Exam Question for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 10 Science teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Science and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 10 Science exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 10th.
Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 10 Science Chapter 5 periodic classification of Elements are very important and should be revised daily.
Exam Question Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: How does the valency of an element be determined, if its electronic configuration is known? What will be the valency of an element with atomic number 9?
Answer:Valency is equal to the number of valence electrons when valence electrons are from 1 to 4 or 8 – no. of
valence electrons when valence electrons are from 5 to 8.
F(9): 2, 7; It can gain 1 electron to become stable, so its valency = 1.
Question: How does the metallic character of elements changes along a period of the periodic table from left to right and why?
Answer:
It decreases due to decrease in atomic size and decrease in tendency to lose electrons
Question: In the periodic table, how does the tendency of an atom to lose electrons changes on moving from (i) left to right across a period?, (ii) top to bottom in a group?
Answer: (i) It decreases due to increase in effective nuclear charge.
(ii) It increases due to decrease in effective nuclear charge.
Question: What is meant by periodicity of properties of elements? Why are the properties of elements placed in the same group of periodic table similar?
Answer:
The repetition of similar properties of elements after a certain interval of elements is called periodicity of properties.
Elements of the same group have same number of valence electrons, same valency and therefore posses similar chemical properties.
Question: How does electronegativity of an element change as we go down a group and across a period? Give reason.
Answer:
Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic size and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
Electronegativity increases along a period due to decrease in atomic size and increase in effective nuclear charge.
Question: Which is bigger (i) O or F, (ii) N or P and why?
Answer:
O is bigger in size than F due to less effective nuclear charge.
P is bigger in size than N due to more number of shells.
Question: Calcium is an element with atomic number 20
(i) Will it be a metal/non-metal? (ii) What will be its valency?
(iii) What would be formula of its chloride?
(iv) Will it be larger/smaller than K?
Answer:
(i) It is a metal. (ii) Its valency is equal to 2.
(iii) CaCl2 is the formula of its chloride. (iv) It will be smaller than K.
Question: Three elements ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ having atomic numbers 11, 7 and 6 respectively react with oxygen to form their oxides.
(a) Arrange these oxides in increasing order of their basic nature.
(b) Give reason for your Answer:
Answer:
X(11): 2, 8, 1; Y(7): 2, 5; Z(6): 2, 4
(a) Y < Z < X
(b) ‘X’ is metallic in nature, therefore it will form basic oxide. ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ are non-metals will form acidic oxides. ‘Y’ will form more acidic oxide than ‘Z’ because it is more non-metallic in nature.
Question: Given below are four elements with their atomic numbers:
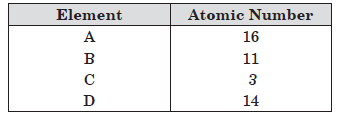
(a) Identify the element which belong to same group of Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange the given elements in decreasing order of atomic size.
(c) Write the formula of the oxide of ‘B’.
(d) Which of the above element is a metalloid?
Answer:
(a) ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to same group.
(b) B > D > A > C
(c) B2O
(d) ‘D’ is a metalloid.
Question: Give reasons for the following:
(a) Lithium atom is smaller than sodium atom.
(b) Chlorine (Atomic number 17) is more electronegative than sulphur (Atomic number 16).
Answer:
(a) It is because Li(2, 1) has two shells whereas Na(2, 8, 1) has three shells.
(b) Chlorine is smaller in size and has more effective nuclear charge than sulphur, therefore it is more electronegative.
Question: Two elements ‘M’ and ‘N’ belong to Group I and II respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of M and N vary:
(a) size of their atoms (b) their metallic characters
(c) their valencies in forming oxides (d) formulae of their chlorides
Answer:
(a) Size of ‘N’ is smaller than ‘M’.
(b) ‘M’ is more metallic than ‘N’.
(c) Valency of ‘M’ is 1 and valency of ‘N’ is 2.
(d) MCl and NCl2 are the formulae of their chlorides.
Question: The following table shows elements represented by the letters A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H:

(i) Which of the element has the atomic size (a) biggest and (b) smallest?
(ii) Which element has valency (a) 3 and (b) Zero
Answer:
(i) (a) ‘A’ is biggest in size
(b) ‘G’ is smallest in size
(ii) (a) ‘C’ has valency 3.
