Notes Chapter 18 Table Creation And Data Manipulation
Creation of Database
- Following command is used to create a Database mysql> CREATE DATABASE <database name >;
For exmysql>
create database school;
Using Database
- Following command is used to use a Database
mysql> USE <database name >;
For ex –
mysql> USE school;
A message will come saying- “database changed”
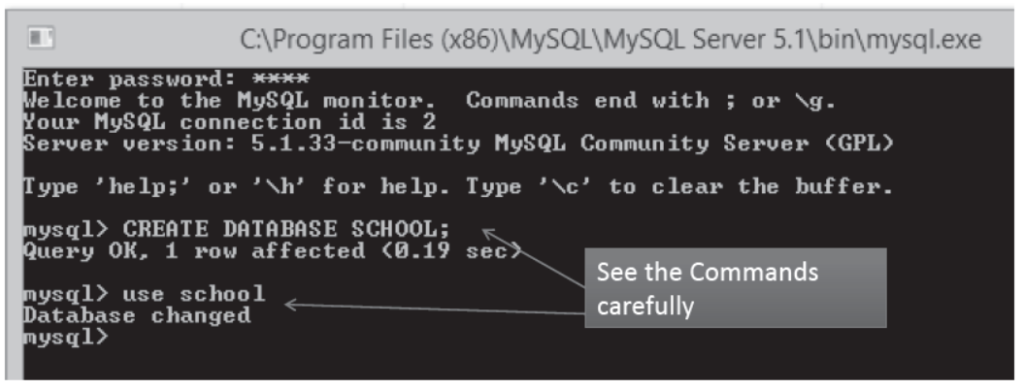
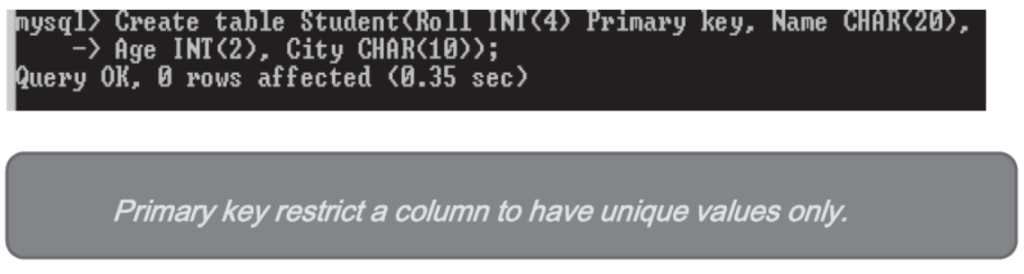
Table Creation
- To create a table in Database, following command is usedmysql>
CREATE TABLE <Table Name> (<Col1> <DataType(Size)>,
<Col2><DataType(size)>, . . . );
For exmysql>
create table student (Roll INT(4) Primary Key, Name CHAR(20),
(Age INT(2), City CHAR(10) ) ;
A message will come saying- “Query OK”
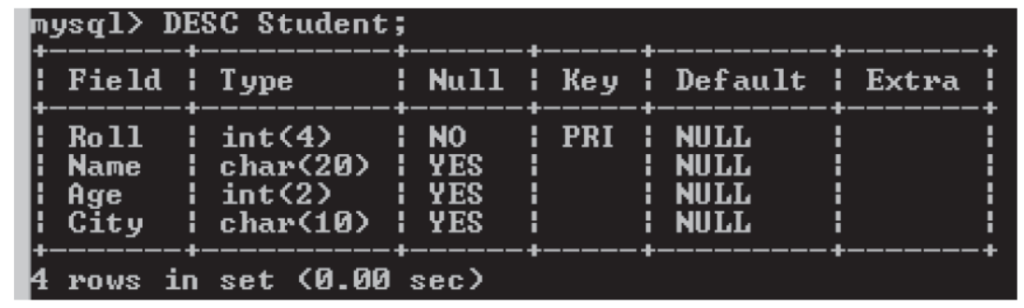
Viewing Table structure
- To see structure of a table in Database, following command is usedmysql>
DESC <TableName>;
For ex –
mysql>DESC Student;
It displays whole structure of the table
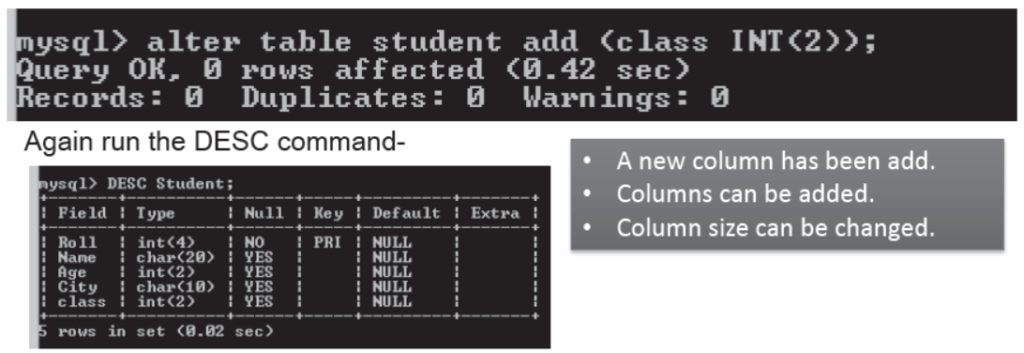
- Modification in Table structure
- To modify structure of a table in Database, following command is usedmysql>
ALTER TABLE <Table name> ADD/MODIFY
(<Col> <type(size)>, . . . .)
