Notes Chapter 5 Organising
Class 12 students can refer to Chapter 5 Organising notes given below which is an important chapter in the class 12 Business Studies book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Business Studies teachers has prepared these notes for class 12 Business Studies for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Organising Notes Class 12 Business Studies
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Organising which is really useful and has been recommended by Class 12 Business Studies teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books.
Organising: Concept and importance , Organising Process , Structure of organisation-functional and divisional, Delegation: concept, elements and importance, Decentralization: concept and importance.
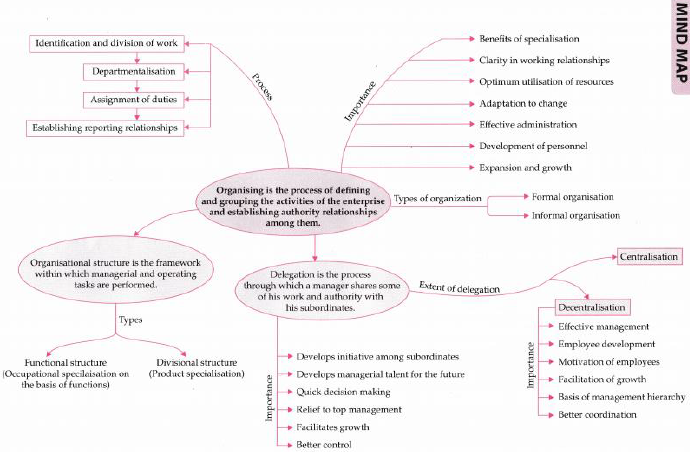
Organising is the process of defining and grouping the activities of the enterprise and establishing authority relationships among them for the realisation of the desired goals. “Hierarchy is the ranking of job positions on the basis of relative roles and responsibilities.”
Steps Involved in the Process of Organizing
♦ Identification and division of work is done in accordance with predetermined plans to avoid duplication of activities and ensure that the burden of work is being shared among the employees.
♦ Departmentalisation involves grouping of similar activities into departments, units, sections etc. using several criteria as a basis to facilitate specialization.
♦ Assignment of duties is done to the members as per their job positions. Once departments have been created, each of them is placed under the charge of an individual.
♦ Establishing reporting relationships While assigning jobs, each member is told that from whom he/she has to take orders and to whom he/she will be accountable. The establishment of such clear reporting relationships help to create a well defined hierarchical structure.
Importance of Organising
♦ Organising offers benefits of specialisation as it leads to a systematic allocation of jobs amongst the workforce as the specific employees are assigned specific job on a regular basis.
♦ It brings clarity in working relationships by establishing a hierarchical order thereby enabling the fixation of responsibility and specification of the extent of authority to be exercised by an individual.
♦ It leads to optimum utilisation of resources through proper allocation of jobs, and minimising the wastage of resources and efforts.
♦ It facilitates adaptation to change and helps to create a stable organisation by incorporating changes in the organisation structure as per the needs of the changing environment.
♦ It leads to effective administration by providing a clear description of jobs and related duties which helps to avoid confusion and duplication.
♦ It fosters development of personnel as delegation helps to build the ability of the subordinate to deal effectively with challenges and helps them to realise their full potential.
♦ It leads to expansion and growth of an enterprise by enabling it to deviate from existing norms and taking up new challenges.
The organisational structure can be defined as the framework within which managerial and operating tasks are performed.
Types of Organisational Structures
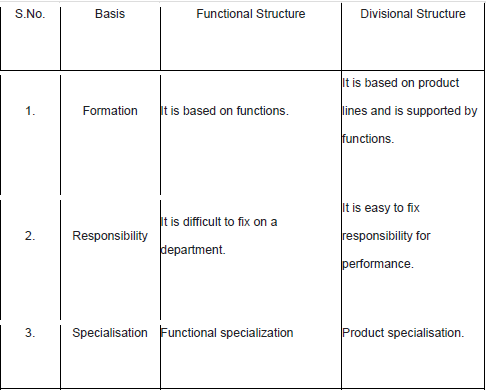
1. Functional Structure
2. Divisional Structure
Features of Functional Structure
♦ A functional structure is an organisational design that groups similar or related jobs together on the basis of functions like production, finance etc.
