Notes for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange
Students can refer to Notes for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange given below. These notes have been prepared keeping into consideration the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE and NCERT. Class 11 Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange Notes is important to understand the topic and solve all questions given in DK Goel Class 11 Textbook
Unit at a Glance:
• Introduction.
• Definition of a Bill of Exchange
• Features of a Bill of Exchange
• Parties to a Bill of Exchange
• Advantages of Bill of Exchange
• Promissory note
• Features of a promissory note
• Parties to a promissory note
• Distinction between bills of exchange and promissory note
• Important terms
• Accounting treatment of bill transactions
• Generally students commit mistakes please avoid it
• Questions
“Bills of Exchange are instrument of credit which facilitate the credit sale of goods.”
INTRODUCTION
A Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note both are legal Instruments which facilitate the credit
sale of goods by assuring the seller that the amount will be recovered after a certain period. Both of
these are legal instruments under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881.
BILL OF EXCHANGE
“A Bill of Exchange is an instrument in writing containing an unconditional order signed by the
maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of, a certain
person or to the bearer of the instrument.” Section 5 of the Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881.
FEATURES OF A BILL OF EXCHANGE ARE
- 1. A Bill of Exchange must be in writing.
- 2. It must contain an order (and not a request) to make payment.
- 3. The order of payment must be unconditional .
- 4. The amount of bill of exchange must be certain.
- 5. The date of payment should be certain.
- 6. It must be signed by the drawer of the bill.
- 7. It must be accepted by the drawee by signing on it.
- 8. The amount specified in the bill of exchange is payable either on demand or on the expiry of a fixed period.
- 9. The amount specified in the bill is payable either to a certain person or to his order or to the bearer of the bill.
- 10. It must be stamped as per legal requirements.
PARTIES TO A BILL OF EXCHANGE
1. DRAWER: Drawer is the person who makes or writes the bill of exchange. Drawer is a person who has granted credit to the person on whom the bill of exchange is drawn. The drawer is entitled to receive money from the drawee (acceptor).
2. DRAWEE: Drawee is the person on whom the bill of exchange is drawn for acceptance. Drawee is the person to whom credit has been granted by the drawer. The drawee is liable to pay money to the creditor/drawer.
3. PAYEE: Payee is the person who receives the payment from the drawee. Usually the drawer and the payee are the same person. In the following cases. drawer and payee are two different persons:
(i) When the bill is discounted by the drawer from his bank- payee is the bank.
(ii) When the bill is endorsed by the drawer to his creditors: payee is the endorsee.
ADVANTAGES OF BILL OF EXCHANGE
1. It helps in purchases and sales of goods on credit basis.
2.It is a legally valid document in the eyes of law. It assures a easier recovery to the drawer if drawee fails to make the payments.
3.A bill can be discounted from the bank before its date of maturity. By discounting with the bank, drawer can get the money before due date if required.
4.It can be easily transferred from one person to another by endorsement.
5.It helps in recovery of debt without sending reminders to the debtor.
6.It assures the seller about the timely recovery of debt. So a drawer and drawee can plan about its cash management.
PROMISSORY NOTE
A Promissory note is an instrument in writing (not being a bank note or a currency note) containing an unconditional undertaking signed by the maker to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument.
FEATURES OF A PROMISSORY NOTE
1.There must be an unconditional promise to pay a certain sum of money on a certain date.
2. It must be signed by the maker.
3. The name of the payee must be mentioned on it.
4. It must be stamped according to its value.
PARTIES TO A PROMISSORY NOTE
1.The maker : The maker is the person who makes the promise to pay the amount on a certain date.
Maker of a bill must sign the promissory note before giving it to the payee.
2.The payee : The payee is the person who is entitled to get the payment from the maker of
promissory note. Payee is the pesson who has granted the credit.
DISTINCTION BETWEEN BILLS OF EXCHANGE AND PROMISSORY NOTE

