MCQs for Chemistry Class 12 with Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Students of class 12 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 12 Chemistry NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 12 Chemistry. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 12 Chemistry examination
Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ with Answers Class 12 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 12. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 12 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. Two compounds benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid are formed from this compound, when this compound is heated in the presence of conc.NaOH, this compound is.
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzylalcohol
(c) Acetophenone
(d) Benzophenone
Answer
A
Question. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde is
(a) Sodium hydrogensulphite
(b) Phenyl hydrazine
(c) Fehling’s solution
(d) Grignard reagent
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reactions will not result in the formation of carbon-carbon bond?
(a) Friedel-Crafts acylation
(b) Wurtz reaction
(c) Cannizzaro reaction
(d) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Answer
C
Question. Iodoform test is not given by
(a) 2-Pentanone
(b) Ethanol
(c) Ethanal
(d) 3-Pentanone
Answer
B
Question. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg2+ ions as a catalyst. Which of the following products will be formed on addition of water to but-1-yne under these condition?

Answer
B
Question. When acetaldehyde reacts with alcohol then produce
(a) Acetal
(b) Ketal
(c) Acetone
(d) None
Answer
A
Question. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
(a) Sodium hydrogensulphite
(b) Phenyl hydrazine
(c) Fehling’s solution
(d) Grignard reagent
Answer
C
Question. The formation of cyanohydrin from propanone is which type of reaction?
(a) Electrophilic substitution
(b) Nucleophilic substitution
(c) Electrophilic addition
(d) Nucleophilic addition
Answer
D
Question. Wolf-Kishner reduction is
(a) reduction of carbonyl compound into alcohol
(b) reduction of carbonyl compound into alkene
(c) reduction of carboxyl compound into alkane
(d) reduction of nitro compound into aniline
Answer
C

(a) Prop–1–en–2–ol, metamerism
(b) Prop–1–en–1–ol, tautomerism
(c) Prop–2–en–2–ol, geometrical isomerism
(d) Prop–1–en–2–ol, tautomerism
Answer
D
Question. Imine derivatives of aldehyde and ketone is called as
(a) Schiff’s reagent
(b) Fehling’s reagent
(c) Schiff’s base
(d) Schiff’s acid
Answer
C
Question. The acid formed when propyl magnesium bromide is treated with CO2 is :
(a) C3H7COOH
(b) C2H5COOH
(c) both
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following reagents is used for the conversion of ethanoic acid to ethanoic anhydride?
(a) P2O5, Δ
(b) SOCl2, Δ
(c) PCl3, Δ
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
A
Question. Primary and secondary alcohols on action of reduced copper give
(a) Aldehydes and ketones respectively
(b) Ketones and aldehydes respectively
(c) Only aldehydes
(d) Only ketones
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?

Answer
A
Question. The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is called
(a) Rosenmund reaction
(b) Wurtz reaction
(c) Etard reaction
(d) Fittig reaction
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds will give brisk effervescence of CO2 on treatment with NaHCO3?
(a) Phenol
(b) Acetic acid
(c) both
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. IUPAC name of ethyl isopropyl ketone is
(a) 4-methyl pent-3-one
(b) 2-methyl pent-3-one
(c) 4-methyl pent-2-one
(d) 2-methyl pent-2-one
Answer
B
Question. The -bond in carbonyl group is formed by
(a) s-s-overlapping
(b) p-p-overlapping
(c) s-p-overlapping
(d) p-d-overlapping
Answer
B

(a) identical
(b) positional isomers
(c) functional isomers
(d) optical isomers
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following on oxidation gives a ketone ?
(a) Primary alcohol
(b) Secondary alcohol
(c) Tertiary alcohol
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. Liquid obtained by distillation of red ant is
(a) formaline
(b) formaldehyde
(c) formic acid
(d) formyl chloride
Answer
C
Question. Who has synthesised the organic compound ‘w·ea’ for the first time?
(a) Friedrich Wohler
(b) Berzelius
(c) Kolbe
(d) Berthelot
Answer
A
Question. Which compound is responsible for perfumery?
(a) Ketones
(b) Ethers
(c) Alcohols
(d) Esters
Answer
D
Question. Colouration of Br2/CCI4 will be discharged by
(a) cinnamic acid
(b) benzoic acid
(c) o-phthalic acid
(d) acetophenone
Answer
A
Question. Oil of winter green is
(a) a carboxylic acid
(b) an alcohol
(c) a ketone
(d) an ester
Answer
D
Question. Acetic acid will be obtained on oxidation of
(a) ethanol
(b) propanal
(c) methanal
(d) glyoxal
Answer
A
Question. C6H5COOH →(i) NH3 (ii)Δ p →NaOBr Q →(i) Cone. H2SO4 (ii) Heat of 460 K R R is
(a) o-bromo sulphanilic acid
(b) sulphanilamide
(c) sulphanillic acid
(d) p-bromo sulphanilamide
Answer
C
Question. In the given reaction, identify compound C.