♦ Each department hasa functional manager responsible for performance and who has authority over the department.
♦ All departments are under the charge of a coordinating head.
♦ These departments may be further divided into sections.
Features of Divisional Structure
♦ A divisional structure is an organisational design that groups similar or related jobs together on the basis of functions. Different products manufactured in the organisation. Structure comprise of separate business units or divisions.
♦ Each department hasa divisional manager responsible for the profit or loss of his division.
♦ Each division is multi-functional because within each division functions like production, marketing, finance, purchase etc., are performed together to achieve a common goal.
Advantages of Functional Structure
♦ A functional structure emphasises on specific functions and ensures that different functions get due attention.
♦ Due to the similarity in the tasks being performed, it promotes control and coordination within a department.
♦ It results in increased profit with the improvement in managerial and operational efficiency.
♦ By focusing only on a limited range of skills, it facilitates the training of employees.
♦ It leads to minimal duplication of effort and leads to economies of scale thereby reducing cost.
Advantages of Divisional Structure
♦ Product specialisation helps a divisional manager to gain experience in all functions related to a particular product and this prepares him for higher positions.
♦ It providesa proper basis for performance measurement and also helps in fixation of responsibility in cases of poor performance of the division as revenues and costs related to different departments can be easily identified.
♦ It leads to faster decision making, promotes flexibility and initiative because each division functions as an autonomous unit.
♦ It facilitates expansion and growth as new divisions can be added just by adding another divisional head and staff for the new product line without interrupting the existing operations
Disadvantages of Functional Structure
♦ It gives less emphasis to overall enterprise objectives than the objectives pursued by a functional head.
♦ It may lead to problems in coordination.
♦ It may lead to conflict of interests if two or more departments are not compatible.
♦ It may lead to inflexibility as the functional heads do not get training and experience in diverse areas.
Disadvantages of Divisional Structure
♦ There may be conflicts among the different division heads, as in pursuit of higher profits, each of them may seek maximum allocation of resources at the cost of other divisions.
♦ The cost is high as each division is provided with separate set of similar functions.
♦ It provides the managers with the authority to supervise all activities related to a particular division. In course of time, such a manager may gain power and in a bid to assert his independence may ignore organisational interests.

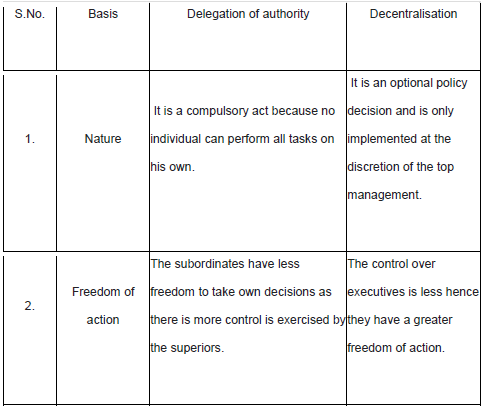
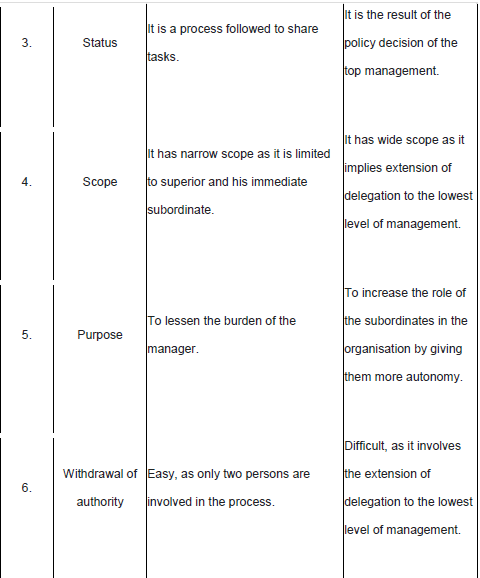
Delegation of Authority: Definition
