Notes for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation
Class 12 commerce students can refer to the Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation notes given below which is an important chapter in class 12 accountancy book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Accountancy teachers have prepared these notes for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation Notes Class 12 Accountancy
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation which are really useful and have been recommended by Class 12 Accounts teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books.
(A) Very Short Answer Questions
1. The financial statements of the Not-for-Profit Organisation are:
(A) Receipts and Payments Account
(B) Income and Expenditure Account
(C) Balance Sheet
(D) All of the above
Answer
(D) All of the above
2. The Receipts and Payments Account is a summary of:
(A) Debit and Credit balance of Ledger Accounts
(B) Cash Receipts and Payments
(C) Expenses and Incomes
(D) Assets and Liabilities’
Answer
(B) Cash Receipts and Payments
3. Receipts and Payments Account is a:
(A) Personal Account
(B) Real Account
(C) Nominal Account
(D) Real and Nominal Account, both
Answer
(B) Real Account
4. Income and Expenditure Account is a:
(A) Personal Account
(B) Real Account
(C) Nominal Account
(D) Real and Nominal Account, both
Answer
(C) Nominal Account
5. Source of income for a not-for-profit organisation is:
(A) Subscription from Members
(B) Donation
(C) Entrance Fees
(D) All of the above
Answer
(D) All of the above
6. Subscription received in advance during the current year is:
(A) An income
(B) An asset
(C) A liability
(D) None of these
Answer
(C) A liability
7. If a general donation of smaller amount is received by a school, that donation will be shown in:
(A) Liability Side
(B) Asset Side
(C) Debit side of Receipt and Payment A/c
(D) Credit side of Receipt and Payment A/c
Answer
(C) Debit side of Receipt and Payment A/c
8. If there is a ‘Match Fund’, then match expenses and incomes are transferred to:
(A) Income and Expenditure A/c
(B) Assets side of Balance Sheet
(C) Liabilities side of Balance Sheet
(D) Both Income and Expenditure A/c and to Balance Sheet
Answer
(C) Liabilities side of Balance Sheet
9. Amount received from sale of grass by a club should be treated as:
(A) Capital Receipt
(B) Revenue Receipt
(C) Asset
(D) Earned Income
Answer
(B) Revenue Receipt
10. Which of the following is not a revenue receipt?
(A) Life Membership Subscription
(B) Donation
(C) Subscription
(D) Interest on Investments
Answer
(A) Life Membership Subscription
11. Out of the following items, which is shown in the ‘Receipts and Payments A/c’ of a not-for-profit organisation?
(A) Subscription received in advance
(B) Last year subscription received
(C) Current year subscription received
(D) All of the above
Answer
(D) All of the above
12. Subscription received in cash during the year amounted to ₹40,000; subscription outstanding at the end of previous year was ₹1,500 and outstanding at the end of current year was ₹2,000. Subscription received in advance for next year was ₹800. The amount credited to Income & Expenditure Account will be:
(A) ₹38,700
(B) ₹39,700
(C) ₹40,300
(D) ₹41.300
Answer
(B) ₹39,700 (40,000+2,000-1,500-800)
13. What amount will be credited to the Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st March 2020 on the basis of the following information?
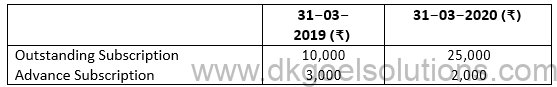
Subscriptions received during the year 2019-20 were ₹4,00,000.
(A) ₹3,84,000
(B) ₹4,16,000
(C) ₹3,86,000
(D) ₹4,14,000
Answer
(B) ₹4,16,000 (4,00,000+25,000+3,000-10,000-2,000)
14. How much amount will be recorded in Income and Expenditure Account in the following case?

