Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Chemistry teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Biology and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry are very important and should be revised daily.
MCQ
Question. The cell constant of a conductivity cell______
a. Changes with change of electrolyte
b. Changes with change of concentration of electrolyte
c. Changes with temperature of electrolyte
d. Remains constant for a cell.
Answer
D
Question. The quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from Al2O3 is
a. 1F
b. 6F
c. 3F
d. 2F
Answer
C
Question. SI unit of conductivity is.
a. Scm-1
b. Scm-2
c. cm-1S-1
d. S-2cm-1
Answer
A
Question. Chemical reaction Zn+2 + 2e– ➔ Zn, is an example of
a. Oxidation process
b. Reduction process
c. redox reaction
d. reversible process
Answer
B
Question. Conductivity k, is equal to______.
a. 1/R(l/a)
b. R(l/a)
c. (l/a)
d. molar conductivity
Answer
A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the use of platinum foil in the hydrogen electrode?
Answer.It is used for the inflow and outflow of electrons.
Question. Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver chloride solution :
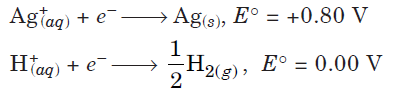
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why?
Answer.The species that get reduced at cathode is the one having higher value of standard reduction potential. Hence, the reaction that will occur at cathode is Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s).
Question. Give reason :
Molar conductivity of CH3COOH increases on dilution.
Answer.Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration. This is because the total volume, V, of solution containing one mole of electrolyte also increases. It has been
found that decrease in K on dilution of a solution is more than compensated by increase in its volume.
Question. Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous copper (II) chloride solution :
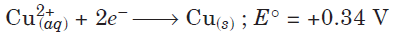

On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why?
Answer. The species that get reduced at cathode is the one which have higher value of standard reduction potential. Hence, the reaction that will occur at cathode is
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
Question. Limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte cannot be determined experimentally. Why?
Answer.In weak electrolyte, the conductivity of the solution increases very slowly with dilution of solution and goes on increasing up to infinity. Therefore, it cannot be measured experimentally.

Question. State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions. Write its one application.
Answer. Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions : It states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.Kohlrausch’s law helps in the calculation of degree of dissociation of weak electrolytes like acetic acid.
Question. What is the necessity to use a salt bridge in a Galvanic cell?
Answer.The salt bridge allows the movement of ions from one solution to the other without mixing of the two solutions.
Moreover, it helps to maintain the electrical neutrality of the solutions in the two half cells.
Question. Express the relation between conductivity and molar conductivity of a solution held in a cell?
Answer.

where, k is the conductivity, M is the molar concentration and Λm is molar conductivity.
Question. Give reason :
On the basis of E° values, O2 gas should be liberated at anode but it is Cl2 gas which is liberated in the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
Answer.The reaction at anode with lower value of E° is preferred i.e., O2 gas should be liberated but on account of over potential of oxygen reaction at anode, preferred reaction is
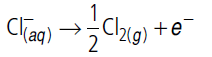
i.e., Cl2 gas is liberated at anode in the electrolysis of aq. NaCl.
Question. Out of HCl and NaCl, which do you expect will have greater value for Lm and why?
Answer. HCl will have greater value of Λm because H+ ions are smaller than Na+ ions and hence H+ ions have greater ionic mobility than Na+ ions.
Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question. The conductivity of 0.001 M acetic acid is
4 × 10–5 S/cm. Calculate the dissociation constant of acetic acid, if molar conductivity at infinite dilution for acetic acid is 390 S cm 2/mol.
Answer.
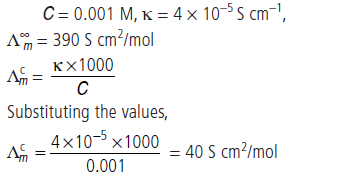