IMPORTANT TERMS
1.Term of Bill : The period intervening between the date on which a bill is drawn and the date on which it
becomes due for payment is called ‘Term of Bill’.
2. Due Date :
Due date is the date on which the payment of the bill is due.
Due date is ascertained in the following manner :
(i) In case of ‘Bill at sight’ –
Due date is the date on which a bill is presented for the payment.
(ii) In case of ‘Bill after Date’ –
Due Date = Date of Drawing + Term of Bill.
(ii) In case of ‘ Bill after sight’ –
Due date = Date of Acceptance + Term of Bill.
3. Days of Grace :
Drawee is allowed three extra days after the due date of bill for making payments. Such 3
days are known as ‘Days of Grace’. It is a custom to add the days of grace.
4. Date of Maturity :
The date which comes after adding three days of grace to the due date of a bill is called
‘Date of maturity’.
Illustration: 1
A bill of exchange for ` 25000 is drawn by A on B on 1st April, 2011 for 3 Months. B accepted
the bill on 10th April, 2011.
Find the DUE DATE and DATE OF MATURITY if
Cash I – The bill is Bill After date
Case II – The bill is Bill After Sight
Solution:

5. Bill at sight/Bill on Demand: When no time for payment is mentioned in the bill of exchange and the bill is payable
whenever it is presented to the drawee for the payment, such bills are known as “Bill at sight” or
“Bill on Demand”.
3 days of grace are not allowed when bill is payable on demand.
6.Bill after Date: Bill after date is the bill in which due date and date of maturity is ascertained from the date on
which the bill is drawn.
3 days of grace are allowed for ascertaining the date of maturity in case of bill after date.
7.Discounting of Bill:
When the bill is encashed from the bank before its due date, it is known as discounting of bill. Bank deducts its charges from the amount of bill and disburses the balance amount.
Illustration 2
Ram sold goods to shyam for Rs. 30,000 at credit on 1st April, 2011. Ram discounted the bill with his
bank on 4th May 2011 @ 9% per annum find out :
(i) The amount of discounting charges.
(ii) The amount that Ram will receive from his bank at the time of discounting the bill.
Solution :
(i) Discounting Charges =

(ii) Ram will receive from his bank Rs. 29,500 (i.e., Rs. 30,000 – 450) at the time of discounting the
bill.
8. Endorsement of Bill:
Endorsement of a bill means the Process of transferring the title of bill from the drawer or holder to their creditors.
The person transferring the title is called ” Endorser” and the person to whom the bill is transferred called ‘Endorsee’. The endorsee can further endorse the bill in favor of his creditors. Endorsement is executed by putting the signature at the back of the bill.
9.Bill sent for Collection:
It is a process when the bill is sent to the bank with instructions to keep the bill till maturity and collect its amount from the acceptor on the date of maturity.
10.Dishonour of Bill:
When the drawee (or acceptor) of the bill fails to make payment of the bill on the date of maturity, it is called ‘Dishonour of Bill.
11.Noting of Bill:
To obtain the proof of dishonour of a bill, it is re-sent to the drawee through a legally authorized persons called Notary Public. Notary Public charges a small fee for Providing this service known as noting charges.
Noting charges are paid to the Notary Public first by the holder of the bill but are ultimately recovered from the drawee, because he is the person responsible for the dishonour.
12.Retirement of a Bill:
When the drawee makes the payment of the bill before its due date it is called ‘Retirement of a bill’.
In such a case, holder of the bill usually allow a certain amount as Rebate to the drawee.
Amount of rebate is calculated at a fixed percentage for the unexpired period only.
13.Renewal of a Bill:
Sometimes, the drawee of a bill finds himself unable to meet the bill on due date. To avoid dishonouring of bill, he may request the holder of the bill to cancel the original bill and draw a new bill in place of old one. It the holder agrees, the old bill is cancelled and a new bill with new terms is drawn on the drawee and also accepted by him. This process is called ‘Renewal of a bill’.
In this case, Noting of the bill is not required as cancellation of the bill is mutually agreed upon by both the parties of the bill.
Normally, the drawer charge interest for the period of new bill. The interest may be paid in cash or may be added in the amount of new bill. If any part payment is made at the time of renewal of a bill, interest is calculated only on the outstanding amount.
Accommodation Bill:
When bills of exchange or promissory note are not drawn to settle a trade between drawer and drawee but are written for the purpose of mutual help and to raise funds temporarily then it is known as Accommodation bill.
15. Insolvency of Acceptor :
When the drawee (i.e., acceptor) of a bill is unable to meet his liabilities on due date, the drawee become insolvent. In such a case, entries for the dishonour of the bill are passed in the books of drawer/holder and drawee of the bill.
Any proportionate amount received from the drawee is recorded in the books of the holder and the amount unrecoverable is debited to ‘Bad Debts A/c’.
ACCOUNTING TREATMENT OF BILL TRANSACTIONS
A. On the Due Date bill is Honoured –
The accounting treatment under this heading is based on the assumption that bill is duly honoured at maturity of the bill. The drawer can treat the bill in the following ways:
Case – I Bill is retained by the drawer till date of maturity:

Case II : When the bill is discounted from the Bank by the Drawer


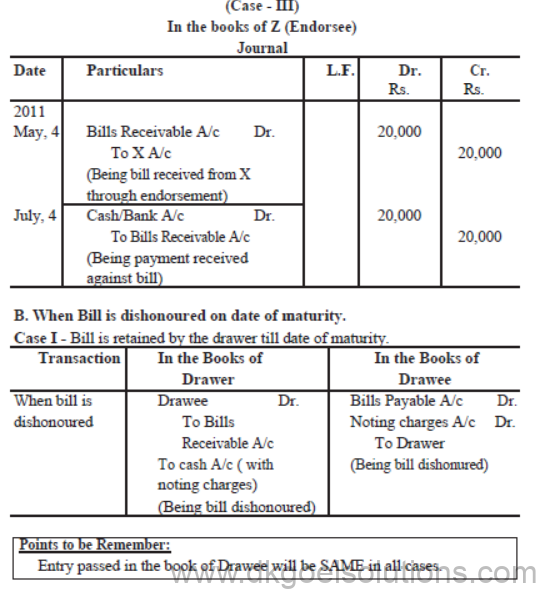
Case III : When bill is endorsed in favour of a creditor

Case – IV When Bill is sent to the Bank for collection

Illustration: 5
X sold goods to Y on 1st April, 2011 for Rs. 20,000 on credit and drew upon him a bill for the same amount payable after 3 months. Y accepted the bill and returned it to X. On the date of maturity bill was presented to Y for the payment and he honoured it.
Pass the Journal Entries in the books of both the parties when :
Case I – Bill is retained by the X till the date of maturity.
Case II – Bill is discounted by X from his bank on 4th April @ 6% per annum.
Case III – Bill is endorsed in favour of Z on 4th May, 2011.
Case IV – Bill is sent to Bank for collection on 1st July, 2011.
Also record the Journal Entries in the books of C (Case – III)



Cass II – Bill is discounted by the drawer from his bank, the following entry is passed, at the time of
maturity, if the bill is dishonoured.

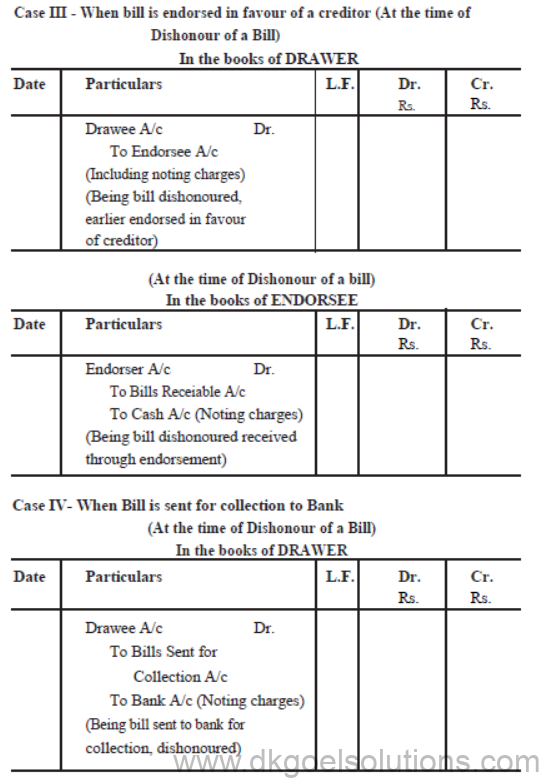
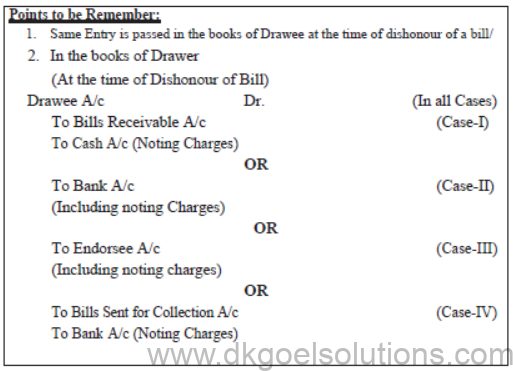
Illustration: 6
A sold good to B on April 1, 2011 for Rs. 20,000 on credit and drew upon him a bill for the same amount payble after 3 months. B accepted the bill and returned into to A. On the due date bill was dishonoured.
Pass Journal entries in the books of A and B if Case I : Bill is retained by
A till the date of maturity.,
Case II : Bill is discounted by A from his bank on 4th April, 2011 @ 6% per annum.
Case III : Bill is endorsed in favour of C on April, 4th, 2011.
Case IV : Bill is sent to bank for collection on July 1, 2011.
Solution :

