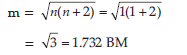Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set C
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set C with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 12 Chemistry issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 12 Chemistry exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry for Set C
Topic-1
Coordination Compounds and their Properties,IUPAC Nomenclature of Mono Nuclear Coordination Compounds
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. The correct IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is
(a) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (II).
(b) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV).
(c) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (I).
(d) Dichloridodiammineplatinum (IV).
Answer
A
Question. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?
(a) Thiosulphato
(b) Oxalate
(c) Glycinato
(d) Ethane-1,2-diamine
Answer
A
Question. Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism.
(a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+
(b) [Pt(NH3)3Cl]
(c) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(d) [Co(CN)5(NC)]3+
Answer
A
Question. When 0.1 mol CoCl3(NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, 0.2 mol of AgCl are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to
(a) 1 : 3 electrolyte.
(b) 1 : 2 electrolyte.
(c) 1 : 1 electrolyte.
(d) 3 : 1 electrolyte.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand?
(a) NO
(b) NH4+
(c) NH2CH2CH2NH2
(d) CO
Answer
B
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.
Column I Column II
(Complex species) (Isomerism)
A. [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ (1) Optical
B. cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (2) Ionisation
C. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 (3) Coordination
D. [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] (4) Geometrical
(5) Linkage
Code :
(a) A(1), B (2), C(4), D(5)
(b) A(4), B (3), C(2), D(1)
(c) A(4), B (1), C(5), D(3)
(d) A(4), B (1), C(2), D(3)
Answer
D
C. Answer the following:
Question. Give IUPAC name of ionization isomer of [Ni(NH3)3NO3] Cl.
Answer. Ionization isomer is [Ni(NH3)3Cl] NO3. IUPAC name is Triamminechloridonickel (II) nitrate.
Question. Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed?
Answer. Orbital splitting energies are not sufficiently large for forcing pairing.
Question. Write the coordination number and oxidation state of Platinum in the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]
Answer. Coordination Number = 6 , Oxidation State = +2
Question. What is the denticity of coordination compound used for the treatment of lead poisoning ?
Answer. In Lead poisoning, EDTA (Ethylene diamine tetraacetate) is used as ligand which is hexadentate i.e., the denticity of EDTA is 6. EDTA binds with metal in octahedral manner by two N-atoms and four acetate oxygen atoms.
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compound [NiCl4]2–.
Answer. Tetrachloridonickelate (II) ion.
Question. Low spin configuration are rarely observed in tetrahedral coordination entity formation.Explain.
Answer. The orbital splitting energies, Δt are not sufficiently large for forcing pairing of electrons in the tetrahedral coordination entity formation.
Question. Give two examples of ligands which form coordination compounds useful in analytical chemistry.
Answer. EDTA (Ethylene-diammine-tetraacetate) and DMG (Dimethylglyoxime).
Question. Write IUPAC name of the complex: [CoCl2(en)2]+.
Answer. Dichloridobis (ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt (III) ion.
Question. A coordination compound with molecular formula CrCl3.4H2O precipitates one mole of AgCl with AgNO3 solution. Its molar conductivity is found to be equivalent to two ions. What is the structural formula and name of the compound?
Answer. [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl
Tetraaquadichloridochromium (III) chloride.
Question. Write the coordination isomer of [Cu(NH3)4[PtCl4].
Answer. [Pt(NH3)4][CuCl4]
Question. Write IUPAC name of the complex [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]+.
Answer. Tetraaminechloronitrocobalt (III) ion.
Question. What is meant by chelate effect ?
Answer. Formation of stable complex with a polydentate ligand due to stronger bonding is known as chelate effect.
Question. What is the IUPAC name of the complex [Ni(NH3)6] Cl2 ?
Answer. Hexaamminenickel (II) chloride.
Question. How many ions are produced from the complex,[CO(NH3)6]Cl2 in solution ?
Answer. Three ions. [CO(NH3)6]2+, 2Cl–.
Question. Which of the following is more stable complex and why ?
[Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(en)3]3+.
