MCQs for Biology Class 11 with Answers Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Students of class 11 Biology should refer to MCQ Questions Class 11 Biology Morphology of Flowering Plants with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 11 Biology NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 11 Biology with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 11 Biology. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 11 Biology examination
Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants MCQ with Answers Class 11 Biology
MCQ Questions Class 11 Biology Morphology of Flowering Plants provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 11. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 11 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. Arrange the below four layers in proper older staring from the outermost to the innermost layer after secondary growth in a woody dicot stem:
I. Phellem
II. Wood
III. Phelloderm
IV. Vascular cambium
(a) I →II →III →IV
(b) I →III→IV→II
(c) IV →III →II→I
(d) III →II →I→IV
Answer
B
Question. Meristems may be classified on the basis o
(a) Origin and development
(b) Position in plant body
(c) Functions
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of following structure is not common in both monocot root and dicot stem?
(a) Well developed Pith
(b) Parenchymatous epidermis
(c) Collenchymatous pericycle
(d) Multilayered parenchymatous cortex
Answer
C
Question. In angiosperm leaves, the protoxylem elements
(a) Face towards the abaxial surface
(b) Face towards the adaxial surface
(c) Are scattered in the middle
(d) Are surrounded by the metaxylem
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following groups of plants are propagated through underground root?
(a) Ginger and Potato,
(b) Bryophyllum and Kalanchoe
(c) Pistia, Chrysanthemum and pineapple
(d) Sweet potato, Asparagus, and Dahlia
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following type of xylem is found in Sunflower stem?
(a) Endarch
(b) Exarch
(c) Mesarch
(d) Centrarch
Answer
A
Question. Observe the following leaf of papaya and state its type-

(a) Pinnately compound leaf
(b) Palmately compound leaf
(c) Simple leaf
(d) Decompound leaf
Answer
C
Question. The placentation in Dianthus flower is correctly displayed by which one of the diagram given below?

Answer
B
Question. Match the following and choose the correct combination from, the option given.
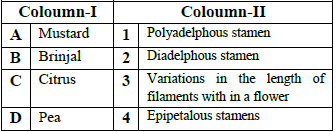
(a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
(b) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
(c) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
(d) A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
Answer
D
Question. How many plants in the list given below have marginal placentation?
Mustard, Gram, Tulip, Asparagus, Arhar, Sunnhemp, Chilli, Colchicum, Onion, Moong,Pea, Tobacco, Lupinus.
(a) Five
(b) Six
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer
B
Question. Identify the correct order where plants show alternate opposite, and whorled phyllotaxy, respectively:
(a) Chinarose, Calotropis and Nerium
(b) Chinarose, Nerium and Calotropis
(c) Nerium,Calotropis and Chinarose
(d) Calotropis, Chinarose and Nerium
Answer
A
Question. The given floral formula corresponds to:
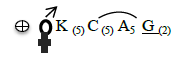
(a) Sunnhemp
(b) Belladonna
(c) Tulip
(d) Soyabean
Answer
B
Question. In all the following the ovary is unilocular with multiple ovules except-
(a) Trifolium
(b) Lupinus
(c) Sesbania
(d) Petunia
Answer
D
Question. When two leaves arise from same node, this type of phyllotaxy called
(a) Alternate
(b) Opposite
(c) Whorled
(d) Spiral
Answer
B
Question. Ovary is inferior in
(a) Guava
(b) Rose
(c) China rose
(d) Peach
Answer
A
Question. A lateral branch with short internodes and each node bearing a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots in aquatic plants, such type of modification is
(a) Runner
(b) Stolon
(c) Sucker
(d) Offset
Answer
D
Question. Find out the right sequence to various regions of root tip from apex to base
(a) Maturation zone, elongation zone, Meristematic zone & root cap
(b) Root cap, Meristematic zone, elongation zone & Maturation zone
(c) Root cap, elongation zone, Meristematic zone & Maturation zone
(d) Maturation zone, meristematic zone, elongation zone & root cap
Answer
B
Question. Mango and Coconut develops from
(a) Monocarpellary gynoecium, inferior ovary
(b) Monocarpellary gynoecium, superior ovary
(c) Multicarpellary gynoecium, inferior ovary
(d) Multicarpellary, superior ovary
Answer
B
Question. When single leaf arises at each node then phyllotaxy is called :-
(a) Alternate
(b) Opposite
(c) Whorled
(d) Pinnate
Answer
A
Question. Lateral branches originate from the basal and underground portion of the main stem, grow horizontally beneath the soil and then comes out obliquely upward giving rise to leafy shoots, such type of modification is
(a) Runner
(b) Stolon
(c) Sucker
(d) Offset
Answer
C
Question. Each ovary bears one or more ovules attached to a flattened cusion like structure called :-
(a) Stigma
(b) Ovary
(c) Placenta
(d) Style
Answer
C
Question. Regarding to symmetry of flower which of the following plant is odd
(a) Pea
(b) Mustard
(c) Datura
(d) Chilli
Answer
A
Question. A dot on the top of the floral diagram shows
(a) Adhesion
(b) Aestivation
(c) Mother axis
(d) Position of ovary
Answer
C
Question. When the veins run parallel to each other within a lamina, the venation is termed as :-
(a) Parallel
(b) Reticulate
(c) Both a & b
(d) Pinnate
Answer
A
Question. Perianth condition is characteristic of
(a) Brassicaceae
(b) Fabaceae
(c) Solanaceae
(d) Liliaceae
Answer
D
Question. Which type of aestivation is found in petals of cotton?
(a) Valvate
(b) Twisted
(c) Imbricate
(d) Vexillary
Answer
B
Question. Seeds in fabaceae are
(a) Non endospermic
(b) Endospermic
(c) Perispermic
(d) Monosporic
Answer
A
Question. In which of the following plant gynoecium occupies the highest position while the other parts situated below it ?
(a) Brinjal
(b) Plum
(c) Rose
(d) Guava
Answer
A
Question. Variation in length of the filament of stamen with in flower can be seen in
(a) Salvia
(b) Mustard
(c) Chinarose
(d) Both a & b
Answer
D
Question. If one margin of the sepal or petal overlaps that of the next one and so on this aestivation is called :-
(a) Twisted
(b) Imbricate
(c) Valvate
(d) Vexillary
Answer
A
Question. A slender lateral branch arises from the base of the main axis and after growing aerially for some time arch downwards to touch the ground. Such type of modification is
(a) Runner
(b) Sucker
(c) Stolon
(d) Offset
Answer
C
