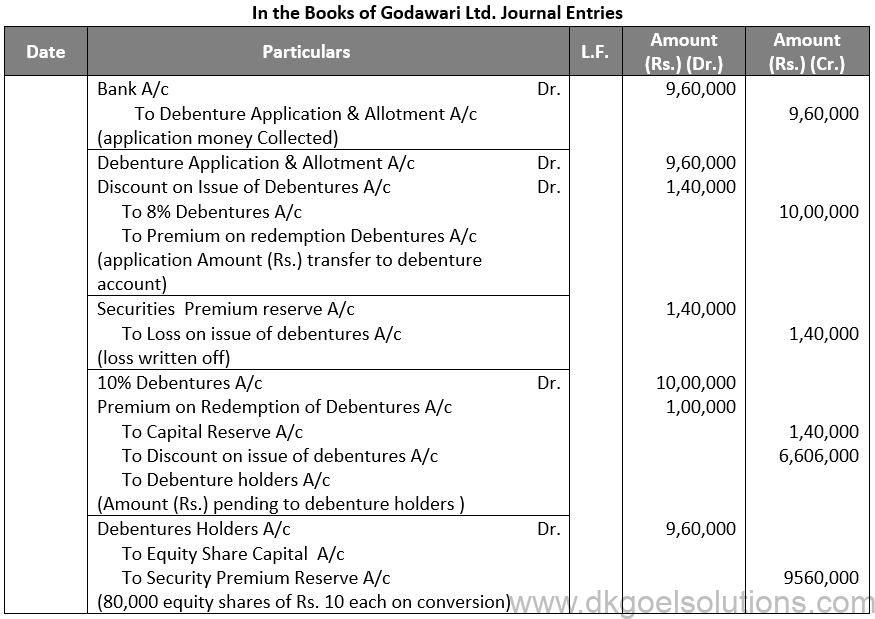
Points for Students:- Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q45.
Sol. 45
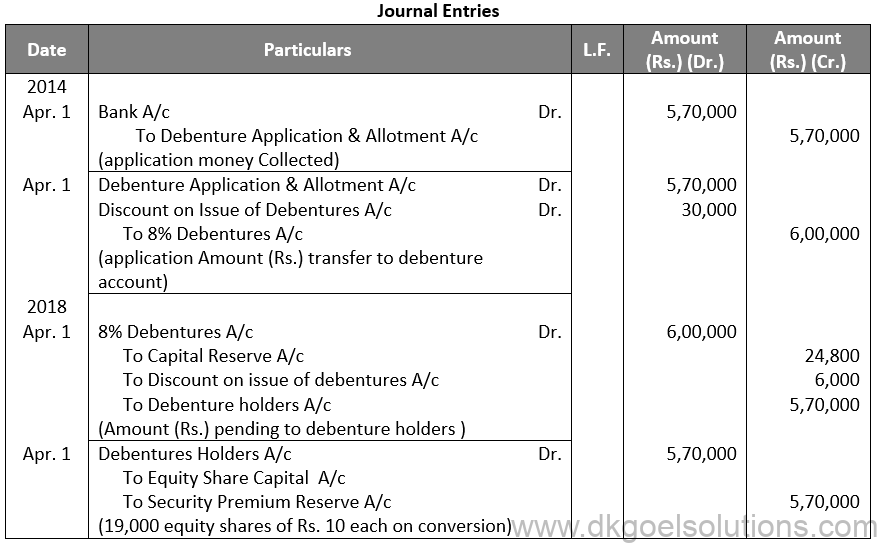
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q46.
Sol. 46
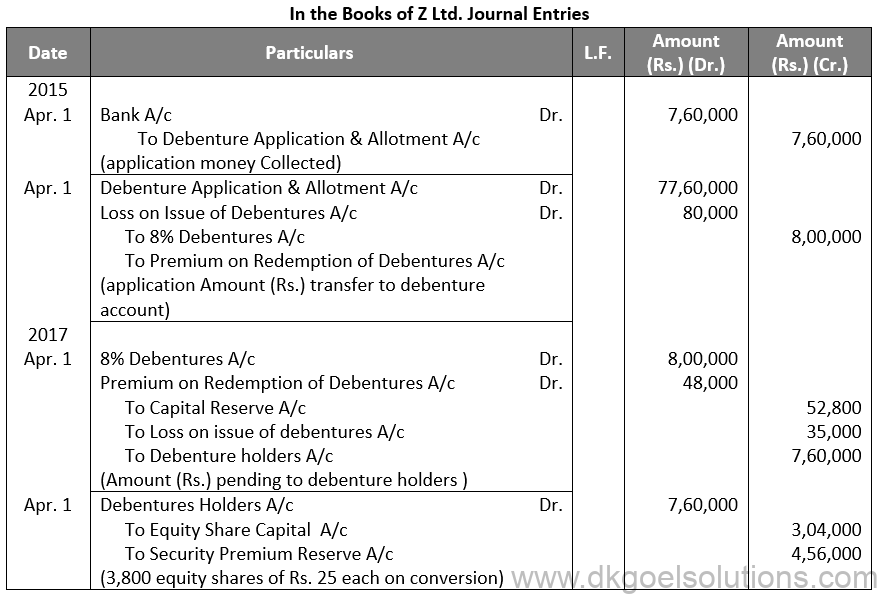
Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q47.