Answer. [Co(en)3]3+ : Because (en) is a chelating ligand/ bidentate ligand.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the following complex :
[Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl
(ii) Write the formula for the following:
Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) chloride
Answer. (i) Tetraamminechloridonitrito-N-cobalt (III) chloride.
(ii) [CoCl2(en)2]Cl
Question. Indicate the types of isomerisms exhibited by the complex [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2.
(At. No. Co = 27).
Answer. Linkage and ionisation isomerism.
It can show linkage isomerism:
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 and [Co(NH3)5(ONO)] (NO3)2
It can show ionization isomerism:
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 and [Co(NH3)5(NO3)] (NO3)(NO2)
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
(ii) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)
Answer. (i) K3[Al(C2O4)3]
(ii) [CoCl2(en)2]+
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the complex [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+. What type of isomerism does it exhibit ?
Answer. (i) Tetraamminedichlorido chromium (III) ion.
(ii) Geometrical isomerism / cis-trAnswer.
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the isomer of the following complex:
[Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4
(ii) Write the formula for the following:
Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum(II)
Answer. (i) Pentaaminechlorocobalt (III) sulphate
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)]
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Sodium dicyanidoaurate (I)
(ii) Tetraamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (IV) sulphate
Answer. (i) Na[Au(CN)2]
(ii) [Pt(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]SO4
Question. (i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex : [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex : Potassium tetrachloridonickelate (II)
Answer. (i) Pentaamminechloridocobalt (III) ion
(ii) K2[NiCl4]
Question. Give evidence that [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl are ionisation isomers.
Answer. When ionisation isomers are dissolved in water, they ionise to give different ions. These ions then react differently with different reagents to give different products.
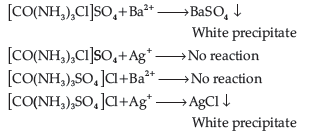
Question. When a co-ordination compound CoCl3.6NH3 is mixed with AgNO3, 3 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write
(i) Structural formula of the complex,
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex.
Answer. (i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3

(ii) IUPAC name : Hexamminecobalt (III) chloride.
Question. When a co-ordination compound CrCl3.6NH3 is mixed with AgNO3, 2 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write
(i) Structural formula of the complex.
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex.
Answer. (i) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O
(ii) Pentaaquachloridochromium (III) chloride monohydrate.
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine)chromium(III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetrahydroxozincate(II)
Answer. (i) [Cr(en)3]Cl3
(ii) K2[Zn(OH)4]
Question. (i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex :[Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine)
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex :
Pentaamminenitrito-o-Cobalt (III).
Answer. (i) Diamminedichloridobisethylenediaminechromium
(III) chloride
(ii) [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the isomer of the following complex:
[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
(ii) Write the formula for the following:
Tetraammineaquachloridocobalt (III) nitrate
Answer. (i) cis/trans-diamminedichloridoplatinum (II)
(ii) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl] (NO3)2
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(en)3]Cl3?
(ii) Write the hybridization and magnetic character of [Co(C2O4)3]2–. (At. no. of Co = 27)
(iii) Write IUPAC name of the following Complex [Cr(NH3)3Cl3]
Answer. (i) Optical isomerism
(ii) d2sp3, diamagnetic
(iii) Triamminetrichloridochromium (III)
Question. (i) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6]?
(ii) Why a solution of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green while a solution of [Ni(CN)4]2– is colourless? (At. No. of Ni = 28) [KVS]
(iii) Write the IUPAC name of the following complex: [Co(NH3)5(CO3)Cl].
Answer. (i) Coordination isomerism
(ii) Unpaired electrons in [Ni(H2O)6]2+/d-d transition
(iii) Pentaamminecarbonatocobalt(III) Chloride
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following :
(i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
(ii) [NiCl4]2–
(iii) K3[Fe(CN)6]
Answer. (i) Hexaamminecobalt (III) chloride.
(ii) Tetrachloridonickelate (II) ion.