Question. (i) Explain why fluorine is the strongest oxidising agent?
(ii) Lithium metal is the strongest reducing agent. Why?
Answer.(i) Because fluorine has highest reduction potential.
(ii) Lithium metal is strongest reducing agent because Li has lowest reduction potential i.e., E°Li+/Li = –3.05 V
Question. Given that the standard electrode potential
(E°) of metals are :
K+/K = –2.93 V, Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V,
Cu2+/Cu = 0.34 V,
Mg2+/Mg = –2.37 V, Cr3+/Cr = –0.74 V,
Fe2+ /Fe = –0.44 V.
Arrange these metals in an increasing order of their reducing power.
Answer. The reducing power increases with decreasing value of electrode potential. Hence, the order is Ag < Cu < Fe < Cr < Mg < K.
Question. The standard electrode potential (E°) for
Daniell cell is +1.1 V. Calculate the DrG° for the reaction.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
(1 F = 96500 C mol–1)
Answer.Here n = 2, E°cell = 1.1 V, F = 96500 C mol–1
ΔrG° = –nFE°cell
ΔrG° = – 2 × 1.1 × 96500 = – 212300 J mol–1
= – 212.3 kJ mol–1
Question. Why a galvanic cell stops working after sometime?
Answer. With time, concentrations of the electrolytic solutions change. Hence, their electrode potentials change when the electrode potentials of the two half-cells become equal, the cell stops working.
Question. Equilibrium constant (Kc) for the given cell reaction is 10. Calculate E°cell.
A(s) + B2+(aq) ⇌ A2+ (aq) + B(s)
Answer.
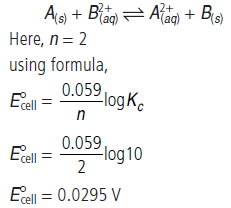
Question. In the plot of molar conductivity (Λm) vs square root of concentration (c1/2),following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B.
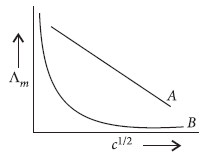
Answer the following :
(i) Predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on extrapolation of Lm to concentration approaching zero for electrolytes A and B?
Answer.
(i) Electrolyte A is a strong electrolyte while electrolyte B is a weak electrolyte.
(ii) For electrolyte A, the plot becomes linear near high dilution and thus can be extrapolated to zero concentration to get the molar conductivity at infinite dilution.
For weak electrolyte B,Λm increases steeply on dilution and extrapolation to zero concentration is not possible. Hence,molar conductivity at infinite dilution cannot be determined.
Question. Define the term degree of dissociation. Write an expression that relates the molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte to its degree of dissociation.
Answer.The fraction of the total number of molecules present in solution as ions is known as degree of dissociation.
Molar conductivity (λm) = αλ°m
where λ°m is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution.
Question. Two half-reactions of an electrochemical cell are given below :
MnO–4(aq) + 8H+(aq) + 5e– → Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l),E° = + 1.51V
Sn2+(aq) → Sn4+(aq) + 2e–, E° = + 0.15 V
Construct the redox equation from the standard potential of the cell and predict if the reaction is
reactant favoured or product favoured.
Answer.

Since, cell potential is positive therefore the reaction is product favoured.
Question. Define electrochemical cell. What happens if external potential applied becomes greater than E°cell of electrochemical cell?
Answer. The device which converts the chemical energy liberated during the chemical reaction to electrical energy is called electrochemical cell.
If external potential applied becomes greater than E°cell of electrochemical cell then the cell behaves as an electrolytic cell and the direction of flow of current is reversed.
Question. What is the difference between electronic and electrolytic conductors?
Answer. The substance which conducts electricity by ions present in solution is called electrolytic conductor e.g., NaCl solution.
Substances which conduct electricity in solid state are called electronic conductors. These are made up of metals. e.g.,Cu, Zn, Al. (Electrolytes are electrolytic conductors while electrodes are electronic conductors).
Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question. Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 mol L–1 KCl solution is 100 W. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 mol L–1 KCl solution is 520 W, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 mol L–1 KCl solution.
The conductivity of 0.1 mol L–1 KCl solution is 1.29 × 10–2 Ω–1 cm–1.
Answer.
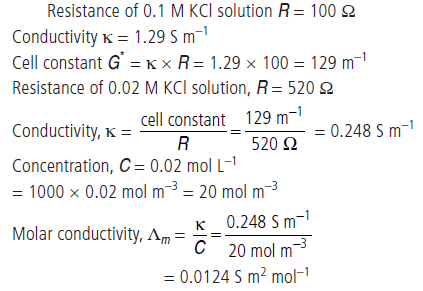
Question. A cell is prepared by dipping copper rod in 1 M copper sulphate solution and zinc rod in 1 M zinc sulphate solution. The standard reduction potential of copper and zinc are 0.34 V and –0.76 V respectively.
(i) What will be the cell reaction?
(ii) What will be the standard electromotive force of the cell?
(iii) Which electrode will be positive?
Answer.