Sol. 47
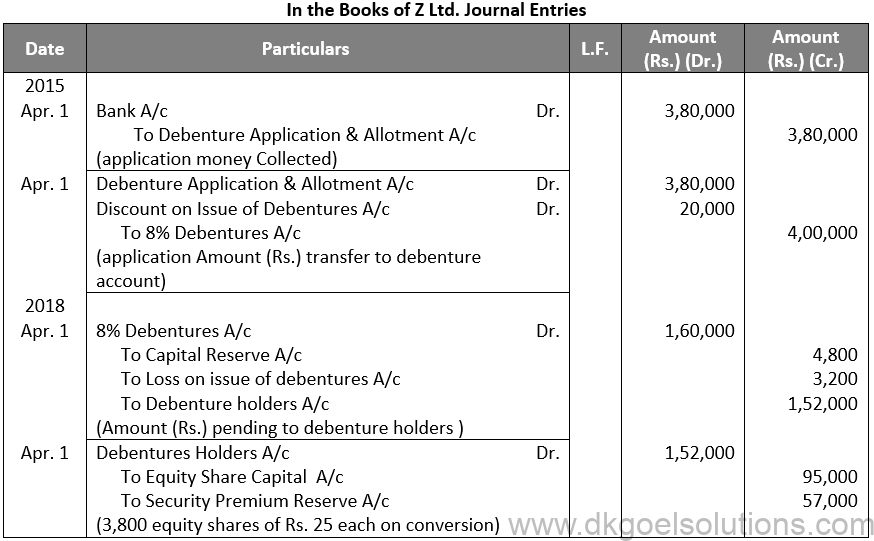
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation. It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q48.
Sol. 48
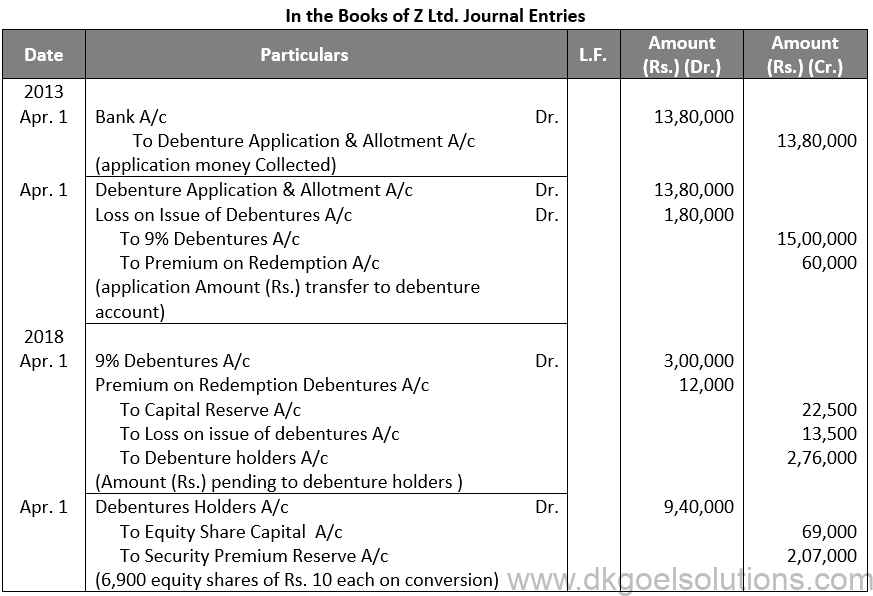
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q49.
Sol. 49
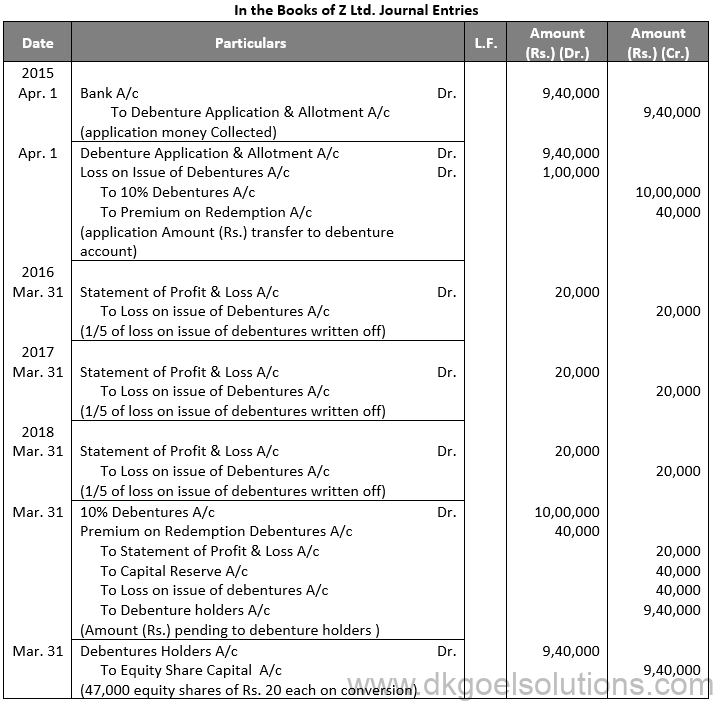
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q50.
Sol. 50

Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q51.
Sol. 51

Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q52.
