MCQs for Chemistry Class 12 with Answers Chapter 7 The P – Block Elements
Students of class 12 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry The P – Block Elements with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 12 Chemistry NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 12 Chemistry. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 12 Chemistry examination
Chapter 7 The P – Block Elements MCQ with Answers Class 12 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry The P – Block Elements provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 12. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 12 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. Which of the following is not tetrahedral in shape?
(a) NH+4
(b) SiCl4
(c) SF4
(d) SO42–
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are peroxoacids of sulphur?
(a) H2SO5 and H2S2O8
(b) H2SO5 and H2S2O7
(c) H2S2O7 and H2S2O8
(d) H2S2O6 and H2S2O7
Answer
A
Question. Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
(a) Cu
(b) S
(c) C
(d) Zn
Answer
C
Question. On addition of conc. H2SO4 to a chloride salt, colourless fumes are evolved but in case of iodide salt, violet fumes come out. This is because:
(a) H2SO4 reduces HI to I2
(b) HI is of violet colour
(c) HI gets oxidised to I2
(d) HI changes to HIO3
Answer
C
Question. Orthoboric acid when heated to red hot gives
(a) metaboric acid
(b) pyroboric acid
(c) boron and water
(d) boric anhydride
Answer
B
Question. SO2 acts as a/an
(a) Oxidising agent
(b) Reducing agent
(c) Bleaching agent
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy (with negative sign) of the given atomic species?
(a) S < O < Cl < F
(b) F < Cl < O < S
(c) Cl < F < S < O
(d) O < S < F < Cl
Answer
C
Question. In qualitative analysis when H2S is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with dil. HCl, a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with dil. HNO3, it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives _____________.
(a) deep blue precipitate of Cu (OH)2
(b) deep blue solution of [Cu (NH3)4]2+
(c) deep blue solution of Cu(NO3)2
(d) deep blue solution of Cu(OH)2.Cu(NO3)2
Answer
B
Question. Which is false in case of boric acid H3BO3?
(a) It acts as a tribasic acid.
(b) It has a planar structure.
(c) It acts as a monobasic acid.
(d) It is soluble in hot water.
Answer
A
Question. Borazole is known as
(a) organic benzene
(b) organic xylene
(c) inorganic benzene
(d) inorganic xylene
Answer
C
Question. Out of the following halides of group 16, which does not possess reducing property?
(a) H2Te
(b) H2Se
(c) H2S
(d) H2O
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following options are not in accordance with the property mentioned against them?
(a) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 Oxidising power.
(b) MI > MBr > MCl > MF Ionic character of metal halide.
(c) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 Bond dissociation enthalpy.
(d) HI < HBr < HCl < HF Hydrogen-halogen bond strength.
Answer
B
Question. When chlorine reacts with hot and conc. NaOH, the product(s) formed are
(a) chloride
(b) hypochlorite
(c) chlorate
(d) mixture of chloride and chlorate
Answer
C
Question. If chlorine gas is passed through hot NaOH solution, two changes are observed in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are ________ and _________.
(a) 0 to +5
(b) 0 to +3
(c) 0 to –1
(d) 0 to +1
Answer
A
Question. Two types of F × F angles are present in which of the following molecule (X = S, Xe, C):
(a) SF6
(b) CF4
(c) XeF4
(d) SF4
Answer
C
Question. The structure of XeF6 is
(a) distorted octahedral
(b) linear
(c) square planar
(d) tetrahedral
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following properties of aluminium makes it useful for food packaging ?
(a) Good electrical conductivity
(b) Good thermal conductivity
(c) Low density
(d) Non toxicity
Answer
C
Question. The set with correct order of acidity:
(a) HClO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4
(b) HClO4 < HClO3 < HClO2 < HClO
(c) HClO < HClO4 < HClO3 < HClO2
(d) HClO4 < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO
Answer
A
Question. The elements commonly used for making transistors are
(a) C and Si
(b) Ga and In
(c) P and As
(d) Si and Ge
Answer
C
Question. The most stable +2 oxidation state is exhibited by
(a) Fe
(b) Sn
(c) Pb
(d) Si
Answer
C
Question. The inert gases compounds are producing maximum number of
(a) He and Ne
(c) Kr and Ne
(b) Ar and Ne
(d) Ar and Xe
Answer
D
Question. Which is the most easily liquefiable rare gas?