(iii) Potassiumhexacyanoferrate (III)
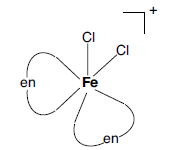
Question. For the complex ion [Fe(en)2Cl2]+ write the hybridization type and magnetic behaviour. Draw one of the geometrical isomer of the complex ion which is optically active. [Atomic No.: Fe = 26]
Answer. Hybridisation: d2sp3
Magnetic character: Paramagnetic
Question. Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes :
(i) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+
(ii) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (en = ethylenediamine)
(iii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
Answer. (i) Linkage isomerism.
(ii) Optical isomerism.
(iii) Cis – trans / Geometrical isomerism.
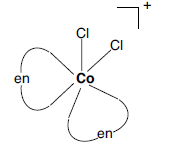
Question. For the complex ion [CoCl2(en)2]+ write hybridization type and spin behaviour. Draw one of the geometrical isomer of the complex ion which is optically active. [Atomic number: Co = 27]
Answer. Hybridisation: d2sp3
Spin: Low spin
Question. Write IUPAC name for each of the following complexes:
(i) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(ii) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(iii) [Co(en)3]3+
Answer. (i) Hexaamminenickel(II) chloride
(ii) Potassium hexacyanidoferrate(III)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) ion
Question. For the complex ion [Ni(CN)4]2– write the hybridization type, magnetic character and spin nature. [Atomic number: Ni = 28]
Answer. Hybridisation : dsp2
Magnetic character : Diamagnetic
Spin nature : Low spin
Question. Write the hybridization, shape and magnetic character of [Fe(CN)6]4–.
Answer. Hybridization : d2sp3
Shape : Octahedral
Magnetic character : Diamagnetic.
Question. (i) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3)5(SCN)]2+?
(ii) Why is [NiCl4]2– paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2– is diamagnetic? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
(iii) Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes rarely observed?
Answer. (i) Linkage isomerism
(ii) In [NiCl4]2-, due to the presence of Cl–, a weak field ligand no pairing occurs whereas in Ni(CN)4]2-, CN– is a strong field ligand and pairing takes place/diagrammatic representation
(iii) Because of very low CFSE which is not able to pair up the electrons.
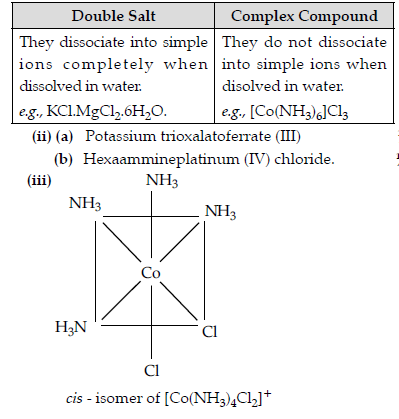
Question. (i) How is a double salt different from a complex ?
(ii) Write IUPAC names of the following :
(a) K3[Fe(C2O4)3]
(b) [Pt(NH3)6] Cl4
(iii) Draw the structure of cis-isomer of [Co(NH3)4 Cl2]+.
Answer. (i)
Question. When a coordination compound CrCl3.6H2O is mixed with AgNO3 solution, 3 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write:
(i) Structural formula of the complex
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex
(iii) Magnetic and spin behavior of the complex
Answer. (i) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(ii) Hexaaquachromium(III) chloride
(iii) Paramagnetic and high spin
Question. A metal complex having composition Cr(NH3)4Cl2Br has been isolated in two forms A and B. The form A reacts with AgNO3 to give a white precipitate readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia whereas B gives a pale yellow precipitate soluble in concentrated ammonia.
(i) Write the formulae of isomers A and B.
(ii) State the hybridisation of chromium in each of them.
(iii) Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only value) of the isomer A.
Answer. (i) Isomer A: [Cr(NH3)4BrCl]Cl
Isomer B: [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Br
(ii) Hybridisation of Cr in isomer A and B is d2sp3.
(iii) Number of unpaired electrons in Cr3+(3d3) is 3
Magnetic moment = √n(n + 2)
= √3(3+ 2)
= 3.87 BM
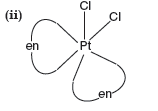
Question. (i) For the complex [Fe(CN)6]3–, write the hybridization, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex. (At. number : Fe = 26).
