Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Term 1 Set A
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Term 1 Set A with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 12 Chemistry issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 12 Chemistry exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry for Term 1 Set A
Section ‘A’
1. Anoxia is a condition related to people who ?
(A) are divers
(B) climb high altitudes
(C) live in snowy region
(D) are obese
Answer
B
2. _____________ is an antifreeze used in cars for cooling the engine.
(A) ethane glycol
(B) methylene glycol
(C) ethylene glycol
(D) none of the above
Answer
C
3. The correct order for increase in density is:
(A) n-C3H7I < n-C3H7Cl < n- C3H7Br
(B) n-C3H7I < n-C3H7Br < n-C3H7Cl
(C) n-C3H7Cl < n- C3H7Br < n-C3H7I
(D) n- C3H7Br < n-C3H7I < n-C3H7Cl
Answer
A
4. Used as a diluent for oxygen in modern diving apparatus:
(A) neon
(B) liquid helium
(C) argon
(D) liquid nitrogen
Answer
B
5. Choose the correct product for the given reaction:
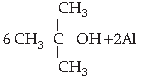
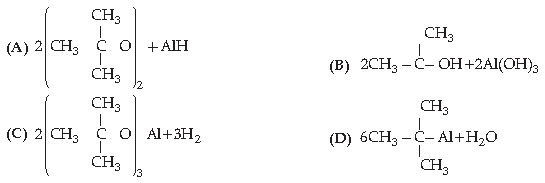
Answer
C
6. Which of the following do not show allotropy ?
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Phosphorus
(C) Arsenic
(D) All of the above
Answer
A
7. In which pair most efficient packing is present?
(A) hcp and bcc
(B) hcp and ccp
(C) bcc and ccp
(D) bcc and simple cubic
Answer
B
8. When there are no unpaired electrons the substance shows __________ while with one or more unpaired electrons, the substance shows ______________:
(A) diamagnetism, paramagnetism
(B) paramagnetism, diamagnetism
(C) ferromagnetism, diamagnetism
(D) diamagnetism, ferromagnetism
Answer
A
9. The dinitrogen gas after preparation is passed through aqueous sulphuric acid containing potassium dichromate to remove:
(A) NO2 and H2SO4
(B) NO and HCl
(C) NO and HNO3
(D) NO2 and HNO3
Answer
C
10. Which of the following shows nucleophilic substitution by SN1mechanism:

Answer
A
11. Aniline on treatment with nitrous acid at 273-278 K gives:
(A) benzene amide
(B) benzene diazonium chloride
(C) benzene peroxide
(D) benzene diazonium oxide
Answer
B
12. Supersonic jet aeroplanes are responsible for depleting the conc. of ozone layer because:
(A) they emit nitrogen oxides.
(B) nitrogen oxides readily combine with ozone.
(C) none of the above
(D) both (A) and (B)
Answer
D
13. When hydrochloric acid reacts with ammonia __________ is produced:
(A) white fumes of NH4OH
(B) white fumes of NH4Cl
(C) hydrogen gas
(D) chlorine gas
Answer
B
14. When measured along different directions in the same crystals some properties like refractive index and electrical resistance have different values.
This nature of solids are known as:
(A) Anisotropic
(B) Isotropic
(C) Pseudo solids
(D) None of the above
Answer
A
15. Which of the following is incorrectly paired ?
(A) chloramphenicol – dengue fever
(B) chloroquine – malaria
(C) halothane – surgery
(D) thyroxine – goiter
Answer
A
16. The acid strength of alcohol is:
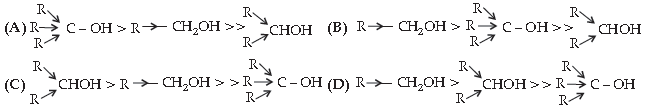
Answer
D
17. Chlorobenzene is fused with NaOH at 623 K and 320 atmospheric pressure. Sodium phenoxide thus obtained undergoes _______ to obtain phenol.
