Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Social Science Notes
Students should read Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Social Science Notes provided below. These notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and books issued by NCERT, CBSE and KVS. These important revision notes will be really useful for students to understand the important topics given in the chapter Minerals and Energy Resources in Class 10 Social Science. We have provided class 10 Social Science notes for all chapters.
Revision Notes Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Social Science
Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources is an important chapter in Class 10 Social Science. The following notes will help you to understand and easily learn all important points to help you score more marks.
Important Facts
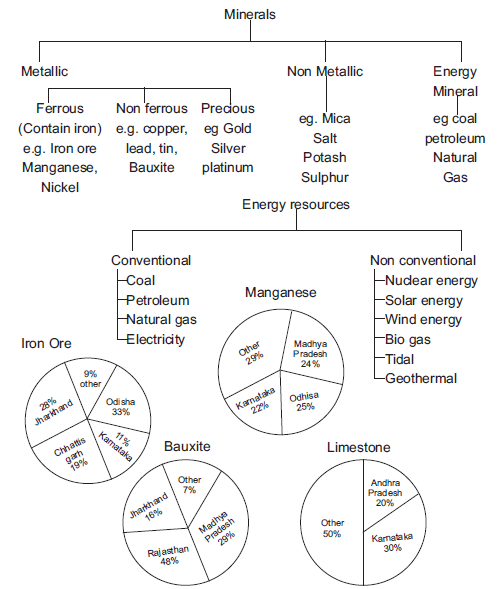
1. Minerals – An indispensable part of our lives. Almost everything we use are made from minerals. Homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.
2. Lignite – A low grade brown coal.
3. Ore – Minerals are usually found in Ores. It is an accumulation of any mineral mixed with other elements.
4. Haematite – The most important industrial iron ore in terms of the quantity used but has only 50-60% iron content.
5. Magnetite – The finest iron ore with a very high content of iron up to 70%
6. Petroleum – Impure or raw mineral oil which is the next major energy source in India after coal.
7. Mining – The extraction of useful and commercially viable minerals.
8. Ferrous Minerals – Containing iron e.g. iron, manganese, nickel, cobalt etc.
9. Mumbai High – The oil field in Arabian sea near Mumbai which produces 63% of India’s Petroleum.
10. Nuclear Power – Nuclear or Atomic (Power Energy) is obtained by altering the structure of atoms.
11. Nuclear Minerals-The matters which consists the nuclear power such as Uranium, Thorium etc.
12. Biogas – Energy which is obtained from the decomposition of organic matters, such as wet-dry grass, agricultural wastes, animal and human defecate ect.
13. Metallic Minerals – Minerals which have more metallic content e.g. iron ore, bauxite etc.
14. Non-Metalic Minerals – Minerals which have no metal portion e.g. lime stone, potash etc.
15. Geologist – Who study the formation of minerals their age and their physical and chemical composition.
Major mineral producing areas in India

Very Short answer type Questions
Question. Which are the non-conventional energy resources?
Ans. Wind energy, solar energy, tidal energy, Geo-thermal energy.
Question. Where does the largest solar plant of India is located?
Ans. At Madhapur near Bhuj (Gujarat).
Question. Where does Manganese used?
Ans. It is used in manufacturing bleaching powder, insecticides and paints.
Question. In which industry lime stone is used as a basic raw material?
Ans. Cement Industry.
Question. Which mineral is found in Monazite sands?
Ans. Thorium.
Question. Name the highest quality hard coal?
Ans. Anthracite.
Question. Where does the largest wind farm cluster is found in India?
Ans. Nagarcoil (Tamil Nadu) and Jaisalmer (Rajasthan).
Question. Name the hardest mineral?
Ans. Diamond is the hardest mineral.
Question. Which minerals largely derived from the ocean waters?
Ans. Magnesium, Common salt and bromine.
Question. Where does the two experimental projects have been set up in India to harness geothermal energy?
Ans. In the Parvati Vally near Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh and in the Puga Valley,Ladakh.
Question. Where does the minerals occur in sedimentary rocks?
Ans. In beds or layers.
Question. Which is the finest quality of iron ore?
Ans. Magnetite Content of iron up to 70%
Question. Name the mineral in which India is the leading producer in the world?
Ans. Mica.
Question. State the importance and uses of copper?
Ans. It is malleable, ductile and a good conductor. Copper is mainly used in electrical cables, electronic and chemical industries.
Question. What is Rat- Hole mining?
Ans. In Jowai and Cherapunjee the coal mining is done by family members in the form of a long narrow tunnel, known as a Rat-Hole mining.
Question. Why Mumbai high is famous for?
Ans. The largest Petroleum producing area of India.63%
Short/Long Answer type questions
Question. ‘The future of Solar energy is bright in India.’ Why?
Ans. (i) India is a tropical country.
(ii) It is pollution free.
(iii) It is a renewable resource.
(iv) Rural house holds can easily take it’s advantage.
Question. Why Mumbai high is famous? What is it’s contribution in National economy?
Ans. The off-shore oil field near Mumbai is called Mumbai High. It produces 63% of total oil production of India. Thus Foreign currency is saved.
Question. How minerals are formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Ans. In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals may occur in the cracks, crvices, faults and joints. The smaller occurences are called veins and the larger are called lodes.In most cases they are formed when minerals in liquid / molten and gaseous forms are forced upward through cavities towards the earth’s surface. They cool and solidify as they rise. Major metallic minerals like tin, copper, zinc and lead etc. are obtained from veins and lodes.
Question. Distinguish between Ferrous and Non-Ferrous minerals?