Answer
D
Question. Acetic anhydride is prepared in the laboratory by heating sodium acetate with
(a) ethyl chloride
(b) acetyl chloride
(c) cone. H2SO4
(d) zinc dust
Answer
B
Question. In the reaction

Answer
C
Question. Sodium ethoxide has reacted with ethanoyl chloride. The compow1d that is produced in the above reaction is
(a) diethyl ether
(b) 2-butanone
(c) ethyl chloride
(d) ethyl ethanoate
Answer
D
Question. Identify Zin the sequence,
CH3COONH4 →Δ X →ΔP2O5 →H2O/H+ Z
(a) CH3CH2CONH2
(b) CH3CN
(c) CH3COOH
(d) (CH3CO)2O
Answer
C
Question. Potassium cyanate is heated with ammonium sulphate. The product formed is
(a) urea
(b) ammonia
(c) potassium sulphate
(d) ammonium cyanide
Answer
A
Question. Give IUPAC name of the product, when acetamide is heated with anhydrous phosphorus pentoxide.
(a) Ethyl atnine
(b) Propane nitrile
(c) Cyano methane
(d) Ethane nitrile
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following will undergo meta-substitution on monochlorination?
(a) Ethoxybenzene
(b) Chlorobenzene
(c) Ethyl benzoate
(d) Phenol
Answer
C
Question. When acetamide is hydrolysed by boiling with acid, the product obtained is
(a) acetic acid
(b) ethyl amine
(c) ethanol
(d) acetamide
Answer
A
Question. Ethyl acetate is obtained when methyl magnesium bromide reacts with
(a) ethyl formate
(b) ethyl chloroformate
(c) acetyl chloride
(d) carbon dioxide
Answer
B
Question. When acetamide is treated with Br2 and caustic soda, the product formed is
(a) N-brommide
(b) bromoacetic acid
(c) methanamine
(d) ethanamine
Answer
C
Question. An ester (A )with molecular formula C9H10O2 was treated with excess of CH3MgBr and the complex so formed was treated with H2SO4 to give an olefin (B) . Ozonolysis of (B) gave a ketone with molecular formula C8H8O which shows positive iodoform test. The structure of (A) is
(a) C6H5COOC2H5
(b) C6H5COOC6H5
(c) C6H5COOCH3
(d) p-H3CO—C6H4—COCH3
Answer
A
Question. The most suitable reagent A, for the reaction

is/are
(a) O3
(b) H2O2
(c) NaOH-H2O2
(d) m-chloroperbenzoic acid
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following will produce only one product on reduction with LiAlH4 ?
(a) C2H5COOCH2CH3
(b) CH3CH2COOCH2CH3
(c) CH3COOC2H5
(d) CH3COOCH2CH2CH3
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following pairs gives effervescence with aqueous NaHCO3 ?
CH3COCI (I)
CH3COCH3 (II)
CH3COOCH3 (III)
CH3COOCOCH3 (IV)
(a) I and II
(b) I and IV
(c) II and III
(d) I and III
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following diacid readily gives anhydride on heating ?
(a) Fumaric
(b) Maleic acid
(c) Malic acid
(d) Terephthalic acid
Answer
B
Question. Hydroxamic acid test is employed to detect
(a) ketones
(b) aldehydes
(c) esters
(d) amides
Answer
C
Question. The product formed in the reaction n-hexanamide +Br2 +KOH, is
(a) hexanamine
(b) propanamine
(c) butanamine
(d) pentanamine
Answer
D
Question. (CH2CO)2O + RMgX →H2O?
(a) ROOC(CH2 )COOR
(b) RCOCH2CH2COOH
(c) RCOOR
(d) RCOOH
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution?
(a) Butan-1-ol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution?
(a) Butan-1-ol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. An aldehyde group can be present
(a) in between carbon chain
(b) at any position in carbon atom
(c) only at the end of carbon chain
(d) at the second carbon atom of the carbon chain
Answer
C