Co(piipi)e r electrode will be positive on which reduction takes place.
Question. Calculate the potential for half-cell containing
0.10 M K2Cr2O7(aq) , 0.20 M Cr3+(aq) and 1.0 × 10–4 M H+(aq). The half cell reaction is :
Cr2O2–7(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e– → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l) and the standard electrode potential is given as
E° = 1.33 V.
Answer.

Question. The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M NaOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 50 cm is 5.5 × 103 ohm. Calculate its resistivity, conductivity and molar conductivity.
Answer.

Question. Estimate the minimum potential difference needed to reduce Al2O3 at 500°C. The Gibbs energy change for the decomposition reaction,
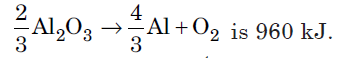
(F = 96500 C mol–1)
Answer.
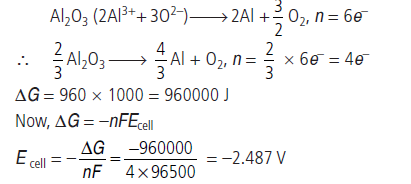

Question. Calculate ΔrG° and logKc for the following reaction.
Cd2+(aq) + Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + Cd(s)
Given : E°Cd2+/Cd = –0.403 V ; E°Zn2+/Zn = –0.763 V
Answer.

Question. Mention few applications of electrochemical series.
Answer.(i) Ions with higher reduction potentials are strong oxidising agents while lower reduction potentials are strong reducing agents.
(ii) The electrode with higher electrode potential (E°) acts as cathode while with lower electrode potential will act as anode.
(iii) Predicting the feasibility of redox reaction.
(iv) Predicting the capability of metal to evolve H2 gas from acid.
Question. For the cell reaction,
Ni(s) | Ni2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s)
Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C.
How much maximum work would be obtained by operation of this cell?
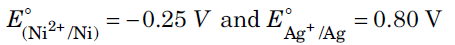
Answer.

Question. When a certain conductance cell was filled with 0.1 M KCl, it has a resistance of 85 ohms at 25°C. When the same cell was filled with an aqueous solution of 0.052 M unknown electrolyte,the resistance was 96 ohms. Calculate the molar conductance of the electrolyte at this concentration.
[Specific conductance of 0.1 M KCl = 1.29 × 10–2 ohm–1 cm–1]
Answer.

Question. The equivalent conductivity of 0.05 N solution of a monobasic acid is 15.8 mho cm2 eq–1.
If equivalent conductivity of the acid at infinite dilution is 350 mho cm2 eq–1, calculate the
(a) degree of dissociation of acid (b) dissociation constant of acid.
Answer.
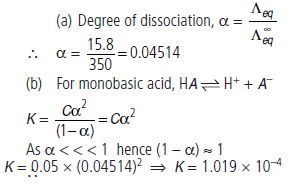
Question. A copper-silver cell is set up. The copper ion concentration is 0.10 M. The concentration of silver ion is not known. The cell potential when measured was 0.422 V. Determine the concentration of silver ions in the cell.
Given :
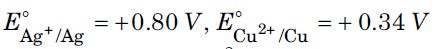
Answer.

Question. A voltaic cell is set up at 25°C with the following half cells :
Al/Al3+ (0.001 M) and Ni/Ni2+ (0.50 M)
Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when the cell generates an electric current and determine the cell potential.
E°Ni2+/Ni = – 0.25 V and E°Al3+/Al = – 1.66 V.
(log 8 × 10–6 = – 5.09)
Answer.

Question. The resistance of 100 cm3 aqueous solution of 0.025 M CuSO4 is 520 ohm at 298 K. Calculate the molar conductivity if the cell constant of the conductivity cell is 153.7 m–1.
Answer.