Salary paid for the year ended 31st March 2020 amounted to ₹75,000.
(A) ₹75,700
(B) ₹74,300
(C) ₹75,300
(D) ₹74,700
Answer
(D) ₹74,700 (75,000+6,000+1,200-6,500-1,000)
15. How much amount will be shown in Income and Expenditure Account in the following case?
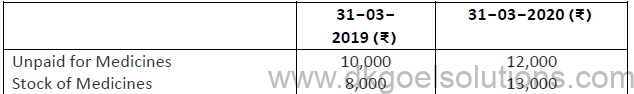
Payment made for medicines during 2019-20 was ₹2,5 0,000.
(A) ₹2,53,000
(B) ₹2,47,000
(C) ₹2,57,000
(D) ₹2,43.000
Answer
(B) ₹2,47,000 (2,50,000+8,000+12,000-13,000-10,000)
16. Which of the following is not an income?
(A) Subscription
(B) Donation
(C) Sale of Ticket
(D) Endowment Fund
Answer
(D) Endowment Fund
17. Scholarships grant to students by the government will be ____________ to Income & Expenditure account.
Answer
Debited
18. Outstanding Subscriptions are shown on the ______________ side of Balance sheet.
Answer
Assets
19. Donations for specific purposes are always ____________.
Answer
Capitalised
20. Purchase of sports material is ______________ to Income & Expenditure account.
Answer
Debited
(B) Short Answer Questions
1. State the meaning and objective of Not-for-profit organisation.
Answer: Not-for-profit organisation is an economic entity that provides services beneficial to the society without making profits. The objective of these organisations is to promote charity, religion, education, literature, sports, art and culture, without aiming at profit.
2. How is ‘Sale of old newspapers and magazines’ treated in Not-for-profit organisation?
Answer: Amount received from the sale of old newspapers and magazine are treated as revenue receipts because it is a regular feature of Not-for-profit organisation. Hence sale of old newspaper etc. are shown on the credit side of income and expenditure account.
3. What is meant by Fund Based Accounting?
Answer: In fund-based accounting separate accounts are maintained for specific activities of the organisation such as sports fund, price fund etc. All items related to the specific fund are recorded fund wise, i.e., incomes related to the fund is added to it and expenses related to the fund are deducted from it. The consolidation of these accounts is presented on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
4. State any three features of income and expenditure account.
Answer: The main features of Income and Expenditure Account:
i) It is prepared for an accounting period on accrual concept following the matching principle.
ii) Only revenue items are considered, while capital items are excluded.
iii) All items both cash and non-cash (depreciation) are recorded.
5. Give any three differences between Receipt & Payment account and Income & Expenditure account.
Answer: Three differences between Receipt & Payment A /c & Income & Expenditure A/c are:

