Notes Chapter 20 Basics of NoSQL Databases MongoDB
Introduction
- Till now we have been working on the databases which were based on SQL consisting of table, row, fields ,records etc.
- It is possibe to have database without any structure or record. NoSQL or Not Only SQL Databases are such databases.
- We will learn NoSQL databases in this chapter.
NoSQL Databases
- These are non-relational databases which does not have any strict or rigid structure.
- These does not store records on the basis of conventional tables.
- These runs in clusters and stores data on the basis of web.
- These are high in scalability. These are also known as bigdata.
- You have worked on several apps/web apps using such databases like Google Mail, Google Earth, Ebay, LinkedIn, facebook, Amazon etc.
- These provides fast response time.
- These can handle data of any kind without any restriction.
- These adopts new features and fast update.
- These does not show down time.
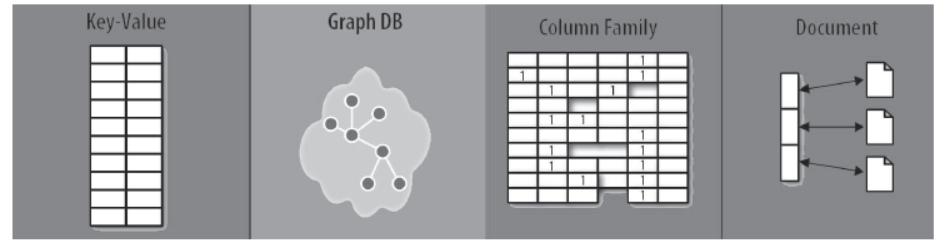
Types of NoSQL Databases
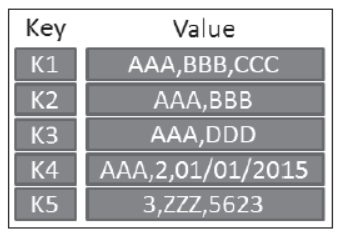
1. Key-value Databases
2. Document Databases
3. Column family stores Databases
4. Graph Databases
Key-Value databases
- Just like python dictionary.
- Very simple and flexible.
- Examples-Cassandra, Amazon DyanmoDB,
ATS (Azure Table Storage, Riak, BerkeleyDB
Document Databases
- These are advanced form of key-value databases.
- Here, key-value pair stores in document in structured or semi-structured form.
- Keys are always of string type, values can be of any type.
- It can be in the form of MS office document, PDFs, XML, JSON ,BSON.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) and BSON (Binary JSON)
- JSON is an open, human & machine understandable standard. Its main format to interchange data on modern web is XML.
- We have learnt use of JSON in Python dictionaries.
- Its examples are – MongoDB, Couch DB DocumentDB etc.

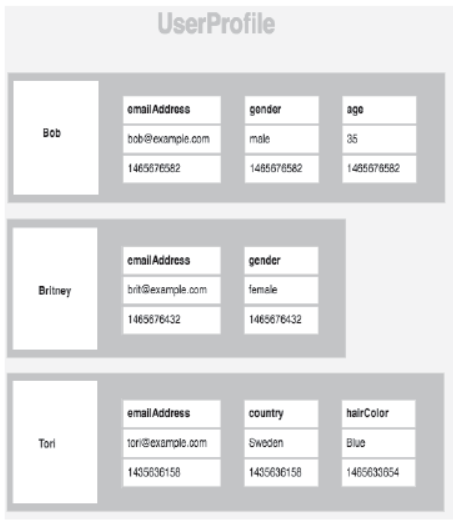
Column Family Store Database
- These are known as column store or column family databases and these are column oriented models.
- Column family is a storage mechanism which can –
- Have multiple rows.
- Each row can have multiple columns.
- In this, there is a row key under which there can be multiple columns as shown in the figure.
- Its examples are- Hbase, Cassandra, HyperTable etc.