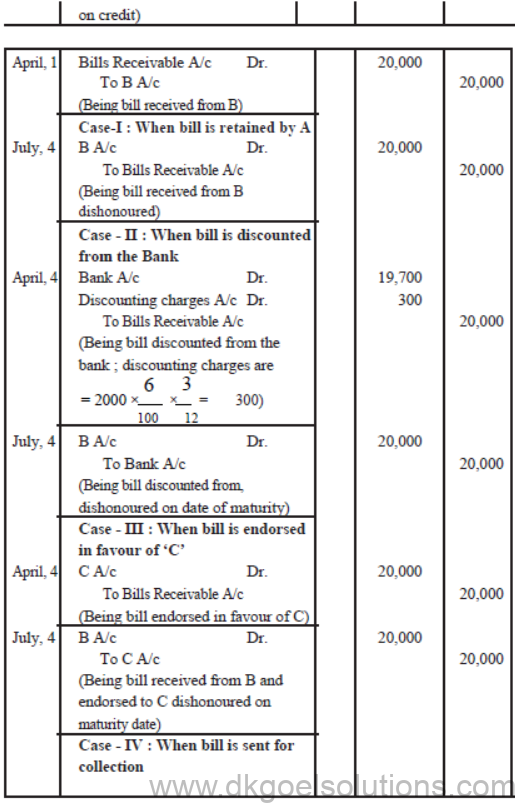
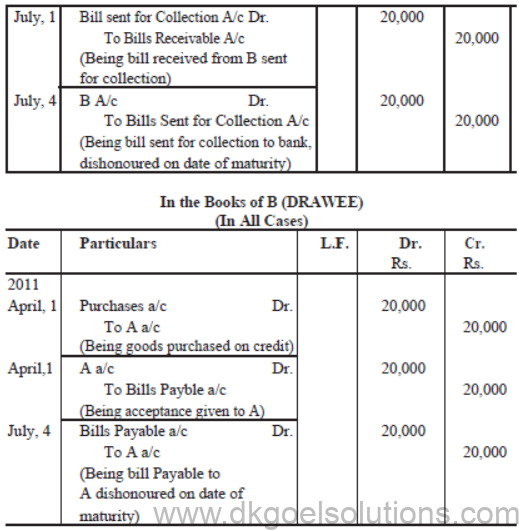
Illustration 7
A sold goods to to B on May 1st, 2011 for ` 30,000 on credit and drew upon him a bill for the same amount payable after 2 months. B accepted the bill and returned it to A. On date of maturity, B fails to make payment of bill.
Noting charges amounted to ` 100.
Pan Journal Entries in the books of A and B if.
Case 1 : A retains the bill till the date of maturity and also paid the noting charges.
Case 2 : A discounts the bill from his bank on 4th June @ 12% per annum. Noting charges has been paid by bank.
Case 3 : A endorses the bill n favour of C on June 1. C paid the noting charges.
Case 4 : A sents the bill to his bank for collection on July 1. Bank paid the noting charges.
Solution :
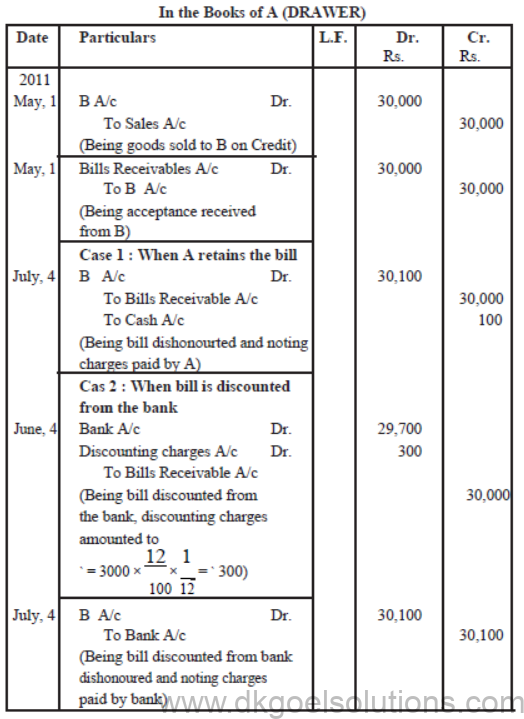