6. What is Receipts and Payments account? State its features.
Answer: Receipts and Payments account is a financial statement prepared by not-for- organization with the help of cash book that is maintained throughout the year. Its features are as follows:
a) It is a summary of cash and bank transactions, prepared at the end of the year.
b) It starts with the opening balance of cash in hand, cash at bank or bank overdraft.
c) It follows cash basis of accounting wherein all capital and revenue items are recorded irrespective of period, i.e. preceding year, current year or succeeding year.
7. How would a “Not- for- profit organization” deal with the following items:
a. Outstanding Subscription
b. Subscription received in advance
c. Tournament Fund
Answer:
a. Outstanding Subscription is credited to Income & Expenditure A/c and shown on assets side of Balance sheet.
b. Subscription received in advance is Deducted from subscription received on income side of Income & Expenditure A/c and shown on liabilities side of Balance sheet.
c. Tournament Fund is a specific Fund which is capitalised, i.e., shown on liabilities side of Balance sheet.
(C) Long Answer Questions
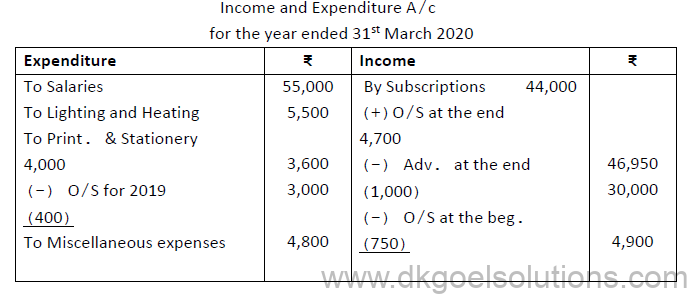
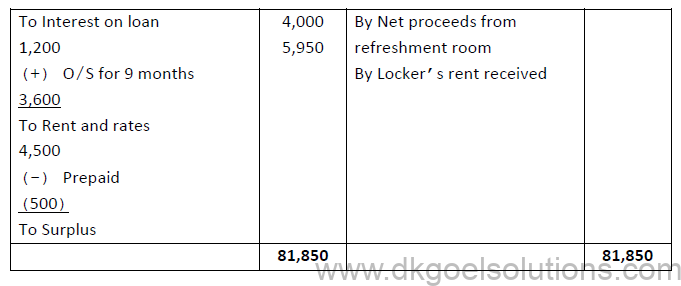
1. From the following information, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March 2020.
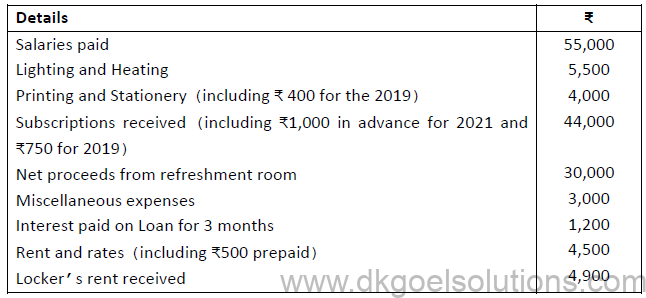
Additional information: Subscription in arrears on 31.03.2020 were ₹4,700 and interest on Loan outstanding for 9 months.
Answer:
2. From the following Receipts and Payment Account of Pioneer Cricket Club and from the information supplied, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March, 2020.
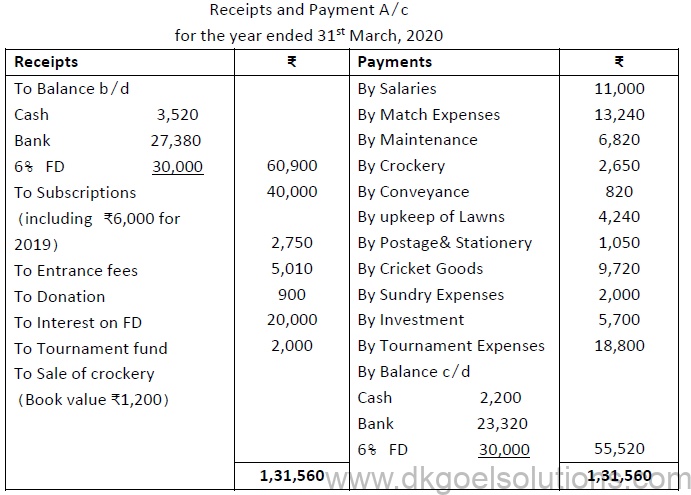
Additional Information:
a) Salary outstanding is ₹1,000
b) Opening balance of stock of postage and stationery and cricket goods is ₹750 and ₹3,210, respectively. Closing stock of the same is ₹900 and ₹2,800, respectively.
c) Outstanding subscriptions for 2018-19 and 2019-20 are ₹6,600 and ₹8,000respectively.
Answer:

3. Prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March 2020 from the following particulars of Arts club which organises art competitions for disabled people during the year:
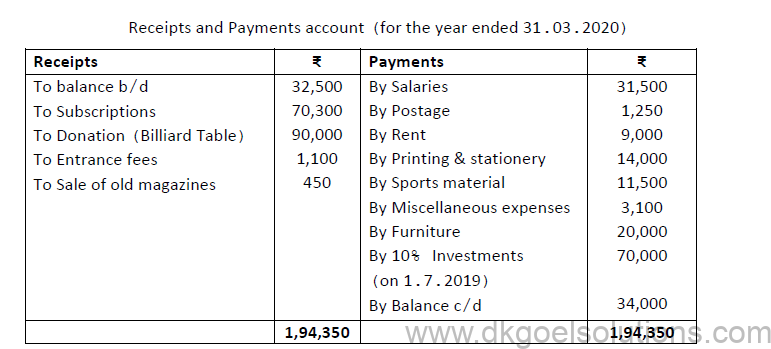
Additional information:
i. ₹4,700 is still in arrears for the year 2019-20 for subscription.
ii. Value of sports material at the beginning and the end of the year was ₹3, 000 and ₹4,500 respectively.
iii. Depreciation to be provided @10% p.a. on furniture.
Answer:

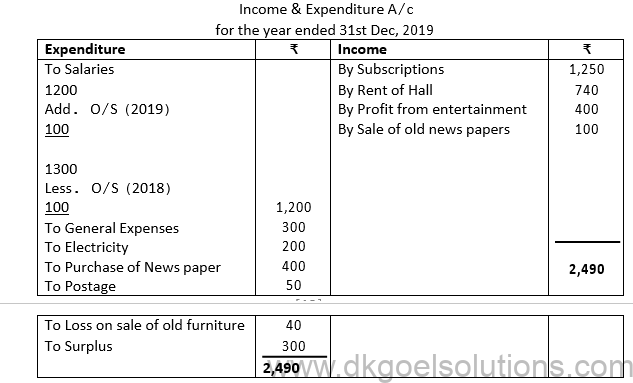
4. From the following Receipts and payments Account of Cosmo Club, from the information supplied, prepare the Income and Expenditure account for the year ended December 31st, 2019 and balance sheet as at that date:

Additional Information:
a) The club has 50 members each paying an annual subscription of ₹25. Subscriptions Outstanding on 31st December 2018 were to value of ₹300.
b) On the 31st December 2019, Salaries outstanding amounted to ₹100. Salaries paid included ₹100 for the year 2018.
c) On January 1, 2019, the club owned land and buildings valued at ₹10,000, Furniture worth ₹600 and Books ₹500.
Answer:

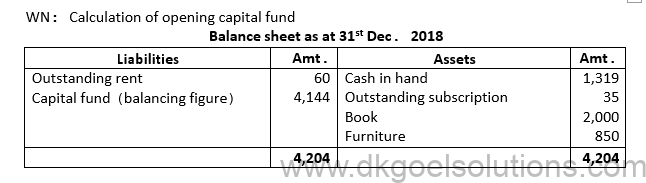
5. Following are the particulars of cash transactions of Geeta Pustakalaya Allahabad for the year ended 31st December 2019.

Additional information:
Library has books worth ₹2,000 and furniture worth ₹850 in the beginning of year. Outstanding subscription was ₹35 in the beginning of year and ₹45 at the end of year. Outstanding rent was ₹60 in the beginning as well as at the end of year. Charge depreciation ₹50 on Furniture and ₹113 on Books.
You are required to prepare Income and Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet of Pustakalaya as on 31st December 2019.
Answer:

Notes for Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation class 12 Accountancy
♦ Meaning of Not-for-Profit Organisations
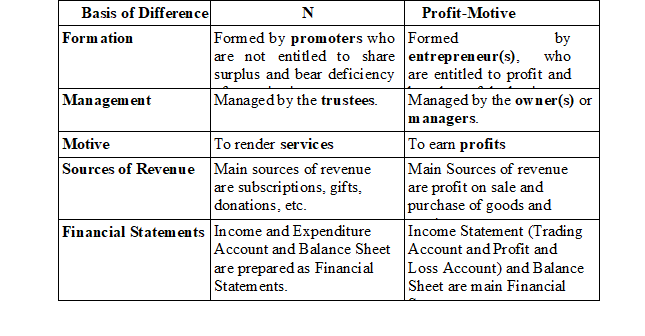
These are the institutions that are set-up with general or specific objectives for rendering services and providing other social activities to enhance the welfare of general or a particular group of people. The main motive of these organisations is to render services for enhancing welfare and not to earn profit. For example, charitable schools, hospitals, etc.
♦ Features or Characteristics of NPO
• These organisations are formed by the promoters who can either be individual or group of individuals and enterprises.
• These organisations are managed and owned by their trustees.
• These organisations have separate existence from its members, i.e. the life of an NPO is unaffected by the life of its members or trustees.
• The sole motive of these organisations is to render services and not to earn profit. For example, charitable schools, colleges, hospitals, etc.
• The main source of their income is subscription, donations, government grants and other receipts.
• Unlike, profit-seeking organisations they do not prepare Profit and Loss Account, rather they prepare Income and Expenditure Account to show the summary of revenue incomes and revenue expenses.
• Unlike profit-seeking organisations, NPOs do not prepare Profit and Loss Account; rather they prepare Income and Expenditure Account to show a summary of revenue incomes and revenue expenses.
♦ Difference between NPO and Profit-Motive Organisation
♦ Basis of Maintaining Accounts by Not-for-Profit Organisations
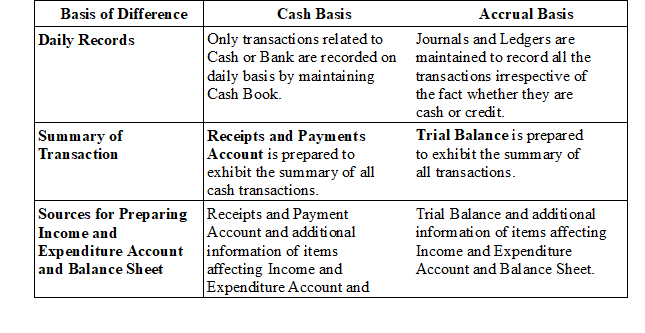
• Cash Basis: Maintenance of accounts on Cash Basis is usually adopted by the organisations that do not strictly follow the Double Entry System and maintain daily records only for cash transactions.
• Accrual Basis: Maintenance of accounts on Accrual Basis provides complete record of each and every transaction. This system helps in proper checking and provides better understanding of financial transactions.
♦ Difference between Cash Basis and Accrual Basis
♦ Meaning of Receipts and Payments Account
Receipts and Payments Account is an account that shows the summary of all cash and bank transactions occurred during an accounting period. It starts with the opening balances of cash and bank and ends with the closing balances of cash and bank. This account is a Real Account and lays the basis for the preparation of Income and Expenditure Account and the Balance Sheet.
♦ Features of Receipts and Payments Account
• It is a Real Account.
• It provides the summary of all cash and bank transactions in a chronological order.
• It records all cash and bank transactions of both capital and revenue nature.
• It is prepared at end of accounting period to show the receipts and payments during an accounting period along with the opening and closing balances of cash and bank
♦ Limitations of Receipts and Payments Account
• As this account is prepared on the Cash Basis, so it does not provide information about credit transactions.
• It is not a perfect substitute of Trial Balance. Unlike Trial Balance, this account fails to reveal the closing balances of all accounts.
♦ Comparison between Receipts and Payment Account and Cash Book
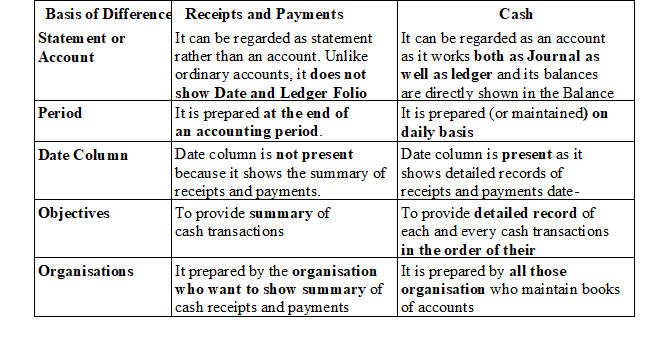
♦ Format of Receipts and Payments Account
Receipts & Payment Account
for the year ending