For exmysql>
Alter Table Student Add (class INT(2));
A message comes saying “Query OK” .
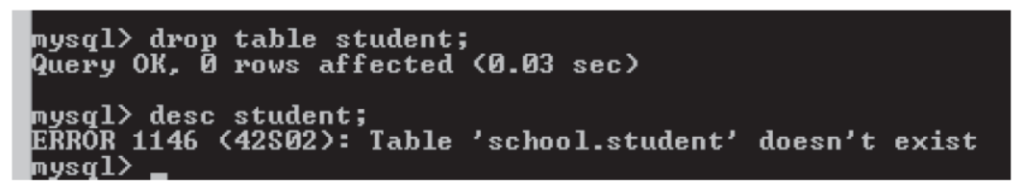
Dropping a Table
- To drop a table in Database, following command is usedmysql>
DROP Table <Table Name>;
For ex –
mysql>drop table <Student>
A message will come saying- “Query OK” now if you want to see the structure of the
table you cant see because it has already been deleted.
Data Integrity by Constraints
- The checks or conditions applied on one or more columns of a table are known as CONSTRAINTS .
- These are set to maintain integrity in a table hence also known as integrity constraints.
- When a constraint is applied on a table, all the data should follow this constraint.
- Constraints are to be set at the time of table creation so that it should be followed at the time of data insertion. Syntax is –
mysql> CREATE TABLE <TableName>
(<Col1> <type(size)> <Column Constraint>
<Col2> <type(Size)> <Column Constraint>, . . . . );
Integrity Constraints
