Notes for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 5 Dissolution of Partnership Firm
Commerce students can refer to the Dissolution of Partnership Firm Notes Class 12 Accountancy given below which is an important chapter in class 12 accountancy book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Accountancy teachers have prepared these notes for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Dissolution of Partnership Firm Notes Class 12 Accountancy
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Dissolution of Partnership Firm which are really useful and have been recommended by Class 12 Accounts teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books for Class 12 Accounts.
I. Multiple Choice Questions:
- Realization account is a _ account
(a) Real
(b) personal
(c) nominal
(d) cash
Answer
C
- At the time of dissolution of a firm, _ account is prepared.
(a) Revaluation
(b) Realisation
(c) Profit and Loss
(d) Trading
Answer
B
- At the time of dissolution, partner’s loan account is closed by
(a) Transferring in realization
(b) payment
(c) abolished
(d) none of these
Answer
B
- Unrecorded assets taken over by any creditor will _
(a) Be debited to realization account
(b) be debited and credited to realization account
(c) be credited to realization account
(d) not be recorded anywhere
Answer
D
- At the time of dissolution, goodwill of the firm is closed by transferring it to _ account
(a) Realization
(b) partners loan
(c) partner’s capital
(d) bank
Answer
A
- Realisation expenses are debited to
(a) Bank a/c
(b) realization a/c
(c) revaluation a/c
(d) either realization or bank a/c
Answer
B
- Accumulated profits and losses are transferred to credit of
(a) Revaluation A/c
(b) Partner’s Capital A/c
(c) Realisation A/c
(d) Bank A/c
Answer
B
- Accumulated losses and reserves are transferred to the debit of __ a/c
(a) Revaluation
(b) partner’s capital
(c) realization
(d) bank
Answer
B
- Unrecorded liabilities when paid are debited to
(a) Realisation a/c
(b) Partner’s Capital a/c
(c) bank a/c
(d) none of these
Answer
A
- On firm’s dissolution, when a partner voluntarily gives his personal asset to firm’s creditor payment, the account credited will be
(a) Realization a/c (
(b) Partner’s Capital a/c
(c) bank a/c
(d) none of these
Answer
B
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. At the time of dissolution of firm assets are ___________ and liabilities are ____________.
Answer
sold, paid off
2. Under partnership at ______, any partner may ask for the dissolution of the firm.
Answer
Will
3. At the time of dissolution, partner’s current account balance will be transferred to ________ account.
Answer
Partner’s Capital
4. Provision for doubtful debts is transferred to _______ side of Realisation A/c.
Answer
Credit
5. If any partner takes any asset, then such partner’s capital account will be ____
Answer
Debited
III. Match the following:
IV. Short Answer Questions:
1. In case of dissolution of a firm which liabilities are to be paid first?Ans: Debt of third parties
- 2. In case of dissolution of a firm, which item on the liabilities is to be paid last?
Ans: Partner’s Capital
3. State any one occasion for the dissolution of the firm on court’s order when a partner becomes.
Ans: Partner becomes permanently incapable of performing his duties as a partner.
4. Give any one difference between reconstitution of firm and dissolution of a firm.
Ans: Reconstitution of firm means change in the existing agreement between partners, whereas dissolution of firm means dissolution of partnership between all partners of the firm.
5. Distinguish between “Dissolution of Partnership’’ and ‘Dissolution of Partnership Firm” on the basis of settlement of accounts.
Ans:In case of Dissolution of Partnership assets are revalued and liabilities are reassessed where as in case of Dissolution of Firm all assets are sold off except cash and liabilities are paid .
6. Mention one difference between Realisation and Revaluation Account.
Ans: Realisation Account is prepared at the time of dissolution of firm where as Revaluation Account is prepared at the time of admission/retirement/death of a partner.
7. On dissolution of a firm, where are assets shown in Balance Sheet transferred?
Ans: On the Debit side of Realisation Account.
8. On dissolution of a firm ,where is cash in hand transferred?
Ans: On the debit side of Cash Account.