Sol. 52
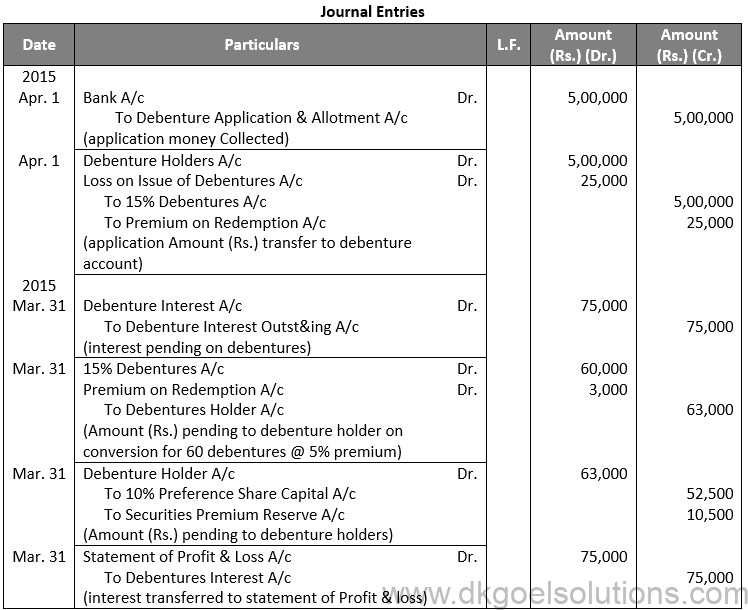
Working Note:-
(i) Conversion of Debentures into Preference Shares:-
Debentures into Preference Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 60,000 + Rs. 3,000 (5% on Premium)
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 63,000
Amount of Preference Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 20
Amount of Preference Share = Rs. 120
Number of Equity Shares = 63,000/120
Number of Equity Shares = 525
Amount of Equity Share Capital = 525 × Rs. 100
Amount of Equity Share Capital = Rs. 52,500
Amount of Security Premium = 525 × Rs. 20
Amount of Equity Share Capital = Rs. 10,500
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q53. (A)
Sol. 53 (A)
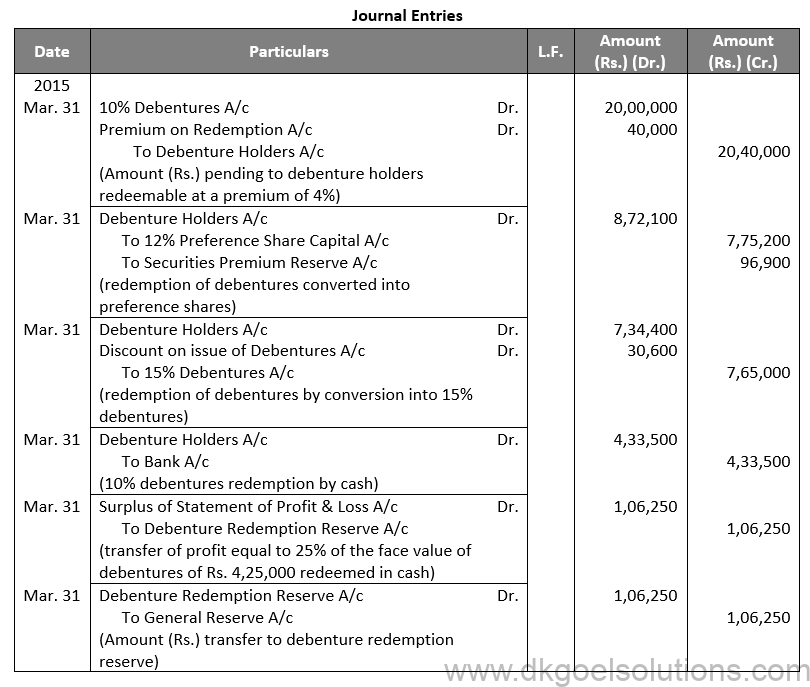
Working Note:-
Debentures to Preference Shares Conversion:
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 8,55,000 + Rs. 17,100 (2% on Premium)
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 8,71,100
Amount of Preference Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 12.5
Amount of Preference Share = Rs. 112.5
Number of Preference Shares to be issued = 8,71,100/112.5 = 7,752
Amount of Preference Share Capital = 7,752 × Rs. 100
Amount of Preference Share Capital = Rs. 7,75,200
Amount of Security Premium = 7,752 × Rs. 12.50
Amount of Security Premium = Rs. 96,900
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q53. (B)
Sol. 53
(B)
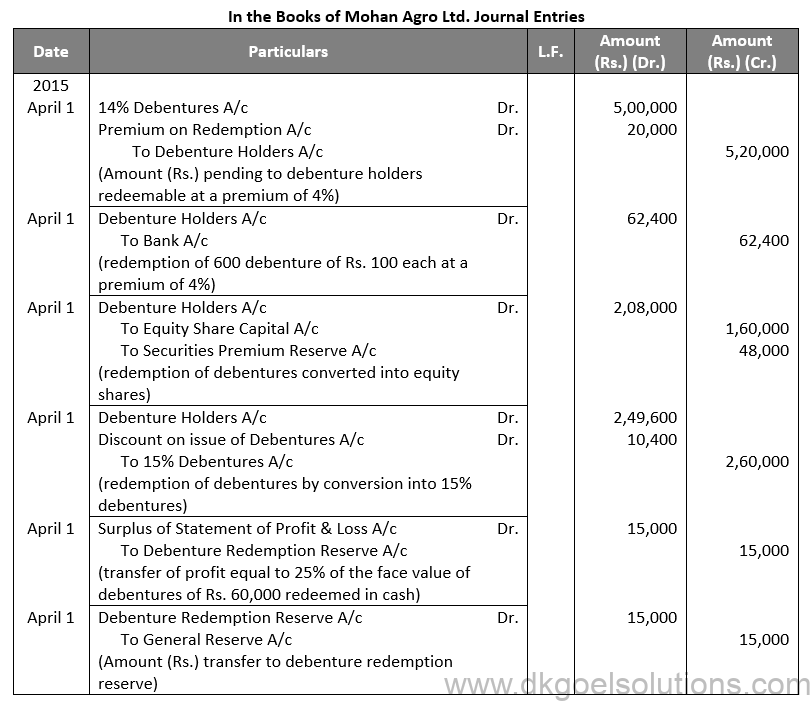
Working Note:-
(i) Conversion of Debentures into Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 2,00,000 + Rs. 8,000 (4% on Premium)
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 2,08,000
Amount of Equity Share = Rs. 10 + Rs. 3
Amount of Equity Share = Rs. 13
Number of Equity Shares = 2,08,000/13
Number of Equity Shares = 16,000
Amount of Equity Share Capital = 16,000 × Rs. 10
Amount of Equity Share Capital = Rs. 1,60,000
Amount of Security Premium = 16,000 × Rs. 3
Amount of Security Premium = Rs. 48,000
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q54.