- Constraints maintains the integrity of a database. Some of the constraints are-
- Unique Constraint : This constraint ensure that all the data of the column should be unique. It allows null values.
- Primary key Constraint : This constraints is used to uniquely identify data. It does not accept null values.
- Default Constraint : This constraint is used to set a default values in case no value is provided by user for a column.
- Check Constraint : This constraint is used to set a limit for a column. for ex- no data should be inserted less than 20 in age column.
- Foreign key Constraint : it is a non –key attribute of one table derived from primary key from other table.
Creation of a Table
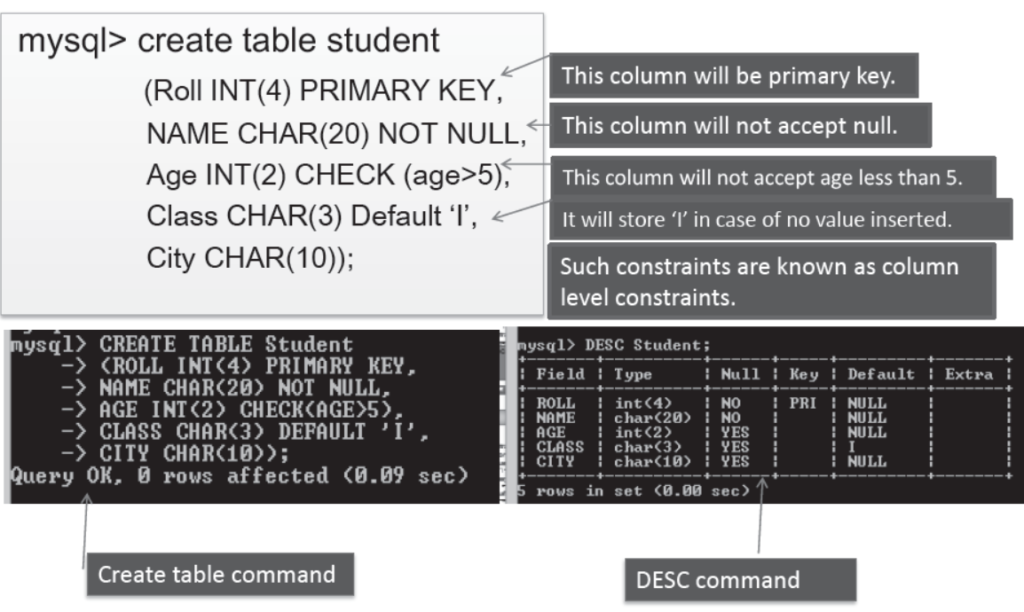
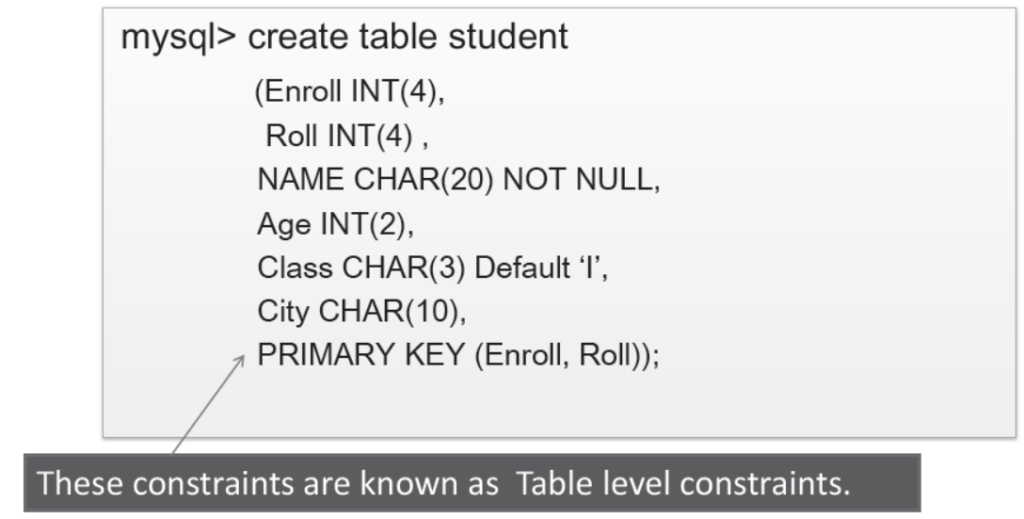
Table level constraints Setting
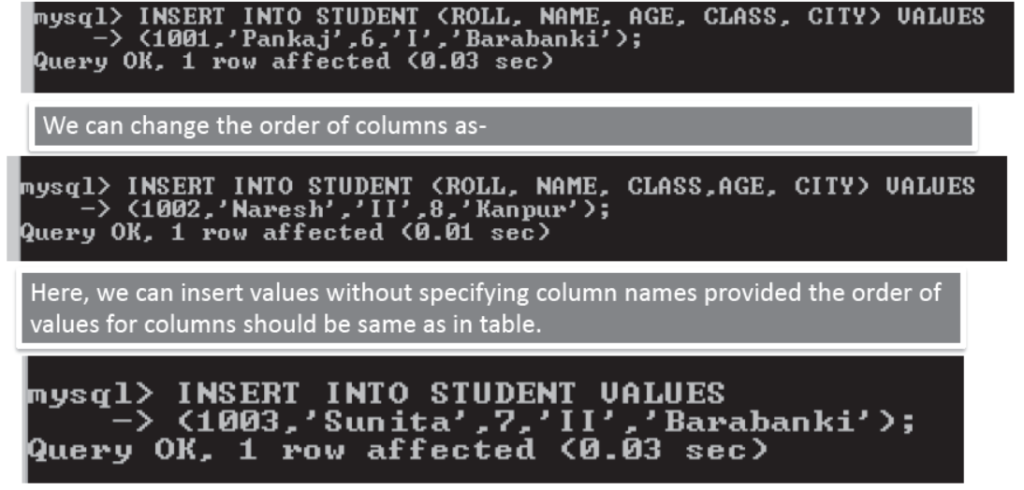
Insertion of a record in Table
The columns in which you are inserting values will have the values. The columns previously set with default vales will have Default value. Other columns will have null .