Question. Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction
Zn(s) + 2Ag+( aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) takes place.
Further show :
(i) Which of the electrode is negatively charged?
(ii) The carriers of the current in the cell.
(iii) Individual reaction at each electrode.
Answer.The reaction is
Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Cell can be represented as
Zn | Zn2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag

(i) The zinc electrode is negatively charged (anode) as it pushes the electrons into the external circuit.
(ii) Ions are the current carriers within the cell.
(iii) The reactions occurring at two electrodes are :
At zinc electrode (anode) : Zn(s) → Zn2+ (aq) + 2e–
At silver electrode (cathode) : Ag+( aq) + e– → Ag(s)
Question. What is the difference between a chemical and a concentration cell?
Answer.A chemical cell is a galvanic cell in which electrical energy produced is due to chemical changes occurring within the cell and no transfer of matter takes place. It involves the use of two different electrode dipped in solutions of different electrolytes.
A concentration cell is a galvanic cell in which electrical energy is produced due to physical change involving transfer of matter from one part of the cell to the other. It involves
the use of the same electrodes dipped in solutions of the same electrolyte with different concentrations (or electrodes of different concentration dipped in the same solution of the electrolyte).
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Calculate standard emf of the cell in which following reaction takes place at 25°C.
Cu(s) + Cl2(g) ⇌ Cu2+ + 2Cl–
E°Cl2/Cl– = +1.36 V, E°Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34 V
Also calculate standard free energy change and equilibrium constant of the reaction.
(b) The emf of a galvanic cell composed of two hydrogen electrode is 0.16 volt at 25°C. Calculate pH of the anode solution if the cathode is in a solution with pH = 1.
Answer.

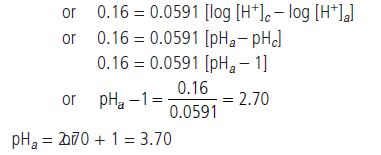
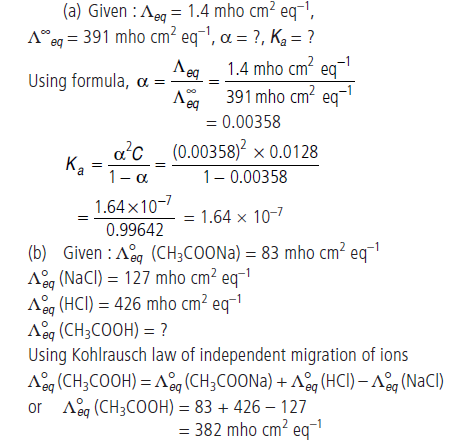
Question. (a) Equivalent conductance of a 0.0128 N solution of acetic acid is 1.4 mho cm2 eq–1 and conductance at infinite dilution is
391 mho cm2 eq–1. Calculate degree of dissociation and dissociation constant of acetic acid.
(b) The equivalent conductances of sodium acetate, sodium chloride and hydrochloric acid are 83, 127 and 426 mho cm2 eq–1 at 250°C respectively. Calculate the equivalent conductance of acetic acid solution.
Answer.
Question. E°cell for the given redox reaction is 2.71 V.
Mg(s) + Cu2+ (0.01 M) → Mg2+ (0.001 M) + Cu(s)
Calculate Ecell for the reaction. Write the direction of flow of current when an external opposite potential applied is
(i) less than 2.71 V and (ii) greater than 2.71 V
Answer.
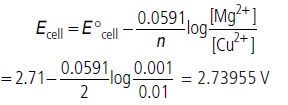
(i) If external opposing potential is less than 2.71 V then current will flow from Cu to Mg.
(ii) If external opposing potential is greater than 2.71 V then current will flow in opposite direction i.e. from Mg to Cu.
Question. (a) Calculate the cell emf and ΔG° for the cell reaction at 25°C for the cell :
Zn(s) | Zn2+ (0.0004 M) || Cd2+ (0.2 M) | Cd(s)
E° values at 25°C : Zn2+/ Zn = – 0.763 V;
Cd2+/Cd = – 0.403 V; F = 96500 C mol–1;
R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1.
(b) If E° for copper electrode is 0.34 V, how will you calculate its emf value when the solution in contact with it is 0.1 M in copper ions? How does emf for copper electrode change when concentration of Cu2+ ions in the solution is decreased?
Answer.

When the concentration of Cu2+ ions is decreased, the electrode potential for copper decreases.