9. In case of dissolution,where are general reserves and accumulated profits and losses transferred?
Ans: In partner’s Capital Accounts in their profit sharing ratio.
10. In the event of dissolution of a partnership firm, where is provision for doubtful debts transferrd?
Ans: On the credit side of Realisation Account.
11. On dissolution, patents appearing in the balance sheet is transferred to which account?
Ans: Realisation Account.
12. If total assets are Rs 2,00,000; total liabilities are Rs 40,000; amount realized on sale of assets is Rs 1,75,000 and realization expenses are Rs 3,000,what will be the profit or loss on realization?
Ans: Loss Rs 28,000 (Realisation A/c Debit 2,43,000 Credit 2,15,000, difference of debit and credit= 28000(loss)
13. How much amount will be paid to creditors for Rs 25,000 if Rs 5,000 of the creditors are not to be paid and the remaining creditors agreed to accept 5% less amount?
Ans : Rs 19000 ( Creditors to be paid 25000- 5000= 20,000; Amount paid= 20,000- 5% of 20,000)
14. How much amount will be paid to A, if his opening capital is Rs 2,00,000 and his share of realization profit amounts to Rs 10,000 and he has taken over assets Rs 25,000 from the firm?
Ans: Rs 2,000 ( opening capital +realisation profit – asset taken over)
15. If creditors are Rs 25,000, capital is Rs 1,50,000 and cash balance is Rs 10,000, what will be amount of sundry assets?
Ans : 1,65,000 ( Sundry Assets= Creditors +Capital -Cash balance)
16. A and B are partners in a firm .Their firm was dissolved on 1.1.2019. A was assigned the work of dissolution. For this work, A was to be paid Rs 500. A paid dissolution expenses from his own pocket. Will any journal entry be passed for Rs 400 paid by A? If yes, pass the entry, If no, give reason
Ans

17. The firm of Ravi and Mohan was dissolved om 31.03.2019. According to the agreement ,Ravi had agreed to undertake the dissolution work for an agreed remuneration of Rs 2,000 and bear all realization expenses. Dissolution expenses were Rs 1500 and the same were paid by the firm. Pass necessary journal entries.
Ans.

- 18. Creditors of Rs 50,000 took over stock at an agreed value of Rs 45,000 and the balance was paid to him. Pass the necessary journal entry.
Ans:For stock taken over by creditor no Journal entry , for the balance paid the entry will be

19. List any four modes of dissolution of partnership firm.
Ans: Dissolution by agreement, Compulsory dissolution, Dissolution by Court, Dissolution by notice in case of partnership at will.
20. Name the assets that are not transferred to the debit side of Realisation Account, but brings certain amount of cash against its disposal at the time of dissolution of the firm.
Ans; Unrecorded Assets.
V. Numerical Questions
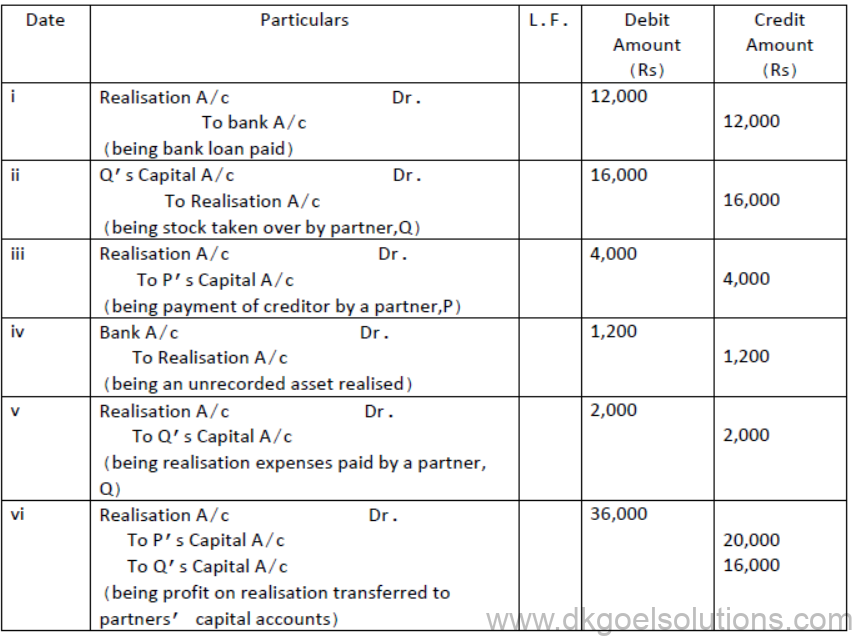
1. Pass the necessary journal entries for the following transactions on the dissolution of the firm of P and Q after the various assets( other than cash) and outside liabilities have been transferred to Realisation account.