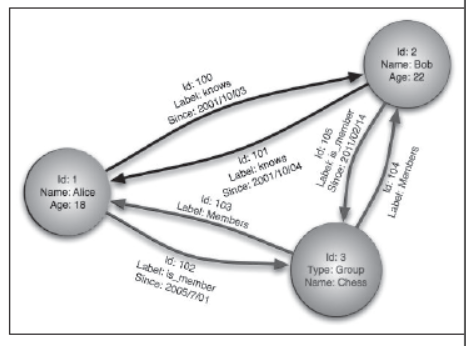
Graph Database
- It uses graphical model to store data.
- Here, nodes are used to show object whereas edges are used to show relation between those nodes.
- Its examples are- Neo4j, Blazegraph, Titan etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NoSQL Databases
Advantages:
- Flexible Data Model These are very flexible database which can store any kind of data.
- Evolving Data Model You can change its schema without downing the system.
- Elastic Scalability Huge database can be stored on a very less cost.
- High Performance Time of throughput and latency is very less.
- Open Source It is available free of cost and you can change it as per yor requirement.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Standardization No standard rules are there for NoSQL database.
- Backup of Database Main problem with NoSQL databases is of backup. MongoDB provides tool for backup but it is also not up to the mark.
- Consistency NoSQL database does not think about consistency. Means here, you can have duplicate data very easily.
Working with MongoDB
- MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database.