Illustration – 8 :
On 1st April, 2011 Anil accepts a bill drawn by Sunil for 2 months for Rs. 15000, in payment of a debt. On the date of maturity bill was dishonoured and Sunil had to pay Rs. 150 as noting charges. On 4th June 2011, Anil requested to Sunil to draw a new bill for the amount due. Sunil agreed to draw a new bill for 73 days but he charged interst @ 15% per annum in cash. This bill is duly met on its maturity.
Pass Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
Solution :
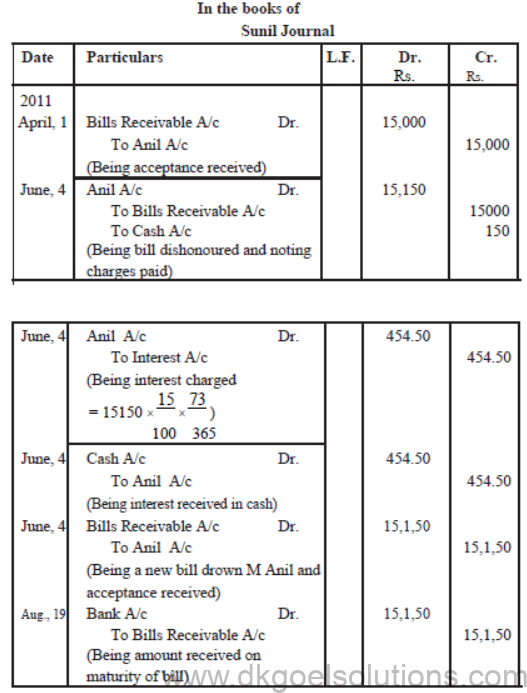

Illustration 9
P sold goods to Q for ` 10,000 on January 1, 2011 and on the same day draws a bill on Q for the same amount for 3 months. Q accept it and returns it to P, who discounts it on 10th January, 2011 with his bank for ` 9850. The acceptance is dishonoured on the due date and the noting charges were paid by bank being ` 50.
On 4th April, Q paid ` 2,050 (including noting charges) in cash and accepted a new bill at 3 months for the amount due to P together with interst @ 12% per annum.
Make Journal Entries in the books of P and Q to record these transactions.
Solution :