Sol. 54
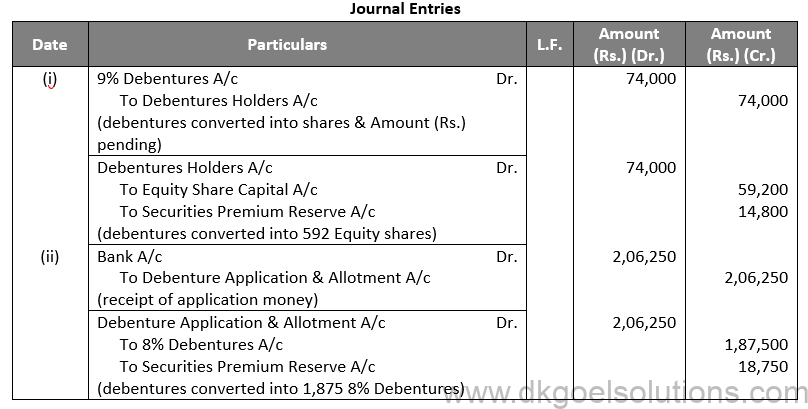
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Shares:-
Debentures into Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 74,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 125
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 225
Number of Equity Shares = 74,000/125
Number of Equity Shares = 592
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q55.
Sol. 55
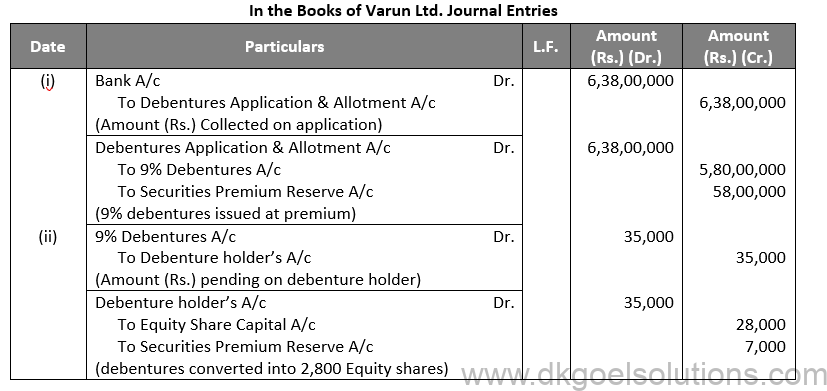
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 35,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 10 + Rs. 2.5
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 12.5
Number of Equity Shares = 35,000/12.5
Number of Equity Shares = 2,800
Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q56.
Sol. 56

Working Note:-
Debentures to Preference Shares Conversion::-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 8,00,000
Amount of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Number of Equity Shares = 8,00,000/125
Number of Equity Shares = 6,400
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q57.
Sol. 57
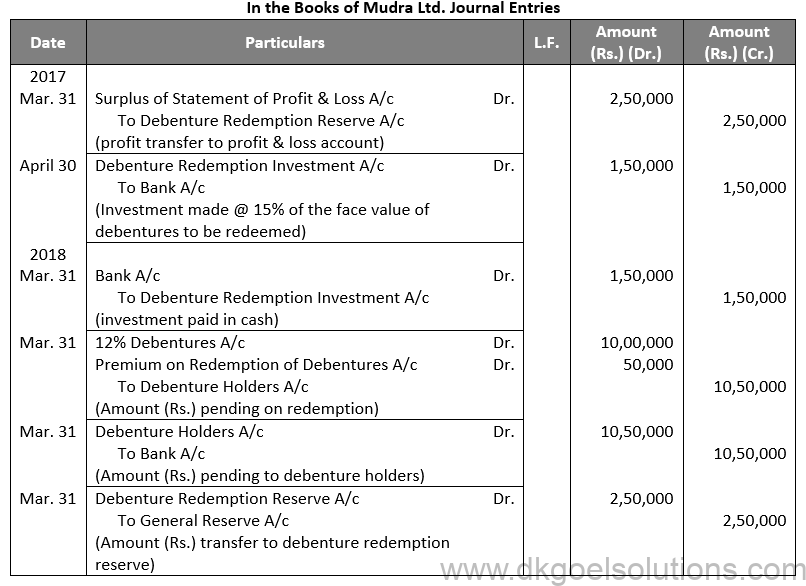
Q58.
Sol. 58
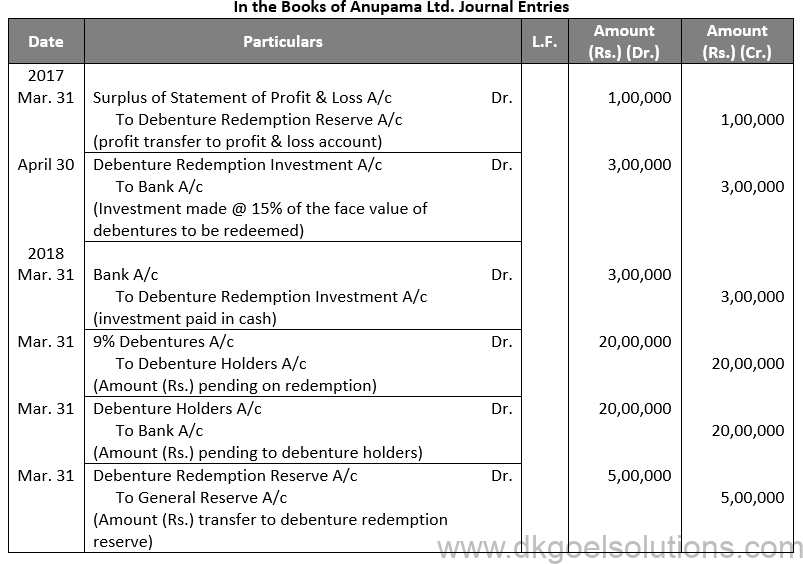
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q59.