- It supports dynamic schemas which shws data in JSON format.
- It is a free open source software which gives scalability and high performance.
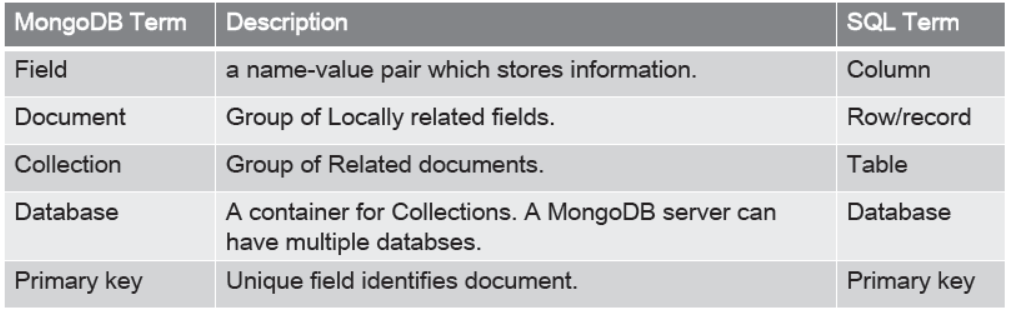
MongoDB Terminology
Installing MongoDB
Copy the following link and paste in browser.
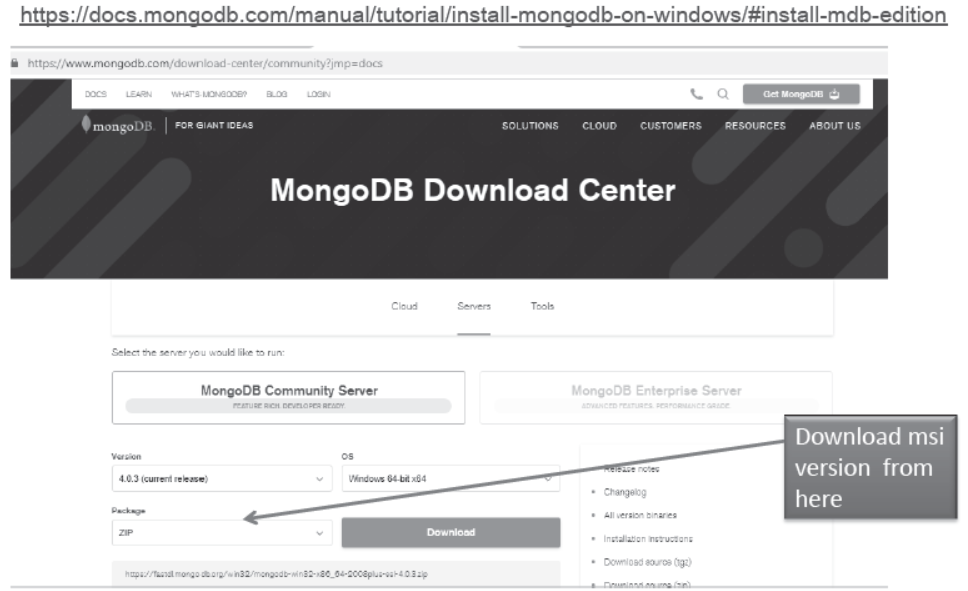
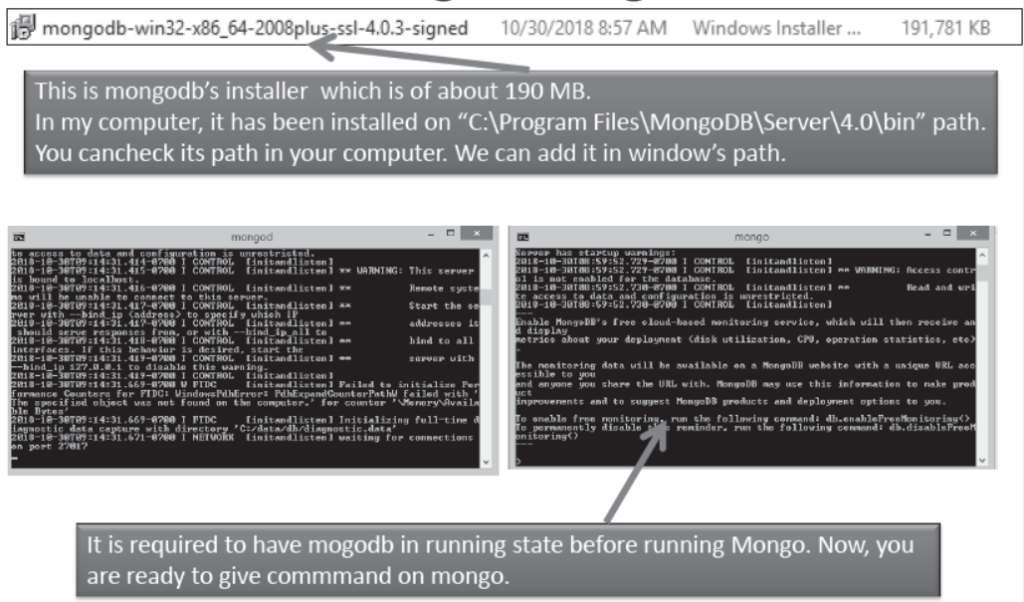
Installation of MongoDB
- Install MongoDB by opeing MSI file.
- After installation, check the availability of mongodb.exe file and mongo.exe file using following path-
- C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\4.0\bin
- After this, create a data folder on c:\ and db folder under data folder i.e. “c:\data\db”.
- Now, run mongodb by using the location C:\Program
- Files\MongoDB\Server\4.0\bin from command prompt.
- Do not close mongodb after run.
- Now, in other command window run mongo using the same path.
Starting MongoDB
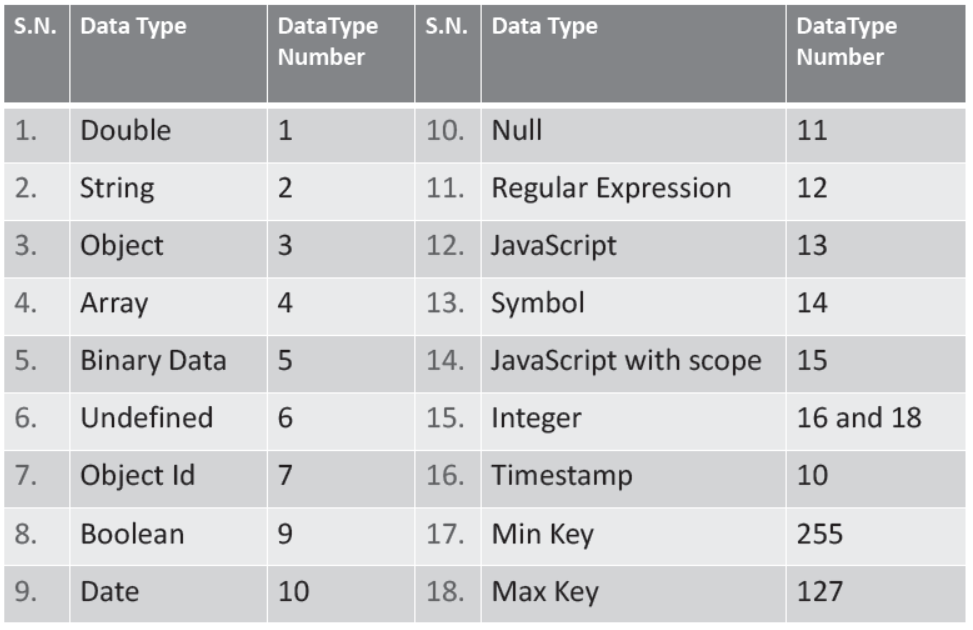
MongoDB Data Types
MongoDB – Basic commands
- Creation of Database →
It is not required to create seperate database in MongoDB. As soon as you insert first information n database, database automaticaly created. - Displaying Current Database→
