Exam Question for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
Objective Questions
Question. The acid used for preliminary separation of biomolecule in a living tissue is
(a) trichlorobenzoic acid
(b) benzoic acid
(c) trichloroacetic acid
(d) acetic acid
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the example of acidic amino acid ?
(a) Lysine
(b) Glutamic acid
(c) Aspartic acid
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. The most basic amino acid is
(a) arginine
(b) histidine
(c) glycine
(d) glutamine
Answer
A
Question. The charged molecule which is electrically neutral is known as
(a) amino acid
(b) zwitterion
(c) amide
(d) peptide
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is/are essential fatty acid(s)?
(a) Linoleic acid
(b) Linolenic acid
(c) Arachidonic acid
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Glycerol is a
(a) tetrahydroxy propane
(b) trihydroxy propane
(c) trihydroxy butane
(d) tetrahydroxy butane
Answer
B
Question. Lecithin is a
(a) phospholipid
(b) carbohydrate
(c) protein
(d) amino acid
Answer
A
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
(a) Long chain molecules of fatty acids are formed by polymerization of 2 carbon compounds.
(b) Lipid molecules are soluble in water.
(c) In lipid, R group may be –CH3 group, –C2H5 group or higher number of –CH2 group (1 to 19 carbon).
(d) Oils have lower melting temperature.
Answer
B
Question. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Ribozymes are nucleic acids with catalytic power.
(b) Proteins are homopolymer made of amino acids.
(c) Inulin is a polymer of fructose.
(d) Glycogen is stored in liver and muscles.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is wrong regarding chitin?
(a) It is a storage of polysaccharide.
(b) It is a heteropolysaccharide.
(c) It is a constituent of arthropods and fungal cell wall.
(d) It is a second most abundant carbohydrate on earth.
Answer
A
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match column I (organic compound) with column II (examples) and choose the correct combination from the given options.
| Column-I (Organic Compounds) | Column-II (Examples) |
| A. Fatty acid | I. Glutamic acid |
| B. Phospholipid | II. Tryptophan |
| C. Aromatic amino acid | III. Lecithin |
| D. Acidic amino acid | IV. Palmitic acid |
(a) A – I; B – II; C – III, D – IV
(b) A – IV; B – III; C – II, D – I
(c) A – II; B – III; C – IV, D – I
(d) A – III; B – IV; C – I, D – II
Answer
B
Question. Match the protein given in column I with its function given in column II and choose the right option.
| Column I (Proteins) | Column II (Functions) |
| A. Collagen | I. Glucose transport |
| B. Trypsin | II. Hormone |
| C. Insulin | III. Intercellular ground substance |
| D. GLUT-4 | IV. Enzyme |
(a) A – III; B – IV; C – II; D – I
(b) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(c) A – II; B – IV; C – I; D – III
(d) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
Answer
A
Question. Match column I (category) with column II (secondary metabolites)and choose the correct option.
| Column I (Category) | Column II (Secondary metabolites) |
| A. Pigments | I. Concanavalin A |
| B. Terpenoides | II. Monoterpenes, Diterpenes |
| C. Alkaloids | III. Morphine, Cadeine |
| D. Lectins | IV. Carotenoids, Anthocyanin |
(a) A – IV; B – II; C – III; D – I
(b) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(c) A – I; B – IV; C – III; D – II
(d) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV
Answer
A
Question. Match column I (function) with column II (Types of enzymes) and select the correct option.
| Column I (Function) | Column II (Types of enzymes) |
| A. Enzymes catalysing breakdown without addition of water. | I. Isomerases |
| B. Enzyme catalyzes the conversion of an aldose sugar to a ketose sugar. | II. Oxidoreductase |
| C. Enzyme where catalysis involves transfer of electrons. | III. Ligases |
| D. Enzyme catalysing bonding of two components with the help of ATP. | IV. Lyases |
(a) A – I; B – IV; C – III; D – II
(b) A – I; B – IV; C – II; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(d) A – IV; B – I; C – III; D – II
Answer
C
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. According to weight percentage, the first three elements in human body are
(a) C > H > O
(b) C > O > N
(c) O > N > C
(d) O > C > H
Answer
D
Question. If all the peptide bonds of a protein are broken down, then what would remain?
(a) Amino acids
(b) Peptides
(c) Polypeptides
(d) Oligopeptides
Answer
A
Question. Nucleotides are building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite molecule formed by
(a) base-sugar-phosphate.
(b) base-sugar-OH.
(c) (base-sugar-phosphate)n.
(d) sugar-phosphate.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not an attribute of enzymes ?
(a) They are substrate specific in nature.
(b) They are proteinaceous in nature.
(c) They are used up in the reaction.
(d) They speed up rate of biochemical reaction.
Answer
C
Question. Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecule on earth, are produced by
(a) some bacteria, algae and green plant cells.
(b) fungi, algae and green plant cells.
(c) all bacteria, fungi and algae.
(d) viruses, fungi and bacteria.
Answer
A
Question. The effectiveness of an enzyme is affected least by
(a) temperature.
(b) concentration of the substrate.
(c) original activation energy of the system.
(d) concentration of the enzyme.
Answer
C
Question. The stored form of sugar in animal is a
(a) homopolysaccharide
(b) heteropolysaccharide
(c) oligosaccharide
(d) diasaccharide
Answer
A
Question. Transition state structure of the substrate formed during an enzymatic reaction is.
(a) permanent but unstable.
(b) transient and unstable.
(c) permanent and stable.
(d) transient but stable.
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions
Question. What kinds of the structures of proteins are shown in the given figure (A, B, C and D)?

(a) A = 1º structure, B = 2º structure, C = 3º structure, D = 4º structure
(b) A = 4º structure, B = 2º structure, C = 3º structure, D = 1º structure
(c) A = 1º structure, B = 4º structure, C = 3º structure, D = 2º structure
(d) A = 4º structure, B = 3º structure, C = 2º structure, D = 1º structure
Answer
C
Question. The adjoining graph shows change in concentration of substrate on enzyme activity. Identify A, B and C.

Answer
C
Question. The given graph shows concept of activation energy with labelled 1, 2, 3, & 4. Co-relate the statements I, II, III & IV with 1, 2, 3 & 4.
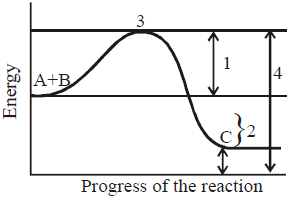
I. Segment representing the energy of activation.
II. Segment representing the amount of free energy released by the reaction.
III. Transition state.
IV. Segment would be the same regardless of whether the reaction were uncatalysed or catalysed.

Answer
B
Question. The curve given below shows enzymatic activity with relation to three conditions (pH, temperature and substrate concentration.) Identify the correct representation of two axes (x and y).

| x – axis | y-axis |
| (a) Enzymatic activity | pH |
| (b) Temperature | Enzymatic activity |
| (c) Substrate concentration | Enzymatic activity |
| (d) Enzymatic activity | Temperature |
Answer
B
Question. The given graph shows the effect of substrate concentration on the rate of reaction of the enzyme greengram-phosphatase. What does the graph indicate?

(a) The rate of enzyme reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration.
(b) Presence of an enzyme inhibitor in the reaction mixture.
(c) Formation of an enzyme-substrate complex.
(d) At higher substrate concentration the pH increases.
Answer
A