(ii) Draw one of the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]2+ which is optically active.
Answer. (i) Hybridization : d2sp3
Magnetic character : Paramagnetic
Spin nature of the complex : Low spin.
Question. For the complex ion [CoF6]3– write the hybridization type, magnetic character and spin nature. [Atomic number: Co = 27]
Answer. Hybridisation : sp3d2
Magnetic character : Paramagnetic
Spin nature : High spin
Question. [Fe(H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas
[Fe(CN)6]3− is weakly paramagnetic. Explain.
Answer.
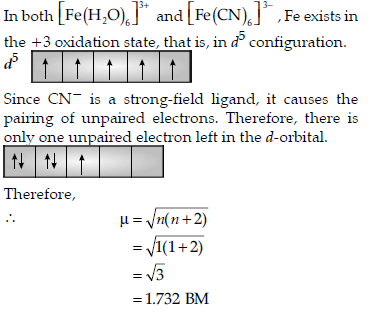
On the other hand, H2O is a weak-field ligand.
Therefore, it cannot cause the pairing of electrons.This means that the number of unpaired electrons is 5.

Question. (a) Write the formula of the following coordination compound :
Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
(b) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 ?
(c) Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex [CoF6]3–. (Atomic No. of Co = 27)
Answer. (i) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
(ii) Ionisation isomerism
(iii) sp3d2 octahedral complex with 4 unpaired electrons
Long Answer Type Questions-II
Question. Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities :
(a) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+
(b) [CoBr2(en)2]+
(c) [PtCl4]2−
(d) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(e) [Cr(NH3)3Cl3]
Answer.
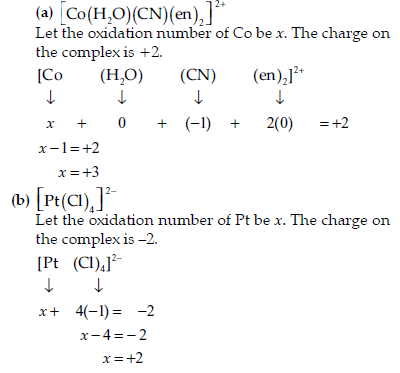

Topic-2
Werner’s Theory Bonding in Coordination
Compound, VBT, CFT and Importance of Coordination Compounds
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4– is 18,000 cm–1.
The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2– will be
(a) 18,000 cm–1
(b) 16,000 cm–1
(c) 8,000 cm–1
(d) 20,000 cm–1
Answer
C
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.

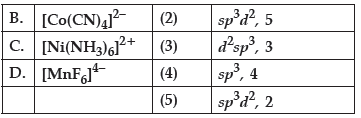
Code :
(a) A(3), B(1), C(5), D(2)
(b) A(4), B(3), C(2), D(1)
(c) A(3), B(2), C(4), D(1)
(d) A(4), B(1), C(2), D(3)
Answer
A
C. Answer the following :
Question. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d6 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when Δ0 < P.
Answer. t32g e3g
Question. Explain the following—
[Fe(CN)6]4– and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ are of different colours in dilute solutions.
Answer. [Fe(CN)6]4– does not have unpaired electrons (CN is a strong field ligand) whereas [Fe(H2O)6]2+ has unpaired electrons and it absorbs light from visible region and radiates complementary colour.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain why [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner complex whereas [Ni(NH3)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex.
(At. no. Co = 27, Ni = 28)
Answer. When the complex formed involves the inner (n – 1) d-orbitals for hybridization (d2sp3), the complex is called inner orbital complex. [Co(NH3)6]3+ involves inner (n – 1) d-orbitals. Therefore, it is called inner orbitals complex. When the complex formed involves the use of outer n d-orbitals for hybridization (sp3d2), the complex is called outer orbital complex. [Ni(NH3)6]2+ involves nd-orbitals.
Therefore, it is outer complex.