i. Bank Loan Rs 12,000 was paid
ii. Stock worth Rs 16,000 was taken over by partner Q
iii. Partner P paid a creditor Rs 4,000
iv. An asset not appearing in the books of accounts realized Rs 1,200
v. Expenses of realisation Rs 2,000 were paid by partner Q
vi. Profit on realisation Rs 36,000 was distributed between P and Q in 5:4 ratio.
Solution :
JOURNAL
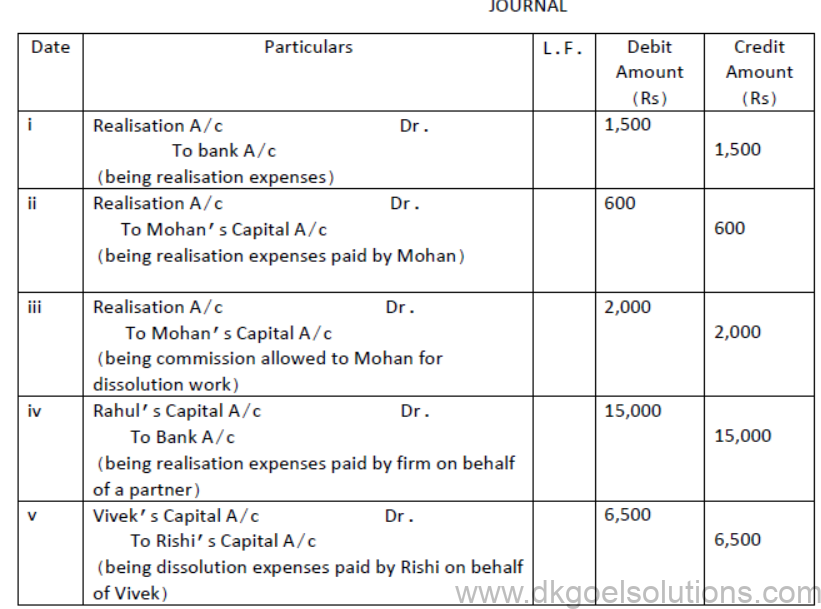
2. Pass Journal entries in the following cases:
i. Expenses of realisation Rs 1500
ii. Expenses of realisation Rs 600 but paid by Mohan, a partner
iii. Mohan, one of the partners of the firm ,was asked to look into the dissolution of the firm for which he was allowed a commission of Rs 2,000.
iv. Realisation expenses of Rs 15,000 were to be met by Rahul, a partner, but were paid by the firm.
v. Vivek a partner was appointed to look after dissolution work and he agreed to bear the dissolution expenses.Actual dissolution expenses Rs 6,500 were paid by Rishi another partner, on behalf of Vivek.