* If the receipts side is more than the payments side then, Closing balance of cash and bank will appear on the credit side of this account.
** If the payments side is more than the receipts side then, Closing balance of bank will appear (as Bank overdraft) on the debit side of this account.
♦ Meaning of Income and Expenditure Account
Income and Expenditure Account is an account that shows all revenue income earned and revenue expenses incurred during an accounting period. It is prepared on the Accrual Basis to ascertain surplus or deficit arising after meeting revenue expenses against revenue incomes at the end of an accounting period.
♦ Features of Income and Expenditure Account
• It a statement showing summary of revenue incomes earned (either received or receivable) and revenue expenses incurred (either paid or payable) during an accounting period.
• It is a Nominal Account. All revenue expenses and losses incurred are recorded on the debit side and all revenue incomes and gains earned are recorded on the credit side of this account.
• It prepared on the Accrual Basis to ascertain Surplus or Deficit arising after meeting all revenue expenses against all revenue incomes at the end of an accounting period.
• It is akin to Profit and Loss Account. Both Income and Expenditure Account as well as Profit and Loss Account provide summary of revenue incomes and revenue expenses incurred during an accounting period.
• The balancing figure of Income and Expenditure Account is expressed in terms of either Surplus (if incomes > expenses) or Deficit (if expenses > incomes).
• It is prepared period at end of an accounting period (say, quarter, half-year or year, etc.)
♦ Format of Income and Expenditure Account
Income and Expenditure Account
for the year ending…
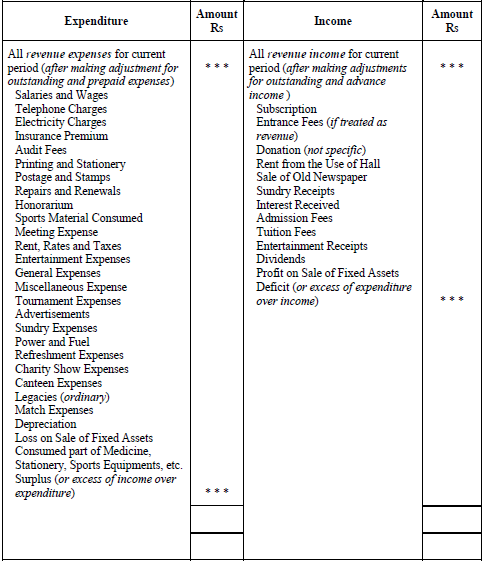
♦ Difference/Comparison between Receipts and Payments Account and Income and Expenditure Account

♦ Difference between Income and Expenditure Account and Profit and Loss Account
| Basis of Difference | Income and Expenditure Account | Profit and Loss Account |
| Summary | It shows the summary of all revenue, income and revenue expenses of a Not-for-Profit Organisation. | It shows summary of all revenue incomes and revenue expenses of a profit-seeking organisation. |
| Objective | To ascertain Surplus or Deficit. | To ascertain Net Profit or Net Loss |
| Sources Required | Receipts and Payments Account is the basis for preparing this account. | Trial Balance is the basis for preparing this account. |
♦ Meaning of Fund Based Accounting
It is an accounting method or practice that is followed for preparation of accounts in which amount (funds) available for specific purpose is shown by under Specific Fund Account (head). Any income (or receipts) and expenditure (or payment) related to the fund is adjusted to that particular fund.
♦ Objective of Fund Based Accounting
• It ensures efficient management of funds.
• It provide information about revenues and expenses attributing to each fund separately from general revenues and expenses
• It ensures whether the funds have been used in the instructed manner or not.
♦ Types of Funds

