Notes for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement
Students can refer to Notes for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement given below. These notes have been prepared keeping into consideration the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE and NCERT. Class 11 Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement Notes is important to understand the topic and solve all questions given in DK Goel Class 11 Textbook
Unit at a Glance:
• Introduction
• Meaning of B.R.S.
• Causes of Differences in Bank Balance as per Cash Book and Pass Book.
• Importance of Bank Reconciliation Statement.
• Procedure of preparation of B.R.S.
• Preparation of Adjusted Cash Book.
INTRODUCTION
Usually all the firms open a current account with the bank as there are so many transactions and record these transactions in the Bank column of the Cash Book. Bank also maintains a separate ledger account of each firm (customer) and periodically supplies a copy of the account to the firm for information. This copy of the firm’s A ccount supplied by the bank is known as Bank Statement or Bank Pass Book.
Since all the transactions with the bank are entered in both the books Cash Book and Pass Book, the balances of the two books should tally with each other. But usually the two balances don’t tally.
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared to reconcile the difference between the Bank Balance shown by the Cash Book and Bank Pass Book.
DEFINITION
A schedule showing the items of difference between the bank statement and the bank column of
Cash Book is known as Bank Reconciliation Statement.
CAUSES OF DIFFERENCES IN CASH BOOK AND PASS BOOK
The differences may be caused by either
A. Time gap in recording transactions or
B. Errors Committed in recording transactions.
(A) Differences Caused by the time gap:-
Reasons for the time gap in recording the transactions in the two books (Cash Book and Pass Book) are as given below-
(1) Cheques issued but not yet presented for payment in the bank.
(2) Cheques deposited or paid into the bank for collection but not yet credited by the bank.
(3) Cheques deposited but dishonoured by the bank.
(4) Interest allowed by the bank.
(5) Interest on overdraft, bank charges, commission etc. charged by the bank.
(6) Direct Deposit by the customers into the bank.
(7) Interest, Dividend etc. collected by the bank.
(8) Direct payments made by the bank on behalf of customer as per standing instruction.
(B) Differences caused by Errors Committed
Such errors may be of two types
(1) Errors committed by the firm
(i) Cheques issued to some creditors but omitted to be recorded in the Cash Book or recorded twice.
(ii) Cheques deposited into the bank omitted to be entered in the Cash Book or recorded twice.
(iii) Error in totaling or balancing the bank column of the Cash Book.
(2) Errors committed by the bank
Sometimes bank records a wrong entry in the customer’s account which causes a difference in the two balances.
NEED AND IMPORTANCE
• It helps in locating and rectifying the errors or omissions committed either by the firm or by the bank.
• Customer becomes sure of the correctness of the bank balance shown by the cash book.
• Facilitates the preparation of amended or revised Cash Book.
• Reduces the chances of fraud by the staff of the firm or bank.
• Helps in keeping a track of the cheques deposited for collection.
Procedure of Preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement
A Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared when we get the duly completed Pass Book from the Bank. On receiving the Cash Book
(1) First of all tally the Debit side entries of the cash book with the Credit side entries of the Pass Book and vice versa.
(2) Tick the items appearing in both the books.
(3) Un ticked items will be the points of differences.
(4) A BRS is then prepared by taking either the balance as per Cash Book or Pass Book as a starting point.
Important Points to Remember:-
(1) If the Starting point is Cash Book Balance then the ending point will be Pass Book Balance.
(2) If the starting point is Pass Book Balance then the ending point will be the Balance as per Cash Book.
(3) Debit Balance as per Cash Book or Credit Balance as per Pass Book, means that the firm has that much amount of deposited at the bank also called favorable balance write the amount under (+) item.
(4) Credit Balance as per Cash Book or Debit Balance as per Pass Book, means that this much amount has been withdrawn in excess of deposit also called over-draft or unfavorable balance write the amount under (-) item.
Method of Preparing BRS Starting with by the Balance / overdraft as per Bank Column of Cash Book.