Ans.
| Ferrous Minerals | Non-Ferrous Minerals |
| 1. Containing iron | 1. No iron portion |
| 2. Iron, ore, manganese, nickel, cobalt etc. | 2. Copper, lead, tin, bauxite etc. |
Question. Why the conservation of mineral resources is essential? Write three measures of conservation of mineral resources?
Ans. Minerals are required in all spheres of our life and thus we are depended on minerals. Agriculture, industries and domestic purposes we are consuming minerals rapidly. This consumption is very fast and sometimes even more than the requirements. Mineral formation requires millions of years to be formed and concentrated. So the judicious use of these is essential. To save these valuable resources from exhaustion and to preserve them for future generation as well, we should conserve our mineral resources. Some of the methods are:
(i) Judicious use and less consumption
(ii) Improved technologies need to be constantly evolved to allow use of low grade ores at low costs.
(iii) Causing minimum wastage of minerals during the process of mining and processing of minerals.
(iv) Using minerals in a planned manner by adopting the policy of recycle and reuse.
(v) Searching some other eco-friendly options like CNG.
Question. Natural gas is an important source of clean energy, support the statement with example.
Ans. Attempt yourself from notes.
Question. Mention about three major iron ore belts of India?
Ans. There are four major iron ore belts in India-
1. Orissa-Jharkhand belt
2. Maharashtra-Goa belt
3. Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt
4. Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt
Question. In which form Mica is found? Mention it’s major deposits area in India? What are the main uses of Mica?
Ans. Mica is made up of a series of plates or leaves.Mica deposits are found in-
(i) The northern edge of the Chota Nagpur plateau.
(ii) Koderma Gaya-Hazaribagh belt of Jharkhand and Bihar.
(iii) Around Ajmer in Rajasthan.
(iv) Nellore mica belt of Andhra Pradesh.
Mica is used in Electric and electronic industries.
Question. How minerals are significant for us?
Ans. Almost everything we use in our daily life, from tiny pin to a big ship all aremade from minerals. Towering buildings, machinery, utensils, means of transport, railway line and bridges too are made from minerals. Even the food that we eat contains the minerals.
Question. How many types of minerals are there and how these are classified?
Ans. There are three types of minerals
(i) Metallic minerals
(ii) Non-Metallic minerals and
(iii) Energy minerals.
This classification is based on their colour, shine, hardness, density and crystallisation.
Question. Name the Natural gas pipe line popular as Artery of gas transport in India? Mention the name of two key users of natural gas?
Ans. The 1700 km long Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur cross country gas pipeline links Mumbai High and Bassien with the fertilizer, power and industrial complexes in western and northern India. The power and fertilizer industries are the key users of natural gas. Use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG)for vehicles to replace liquid fuels is gaining popularity in the country.
Question. Differentiate between Thermal power and Hydel power?
Ans.
| Thermal Power (Thermal electricity) | Hydel Power (Hydro electricity) |
| 1. This electricity is generated by the use of coal, petroleum and natural gas. | 1. This is generated by fast flowing water power which force to run the turbines. |
| 2. This is full of pollution. | 2. This is pollution free. |
| 3. Not a permanent source of energy. | 3. A permanent energy resource. |
| 4. Based on non-renewable resources like coal. | 4. Based on renewable resource i.e. water. |
| 5. More then 310 thermal power stations are in India like Talcher, Panki, Namrup, Uran, Neyveli etc. | 5. India has a number of multi-purpose projecs like the Bhakra Nangal, Damodar valley corporation, the Kopili Hydel Project etc. |
Question. Why do we need to conserve the minerals ? Mention some ways of mineral conservation?
Ans. (i) Minerals are the base of our agriculture and Industries.
(ii) Are finite and non-renewable.
(iii) The stock is very limited. The total deposits is an insignificant fraction i.e. one percent of the earth’s crust.
(iv) Takes millions of years to be created and concentrated.
(v) We are rapidly consuming mineral resources.
Methods of conservation of Resources-
(i) Low wastage during mining and excavation.
(ii) As far as possible use wood or plastic (Certified).
(iii) Re use the junk waste and old things.
(iv) Recycle metals, use scrap metals and search other substitute.
(v) Use in a planned and sustainable manner.
Question. “Solar energy is an important energy resource for India in future.” Write your views in favour of the statement.
Ans. India is a tropical country. It has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. India has a great potential of Solar energy. If used in appropriate way, it can prove beneficial in the future. Solar energy is becoming fast popular in different parts of the country, especially in rural and remote areas. It can be used for cooking, heating of water, pumping, refrigeration, street lighting and room heating as well as water boiling in cold areas. The largest solar plant in India is located at Madhapur near Bhuj in Gujarat. Here the Solar energy is used to sterilize the big milk cans. Solar energy can be used in future by following ways:
(i) For environmental conservation
(ii) To generate and provide electricity
(iii) To provide fuel to vehicles
(iv) To run machines and tools
(v) To minimize the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes and providing them a source of lighting and cooking and thus giving a lot of organic manure for agriculture.
Question. Why does the mining industry is called a killer industry?
Ans. This industry effects the health of the miners and the environment.
(i) They have to breath in dust and noxious fumes
(ii) Miners inhales this regularly which make vulnerable to pulmonary diseases.
(iii) The risk of collapsing mine roofs, inundation and fires in coalmine are a constant threat to miners.
(iv) The water sources in the region get contaminated due to mining
(v) Dumping of waste and slurry leads to degradation of land, soil and increase in stream and river pollution.
Question. How can we save or conserve energy?
Ans. (i) The electric switches should be off when not in use.
(ii) Public transport or pooling should be used.
(iii) As the conventional sources of energy are limited they should be used carefully.
(iv) Renewable resources should be used.
(v) The power saving instruments and devices should be used.