(b) H has zero valency
Question: What is a metalloid? Name any one of them.
Answer: The element which resembles both with metals and non-metals is called a metalloid, e.g. Boron, Silicon.
Question: What is place of metalloid in the periodic table?
Answer: They are placed between metals and non-metals in a zig-zag manner.
Question: State the common characteristic of the following elements: Boron, Silicon, Germanium and Arsenic
Answer: Boron, silicon, Germanium and Arsenic elements are metalloids. They possess the properties of both metals and non-metals.
Explanation: Metals lie on the left hand side of the Modern Periodic Table while the non- metals are found on the right-hand side. A zig-zag line separates metals from non-metals and the borderline elements show the properties of left hand side elements (metals) and right hand side elements (non-metals and are called metalloids or semi-metals).
Question: Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is solid with a high melting point.
X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as (a) Na (b) Mg (c) Al (d) Si.
Answer: As the formula of chloride of element X is XCl2, it is a metal with valency 2 as it has a high melting point and is combining with Cl which is a non-metal having valency 1. Of the given elements, valency of (b) Mg is 2 (Atomic No. 12). Therefore, X will be in the same group as Mg in the Periodic Table.
Question: How does valency of an element vary across a period?
Answer: The valency of an element first increases and then decreases across a period.
Question: The atomic radii of three elements A, B and C of a periodic table are 186 pm, 104 pm and 143 pm respectively. Giving a reason, arrange these elements in the increasing order of atomic numbers in the period.
Answer: Since atomic size decreases along a period and the atomic number increases. So, the element with smaller radii, has the highest atomic number.
Hence, B has the highest atomic number followed by C and A i.e. A < C < B
Explanation: The atomic size is the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the autermost shell of an isolated atom. The atomic radius is measured in picometre, (1 pm = 10–12 m).
The atomic radius decreases in moving from left to right along a period. This is due to:
As the atomic number increases, the nuclear charge increases. Increase in nuclear charge tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleur and reduce the size of the atom.
Question: How does the metallic character vary across the period? Explain.
Answer: Metallic character decreases as we move across a period in the periodic table from left to right.
This occurs because as we move across a period, the nuclear charge increases and the tendency of the element to lose electrons decreases.
Question: State modern Periodic Law of classification of elements.
Answer: The Modern Periodic Law states that ‘Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.’
Question: Consider the following :
20Ca, 8O, 16S, 4Be
Which of the above elements would you expect to be in group 2 of the Modern Periodic table?
Answer: Consider the electronic configuration of elements:
Ca: 2, 8, 8, 2
O: 2, 6
S: 2, 8,6
Be: 2, 2
As Ca and Be all have the same number of valence electrons (2), they belong to Group 2 of the Modern Periodic Table.
Question: Two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’ belong to group 1 and 2 respectively in the same period. Compare them with respect to size of their atoms.
Answer: Size of B will be smaller than the size of A because on moving from left to right in a period, the size of atoms decreases. When we move from left to right in a period, the number of electrons and protons increases. Due to the large positive charge on the nucleus, electrons are pulled more strongly towards the nucleus.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Questions: Elements have been arranged in the following sequence on the basis of their increasing atomic masses:
F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K
(A) Pick two sets of elements which have similar properties.
(B) The given sequence represents which law of classification of elements?
Answer: (A) In this sequence, the elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses.
According to Newlands’ law of octaves, every eighth element will show similar properties as that of the first element.
Hence, F and Cl, Na and K will show similar properties.
Therefore, set I is F and Cl and set II is Na and K.
Note: Although Na and K have similar properties but they are not related as first and eighth element in the above sequence.
(B) The given sequence represents Newland’s law of octaves. In the given sequence, elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic mass and each 8th element shows similar properties. So, it represents Newlands’ law of octaves.
F Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K
Questions: The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 4. State its:
(A) group and period in the Modern Periodic Table.
(B) name and write its one physical property.
Answer: (A) As the number of valence electrons in the given element is 4, it belongs to Group 14 of the Modern Periodic Table.
As the number of occupied shells is 3 (since electrons are filled in K, L and M shells), the element belongs to third period.