>show dbs it shows database
>show collections it shows collections of current database - Using Database→
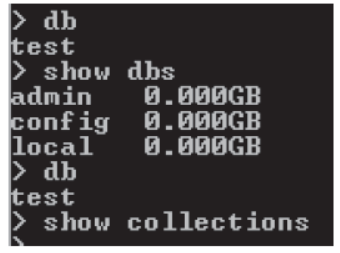
- >use mydb
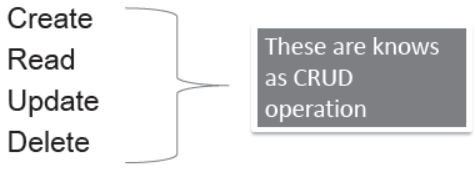
- CRUD operations →
The operations are as under –
MongoDB – Basic commands
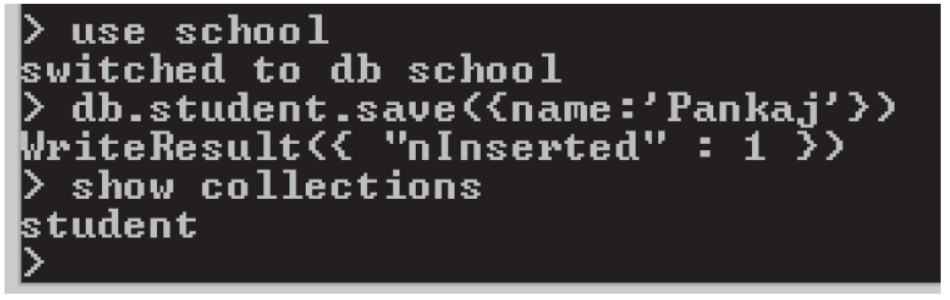
- Creation of databse using Save operation →
It is not required to create seperate database in MongoDB. As soon as you insert first information n database, database automaticaly created. - You can input data in collection by save or insert commanddb.< collection-name>.save({<document details>})
- We can use show collections command to confirm creation of collection.
- >USE <DatabaseName> can also be used to create database
- Following example shows creation of school database and input of 1 collection.
MongoDB – Basic commands
- Creation of databse using Save operation→
- We can insert multiple document like —
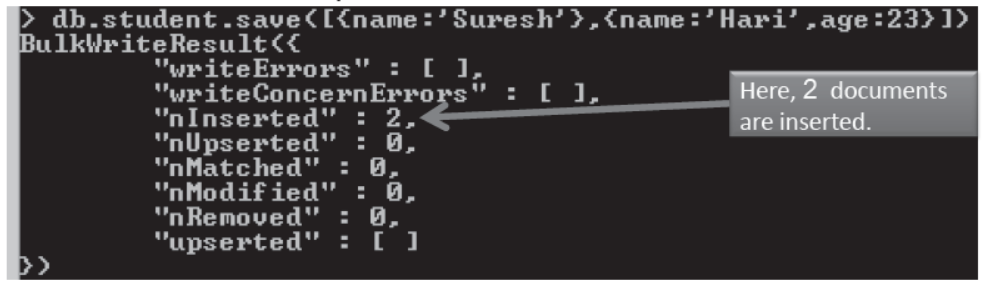
- When you insert a document, mongoDB adds a field itself “_id” it sets its value in increasing order. This process is not visible to us. If we desire, we can give value of “_id” at the time of insertion.