[Co(NH3)6]3+ Co = 27 = 4s23d7
Co3+ = 3d6
As ammonia is a strong ligand, pairing occurs.

Question. Explain why [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has magnetic moment value of 5.92 BM whereas [Fe(CN)6]3– has a value of only 1.74 BM.
Answer. [Fe(H2O)6]3+ and [Fe(CN)6]3– exist in the +3 oxidation state i.e., in d5 configuration.
Due to presence of five unpaired electrons [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has magnetic moment 5.92 BM whereas [Fe(CN)6]3– has 1.74 BM moment due to presence of one unpaired electron.
Question. Using the Valence Bond theory predict the geometry and magnetic behaviour of [CoF6]3–.
[At. no. of Co = 27]
Answer.
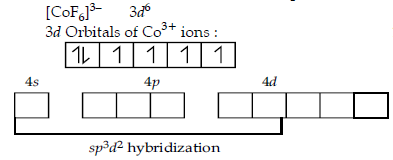
Fluorine ion is a weak ligand so pairing will not occur, so it possess octahedral geometry and paramagnetic in nature.
Question. State reason for each of the following :
(i) CO is stronger complexing reagent than NH3.
(ii) The molecular shape of Ni(CO)4 is not the same as that of [Ni(CN)4]2–.
Answer. (i) CO can form s as well as p bond, whereas NH3 has lone pair of electrons and can form s bond only.
Therefore, CO is a better complexing reagent than NH3.
(ii) Electronic configuration of :
Ni : [Ar] 4s2, 3d8
So Ni (0) : [Ar] 4s0, 3d10
CO ligand causes pairing of electrons and shifting of electrons from 4s to 3d.

Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) For the complex [Fe(CN)6]3–, write the hybridization, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex.
(At. number : Fe = 26).
(ii) Draw one of the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]2+ which is optically active.
Answer. (i) [Fe(CN)6]3–
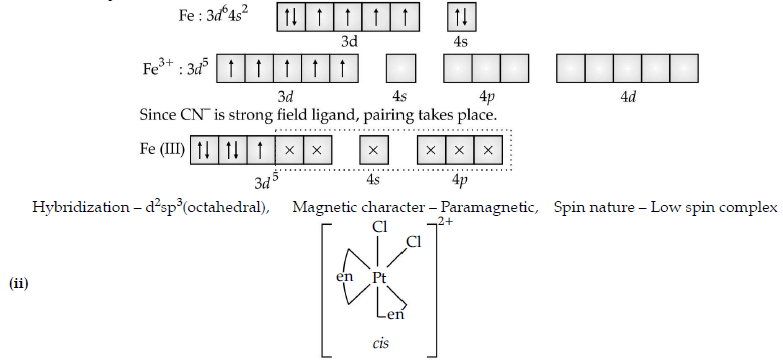
Question. (i) Describe the type of hybridisation for the complex ion [Fe(H2O)6]2+.
(ii) Write the IUPAC name of the ionisation isomer of the coordination compound [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4.
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the two compounds.
Answer. (i) Fe exists as Fe2+. Fe (II) in [Fe(H2O)6]2+ = 3d6 4s0 4p0 4d0
As water is a weak ligand, pairing does not occur and the 6 lone pairs available from each water molecule moves to one 4s, three 4p and two 4d orbitals. Thus, the hybridisation involved is sp3d2.(marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically)
(ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is Pentaamminesulphatocobalt (III) bromide.
The isomer [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 gives a white precipitate of BaSO4 with BaCl2 solution whereas the isomer [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br does not form this precipitate. (or any other relevant test)
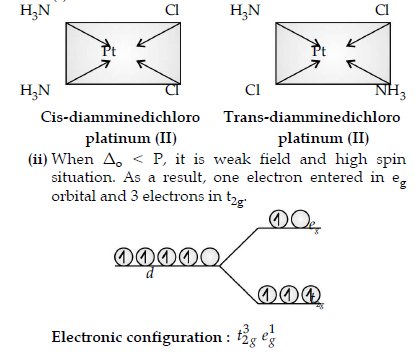
Question. (i) Draw the geometrical isomers of complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2].