Note : To get more from less means something is to be added therefore + item & To get less from more, something is to be deducted therefore _ item.
1. First of all write
Under Plus Item – If the Cash Book Balance is debit or favorable or simple balance.
Under Minus Item – If the Credit Balance or overdraft as per Cash Book is given.
2. Now study the point of difference.
(a) If the entry is done in the Cash Book and not in the Pass Book then .
(i) if it is done on the debit side of Cash Book, Balance in the Cash Book will be more as compared to Pass Book and hence the item will be(–) item as shown in the box above.
(ii) where as if the entry is done on the Credit side of Cash Book, the Balance in the Cash Book will be less as compared to Pass Book and hence the item will be (+) item.
(b) If the entry is done in the Pass Book and not in the Cash Book then.
(i) if done on the Credit side of Pass Book –
Pass Book Balance is more as compared to Cash Book (–) item.
(ii) It it is done on the Debit side of Pass Book –
Pass Book Balance is less as compared to Cash Book (–) item
3. At the end + items and – items are totaled.
(a) If total of Plus Items is more than the total of (–) items Difference is Cr Balance or favorable balance as per Pass Book.
(b) Whereas if the – items total is more than the (+) items total Difference is Dr Balance or overdraft as per Pass Book.
Ready Reference
(+) Items (Items which increases the Pass Book Balances or decreases the Cash Book Balance)
(1) Cheques issued but not yet presented.
(2) Credits made by the bank for Interest.
(3) Amount directly deposited by the customers in our bank A/c.
(4) Interest and dividend collected by the bank.
(5) Cheques paid into the bank but omitted to be recorded in the Cash Book.
(–) Items (Items which, decreases the Pass Book Balance or increase the Cash Book
Balance)
- Cheques sent to the bank for collection but not yet credited by the bank.
- Cheques paid into the bank but dishonoured.
- Direct payments made by the bank.
- Bank charges, commission etc. debited by the bank.
- Cheqes issued but omitted to be recorded in the Cash Book.
Illusration: Balance as per Cash Book is given
Prepare BRS as on 31st July 2011
(1) Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 25,000 as on 31st July 2011.
(2) Cheques for Rs. 15,000 were deposited into the Bank in the month of July but only cheques for Rs.11,000 were credited by the bank till 31st July 2011.
(3) Cheues issued for Rs. 13,000 in July, out of which a cheque for Rs. 3,800 was presented for payment on 3rd August.
(4) Bank charged Rs. 50 as Bank charges and credited interest of Rs. 370.
(5) A customer directly deposited Rs. 1,550 in firm’s bank A/c.
(6) Bank paid the Insurance Premium of Rs. 1,200 as per standing instructions on 25.07.2011.
SOLUTION:-

Explanation :
(1) Balance per Cash Book means favourable Balance, hence + item. If nothing b(i.e. Debit or Credit) is written with the Balance given, it is treated as favourable.
(2) Cheques were deposited into the bank for Rs. 15,000 but credited by the bank for Rs. 11,000 in the month of July, implies that cheques for Rs. 4,000 (15,000– 11,000) are entered in the Cash Book but not in the Pass Book increasing the Cash Book Balance by Rs. 4,000 as compared to Pass Book. Hence to get Pass Book Balance from the Cash Book Balance Rs. 4,000 will have to be deducted. – item
(3) Cheque issued but not presented for payment till 31st July is for Rs. 3800 entered more on the credit side of Cash Book as compared to Pass Book.
Cash book Balance is less by Rs. 3800 as compared to Pass Book (+) item.
(4) (a) Bank charges of Rs. 50 entered in the Pass Book decreases the Balance of Pass Book. To reach Pass Book Balance from Cash Book Balance, this item has to be deducted i.e. (–) item.
(b) Interest credited by the Bank Rs. 370 entered in Pass Book increases the, balance of Pass Book, hence to search the Balance from cash book and this item is to be added (+) item.
(5) Direct deposit by a customer Rs. 1,550 increases the Pass Book Balance (+ )item.
(6) Payment made by the bank for insurance premium decreases the Pass Book Balance (–) item.
(7) (+) items total Rs. 30,720 is more than( –) item total Rs. 5250 by Rs. 25,470. Hence the difference of Rs. 25,470 will be (+) item i.e. Favaurable Balance or Cr. Balance as per Pass Book.
Illustration:–when overdraft as per Cash Book is given
(1) Overdraft as per Cash Book is Rs. 10,500 on 30th June 2011.
(2) Cheques deposited but not yet collected Rs. 2,000.
(3) Chequs issued but not yet presented for payment of Rs. 2,800.
(4) Bank charges of Rs. 50 and Interest on overdraft of Rs. 250 are charged by the bank.
(5) A customer directly deposited Rs. 1,200 into the Bank.
(6) Insurance Premium of Rs. 1,500 is paid by the bank as per standing instructions. Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement for the month of June 2011.
SOLUTION :

Overdraft means unfavorable balance or Negative Balance Hence put it under –
item.
Explanation for all other items is similar as example 1 except the following.
(1) Item No. 4 (b) – Interest on overdraft decreases the Pass Book Balance hence it is to be deducted from Cash Book Balance to reach at Pass Book Balance item.
(2) This time the total of (–) items Rs. 14,300 is more to the total of + item is Rs. 4,000 by Rs. 10,300.
Hence this is a (–) item or in other words overdraft as per Pass Book.
Case II – Starting with Pass Book Balance / overdraft.