- If you insert a document using Save or insert and name is not received from given database or collection then mongoDB creates a new database for it.
MongoDB -Basic commands
- Creation of database from Insert operation→
- You can insert data in collection using insert commanddb.< collection-name>.insert({<document details>})
- We can use show collections command to confirm creation of collection.
- Following example shows creation of school database and input of 1 collection.
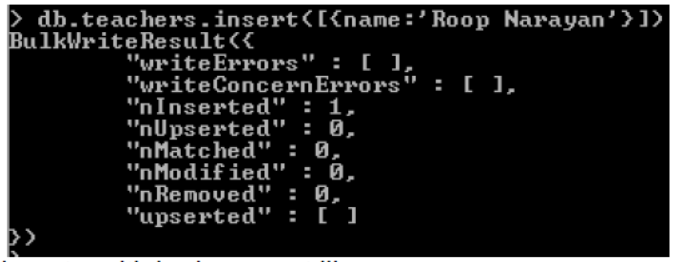
- We can insert multiple document like
- >db.teachers.insertMany([{name:’Ratan’},{name:’Krishna’,age:45}])
MongoDB -Basic commands
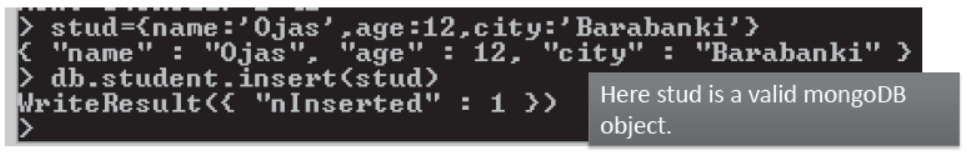
- Document can also be inserted by object creation.
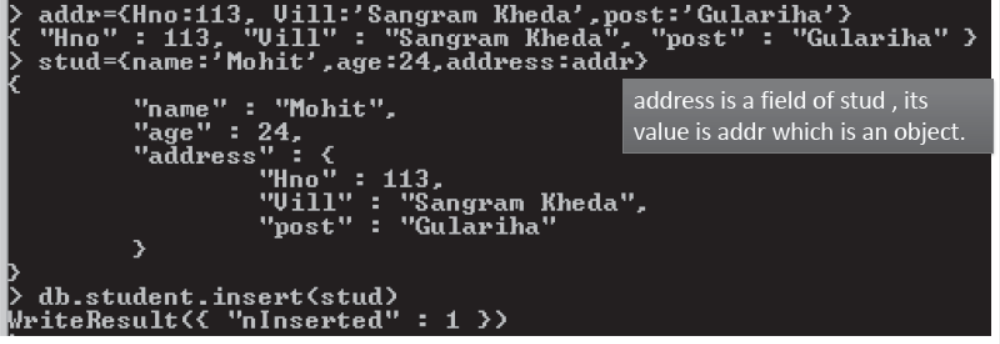
- An object can have a field which is an object itself.
MongoDB -Basic commands
An Object can have arrays too. For ex –
Name: Himanshu
Class:11
Section: A
Subjects: English, Hindi, Maths, Physics, Chemistry
Here subject is an array
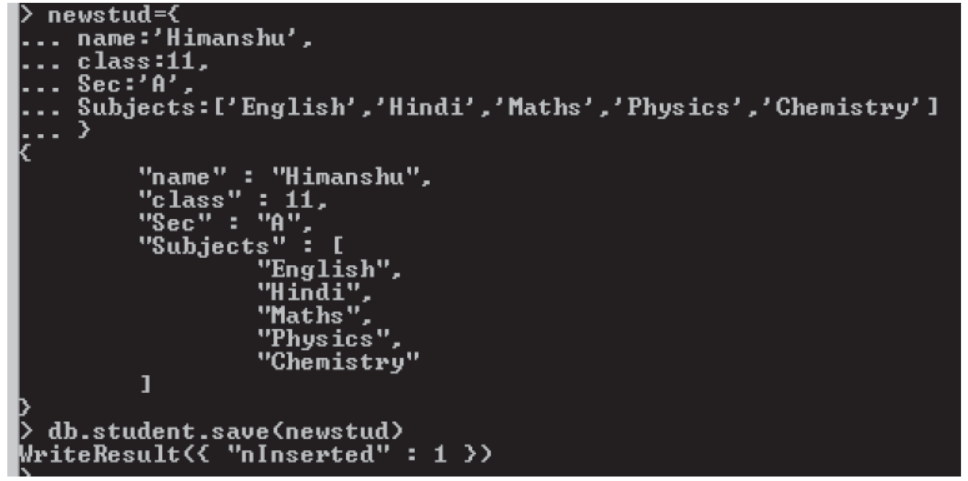
MongoDB -Basic commands
Read Operation:
Read operation is used access documents from collection of database.