Syntax to insert a record in a Table is
mysql> INSERT INTO <TableName> (<Col1> <Col2> <Col3> <Col4>
VALUES (<val1>,<val2>,<val3>,<val4>,. . .);
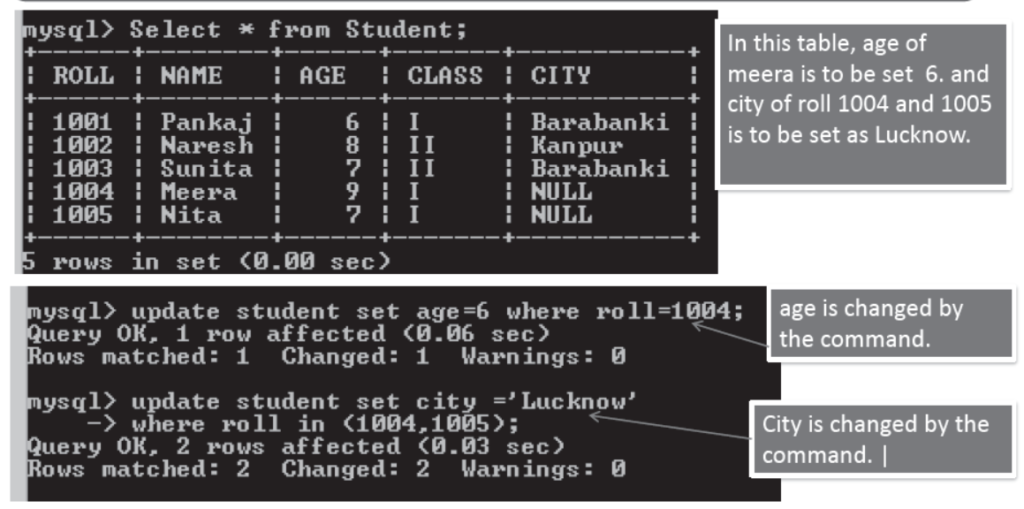
Updating a record in Table
Syntax to update a record in a Table is
mysql> UPDATE <TableName> SET <ColName>=<NewValue>
WHERE <Condition>
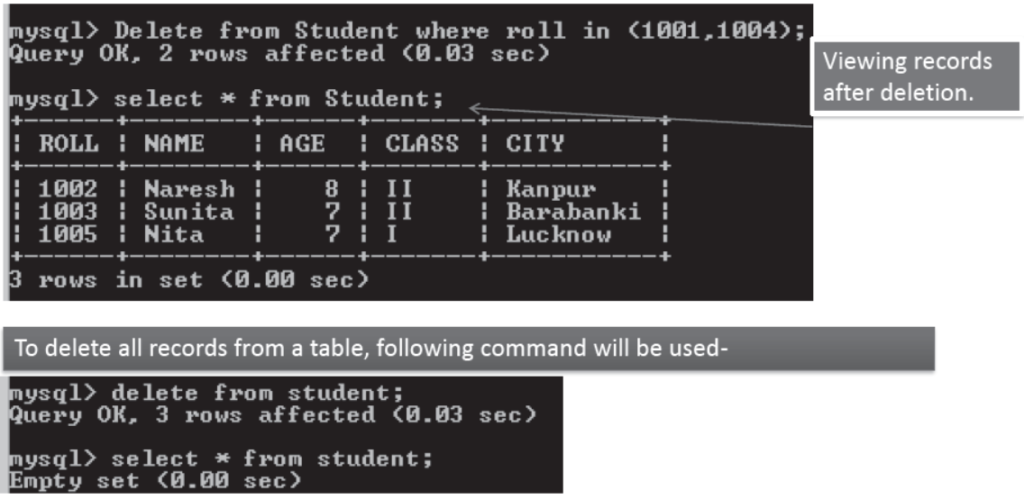
Deletion of a record from a Table
- Syntax to delete a record from a Table is
mysql> DELETE FROM <TableName> WHERE <Condition>
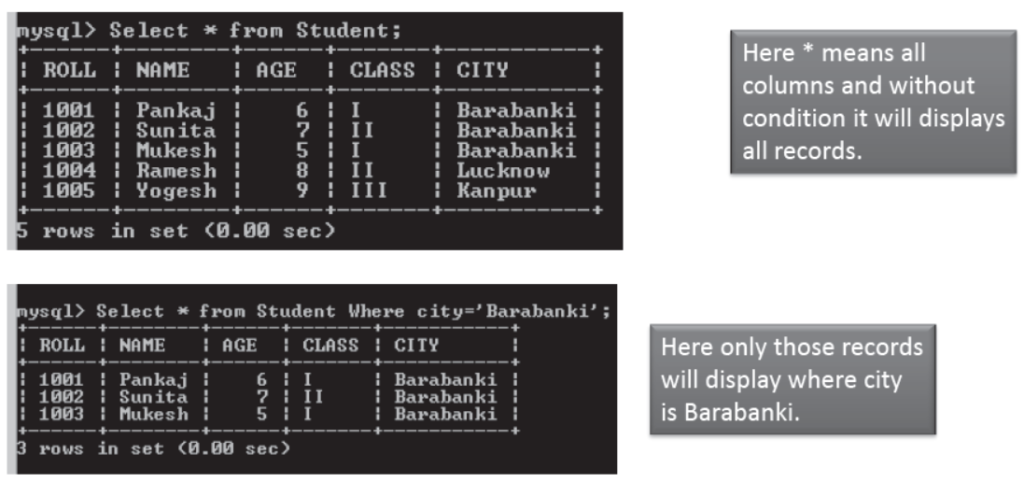
Accessing a Table
Syntax to access Data from a table is
mysql> SELECT <Col Names> FROM <Table Name>
WHERE <Condition>
Accessing a Table
Syntax to access Data from a table is
mysql> SELECT <Col Names> FROM <Table Name>
WHERE <Condition>

Distinct keyword

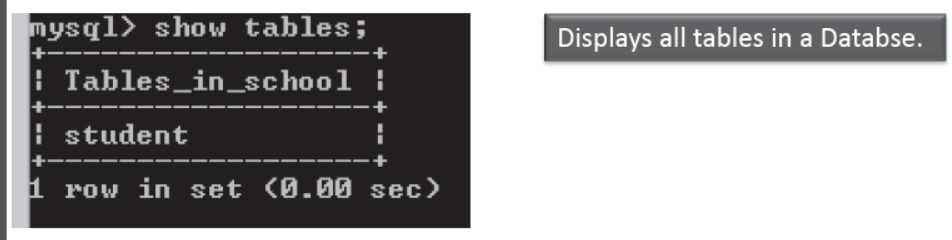