- First of all write under
- Item – If Cr Balance, favaurable balance or Simply Balance as per Pass
Book is given.
(–) Item If Debit Balance or overdraft as per Pass Book is given.
2. Now study the point of difference between the Cash Book and Pass Book.
(a) If the entry is done in the Cash Book and not in the Pass Book then.
(i) If is done on the Debit side of Cash Book Balance in the Cash will be more as compared to Pass Book and hence the item is to be added in the Pass Book Balance to get the Cash Book Balance i.e. (+) item.
(ii) Where as if the entry is done on the Credit side of Cash Book Cash Book Balance will be less as compared to Pass Book hence (–) item
(b) If the entry is done in the Pass Book and not in the Cash Book then.
(i) if it is done on the Debit side of Pass Book Pass Book Balance is less as compared
to Cash Book item is to be added in Pass Book Balance to get the Cash Book Balance + item.
(ii) if is done on the Credit side of Pass Book Pass Book Balance is more as compare
to Cash Book item. (–) item
3.At the end + item and – item are totalled
(a) If total of (+) items is more than the total of (–) ⇒ Differences is favourable Balance or Debit Balance as per Cash Book .
(b) Where as if the total of (–) items is more than the total of + items ⇒Difference is Dr Balance or overdraft as per Pass Book.
Difference is unfavourable or overdraft as per Cash Book.
Ready Reference
(+) Items [items which increases the Cash Book Balances or decreases the Pass Book Balance]
1) Cheques sent for collection to the bank but not yet credited / collected by the bank.
2) Cheques deposited into the bank but dishonoured.
3) Direct Payments made by the bank.
4) Bank charge, commission etc. debited by the bank.
5) Cheques issued but omitted to be recorded in the Cash Book.
(–) Item [Items which decreases the Cash Book Balance or increases the Pass Book
Balance]
(1) Cheques issued but not yet presented.
(2) Credits made by the bank for interest.
(3) Amount directly deposited by the customers into the Bank.
(4) Interest and dividend collected by the Bank.
(5) Cheques paid into the bank but omitted to be recorded in the Cash Book.
Illusration: Balance as per Pass Book is given
Given (1) Balance as per Pass Book is Rs. 25,470 Point No. (2) to (6) are same as given in example (1)
Prepare B.R. Statement for the month of July 2011.
SOLUTION :

Important Points –
• Starting and Ending Points are reversed as compared to Example No. 1, Hence + items and (–) items are interchanged.
• Favourable balance whether of Cash Book or Pass Book is always a + item.
• If + items total is more than the – items total then the difference in the two totals is always a 60 favourable balance.
• where as if + items total is less than the – items total then the difference in the two totals is
overdraft.
E xample:- 4 – Overdraft as per Pass Book is given.
Given that (1) Overdraft as per Pass Book is Rs. 10,300 Rest of the contents (points 2 to 6) are same as given in example No. 2
Prepare B.R. Statement for the month of June 2011.
SOLUTION

Important Points –
1. Overdraft whether as per Cash Book or Pass Book is always a (–) items.
2. Starting and Ending points are interchanged as compared to Example No. 2, hence + items and (–)
are also interchanged.
3. Here (–) items total is more as compared to (+) items total, therefore the difference in the two
balance is a negative items i.e. overdraft as per Cash Book.
Amended Cash Book Method:-
Introduction : So far we have studied the preparation Bank Reconcilliation State-ment simply by
reconciling the causes of differences between the Cash Book and Pass Book. In actual practice
adjustments are done in the Cash Book by comparing the Bank column of Cash Book with the Bank
S tatement and after that B.R. Statement is prepared. It is called Amended Cash Book Method.
Procedure
1) Adjusted Cash Book is prepared starting with the Balance of the Cash Book given in the question.
2) All errors that have been committed in the Cash Book will have to be rectified by passing adjusting entries in the Cash Book.
Usual or General Errors are
(a) Overcasting or Undercasting of Debit / Credit Column of Cash Book.
(b) Cheques deposited or Issued but omitted to be entered in the Cash Book.
(c) Incorrect amount (if any) entered in the Cash Book.
(d) Entries on the incorrect side or in the wrong column of Cash Book. (e)
(e) Any amount recorded twice in the Cash Book.
(3) Certain amounts for which Bank has debited our A/c will be recorded on the Credit side
of Cash Book. Such items are
(a) Interest charged by the bank on overdraft etc.
(b) Debits made by the bank for the bank charges, commission etc.
(c) Direct payments made by the Bank on behalf of the A/c holder.
(d) Cheques sent for collection but dishonoured by the bank.
(4) Cash Book is then balanced and the new Balance of the Cash Book is taken as the Starting point
for preparing the B.R. Statement.