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo < P.
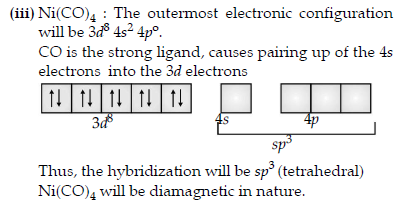
(iii) Write the hybridization and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Ni(CO)4].
Answer. (i)
Question. A metal ion Mn+ having d4 valence electronic configuration combines with three bidentate ligands to form a complex compound. Assuming Δo > P.
(i) Write the electronic configuration of d4 ion.
(ii) What type of hybridisation will Mn+ ion has?
(iii) Name the type of isomerism exhibited by this complex.
Answer.

(iii) optical isomerism
Question. (i) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 ?
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo > P.
(iii) Write the hybridization and shape of [CoF6]3–.
(Atomic number of Co = 27)
Answer. (i) Hydration isomerism
(ii) Electronic configuration is t2g4 or by diagram.
(iii) Hybridization is sp3d2 and shape is octahedral.
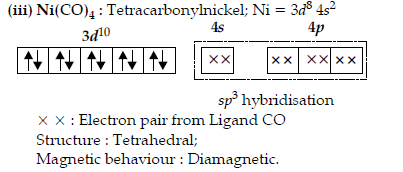
Question. Write the name, the structure and the magnetic behaviour of each one of the following complexes :
(i) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)]
(ii) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl
(iii) Ni(CO)4
(At nos. Co = 27, Ni = 28, Pt = 78)
Answer.

Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the complex [Cr(NH3)4 Cl2] Cl.
(ii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(en)3]3+ ? (en = ethane-1, 2-diammine)
(iii) Why is [NiCl4]2– paramagnetic but [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic ?
(At. nos. : Cr = 24, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) Tetraamminedichloridochromium (III) chloride.
(ii) Optical isomerism.
(iii) In [NiCl4]2–; Cl– act as weak ligand therefore does not cause forced pairing, thus electrons will remain unpaired hence paramagnetic.
In [NiCO4]; CO act as strong ligand therefore causes forced pairing, thus electrons will become paired hence diamagnetic.
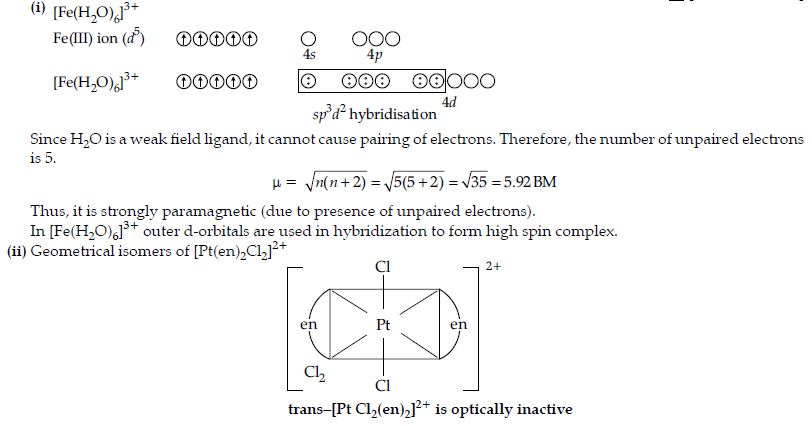
Question. (i) For the complex [Fe(H2O)6]3+, write the hybridization, magnetic character and spin of the complex. (At. number : Fe = 26)
(ii) Draw one of the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]2+ which is optically inactive.
Answer.
Question. (i) Using valence bond theory explain the geometry and magnetic behaviour by [Cr(NH3)6]3+. (At. no.Cr = 24)
(ii) Write the IUPAC name of ionization isomer of [Ni(NH3)3NO3]Cl.
Answer. (i) The complex [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is formed by d2sp3 hybridization therefore, it has octahedral geometry.Since it has three unpaired electrons, therefore, it is
paramagnetic in nature.