Delegation of authority merely means the granting of authority to subordinates to
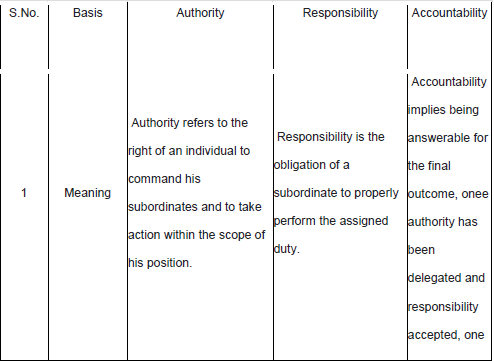
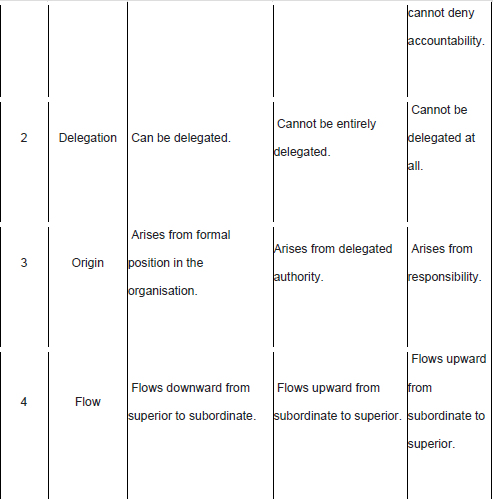
Elements Of Delegation
1. Authority
2. Responsibility
3. Accountability.
Importance of Delegation
♦ It leads to effective management as by relieving the employees from doing routine work, it provides them with time to excel in new areas.
♦ It promotes employee development as they are entrusted with more opportunities to utilise their talent, perform complex tasks and assume those responsibilities which are likely to improve their career prospects.
♦ It helps to motivate employees as when a subordinate is entrusted with a task, it is not merely the sharing of work but involves trust on the superior’s part and commitment on the part of the subordinate.
♦ It facilitates the growth of an organisation as it seeks to enrich the quality of manpower and widens the scope of using internal recruitment by providing them with training and experience through exposure to varied jobs.
♦ It provides the basis of management hierarchy as it establishes superior-subordinate relationships, which are the basis of hierarchy of management
♦ It facilitates better coordination amongst the departments, levels and functions of management by providing clarity in reporting relationships.
Decentralisation: Definition
Decentralisation refers to systematic dispersal of authority to the lowest level, except that which can be exercised at central points.
Need for Decentralisation
As an organisation grows in size and complexity, the departmental or branch heads are directly and closely involved with certain operations and are likely to have more knowledge about them as compared to the top management which may be associated with individual operations only indirectly.
Importance of Decentralisation
♦ It seeks to develop initiative in the subordinates by promoting self-reliance and confidence amongst them and also helps to identify those executives who have the necessary potential to become dynamic leaders.
♦ It provides relief to top management as the subordinates are allowed to operate independently within their area of jurisdiction. Consequently, the need for direct supervision is reduced.
♦ It facilitates quick decision making as the employees are allowed to act independently within their are a of jurisdiction without consulting others.
♦ It develops managerial talent for the future by providing the employees with the necessary training and experience through exposure to varied challenging jobs and also facilitates identification of those employees who may and those who may not be successful in assuming greater responsibility.
♦ It facilitates growth of the organisation by increasing its productivity and profitability through assigning greater autonomy to the lower levels of management as well as divisional or departmental heads.
♦ It facilitates better control by ensuring continuous evaluation of performance at each level and the contribution of each department so that they can be individually held accountable for their results.
MIND MAP