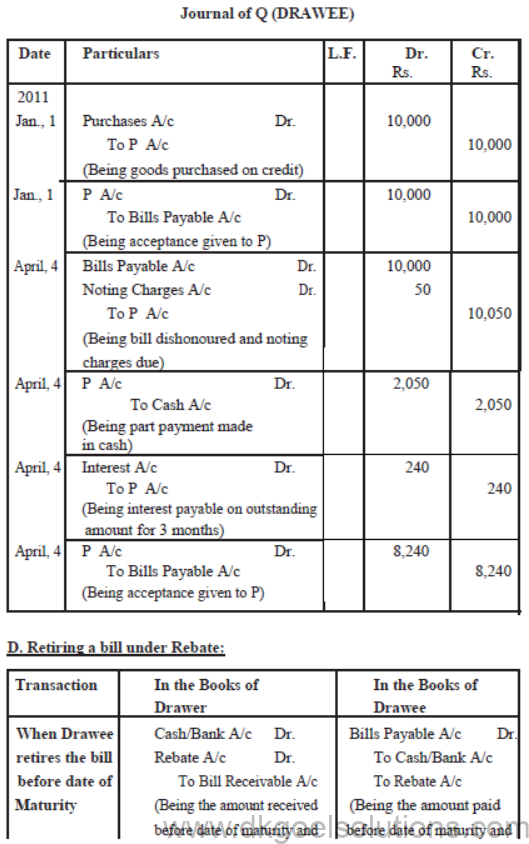

Illustration: 10
Mukesh sold goods to Jitender on July 1, 2011 for ` 30,000 and drew a bill for the some amount for 3months. Jitender accepted the bill and returned it to Mukesh. Jitender retired his acceptance on 4th August, 2011 under rebate of 8% per annum Give Journal entries in the books of Mukesh and Jitender.
Solution :
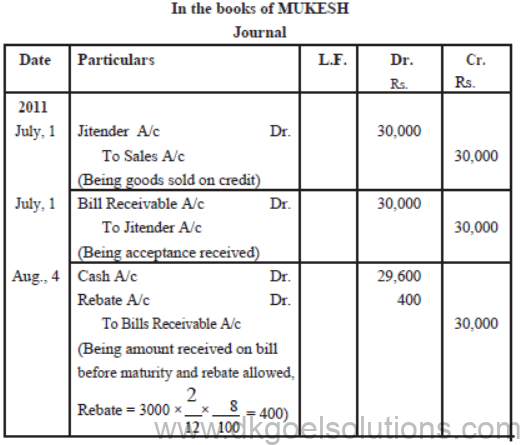

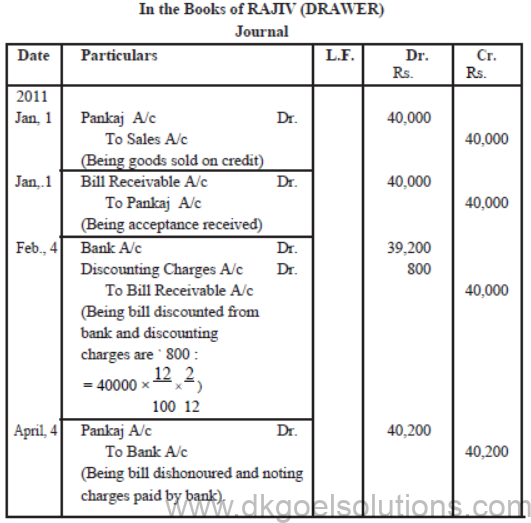
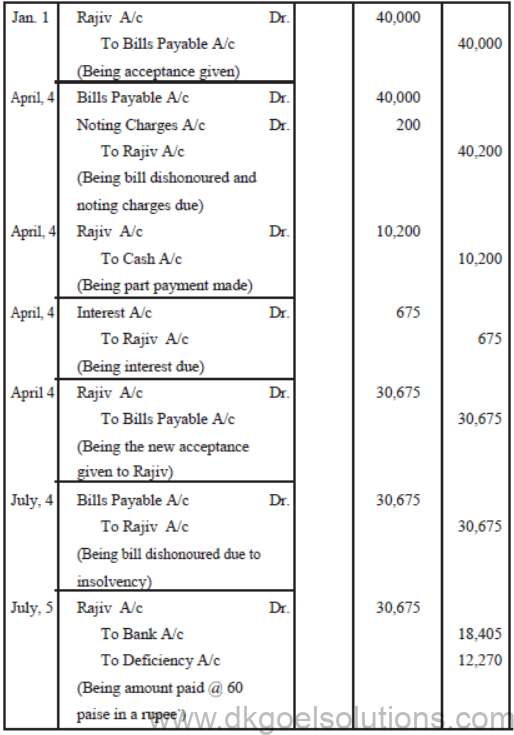
Illustration – II
Rajiv sold goods to Pankaj for ` 40,000 on January 1st, 2011. On the same date Rajiv drew a bill of the same amount at 3 month on Pankaj. The bill was accepted by Pankaj. Rajiv discounted the bill with his bank on 4th February, 2011 @ 12% per annum. On date of maturity, the bill was dishonoured and noting charges ` 200 were paid by bank.
Pankaj agreed to pay ` 10,200 and accpted another bill for the remaining amount for 3 months together wih interest @ 9% per annum. On July 4, 2011, Pankaj becomes insolvent and a first and final dividend of 60 paise in a rupee was received from his private estate on 15th July, 2011.
Give Journal Entries in the books of Rajiv and Pankaj.
Solution :