(a) Tollens’ reagent
(b) Benzoyl peroxide
(c) I2 and NaOH solution
(d) Sn and NaOH solution
Answer
C
Question. Acetaldehyde reacts with
(a) Electrophiles only
(b) Nucleophiles only
(c) Free radicals only
(d) Both electrophiles and nucleophiles
Answer
C
Question. Carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition because of
(a) electronegativity difference of carbon and oxygen atoms
(b) electromeric effect
(c) more stable anion with negative charge on oxygen atom and less stable carbonium ion
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following contain an aldehyde?
(a) Vanilla beans
(b) Meadow sweet
(c) Cinnamon
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following have pleasant smell?
(a) Methanal
(b) Propanal
(c) Ethanal
(d) Hexanal
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following can be oxidised to the corresponding carbonyl compound?
(a) 2-hydroxy-propane
(b) Ortho-nitrophenol
(c) Phenol
(d) 2-methyl-2 hydroxy-propane
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?

Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is false ?
(a) Cannizzaro reaction is given by aldehydes in presence of alkali
(b) Aldol condensation is given by aldehydes in presence of alkali
(c) Aldol condensation is given by aldehydes and ketones in presence of acids
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. If formaldehyde and KOH are heated, then we get
(a) methane
(b) methyl alcohol
(c) ethyl formate
(d) acetylene
Answer
C
Question. Iodoform test is not given by
(a) 2-Pentanone
(b) Ethanol
(c) Ethanal
(d) 3-Pentanone
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not used in the preparation of ketone?
(a) Oxidation of secondary alcohols
(b) Dehydrogenation of 2° alcohol
(c) Pyrolysis of calcium acetate
(d) Acid hydrolysis of alkyl cyanide
Answer
D
Question. Cannizzaro’s reaction is not given by _.

Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is used to prepare ketone from acyl chloride ?
(a) R-MgX
(b) R2Cd
(c) CO + HCl
(d) CrO3
Answer
B
Question. What is formed when a primary alcohol undergoes catalytic dehydrogenation ?
(a) Aldehyde
(b) Ketone
(c) Alkene
(d) Acid
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of increasing acidic strength is _____________.
(a) Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
(b) Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
(c) Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
(d) Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol < Ethanol
Answer
C
Question. The weakest acid among the following is:
(a) CHCl2COOH
(b) CH3COOH
(c) CH2ClCOOH
(d) CCl3COOH
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following forces explain the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones?
(a) Hydrogen bonding
(b) van der Waal’s forces
(c) Dipole-dipole attraction
(d) None of these
Answer
C

Answer
C
Question. Which is highly soluble in water?
(a) Methanal
(b) Propanal
(c) Propanone
(d) Butanone
Answer
A
Question. Which reaction is used for detecting the presence of carbonyl group?
(a) Reaction with hydrazine
(b) Reaction with phenyl hydrazine
(c) Reaction with hydroxylamine
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. The product formed in Aldol condensation is
(a) a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or a beta-hydroxy ketone
(b) an alpha-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
(c) an alpha, beta unsaturated ester
(d) a beta-hydroxy acid
Answer
A
Question. The product obtained by the reaction of an aldehyde and hydroxylamine is
(a) hydrazone
(b) aldoxime
(c) primary amine
(d) alcohol

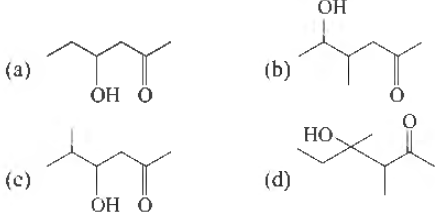
(a) B < C < A < D
(b) A < B < C < D
(c) C < B < D < A
(d) C < D < B < A
Answer
D
Question. Schiff’s reagent gives pink colour with
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) acetone
(c) acetic acid
(d) methyl acetate
Answer
A

We hope the above multiple choice questions for Class 12 Chemistry for Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids is an important chapter in Class 12 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 12 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