(A) hydrolysis
(B) hydrogenation
(C) acidification
(D) neutralisation
Answer
C
18. In SN2 reactions tertiary halides are least reactive due to:
(A) halide group
(B) three hydrogen atoms
(C) three methyl group
(D) conc. of halide group
Answer
C
19. Which of the following is the correct order ?
(A) N2O –basic oxide
(B) Al2O3 – neutral oxide
(C) Na2O -amphoteric oxide
(D) CrO3 – acidic oxide
Answer
D
20. The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C—X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds:

(A) IV < III < II < I
(B) I < II < III < IV
(C) III < II < I < IV
(D) II < III < I < IV
Answer
C
21. Which of the following is an ambident nucleophile ?
(i) cyanides
(ii) hydroxyl
(iii) nitrites
(A) (i), (ii)
(B) (i), (ii), (iii)
(C) (i), (iii)
(D) (ii), (iii)
Answer
C
22. The presence of strong hydrogen bonding in H2O as compare to H2S is due to:
(A) small size of oxygen
(B) high electronegativity in O
(C) low electronegativity in O
(D) both (A) and (B)
Answer
D
23. Which of the following solutions possess lowest freezing point?
(A) 1 M KCl
(B) 1 M K2SO4
(C) 1 M glucose
(D) 1 M Urea
Answer
B
24. Which of the following compounds does not exist ?
(A) NeF2
(B) XeF2
(C) XeO3
(D) XeOF4
Answer
A
25. Ethanol on heating with conc. sulphuric acid at 170˚C gives:
(A) Ethyl hydrogen sulphate
(B) Diethyl ether
(C) Diethyl sulphate
(D) Ethylene
Answer
D
Section ‘B’
26. Which is the correct relation between mole fraction and molality ?

Answer
A
27. Which of the following is dependent on temperature ?
(A) mass %
(B) parts per million
(C) molarity
(D) molality
Answer
C
28. Which of the following unit is used in medicine and pharmacy:
(A) mass by volume percentage
(B) parts per million
(C) mass percentage
(D) molarity
Answer
A
29. Find the molarity of a solution having 5 g of NaOH is 450 ml of solution:
(A) 0.125 mol
(B) 0.278 mol/L
(C) 27.8 mol/L
(D) 450 mL
Answer
B
30. A solution of glucose is prepared with 0.052 g of glucose in 80.2 g of water. (Kf = 1.86 K kg/mol and Kf = 5.2 K kg/mol).Molality of the given solution is:
(A) 0.0052 m
(B) 0.0036 m
(C) 0.0006 m
(D) 1.29 m
Answer
B
31. When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will:
(A) boil above 100°C and freeze above 0°C
(B) boil below 100°C and freeze above 0°C
(C) boil above 100°C and freeze below 0°C
(D) boil below 100°C and freeze below 0°C
Answer
C
32. Colligative properties are:
(A) dependent only on the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s and solute’s identity.
(B) dependent only on the identity of the solute and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s identity.
(C) dependent on the identity of the solvent and solute and thus on the concentration of the solute.
(D) dependent only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solute’s identity.
Answer
C
33. Assume three samples of juices A, B and C have glucose as the only sugar present in them.
The concentration of sample A, B and C are 0.1M, 0.5 M and 0.2 M respectively. Freezing point will
be highest for the fruit juice:
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) All have same freezing point
Answer
A
34. Identify which of the following is a colligative property:
(A) freezing point
(B) boiling point
(C) osmotic pressure
(D) all of the above
Answer
C
35. The vapour pressure of a liquid can be lowered by:
(A) decreasing the temperature
(B) adding a non- volatile solute
(C) either of the two
(D) None of the two
Answer
C
36. On hydrolysis of proteins ________________ is obtained.
(A) α- amino acids
(B) β−amino acids
(C) γ-amino acids
(D) none of the above
Answer
A
37. Choose the wrong pair:
(A) CH3 -alanine
(B) HO-CH2 – serine
(C) C6H5 -OH – Phenylalanine
(D) H – glycine
Answer
C
38. A compound may have excess metal ion if a negative ion is absent from its lattice position, leveing a hole, which is occupied by electron This defect belongs to:
(A) Stoichiometric defect
(B) Non-Stoichiometric defect
(C) Line defect
(D) Frenkel defect
Answer
B
39. Mark the incorrect statement:
(A) The solution which obey Raoult’s law are called non-ideal solution.