• General Funds– These funds are is used to carry out the general operations of a business. The incomes (or receipts) and expenses (or payments) which are not attributed to any specific fund are adjusted to the general fund. For example, Surplus or Deficit arising from the ordinary revenue transactions are adjusted to the Capital Fund
• Restricted/Specific Funds– These funds are created and maintained to carry out specific operations of a business. The receipts (or incomes) and expenses (or payments) are attributed to a particular fund that must be adjusted to that specific fund only.
• Specific Revenue Funds– These funds are created and maintained to show the incomes and expenses related to the specific operation separately from the general revenue incomes and expenses. Amount available in these funds (after meeting the expenses attributing to the fund) are shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. Treatment of receipts and expenditures related to the specific fund can be better understood with the help of the following example of Tournament Fund.
Example: Treatment of Tournament Fund
Balance Sheet
as on …………………

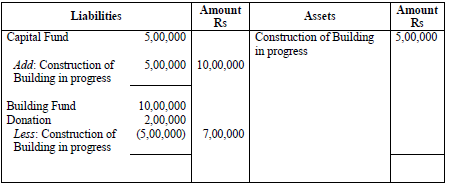
Capital Project Funds– These funds are also shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. Donation and other receipts to acquire or construct specific fixed assets (such as, donation for construction of pavilion) or to carry out a specific project of capital nature are shown in the separate fund account.
Treatment of receipts and expenditure relating to the fund can be understood with help of following example.
Example: Donation for Building Fund
Balance Sheet
as on …………………
Endowment Funds-These funds arises from the gift or bequest. It is created with the condition that income arising from the investment of such funds will be used for a specific purpose (to provide the benefit to the specified beneficiary or to meet specific expenses). Thus, the principal amount of these funds remains unchanged. These funds may be permanent or temporary for a specific period.
• Annuity Funds– These funds are created to pay regular fixed amount at fixed interval of time (annually) to the specified beneficiary. This amount is paid during the life time of the beneficiary or till the termination of agreement. After the death of the beneficiary or termination of the agreement, the funds become the property of the organisation.
• Loan Funds– These funds are maintained to provide loan for specific purposes. These loans are subject to repayment, interest and fines. Its purpose is not to earn profits but to assist the person who is in need. For example, Education Loan to the students to prosecute the studies and loans to victim of an earthquake disaster, etc.
♦ Balance Sheet
It is a statement that reveals the financial position of an organisation at the end of an accounting period. It is simply a statement of assets and liabilities.
♦ Opening Balance Sheet- It shows the balances of all the assets, liabilities, funds and reserves in the beginning of an accounting period. It is usually prepared to ascertain the capital fund in the beginning or any other missing item.
• Need for Preparing Opening Balance Sheet
In case, the Capital Fund is not mentioned in the question, then in order to ascertain the Capital Fund we need to prepare the Opening Balance Sheet. All the opening balances of assets such as, building, furniture, outstanding subscription (at the beginning), etc. and all the opening balances of liabilities such as, creditors, advance subscription (at the beginning), outstanding expenses etc. are recorded in this balance sheet. The excess of the total of the Assets over the total of the Liabilities is regarded as Capital Fund.
♦ Closing Balance Sheet– It is prepared to assess the true and fair financial position of an organisation at the end of an accounting period.
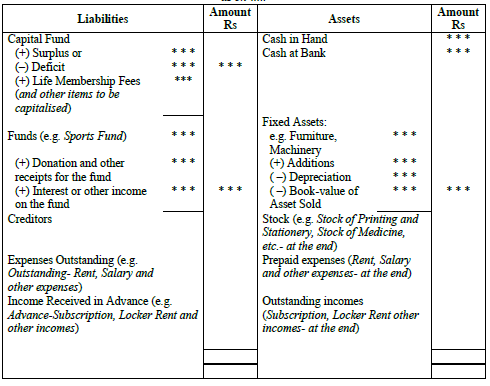
♦ Format of Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet
as on …..
♦ Treatment of Some Peculiar Items and Adjustments in the Income and Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet
• Subscription