(b) The given element is Silicon (atomic symbol: Si). It’s physical property is:
(i) Silicon is a solid
(ii) It is a semi-conductor
(iii) It exhibits allotropy
(iv) It has a metallic luster
Questions: Na, Mg and Al are the elements having one, two and three valence electrons respectively.
Which of these elements (a) has the largest atomic radius, (b) is least reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each.
Answer. (a) Na has the largest atomic radius because it has 11 protons and 11 electrons, therefore least effective nuclear charge.
(b) Al is least reactive because it has smallest atomic size due to 13 protons and 13 electrons, it has greater effective nuclear charge, therefore, cannot lose electrons easily, hence it is least reactive.
Questions: (a) How are the following related?
1. Number of valence electrons of different elements in the same group.
2. Number of shells of elements in the same period.
(b) How do the following change?
1. Number of shells of elements as we go down a group.
2. Number of valence electrons of elements on moving from , left to right in a period.
3. Atomic radius in moving from left to right along a period.
4. Atomic size down a group.
Answer. (a)
1. Different elements in same group have same number of valence electrons.
2. Number of shells of elements in same period are equal.
(b)
1. Number of shells of elements goes on increasing down the group.
2. Number of valence electrons of elements goes on increasing on moving from left to right in a period, e.g. lithium has 1, beryllium has 2, boron has 3, carbon has 4, nitrogen has 5, oxygen has 6, fluorine has 7 and neon has 8 valence electrons.
3. Atomic radius goes on decreasing in moving from left to right along a period.
4. Atomic size goes on increasing down a group.
Questions: (a) How many periods are there in the Modern Periodic Table of elements?
(b) How do atomic radius, valency and metallic character vary down a group?
(c) How do the atomic size and metallic character of elements vary as we move from left to right in a period?
Answer. (a) There are 7 periods.
(b) Atomic radius goes on increasing down the group, valency remains same. Metallic character increases down the group.
(c) Atomic size decreases along a period from left to right. Metallic character decreases along a period from left to right.
Questions: From the elements Li, K, Mg, C, Al, S identify the:
(a) elements belonging to the same group.
(b) element which has the tendency to lose two electrons.
(c) element which prefers sharing of electrons to complete its octet.
(d) most metallic element.
(e) element that forms acidic oxide.
(f ) element that belongs to group 13.
Answer: (a) Li, K (b) Mg (c) C
(d) K (e) S (strongly acidic, C (weakly acidic) (f) Al
Explanation:
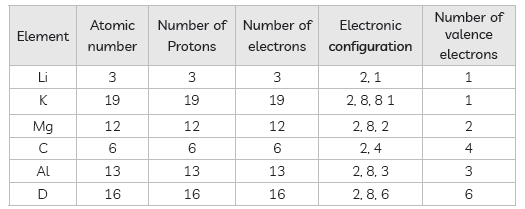
(1) All the elements in any group of the periodic table have identical or valence
shell electronic configuration i.e. the same number of valence electrons. Li and K belong to group 1 as both of them have one electron in the outermost shell though the number of filled shells have increased from 2 to 4.
(2) Elements having 1, 2 or 3 electrons in their respective valence shells have a tendency to lose electrons to form positive ions. So they are metals and are called electropositive element.
Magnesium has 2 electrons in its outer most shell so it has tendency to lose 2 electrons.
(3) C has four valence electrons so it is diffcult for C to lose or gain 4 electrons to become C4+ or C4– ions, so it prefers sharing of electrons.
(4) Most metallic element is K since it has to lose only one electron to form electropositive element K→ K+ + e–
(5) As we move across a period from left to right, metallic character decreases and non- metallic character increases.
(6) Al belongs to group 13 as number of valence electrons are 3 so the group number is (10 + 3) = 13.
Questions: How it can be proved that the basic structure of the Modern Periodic Table is based on the electronic configuration of atoms of different element?
Answer: The Modern Periodic table consists of 18 vertical columns or ‘groups’ and 7 horizontal rows or ‘periods’.
As we move from left to right along a period, we observe that the elements have the same number of valence shells but the number of valence electrons increases by one unit.
Similarly, as we move down a group, we observe that elements have the same number of valence electrons but the number of shells increases by one.
This proves that the Modern Periodic Table is based on electronic configuration of atoms of elements.
Questions: In the following table, are given eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H (here letters are not the usual symbols of the elements) of the Modern Periodic Table with the atomic numbers of the elements in parenthesis.