Syntax is-
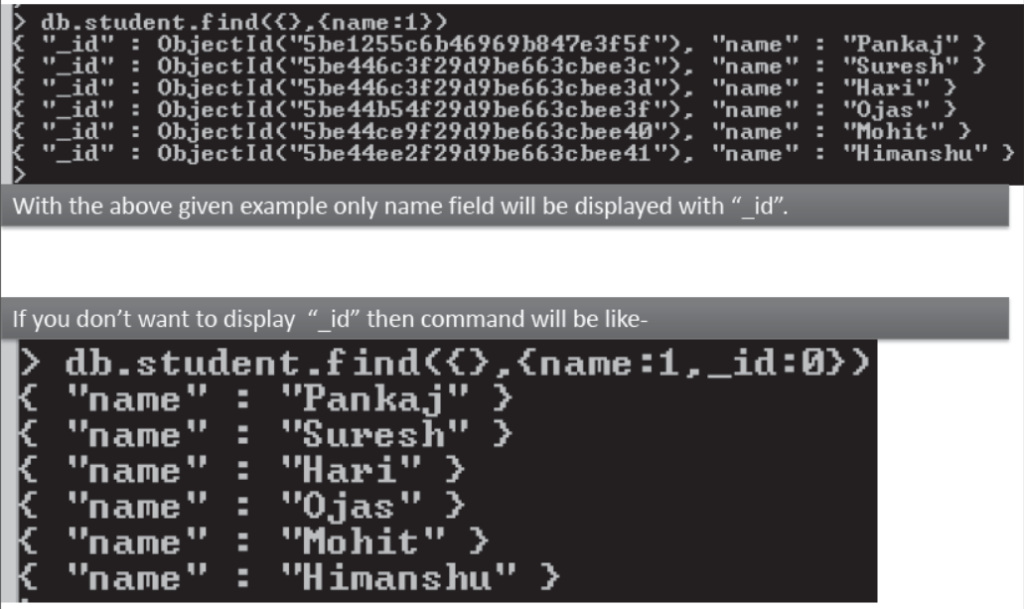
>db.<collection-name>.find() will show all documents of collection.
>db.<collection-name>.findOne() will show only one record.
>db.<collection-name>.findOne({<key>:<value>}) it will work like search criteria.

MongoDB -Basic commands
•Read Operation:

MongoDB -Basic commands
•Read Operation:
MongoDB -Basic Operators
•Comparison Operator:
Like other databases, mongoDB also provides operators so that we can perform delete, read or update operations.