(B) The vapour pressure of the ideal solution always lies between the vapour pressure of the pure components.
(C) For ideal solution ΔHmixing = 0
(D) For non-ideal solutim ΔHmixing ≠ 0
Answer
A
40. Peroxide effect in unsymmetrical alkenes applies to the addition of:
(A) HCl
(B) HBr
(C) HI
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer
B
41. The structural formula of resorcinol is:
Answer
A
42. Which of the following hydrides of halogen can be used for Etching of glass ?
(A) HF
(B) HCl
(C) HBr
(D) HI
Answer
A
43. Find the product
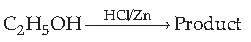
(A) C2H4
(B) C2H5Cl
(C) (C2H5)2 Zn
(D) CH3CHO
Answer
B
44. Mark the odd one out:
(A) Proline
(B) Lysine
(C) Valine
(D) Alanine
Answer
D
From Q. 45 to Q. 49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
45. Assertion (A): In one dimensional close packed arrangement, the coordination number is 2.
Reason (R): Each sphere is in contact with two of its neighbours.
Answer
A
46. Assertion (A): Except nitrogen, no other element forms pπ – pπ bonds.
Reason (R): Nitrogen show anomalous property due to small size and high electronegativity.
Answer
A
47. Assertion (A): Ag CN forms isocyanide when react with haloalkanes while KCN form alkyl cyanides.
Reason (R): KCN is ionic while Ag CN is covalent in nature thus providing different ions in solution.
Answer
B
48 Assertion (A): SN2 reaction proceeds with inversion of configuration.
Reason (R): SN1 reaction are accompanied by racemisation.
Answer
C
49. Assertion (A): Elements of group 16 generally show lower value of first ionisation enthalpy as compared to the group 15 elements.
Reason (R): Larger amount of energy is required to remove electrons from group 16.
Answer
C
Section ‘C’
50. Match the following:
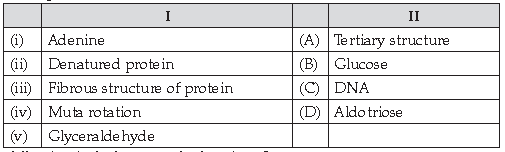
Answer
D
51. Which of the following analogies is correct:
(A) BCC: 2 atoms per unit cell:: FCC: 4 atoms per unit cell
(B) Monoclinic crystal: Face centred:: Triclinic crystal: primitive
(C) BCC: Copper:: FCC: Silver
(D) NaCl: Schottky defect:: KBr: Frenkal defect
Answer
A
52. Complete the following analogy:
Number of moles of solute per litre of solution: A:: Number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent : B
(A) A: Normality B: Molality
(B) A: Formality B: Molarity
(C) A: Molality B: Molarity
(D) A: Molarity B: Molality
Answer
D
CASE 1: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55
The chief sources of proteins are milk, cheese, pulses, peanuts, fish, meat, etc. They occur in every part of the body and form the fundamental basis of structure and functions of life. They are also required for growth and maintenance of body. The word protein is derived from Greek word, “proteios” which means primary or of prime importance.
Amino acids contain amino (–NH2) and carboxyl (–COOH) functional groups. Depending upon the relative position of amino group with respect to carboxyl group, the amino acids can be classified as α, β, γ, δ and so on.
53. Name the most abundant bio molecule of the living system:
(A) carbohydrates
(B) proteins
(C) vitamins
(D) enzymes
Answer
B
54. Choose the correct function of proteins:
(A) Regulation of body tissues and organs
(B) They are needed for the progress of reaction.
(C) Major source of energy in living organism.
(D) They are responsible for initiating cell division.
Answer
A
55. Which of the following is the correct structure of amino acids?

Answer
C