Solution
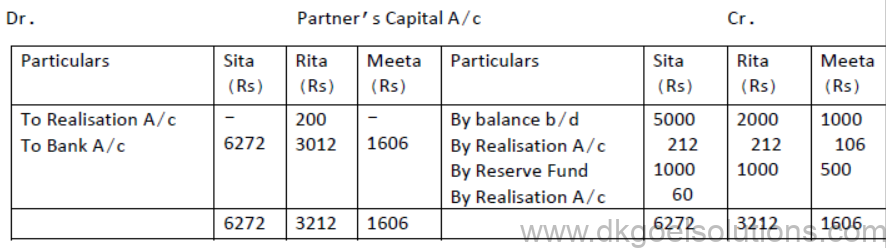
3. Sita , Rita and Meeta are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio 2:2:1. Their balance sheet as on March 31, 2020 is as follows:
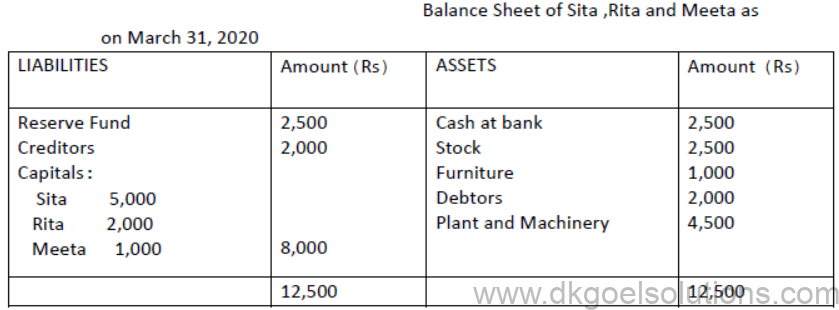
They decided to dissolve their business. The following amounts were realized:
Plant and machinery rs 4,250, Stock Rs 3,500 , Debtors s 1,850, Furniture 750. Sita agreed to bear all realisation expenses. For the service Sita is paid Rs 60.
Actual expenses on realisation amounted to Rs 450.Creditors were paid 2%less.
There was an unrecorded asset of Rs 250 , which were taken over by Rita at Rs 200.
Prepare Realisation Account, Partners’Capital Accounts and Bank Account.
Solution:


4. Surjit and Rahi were sharing profits(or losses) in the ratio of 3:2, their Balance Sheet as on march 31, 2020 is as follows:
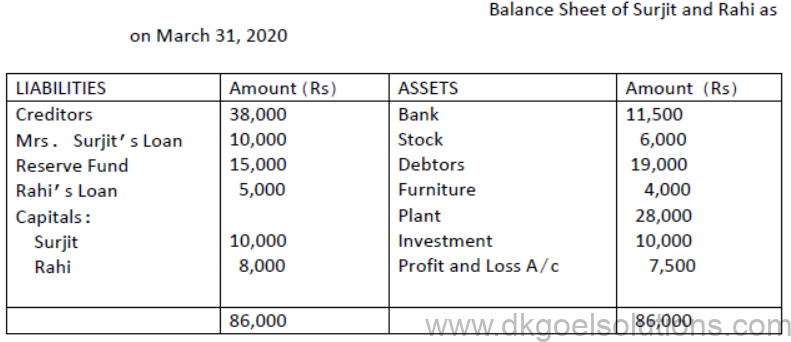
The firm was dissolved on March 31, 2020 on the following terms:
i. Surjit agreed to take investments at Rs 8000 and to pay Mrs.Surjit’s Loan.
ii. Other assets were realised as follows:
Stock – Rs 5000,Debtors – Rs18,500, Furniture –Rs 4,500,Plant – Rs 25,000
iii. Expenses on realisation amounted to Rs 1,600
iv. Creditors agreed to accept Rs 37,000 as a final settlement.
Pass necessary journal entries on dissolution of the firm.