[Cr(NH3)6]3+
Cr = 24 = 4s13d5
Cr3+ = 3d3

(ii) The IUPAC name of ionization isomer is triamminechloridenickel (II) nitrate.
Question. Name the following coordination entities and describe their structure :
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4–
(ii) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+
(iii) [Ni(CN4)]2–
(Atomic numbers Fe = 26, Cr = 24, Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) [Fe(CN)6]4– : Hexacyanoferrate (II) ion; Fe2+ (3d6)

Question. (i) Define crystal field splitting energy. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo > P.
(ii) [Ni(CN)4]2– is diamagnetic whereas [NiCl4]2– is paramagnetic. Give reason. (At. no. of Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) It is the magnitude of difference in energy between the two sets of d orbital i.e. t2g and eg 1 t42ge0g
(ii) In [Ni(CN)4]2-, CN– is a strong field ligand and pairing takes place whereas in [NiCl4]2-, due to the presence of Cl-, a weak field ligand no pairing occurs/diagrammatic representation.
Question. (i) Define crystal field splitting energy. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo < P.
(ii) [Ni(CN)4]2– is colourless whereas [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green. Why? (At. no. of Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) It is the magnitude of difference in energy between the two sets of d orbital i.e. t2g and eg t32ge1g
(ii) In [Ni(H2O)6]2+, Ni+2(3d8) has two unpaired electrons which do not pair up in the presence of weak field ligand H2O.
Long Answer Type Questions-II
Question.1. Write down the IUPAC name for each of the following complexes and indicate the oxidation state, electronic configuration and coordination number. Also give stereochemistry and magnetic moment of the complex :
(a) K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2].3H2O
(b) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
(c) [CrCl3(py)3]
(d) Cs[FeCl4]
(e) K4[Mn(CN)6]
Answer. (a) K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2].3H2O :
IUPAC name :
Potassiumdiaquadioxalatochromate(iii)trihydrate.
Oxidation state of chromium : 3
Electronic configuration : 3d3 : t2g3
Coordination number : 6
Shape : Octahedral
Stereochemistry :

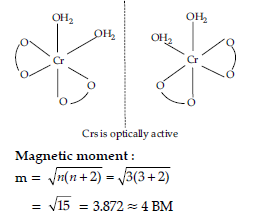
(b) [CO(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 :
IUPAC name :
Pentaamminechloridocobalt(III)chloride
Oxidation state of Co : +3
Coordination number : 6
Shape : Octahedral
Electronic configuration : d6 : t2g6
Stereochemistry :
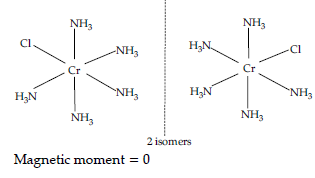
(c) CrCl3(py)3 :
IUPAC name :
Trichloridotripyridinechromium (III)
Oxidation state of chromium : +3
Electronic configuration for d3 : t2g3
Coordination number : 6
Shape : Octahedral
Stereochemistry :
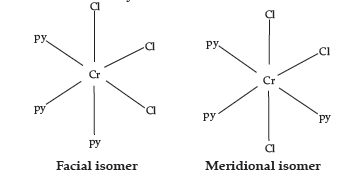
Both isomers are optically active. Therefore, a total of four isomers exist.
Magnetic moment :

(d) Cs[FeCl4] :
IUPAC name : Caesiumtetrachloroferrate (III)
Oxidation state of Fe : +3
Electronic configuration of d6 : eg2t2g3
Coordination number : 4
Shape : Tetrahedral
Stereochemistry : Optically inactive
Magnetic moment :
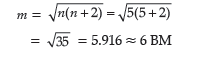
(e) K4[Mn(CN)6] :
IUPAC name : Potassium hexacyanomanganate(II)
Oxidation state of manganese : +2
Electronic configuration : d5+ : t2g5
Coordination number : 6
Shape : Octahedral.
Stereochemistry : Optically inactive
Magnetic moment :