(a) What is the electronic configuration of F?
(b) What is the number of valence electrons in the atom of F?
(c) What is the number of shells in the atom of F?
(d) Write the size of the atoms of E, F, G and H in decreasing order,
(e) State whether F is a metal or a non-metal.
(f) Out of the three elements B, E and F, which one has the biggest atomic size?
Answer. (a) F has electronic configuration 2, 8, 2.
(b) F has 2 valence electrons.
(c) There are three shells in ‘F’.
(d) H > G > F > E is decreasing order of size of atoms.
(e) ‘F’ is a metal.
(f) ‘B’ is having biggest atomic size among B, E and F
Questions: The atomic number of an element is 16. Predict
(a) the number of valence electrons in its atom
(b) its valency
(c) its group number
(d) whether it is a metal or a non- metal
(e) the nature of oxide formed by it
(f) the formula of its chloride
Answer. The electronic configuration of S(16) is 2, 8, 6.
(a) 6
(b) 2
(c) 16
(d) Non-metal
(e) Acidic oxide
(f) SCl2 is a formula of its chloride.
Questions: The position of three elements A, B and C in the Modern periodic table is as follows:

(A) Write formula of compound formed between:
(i) B and A
(ii) B and C
(B) Is any of the three elements a metal? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer:
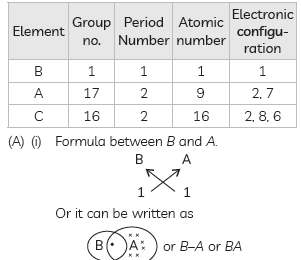
Explanation: ‘B‘ element has one valence electron. It needs only one electron to complete its duplet i.e. K shell. ‘A‘ element has one valence electrons it also needs one electron to complete its octet i.e. L shell. These two elements will share electrons and form covalent bond.
(ii) B and C

Explanation: ‘C‘ element has6 valence electrons and it needs two electrons to complete its octet i.e. M shell. So it will share two electrons with two atoms of B and form B2C and the bonding is covalent bonding.
Questions: The positions of three elements A, B and C in the periodic table are indicated below:
Group 16 Group 17
— — (First Period)
— A (Second Period)
— — (Third Period)
B C (Fourth Period)
(a) State whether element C would be a metal or a non-metal. Why?
(b) Which is the more active element, A or C? Why?
(c) Which type of ion (cation or anion) will be formed by the element C? Why?
Answer. (a) ‘C will be non-metal because it has 7 valence electrons, it can gain one electron easily.
(b) ‘A’ is more active element than ‘C’ because ‘A’ can gain electron easily.
(c) ‘C’ will gain electron to become negative ion, ie. anion because it will have electrons more than protons.
Questions: F, Cl and Br are the elements each having seven valence electrons. Which of these (a) has the largest atomic radius, (b) is most reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each.
Answer. (a) Bromine has largest atomic radius because it has four shells: 2, 8, 18, 7.
(b) Fluorine is most reactive because it is smallest in size and can gain electron easily.
Questions: Can the following groups of elements be classified as Dobereiners triad?
(A) Na, Si, Cl (B) Be, Mg, Ca
Atomic mass of Be 9; Na 23; Mg 24; Si 28; Cl 35; Ca 40.
Explain by giving reason.
Answer: For a group to be Dobereiner’s triad, the atomic mass of the middle element must be average of the atomic masses of the first and the third elements.
(A) No, Na, Si, Cl cannot be classified as Dobereiner’s triad because all these elements do not have similar properties, although the atomic mass of silicon is the average of the atomic masses of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl).
Atomic mass of Si =23 + 35/2
= 58/2=29
(B) Yes, Be, Mg, Ca can be classified as Dobereiner’s triad because they have similar properties and the mass of magnesium (Mg) is roughly the average of the atomic mass of Be and Ca.
Atomic mass of Mg =9 + 40/2 =49/2= 24.5
Question: Two elements X and Y have atomic numbers 12 and 16 respectively. To which period of the modern periodic table do these two elements belong? What type of bond will be formed between them and why? Also give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
Answer: Electronic configuration of X: 2,8,2, Y: 2,8,6 Both X and Y belong to 3rd period.Ionic bond will be formed.