Solution:
JOURNAL
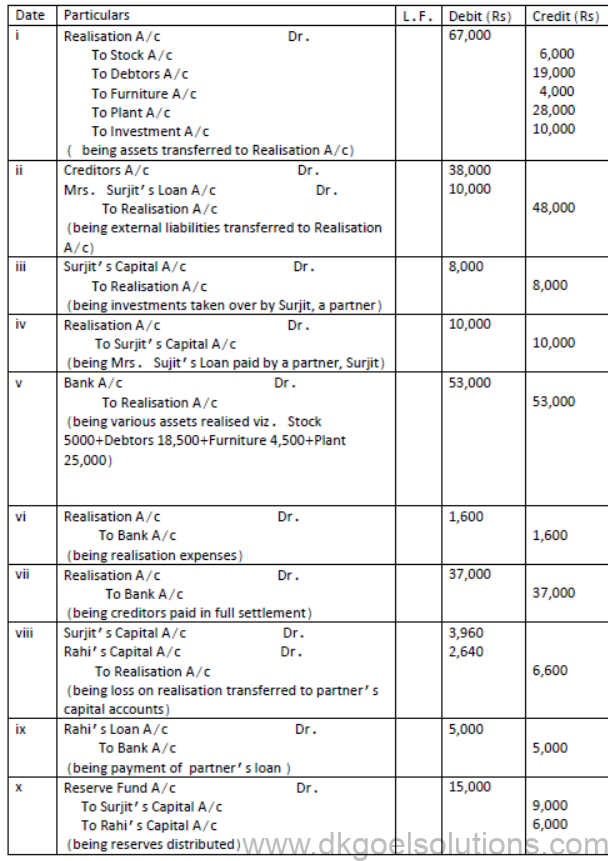
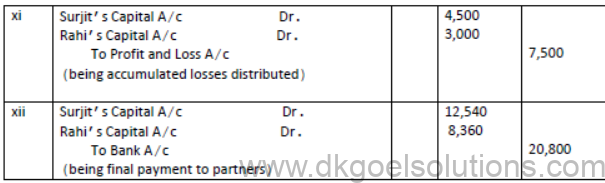
5. Ashish and Neha were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio 4:3. They decided to dissolve the firm on 31st Mar, 2019. From the following information given below, complete Realisation A/c, Partner’s Capital A/c s and bank A/c:

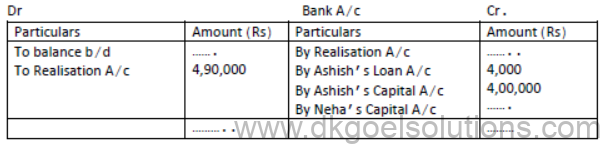
Solution:
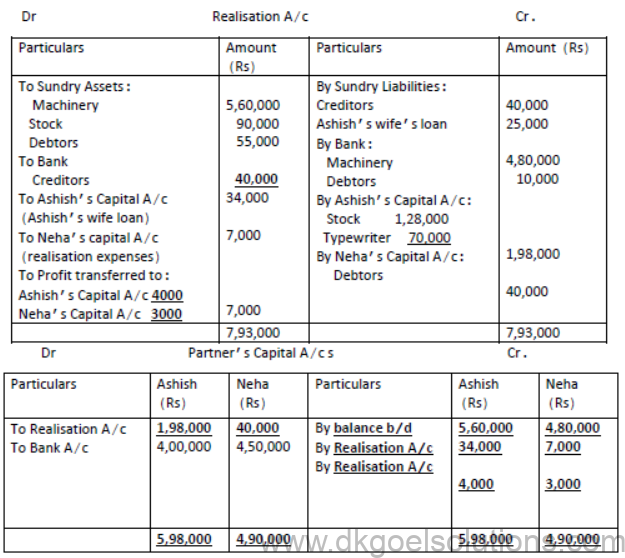

Notes for Dissolution of Partnership Firm Class 12 Accountancy
Dissolution of a firm : As per Indian Partnership Act, 1932 : “Dissolution firm means termination of partnership among all the partners of the firm”
When a firm is dissolved, the business of the firm terminates. All the assets the firm are disposed off and all outsiders’ liabilities and partners’ loan and partner capital are paid.
Dissolution of Partnership : Dissolution of Partnership refers to terminal of old partnership agreement (i.e., Partnership Deep) and a reconstruction the firm.
It may take place on
· Change in profit sharing ratio among the existing partner:
· Admission of a partner; and
· Retirement of Death of partner.
It may or may not result into closing down of the business as the remount partners may decide to carry on the business under a new agreement.