Sol. 59
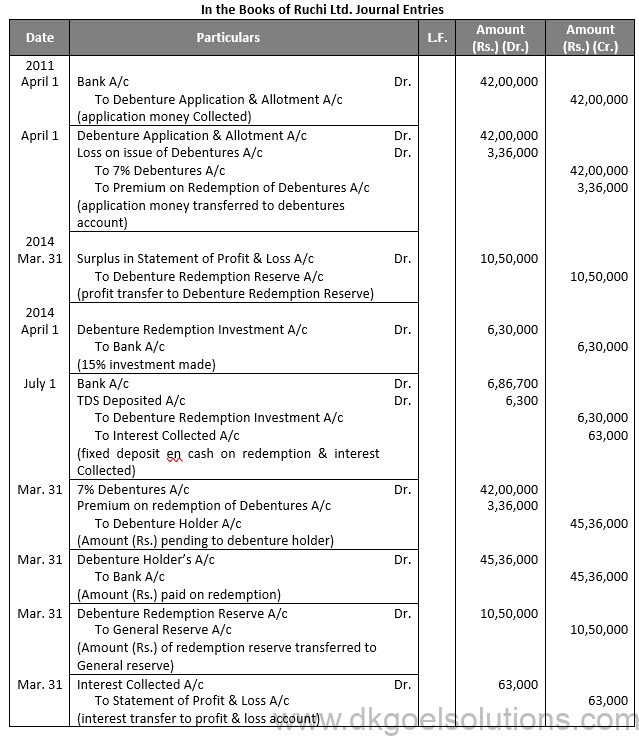
Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q60.
Sol. 60

Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them.
Q61.
Sol. 61
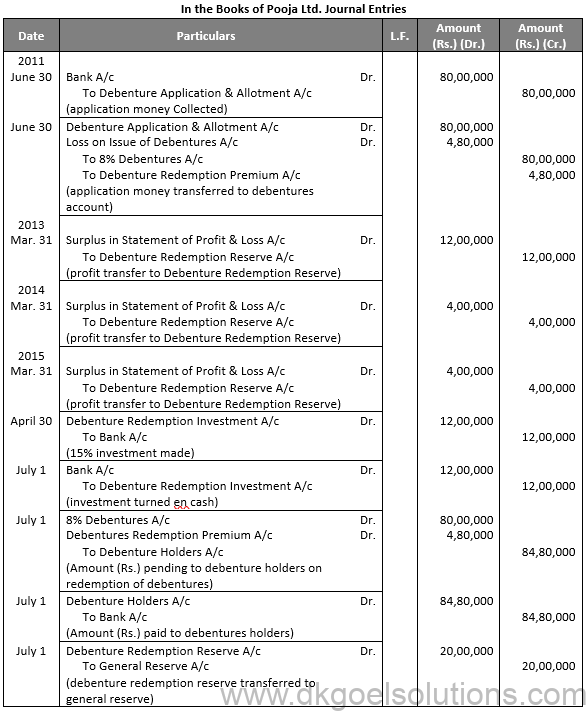
Points for Students:- Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q62.
Sol. 62

Profit on redemption = Rs. 5,00,000 – Rs. 4,90,000 = Rs. 10,000
Hence, the profit on redemption is Rs. 10,000.
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q63.
Sol. 63
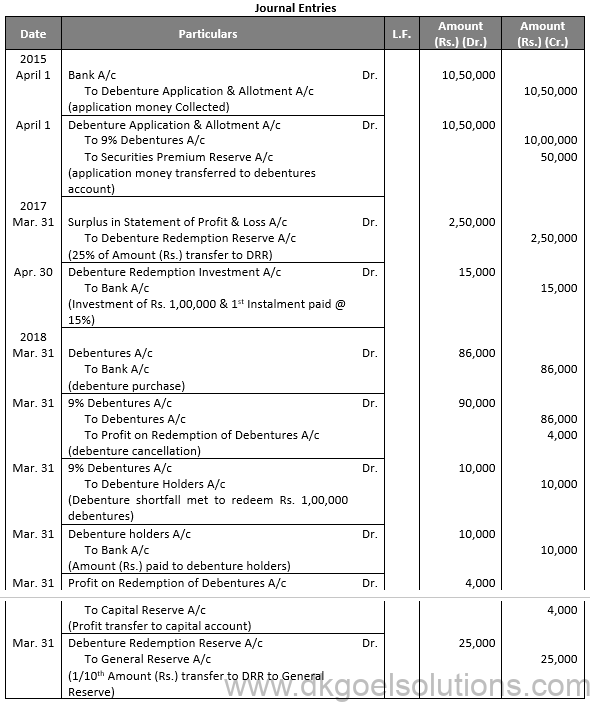
Working Note:-
Computation of Amount of Debenture Purchased:-
Amount of Debenture Purchased = 400 Debentures @ Rs. 95 + 500 Debentures @ Rs. 96
Amount of Debenture Purchased = Rs. 38,000 + Rs. 48,000 Total Amount Paid = Rs. 86,000
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q64.
Sol. 64
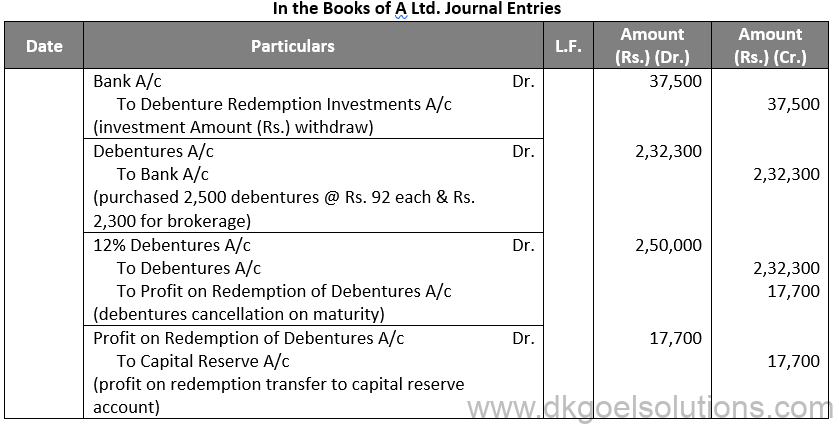
Working Note:-
Computation of Amount of Debenture Purchased:-
= 2,500 Debentures @ Rs. 92 + Brokerage 1%
= Rs. 2,30,000 + Rs. 2,300 = 2,32,300
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q65.