(a) Xe
(b) Kr
(c) Ar
(d) Ne
Answer
A
Question. The formation of O+2 [PtF6]– is the basis for the formation of xenon fluorides. This is because
(a) O2 and Xe have comparable sizes
(b) Both O2 and Xe are gases
(c) O2 and Xe have comparable ionisation energies
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Xenon hexafluoride reacts with silica to form a xenon compound X. The oxidation state of xenon in Xis
(a) + 2
(b) + 4
(c) + 6
(d) 0
Answer
C
Question. The noble gas used in atomic reactor, is
(a) krypton
(b) oxygen
(c) neon
(d) helium
Answer
D
Question. When radioactive minerals like clevite, monazite and pitchblende are heated to 1273 K in vacuo the noble gas obtained is
(a) Rn
(c) He
(b) Kr
(d) Ne
Answer
C
Question. The noble gas mixture is cooled in a coconut bulb at 173 K. The gases that are not adsorbed are
(a) Ne and Xe
(b) He and Xe
(c) Ar and Kr
(d) He and Ne
Answer
D
Question. The gas not adsorbed by coconut charcoal is
(a) He
(b) Ne
(c) Ar
(d) Kr
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statements regarding helium is incorrect ?
(a) It is used to fill gas balloons instead of hydrogen because it is lighter and non-inflammable
(b) It is used as a cryogenic agent for carrying out experin1ents at low temperatures
(c) It is used to produce and sustain powerful superconducting magnets
(d) It is used in gas-cooled nuclear reactors
Answer
C
Question. Helium is used in balloons in place of hydrogen because it is
(a) incombustible
(b) lighter than hydrogen
(c) radioactive
(d) more abundant than hydrogen
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following noble gases is most reactive?
(a) He
(b) Ne
(c) Ar
(d) Xe
Answer
D
Question. The noble gas which is not found in atmosphere
(a) Ne
(b) Ar
(c) Rn
(d) Kr
Answer
C
Question. Noble gases are adsorbed by
(a) anhydrous calcium chloride
(b) ferric hydroxide
(c) cone. H2SO4
(d) activated coconut charcoal
Answer
D
Question. In clathrates of xenon with water, the nature of bonding between xenon and water molecule is
(a) dipole induced dipole interaction
(b) coordinate
(c) hydrogen bonding
(d) covalent
Answer
A
Question. For advertisement, the coloured discharged tubes contain
(a) He
(b) Ne
(c) Ar
(d) Kr
Answer
B
Question. End-product of the hydrolysis ofXeF6 is
(a) XeF4O
(b) XeF2O2
(c) XeO3
(d) XeO–3
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following noble gases is used in miner’s cap lamps ?
(a) Helium
(b) Neon
(c) Argon
(d) Krypton
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following represents noble gas configuration ?
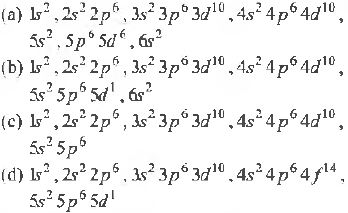
Answer
C
Question. What is the co1Tect order of occurrence(% by weight) in air of Ne, Ar and Kr?
(a) Ne > Ar > Kr
(b) Ar > Ne > Kr
(c) Ar > Kr > Ne
(d) Ne > Kr > Ar
Answer
B
Question. In Fischer-Ringe’s method of separation of noble gas mixture from air, ………. is used.
(a) 90% CaC2 + 10% CaCI2
(b) coconut charcoal
(c) soda lime+ potash solution
(d) 90% CaCO3 + 10% urea
Answer
A
Question. Which inert gas have highest boiling point ?
(a) Xe
(b) Ar
(c) Kr
(d) He
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the pure form of carbon ?
(a) Diamond
(b) Fullerene
(c) Graphite
(d) All three forms are equally pure
Answer
B
Question. Crystalline form of silica is called
(a) crystalline silicon
(b) quartz
(c) rock
(d) talc
Answer
B
Question. In which case, order of acidic strength is not correct?
(a) HClO4 > HClO3 > HClO2
(b) HI > HBr > HCl
(c) HF > H2O > NH3
(d) HIO4 > HBrO4 > HClO4
Answer
C
Question. Which of the statement given below is incorrect?
(a) ONF is isoelectronic with O2N–
(b) O3 molecule is bent
(c) OF2 is an oxide of fluorine
(d) Cl2O7 is an anhydride of perchloric acid
Answer
C
Question. The element which shows least metallic character is
(a) Indium
(b) Boron
(c) Aluminium
(d) Gallium
Answer
B
Question. Aluminium vessels should not be washed with materials containing washing soda because
(a) washing soda is expensive
(b) washing soda is easily decomposed
(c) washing soda reacts with aluminium to form soluble aluminate
(d) washing soda reacts with aluminium to form insoluble aluminium oxide
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following pairs, the two species are isostructural?