Types of dissolution of firms: A Partnership firm can be dissolved in any the following ways:
(A)Without the intervention of the court:
(1) When all partners agree to dissolve the firm (Sec. 40);
(2) Compulsory Dissolution (Sec. 41)
(i) When all or except but one partner of the firm become insolvent
(ii) When business of the firm become unlawful.
(3) On the happening of any of the following events: (Sec. 42)
(i) On the insolvency of a partner.
(ii) On the fulfillment of the objective of the firm for which the for was formed.
(iii) On the expiry of the (period) for which the firm was formed.
(4) By Notice (Sec. 43) : When the duration of the partnership firm is a fixed and it is at will of the partners. Any partner by giving notice other partners can dissolve the firm.
(B) Dissolution by order of the court (Sec. 44) :
A court on application by a partner may order the dissolution of the firm under the following circumstances:
(1) When a partner has become of unsound mind.
(2) When a partner has become permanently incapable of performing his duties as a partner.
(3) When a partner is found quality of misconduct that may harm the partnership.
(4) When a partner consistently and deliberately commits breach of partnership agreement.
(5) When a partner transfer whole of is interest in the business firm to a third party, without the consent of existing partners.
(6) When the court is satisfied that the partnership firm cannot be carried on except at a loss.
(7) When the court finds that the dissolution of firm is justified and equitable.
ACCOUNTING TREATMENT OF DISSOLUTION
On dissolution of a firm, the following accounts are opened to close the books of the firm .
· Realisation Account;
· Partner’s Loan Account;
· Partner’s Capital Accounts; and
· Cash or Bank Account.
Realisation Account : It is nominal account opened on the dissolution of a firm to ascertain the profit or loss on realization of assets and payment of outsiders liabilities. This
account is closed by transferring the balance (i.e., profit or loss on realization) to partner’s capital accounts.
PREPARATION OF REALISATION ACCOUNT
The following Journal Entries are passed :
A. For Closing Assets Accounts:
Realisation A/cDr.
To sundry Assets A/c
(Being assets transferred to Realisation A/c)
Note :
1. Cash and Bank balance are not transferred to Realisation Account.
2. Assets (tangible and intangible) are transferred to Realisation Account to their Gross Value
3. Fictitious Asset such as Debit balance of Profit and Loss Account of Advertisement Suspense’s Account etc. are not transferred to Realisation Account. These are directly debited to partners’ capital accounts in their profit sharing ratio by passing the following entry.
Partner’s capital A/cDr.
To Profit and Loss A/c
To Advertisement Suspense A/c
(Being Balance of losses transferred to capital accounts)
4. Provision against assets such as Provision for Depreciation of Provision for Bad & Doubtful debts etc. are transferred to Realisation Account by passing a Separate entry:
Provision’s for Bad Debts A/cDr.
Provision’s for Depreciation A/cDr.
Investment Fluctuation Fund A/cDr.
Machinery Replacement Reserve A/cDr.
To Realisation A/c
(Being Provision & Reserves Against Assets transferred to Realisation Account)
B. For Closing Liabilities Accounts:
Sundry Liabilities A/cDr.
To Realisation A/c
(Being sundry liabilities transferred to Realisation A/c)
Note :
1. Only third parties liabilities/outsiders ‘liabilities are transferred to Realisation A/c
2. Balance of Partner’s Loan Accounts are not transferred to Realisation Account Separate accounts are opened to settle such liabilities.
3. Undistributed profits and reserves are also not transferred to Realisation A/c. These are directly credited to partners’ capital accounts in their profit sharing ratio by passing the following entry.
Profit and Loss A/cDr.
General Reserves A/cDr.
Reserve fund A/cDr.
Contingency Reserve A/cDr.
To Partner’s Capital A/cs
(Being balance of undistributed profits transferred to capital accounts)
4. Provident Fund is a liability on the firm towards employees and hence it is transferred to Realisation A/c.
5. If any liability is expected to arise against any found or reserve e.g., Workmen’s Compensation Fund, then an amount equal to such liability is transferred to Realisation A/c balance, if any, distributed among the partners in their profits-sharing ratio by passing the following entry.