Sol. 65


Points for Students:-
Below are the sources of Finance for the Redemption of Debentures:-
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a Company from the following sources:
(1) Redemption from the proceeds of fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(2) Redemption of Debentures out of Capital.
(3) Redemption of Debentures out of Profits.
Q66.
Sol. 66

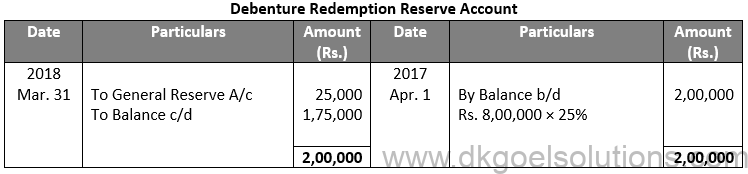
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q67.
Sol. 67

Working Note:-
i) Debentures to Preference Shares Conversion:
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 15,000
Amount of Equity Shares = Rs. 10
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 15,000 / 10
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 1,500
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
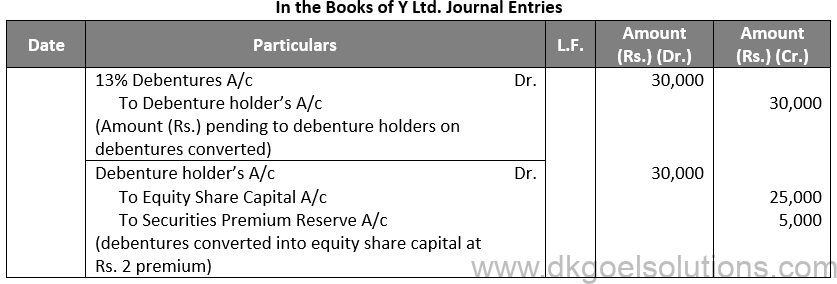
Q68.
Sol. 68
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 30,000
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 10 + Rs. 2
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 12
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 30,000 / 12
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 2,500
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
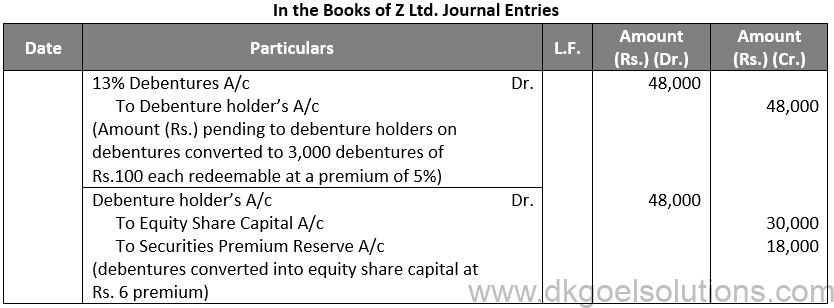
Q69.
Sol. 69
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 48,000
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 10 + Rs. 6
Rate of Equity Shares = Rs. 16
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 48,000 / 16
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 3,000
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
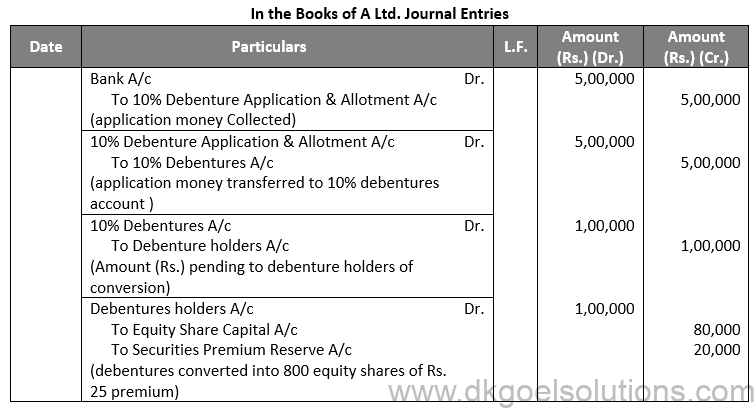
Q70.
Shivansh, holder of 200 debentures, informed on Jan.1, 2015 that he wanted to exercise the option of conversion of debentures into equity shares.
The company accepted his request & converted debentures into equity shares.
Pass necessary journal entries to record the issue of debentures on Jan. 1, 2013 & conversion of debentures on Jan. 1, 2015.
Sol. 70
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 1,00,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 1,00,000 / 125
Number of Equity Shares = 800
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q71.
Sol. 71
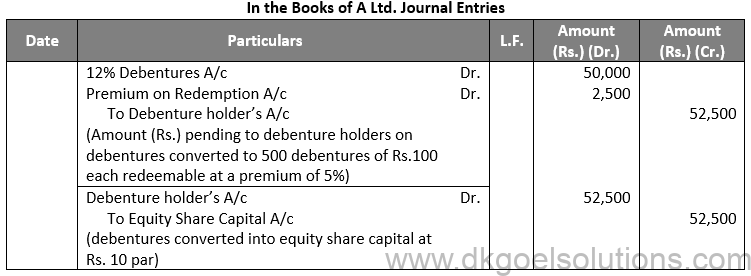
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Debentures:-
Debentures into 15% debentures
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 1,05,000
Rate of 15% debentures = Rs. 10
Number of 15% debentures = 52,500 / 10
Number of 15% debentures = Rs. 5,250
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q72.