Viewing Tables in a Database
Pattern Matching

In above example all the names starting with ‘S’ are shown.
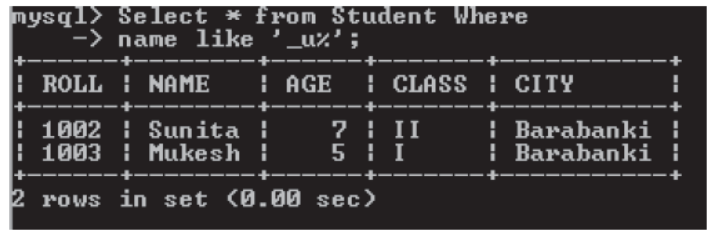
In example given below all the names having ‘u’ as second character are shown.
Creation of Table from another Table
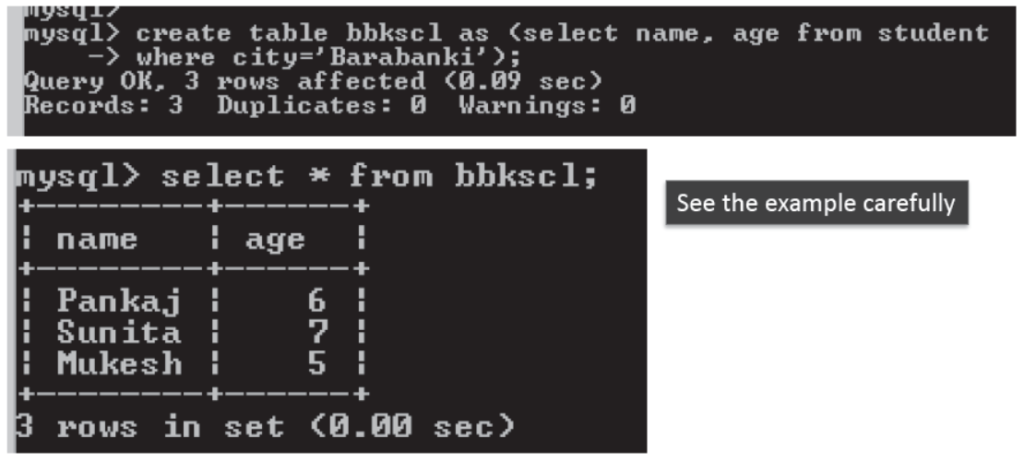
See the example carefully Syntax for creation of a table from another table is –
mysql>CREATE TABLE <TableName>
AS (SELECT <Cols> FROM <ExistingTable>
WHERE <Condition>);
Other SQL Commands
- Select * from Student where city in (‘Jaipur’,’Ajmer’);
- Select * from Student where city Not in (‘Jaipur’,’Ajmer’);
- Select * from Student where age between 5 and 7;
- Select * from Student Order by name DESC ;
- Select 5 * 6 from DUAL ;
- Select avg(age) from student; //Similarly count etc functions