(a) SF4 and XeF4
(b) BF3 and NF3
(c) BrO–3 – and XeO3
(d) SO2-3 and NO–3
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement is not true for helium?
(a) He is used in gas-cooked nuclear reactors.
(b) He is used as cryogenic agent for carrying out experiments at low temperature.
(c) He is used to fill gas balloons instead of hydrogen because it is lighter than hydrogen and non-inflammable.
(d) He is used as a diluent for oxygen in modern diving apparatus.
Answer
C
Question. When Al is added to KOH solution
(a) no action takes place
(b) oxygen is evolved
(c) water is produced
(d) hydrogen is evolved
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following does not react with aqueous NaOH ?
(a) B
(b) Al
(c) Ga
(d) Tl
Answer
A
Question. Boric acid is polymeric due to
(a) its acidic nature
(b) the presence of hydrogen bonds
(c) its monobasic nature
(d) its geometry
Answer
B
Question. In diborane
(a) 4–bridged hydrogens and two terminal hydrogens are present
(b) 2– bridged hydrogens and four terminal hydrogens are present
(c) 3–bridged and three terminal hydrogens are present
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following has the lowest m.p.?
(a) B
(b) Al
(c) Ga
(d) Tl
Answer
C
Question. The group 13 element that is liquid during summer and used for measuring high temperature is
(a) Boron
(b) Aluminium
(c) Gallium
(d) Indium
Answer
C
Question. Thallium shows different oxidation states because
(a) it is transition element
(b) of inert pair effect
(c) of its amphoteric character
(d) of its higher reactivity
Answer
B
Question. Aluminium chloride is a/an
(a) Bronsted – Lowery acid
(b) Arhenius acid
(c) Lewis acid
(d) Lewis base
Answer
C
Question. Which metal is protected by a layer of its own oxide?
(a) Al
(b) Ag
(c) Au
(d) Fe
Answer
A
Question. Diborane upon hydrolysis gives
(a) boric anhydride
(b) metaboric acid
(c) orthoboric acid
(d) boron oxide
Answer
C
Question. The element which is exclusively applied as semi-conductor
(a) Au
(b) Ge
(c) Pt
(d) Si
Answer
B
Question. B(OH)3 is
(a) monobasic acid
(b) dibasic acid
(c) tribasic acid
(d) triacidic base
Answer
A
Question. The compounds of boron and hydrogen are collectively called
(a) diboranes
(b) borazoles
(c) boracits
(d) boranes
Answer
C
Question. The inert pair effect is most prominent in
(a) C
(b) Pb
(c) Ge
(d) Si
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in diamond ?
(a) Ionic
(b) Covalent
(c) Dipolar
(d) van der Waal’s
Answer
B
Question. The structure of diborane ( B2H6 ) contains
(a) four 2c-2e bonds and four 3c-2e bonds
(b) two 2c-2e bonds and two 3c-3e bonds
(c) two 2c-2e bonds and four 3c-2e bonds
(d) four 2c-2e bonds and two 3c-2e bonds
Answer
C
Question. In graphite, electrons are
(a) localised on every third C-atom
(b) present in anti-bonding orbital
(c) localised on each C-atom
(d) spread out between the structure
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is not an allotrope of carbon ?
(a) Carborundum
(b) Diamond
(c) Soot
(d) Graphite
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following species is:
(a) Cl2O < ClO–2 < ClO2
(b) ClO–2 < Cl2O < ClO2
(c) Cl2O < ClO2 < ClO–2
(c) Cl2O < ClO2 < ClO–2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is isoelectronic pair?
(a) ICl2, ClO2
(b) BrO–2, BrF+2
(c) ClO2, BrF
(d) CN–, O3
Answer
B
Question. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken O2 Pt F6 + – as a base compound. This is because:
(a) both O2 and Xe have same size.
(b) both O2 and Xe have same electron gain enthalpy.
(c) both O2 and Xe have almost same ionisation enthalpy.
(d) both Xe and O2 are gases.
Answer
C

We hope the above multiple choice questions for Class 12 Chemistry for Chapter 7 The P – Block Elements provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. The P – Block Elements is an important chapter in Class 12 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 12 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