Workmen’s Compensation Fund A/CDr.
To Realisation A/c(Liability)
To Partners’ Capital A/cs(Balance, if any)
(Being liability against workmen’s compensation fund transferred to Realisation A/c and balance Distributed among partners.
C. For Realisation of Assets (Whether recorded or unrecorded)
a. When assets are sold for cash
Cash/Bank A/cDr.
To Realisation A/c
(Being assets sold for cash)
b. When assets are taken over by any partner.
Partner’s Capital A/cDr.
To Realisation A/c
(Being assets taken over by any partner)
c. When assets are taken over by any creditor in part of full payment his dues :
I. In case of Full Settlement:
i. NO ENTRY is passed for the transfer of assets to the creditor.
ii. NO ENTRY is passed for the payment to creditor.
II. In case of Part Settlement:
i. NO ENTRY is passed for the transfer of assets to the creditor.
ii. The agreed amount of asset is deducted from the claims of it creditors and the balance is paid to him.
Note :
1. The realized value of each asset must be given at the time of dissolution.
D. For Payment of Liabilities
a. When liabilities are paid in cash
Realisation A/cDr.
To Cash/Bank A/c
(Being liabilities paid in cash)
b. When liabilities are taken over by any partner
Realisation A/cDr.
To Partner’s Capital A/c
(Being liabilities taken over by a partner)
Note : If nothing is stated regarding the settlement of any outside liability, then it should be assumen that the amount equal to book value is paid.
E. For Realisation Expenses
a. When expenses are paid by firm and borne by firm:
Realisation A/cDr.
To Cash/Bank A/c
(Being realization expenses paid in cash).
b. When expenses are paid by any partner and borne by firm :
Realisation A/cDr.
To Partner’s Capital A/c
(Being realization expenses paid by a partner).
c. When expenses are paid by firm (on behalf of any partner) and born by an partner.
Partner’s Capital A/cDr.
To Cash/Bank A/c
(Being realization expenses paid on behalf of partner).
e. When a partner is paid a fixed amount for bearing realization expenses then: Actual
expenses are not be considered;
ii. Realization A/cDr. (With Fixed Amount)
To Partner’s Capital A/c
(Being realization expenses paid by a partner)
f. When expenses are paid by one partner and borne by another partner;
Partner’s Capital A/cDr. (Who borne the expenses)
To Partner’s Capital A/c (Who pays the expenses)
(Being realization expenses paid by one partner and borne by another partner).
In case the realization expenses are borne by a partner, clear indication should be given regarding the payment there of.
F. For Closing Realisation Account
a. When Realization A/c Discloses profit (in case total of credit side is more than the total of debit side)
Realisation A/cDr.
To Partner’s Capital A/cs
(Being profit on realization transferred to partners’ capital A/cs)
b. When Realisation A/c discloses loss (in case total of debit side is more than the total of credit side)
Partners’ Capital A/cDr.
To Realisation A/c
(Being loss on realization transferred to partners capital A/cs)
FORMAT OF REALISATION ACCOUNT
Realization A ccount
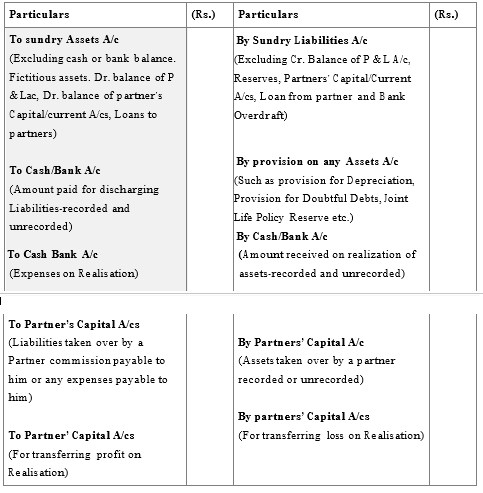
PREPARATION OF PARTNERS’ LOAN ACCOUNT
If a partner has given any loan to firm, his loan will be paid
· After payment of all the outside liabilities : but
· Before making any payment to partners on account of capital
Partner’s Loan A/cDr.