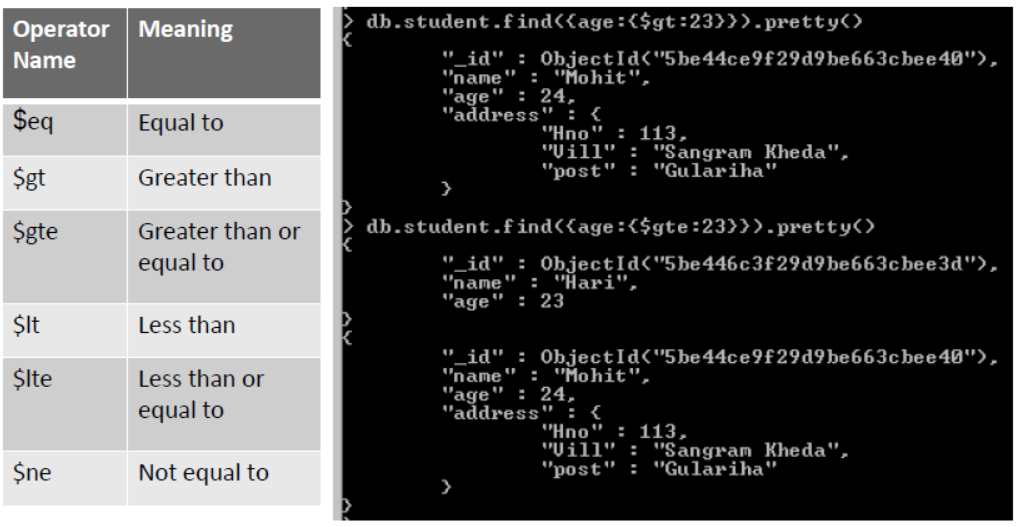
MongoDB-Basic Operators
•Comparision Operator:
Conditional base or range is to be given as-
{field:{$gte:<lower value>, $lte:<upper value>}}
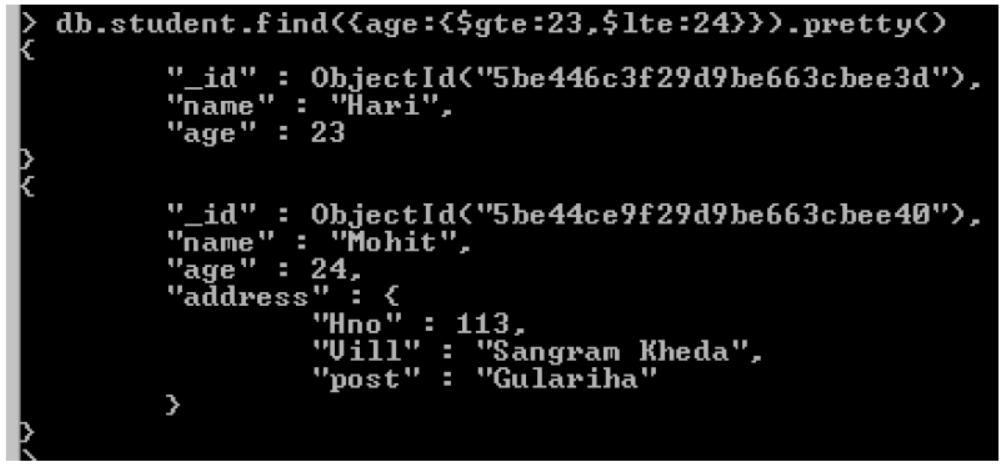
MongoDB -Basic Operators
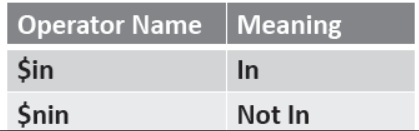
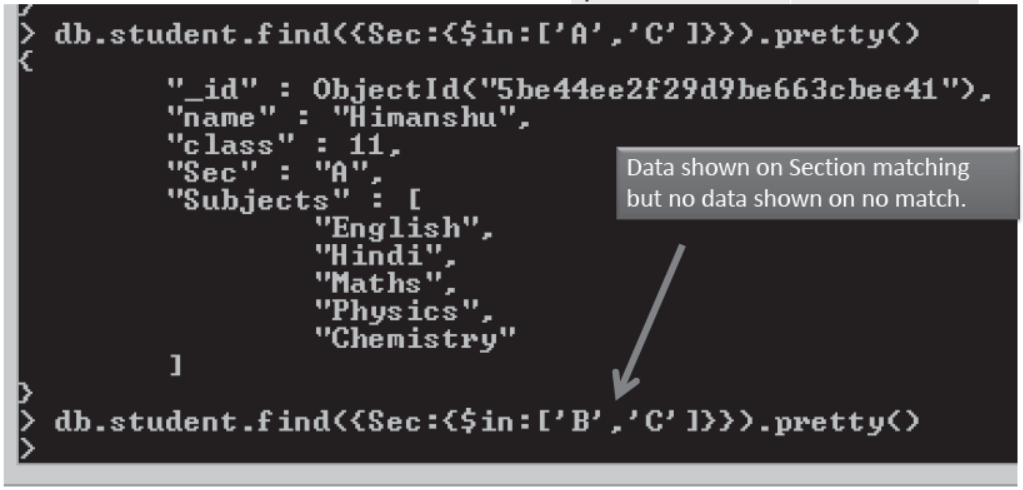
•Condition based on List/Array
{ field :{ $in : [ val1,val2, . . . . . ] } }
{ field :{ $nin : [ val1,val2, . . . . . ] } }
MongoDB-Basic Operators
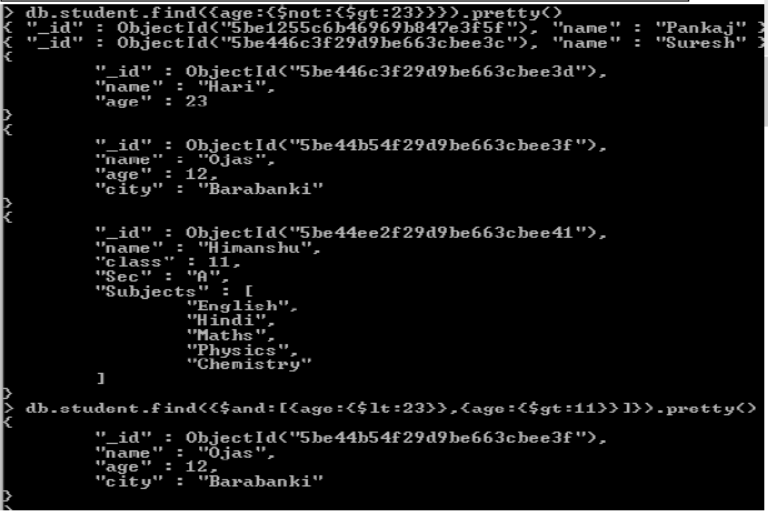
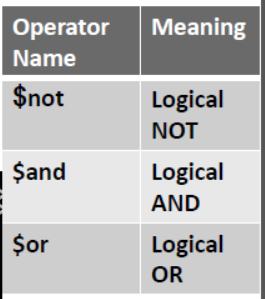
•Logical Query Operators