Special Subscription- It is a type of subscription that is received for accomplishing a specific task or organising specific activities from the participants. For example, subscription for tournament, subscription for governor’s party, etc.
Accounting Treatment: Special Subscription are shown separately on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet and the expenses attributing to the subscription is deducted from such subscription.
Situation 1: After completing the specific task, if any surplus remains, then it will be added to the capital fund.
Situation 2: If expenses are more than the subscription amount, then the expenses that remain after adjusting all the expenses from the subscription amount will be shown on the Expenditure side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
(Ordinary) Subscriptions– It is the main source of revenue income which is received from the members of an NPO. Members pay their amount of subscription periodically to keep their membership alive with the organisation.
Calculation of Subscription Amount

Accounting Format
Subscription Account

• Legacy– Legacy is a donation that is received as per the WILL of a deceased person.
Accounting Treatment: The treatment of legacy depends on the nature of receipt and the condition specified with that receipt.

Honorarium– It is a payment that is made to a person in honour of his/her voluntary services to the organisation. This payment is of revenue nature. It can be either in cash or in kind.
Accounting Treatment: It is shown on the Expenditure side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
• Life Membership Fees– The fee that is paid by the people to get the membership of an organisation for the lifetime. Usually, this fee is treated as a capital receipt as it is non- recurring in nature and the benefit of this fee is available for the lifetime.
Accounting Treatment: Its accounting treatment depends on the practices adopted by an organisation. If nothing is specified about the Life Membership Fee, then it is treated as a capital receipt and added to the Capital Fund on the Liabilities side of the Closing Balance Sheet.
♦ Donations: Donations are a kind of gift which are received by an organisation either in cash or in any other form. Donations can be both general as well as specific donations.
• General Donation– These donations are received as gifts from the donor without any specific condition. These donations can be use for carry out the general operations of an organisation.
Accounting Treatment: General Donation can be either treated as General Revenue Receipt or General Capital receipt.
If it is treated a general revenue receipt, then it is shown on the Income side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
If it is treated as general capital receipt for general, then it is directly added to the Capital Fund on the Liabilities side of the closing Balance Sheet.
• Specific Donations- These are the donations that are received as gifts with specific conditions attached. These donations can only be used to carry out the specific operation (as per the condition attached with the donation). These donations are used to accomplish a particular objective. For example, donations for building cannot be used for any other purpose other than constructing building.
Accounting Treatment– These donations are transferred to respective Fund Account and are shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
♦ Sale of Old Assets
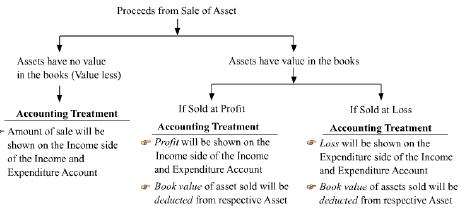
♦Sale of Old Newspapers, Magazines, etc.
The sale of items such as, magazines, newspapers, etc. are of recurring nature, thereby the income received from their sale is considered as revenue income.
Accounting Treatment: As the income received from the sale of such items is considered as revenue income, so the sale of old newspapers, etc. is shown on the Income side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
♦ Government Grants– These are the financial assistance from the government agencies to the NPOs such as, schools, colleges, hospital, etc. It is a source of revenue for the NPOs. There can be following two cases with respect to the government grants.
Situation 1– If the government grant is revenue in nature and nothing is specified for the use of grant.
Accounting Treatment– It will be shown on the Income side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
Situation 2– If the purpose of the government grant is specified
Accounting Treatment– It will be shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. The expenses attributing to the grant will be deducted from the amount available in the account of such grant.

Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation Notes are really useful for Class 12 students as if you revise them properly If you revise them properly just before your class 12 examinations then for sure you will be able to understand all the difficult topics which are there in your NCERT book for class 12 accountancy and you will be able to learn the difficult topics which have been given in Chapter Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation. As this is a very important topic therefore students are suggested to go through these concepts and questions which we have provided above and learn them thoroughly for your examination as this will give you confidence and help to Boost Your rank.