To Cash/Bank A/c
(Being loan of a partner paid)
Partner’s Loan A/c
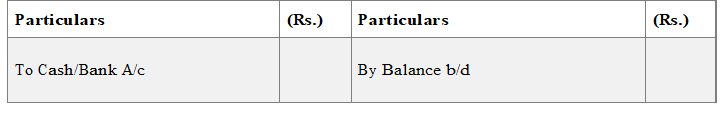
If the firm has given a loan to any partner then such loan account will show a debti balance and will appear on the asset side of Balance Sheet of the firm. Such loan accounts are settled through partner’s capital account by passing the following entry:
Partner’s Capital A/c Dr.
To Partner’s Loan A/c
(Being loan to partner transferred to his Capital A/c)
Preparation of partner capital Accounts
After the Transfer of
· Undistributed profits and reserves
· Profit on Realisation
· Any liability taken over by any partner
And
· Undistributed losses and fictitious assets
· Loss on realization
· Any assets taken over by any partner
The balance of partners’ capital A/cs are closed in the following manner
a. For making final payment to a partner (if total of credit side is more than the total of debit side)
Partner’s Capital A/c Dr.
To Cash/Bank A/c
(Being excess paid to partner in cash)
b. For any amount received form a partner against debit balance in his capital account.
Cash/Bank A/c Dr.
To Partner’s Capital
(Being cash brought in by any partner)


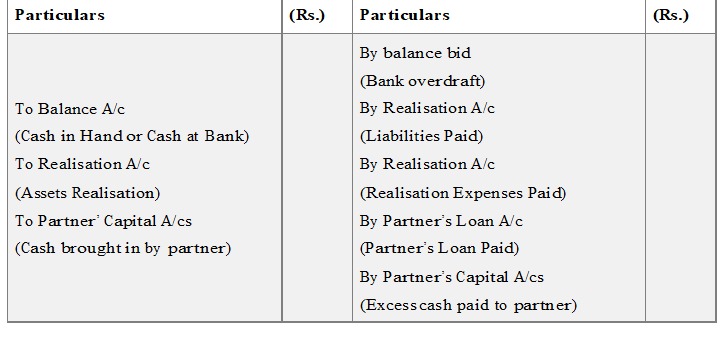
Preparation of Cash or Bank Account
This account is prepared at the end closed last of all. This account helps to verification of the arithmetically accuracy of accounts as both sides of this account must be equal.
Note: If cash and bank balance both are given in the Balance Sheet, one A/c to prepared, either a Cash A/c or a Bank A/c If Cash A/c is opened, an entry of with drawing the bank balance is made:
Cash A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
(Being cash withdrawn from Bank)
If Bank A/c is opened, an entry for depositing the cash into bank is passed.
Bank A/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
(Being cash deposited into Bank)
Cash/Bank A/c
Distinction between Revaluation Account Realisation Account

PREPARATION OF MEMORANDUM BALANCE SHEET
If a balance sheet on the date of dissolution is not given in the question, there is always advisable to prepare Memorandum Balance Sheet on the date of dissolution to ascertain the
amount of balancing figure.
Note
• In the absence of any other information “Sundry Assets” should be treatment as balancing figure on the assets side of Balance Sheet.
• If the balance of Partners’ Capital A/cs are not given as on the date on dissolution, first we will find the balance of partners’ capital accounts as on the date of dissolution by recasting
the capital accounts.
· When “Sundry Assets” are given in the question and nothing is specified about the difference on the asset side of Balance Sheet, the different should be treated as Dr. balance
of Profit and Loss A/c.
Some common mistakes committed by students
• Entries for assets or liabilities taken by partners
• Dissolution Expenses
• Realisation of unrecorded assets
• Payment of Unrecorded Liabilities
• Treatment of Fictitious Assets
Due care should be taken while showing the effect of above mentioned items.

Also Read : Printable Worksheets for Class 12 Accountancy