{ field :{ $not :{<op-Exp>}} }
{ field :{ $and :[{<op-Exp>}, {<op-Exp>},..]} }
{ field :{ $or :[{<op-Exp>}, {<op-Exp>},..]} }
Update Operation:
Update operation can be used in two ways-
>update/updateOne or >updateMany ($set operator is used with it)

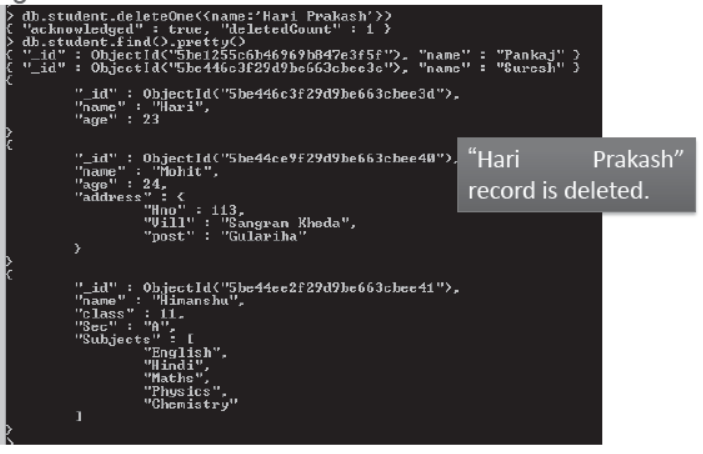
Delete Operation:
Delete operation can be used in two ways-
>deleteOne or >deleteMany
>db.<CollectionName>.deleteOne({<filter Exp>}) it will delete only one record even on multiple matching.
>db.<CollectionName>.deleteMany({<filter Exp>}) it will delete multiple records on multiple matching.