GENERALLY STUDENTS COMMIT MISTAKES PLEASE AVOID IT:-
1. When calculating Date of Maturity the following points must be considered:
3.In case of “Bill at sight” or “Bill on demand” 3 days of grace are NOT allowed.
4.When the term of bill is mentioned in no of days, then Date of drawing the bill is not included.
• Date of payment is included in determining date of maturity .
• If date of maturity falls on a day which is public holiday, the maturity date of the bill shall be “PRCEDING DAY’.
• If maturity date is on an emergent holiday declared under the Negotiable
• Installment Act. 1881, the next working day immediately after the holi day will be considered as the date of maturity.
When the period is stated in months the date of maturity shall be calculated in terms of calendar months ignoring the no. of days in a month.
(7) Noting Charges :
1. Noting charges are not an expense for the drawer.
2. It is always debited as ‘Noting chargers in the books of drawee.
3. Noting charges are recovered by drawer from drawee.
4. Noting charges are paid only when noting of the bill is necessary any at the time DISHONOUR of bill.
Noting of the bill is NOT required when the bill is CANCELLED with the consent of both the
parties, specially at the time of RENEWAL of Bill.
Questions
1. State any four essential features of bill of exchange.
2. What is meant by maturity of a bill of exchange?
3. What is meant by acceptance of a bill of exchange?
4. What is Noting of a bill of exchange.
5. What is meant by renewal of a bill of exchange?
6. What is retirement of a bill of exchange?
7. What is meant by insolvency?
8. Give the meaning of rebate.
9. Distinguish between bill of exchange and promissory note.
10. Briefly explain the purpose and benefits of retiring a bill of exchange to the debtor and the creditor.
Numerical Questions
1. On Jan 15, 2006, Sankar Sold goods for Rs.30,000 to Parvati and drew upon
him three bills of exchanges of Rs.10,000 each payable after one month, two
month, and three months respectively. The first bill was retained by Sankar till
its maturity. The second bill was endorsed by him in favour of his creditor
Ratna and the third bill was discounted by him immediately @ 6% p.a. All the
bills were met by Parvati. Journalise the above transactions in the books of
Sankar and Parvati. Also prepare ledger accounts in books of Sankar and
Parvati.
2. BSNL sold goods worth Rs.19,000 to MTNL on March 02, 2006. Rs.4,000
were paid by MTNL immediately and for the balance she accepted a bill of
exchange drawn upon her by BSNL payable after three months. BSNL
discounted the bill immediately with her bank. On the due date MTNL
dishonoured the bill and the bank paid Rs.30 as noting charges. Record the
necessary journal entries in the books of BSNL and MTNL.
3. Tina and Mina were in need of funds temporarily. On August 01 2005 Tina
drew upon Mina a bill for Rs. 12,000 for 4 months. Mina Accepted the bill and
returned to Tina. Tina discounted the Bill @ 8% p.a. Half amount of the
discounted bill remitted to Mina. On due date, Tina sent the required sum to
Mina, who met the bill. Journalise the transaction in the books of both the
parties.
4. On Jan 01, 2006 Mr. Dalvi sold goods for Rs.20,000 to Mr. Vaghela and drew
upon her a bill of exchange payable after two months. One month before the
maturity of the bill Mr. Vaghela approached Mr. Dalvi to accept the payment
against the bill at a rebate @ 12% p.a. Mr. Dalvi agreed to the request of Mr.
Vaghela and Mr. Vaghela retired the bill under the agreed rate of rebate.
Journalise the above transaction in the books of Mr. Dalvi and Mr. Vaghela.