Illusration:
The Cash Book of Mr. Sharma showed a balance of Rs. 3,560 as on 31st Dec. 2010 at the Bank
where as Pass Book showed a balance of Rs. 4,230 Comparison of the Cash Book and Pass Book
revealed the following.
(1) The Bank has debited Mr. Sharma with Rs. 460, the annual premium of his life policy according
to his standing instructions and Rs. 20 as Bank charges.
(2) Mr. Sharma paid into the Bank cheques totaling Rs. 3,100 on Dec. 26th 2010 of which those for
Rs. 2,500 were collected in December. One cheque for Rs. 200 was returned deshonoured on 2nd
Jan. 2011.
(3) The Bank has credited Mr. Sharma by Rs. 1,600, the proceeds of a bill.
(4) Cash collected on 31st Dec. 2010 totaling Rs. 850 was entered in the Cash Book in the Bank
column on the same date but banked on 2.1.2011.
(5) Mr. Sharma issued cheques totaling Rs. 2,300 in the month of Dec. out of which cheques for Rs.
1000 have not been presented for payment till 31st Dec.
SOLUTION:-
A mended Cash Book (Bank Column only) as on 31st Dec. 2010

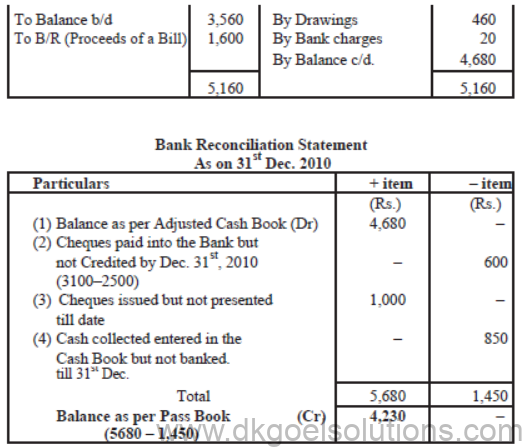
GENERALLY STUDENTS COMMIT MISTAKES PLEASE AVOID:
Amended or adjusted Cash Book is started with the given balance of bank as per Cash Book.
Closing Balance of the adjusted Cash Book is the opening balance of Bank Reconciliation
statement.
Entry for the dishouner of the cheques of Rs. 200 is not done.
- In the Cash Book as it was dishonoured after 31st Dec.
- In Bank Reconciliation Statement it is included in the adjustment (Rs. 3100– 2500)
QUESTIONS
Q.(1) Give journal entries of M/s Krutagna traders, Post them to the Ledger from the following
transactions and prepare a Trial Balance :

Q. (2) Journalise the following transactions in the Books of M/s Bhuj traders. Also post them in the
ledger and prepare a Trial Balance.
Bank Reconciliation Statement
Q.(1) The cash book shows a bank balance of Rs. 7,800. On comparing the cash book with
passbook the following discrepancies were noted :
(a) Cheque deposited in bank but not credited Rs. 3,000
(b) Cheque issued but not yet present for payment Rs. 1,500
(c) Insurance premium paid by the bank Rs. 2,000
(d) Bank interest credit by the bank Rs. 400
(e) Bank charges Rs. 100
(d) Directly deposited by a customer Rs. 4,000
(Ans: Balance as per passbook Rs. 8,600).
Q.(2) The passbook of Mr. Mohit current account showed a credit Balance of Rs. 20,000 on
dated December 31, 2005. Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement with the following
information.
(i) A cheque of Rs. 400 drawn on his saving account has been shown on current account.
(ii) He issued two cheques of Rs. 300 and Rs. 500 on of December 25, but only the first cheque was presented for payment.
(iii) One cheque issued by Mr. Mohit of Rs. 500 on December 25, but it was not presented for payment whereas it was recorded twice in the cash book.
(Ans: Balance as per cash book Rs. 18,900).
Q.(3) Prepare bank reconciliation statement.
(i) Overdraft shown as per cash book on December 31, 2005 Rs. 10,000.
(ii) Bank charges for the above period also debited in the passbook Rs. 100.
(iii) Interest on overdraft for six months ending December 31, 2005 Rs. 380 debited in the passbook.
(iv) Cheques issued but not in cashed prior to December 31, 2005 amounted to Rs. 2,150.
(v) Interest on Investment collected by the bank and credited in the passbook Rs. 600.
(vi) Cheques paid into bank but not cleared before December, 31 2005 were Rs.1,100.
(Ans: overdraft as per passbook Rs. 8,830).