Sol. 72
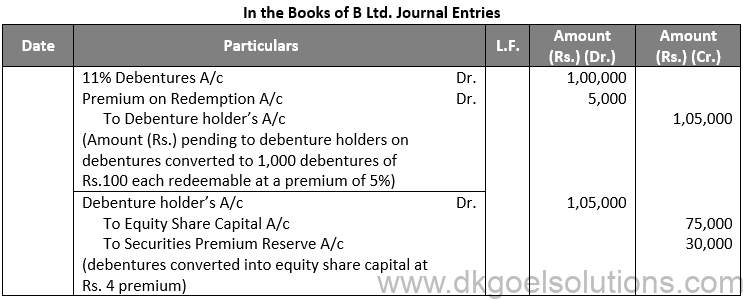
Working Note:-
Debentures to Equity Shares Conversion:
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 1,05,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 10 + Rs. 4
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 14
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 1,05,000 / 14
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 7,500
Points for Students:- When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q73.
Sol. 73
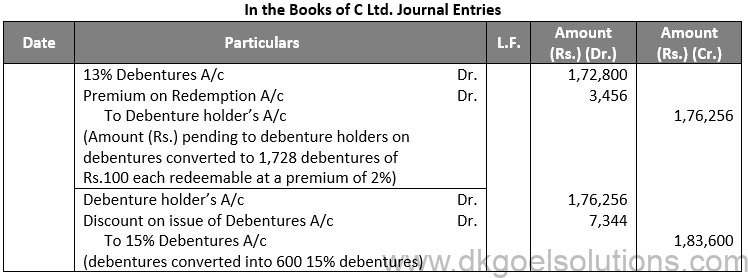
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 1,76,256
Rate of Equity Share = 96%
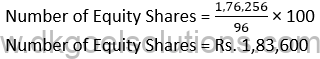
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q74.
Sol. 74
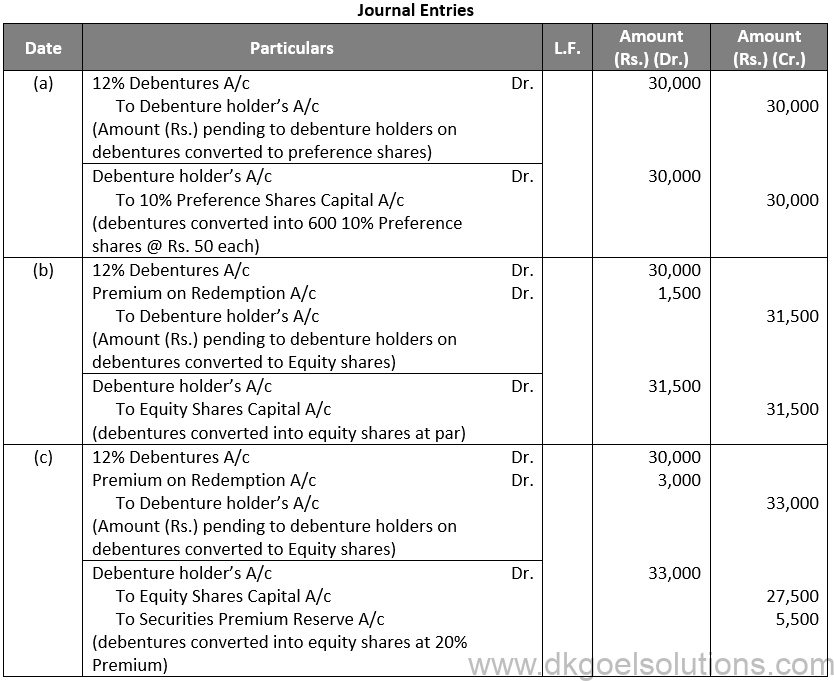
Working Note:-
Computation of Face Value of Share & Securities Premium Reserve:-

Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q75.
Sol. 75

Working Note:-
1.) Conversion of Debentures into Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 40,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 40,000 /25
Number of Equity Shares = 400
(2) Amount of Debentures = Rs. 60,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 60,000 / 125
Number of Equity Shares = 480
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q76.
Sol. 76
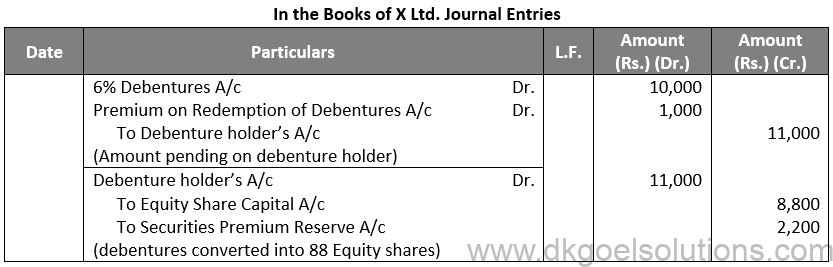
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 11,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 11,000 / 12
Number of Equity Shares = 88
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them.
Q77.
Sol. 77
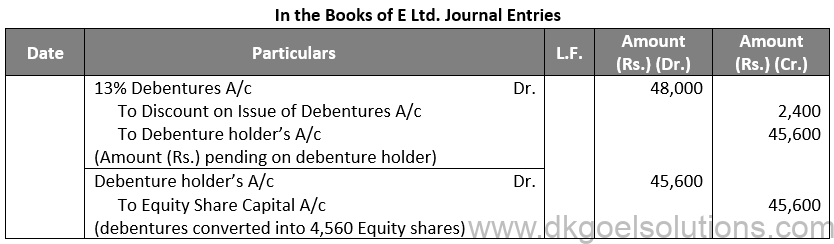
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Shares:-
Debentures into Shares:-
Amount (Rs.) of Debentures = Rs. 45,600
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 45,600 / 100
Number of Equity Shares = 4,560
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.
Q78.
Sol. 78
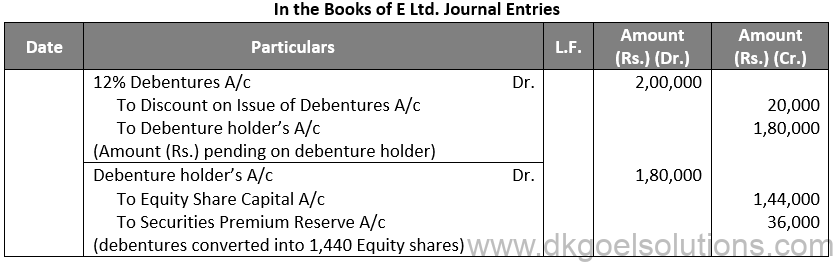
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 1,44,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 1,80,000 / 125
Number of Equity Shares = 1,440
Points for Students:-
The term “redemption out of capital” refers to when no profits are set aside for debenture redemption. No benefit is passed to the debenture redemption reserve in this situation.
It is not possible to redeem debentures solely out of capital because Section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines require the establishment of a Debenture Redemption Reserve equal to at least 50% of the amount of debentures issued before redemption begins.
Q79.
Sol. 79
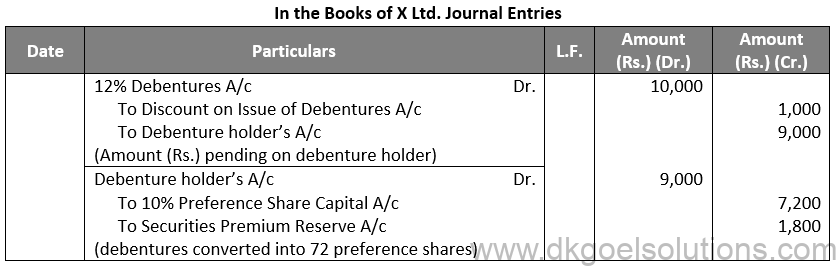
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount of Debentures = Rs. 9,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 9,000 / 125
Number of Equity Shares = 72
Points for Students:-
Unsecured debentures are also called Naked Debentures. These Debentures are those which are not given any security. The holders of such debentures are treated as unsecured creditors at the time of liquidation of the Company. Such debentures are not very common these days, so much so that, unless otherwise stated, a debenture is presumed to be secured.
Q80.
Sol. 80

Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
Conversion of Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Amount (Rs.) of 8% Debentures = Rs. 1,00,00,000
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 100 + Rs. 25
Rate of Equity Share = Rs. 125
Number of Equity Shares = Rs. 1,00,00,000 / 125
Number of Equity Shares = 80,000
Points for Students:-
Secured or Mortgage Debentures are those which are secured either on particular assets of the Company called fixed charge or on all assets of the company in general, called a floating charge. Fixed charge denies the company from dealing with mortgaged assets, whereas the floating charge does not prevent the Company from using the assets. If the company is unable to repay the debentures on the due date, the debenture holders can realise their money from the assets mortgaged with them. First mortgage debentures are those that have a first claim on the assets charged and second mortgage debentures are those having a second claim on the assets charged. In India, debentures have necessarily to be secured.
Q81.
Sol. 81
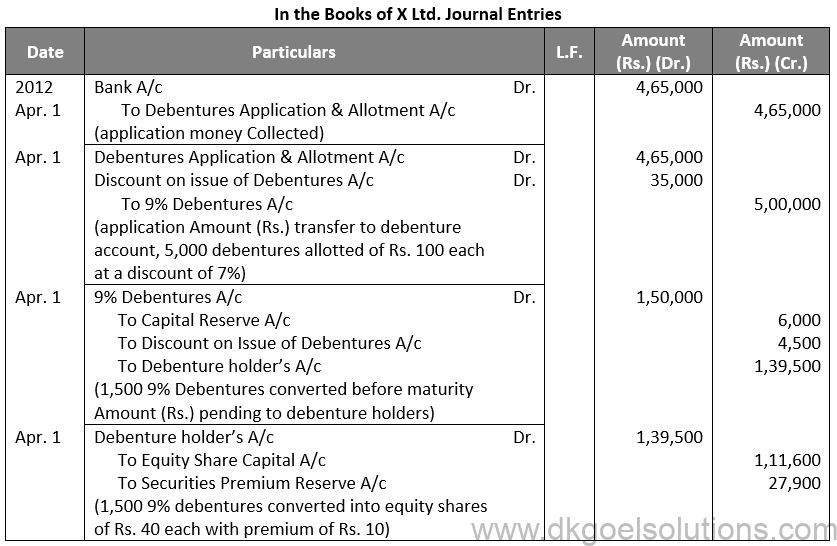
Working Note:-
Conversion of Debentures to Shares:-
Debentures into Equity Shares:-
Number of Debentures converted into Shares = 1,500
Discount on Debentures = 1,500 × Rs. 7 Discount on Debentures = Rs. 10,500
Points for Students:-
When a company needs more money to pay off its debentures, it may decide to issue new equity shares, preferred shares, or debentures. The proceeds from the new share capital and debenture issue are used to pay off the old debentures. The Company’s financial status is not harmed as a result of this form of redemption.

Redemption of debentures can be defined as the process of repayment of the debentures issued by a firm to its debenture holders. Typically, it is the process of repayment of the principal amount to the debenture holders.
Debenture Redemption Reserves depict a fund supervised by the debenture issuing company. The primary objective behind the creation of DRR is to clear off the risk of default on the repaying of the debentures. These funds help the companies meet the obligations of the debenture holders. According to the Indian Companies Act, all companies shall mandatorily create a debenture redemption reserve before the expiry date of a specific debenture.
A company can conveniently turn the old debentures into a new class of debentures or shares to reclaim them. If the deal is beneficial for the debenture holders, they can simply use their rights to transform the existing debentures into new shares or debentures. However, the convertible debentures are only applicable to this method of reclamation.
In case the company desires to repay the amount through monthly installments, the debenture holder accepts payment in a series of installments at regular or irregular intervals as per the terms and conditions defined by the redemption of the debentures.
In this case, the firms which desire to purchase debentures on the market have the authority to cancel them immediately. In case the debentures are picked at a discount rate, the firms get the chance to push down the overall redemption payment, which helps them to elevate their business revenue.
Also refer to TS Grewal Solutions for Class 12