Reason: X will lose 2 electrons and Y will gain 2 electrons to complete their octet and become stable.
Formula is XY.
Question: Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev.
Answer: Eka-silicon is identified as germanium (Ge), which is placed in group 4 of Mendeleev’s periodic table. The valency of germanium is 4,so the chemical formula of its chloride must be GeCl4.
Eka-aluminium was later identified as gallium (Ga). It is placed in group 3 of Mendeleev’s periodic table. Hence, the valence of gallium is 3 and the formula of chloride would be GaCl3.
Question: Compare the radii of two species X and Y. Give reasons for your answer.
• X has 12 protons and 12 electrons
• Y has 12 protons and 10 electrons
Answer: Here, X has the same number of electrons and protons, therefore, it is a neutral atom, whereas Y contains 12 protons and 10 electrons, so there are 2 protons extra, giving Y a charge of +2. The electronic configurations of the two species can
be expressed as:
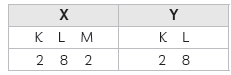
The atomic size of a cation is always smaller than a neutral atom containing the same
number of protons. This is because cation has less number of electrons, due to which the nuclear attraction is more on electrons. Hence, the size of a cation is smaller than that of the neutral atom.
Hence, atomic radius of Y is smaller than that of X.
Question: Write the formula of the product formed when the element A (atomic number 19) combines with the element B (atomic number 17). Draw its electronic dot structure. What is the nature of the band formed?
Answer: The electronic configuration of element A with atomic number 1?? would be 2, 8, 8, 1. Since it has only one valence electron, it must be a metal that is potassium.
The electronic configuration of element B would be 2, 8, ?? with ?? valence electrons. So, it must be a non-metal that is chlorine.
A metal and a non-metal usually combine through ionic bond because metals have a
tendency to lose electrons and form cations, whereas non-metals can accept electrons to form anions.
Potassium and chlorine will form potassium chloride (KCl).
The electron dot structure of KCl is as given below:
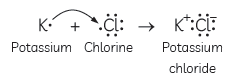
Question: Identify and name the metals out of the following elements whose electronic configurations are given below:
(a) 2, 8, 2 (b) 2, 8, 1
(c) 2, 8, 7 (d) 2, 1
Answer: Elements having 1 to 3 valence electrons are usually metals, whereas elements with 4 or more valence electrons are usually non-metals or metalloids.
The following elements whose electronic confi- gurations are given below:
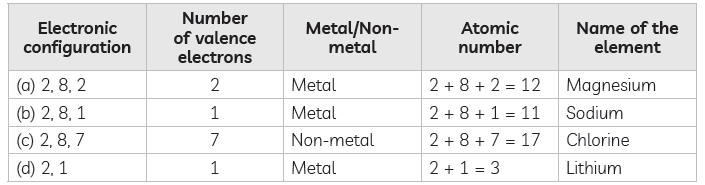
Thus, elements (a), (b) and (d) are metals, while (c) is a non-metal.
Question: An element ‘X’ belong to 3rd period and group 13 of the Modern Periodic Table.
(A) Determine the valence electrons and the valency of ‘X’.
(B) Molecular formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ reacts with an element
‘Y’ (atomic number = 8).
(C) Write the name and formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ combines with chlorine.
Answer: As the element ‘X’ belongs to the 3rd period and group 13 of the modern periodic table, its electronic configuration is: 2, 8, 3 (K-shell: 2, L-shell: 8, M-shell: 3) and atomic number is 13.
(A) The valence electrons of ‘X’ are 3 and it is a metal having valency = 3 (valency = no. of valence electrons).
(B) As atomic number of ‘Y’ is 8, it’s electronic configuration is 2, ??. It is a non-metal having valency 2.
Therefore, when ‘X’ (a metal having valency
3) reacts with ‘Y’ (a non-metal having valency 2), the formula of compound formed will be X2Y3 as shown below.
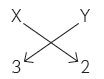
(C) Atomic number of chlorine = 1?? and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7. Therefore, its valency = 1.
The formula of compound formed when ‘X’ combines with Chlorine will be XCl3.

As ‘X’ is aluminium (atomic number=13), formula of its chloride is AlCl3 and its name is aluminium chloride.
Question: An element X has mass number 35 and the number of neutrons is 18. Identify the group number and period of X.
Answer: Mass no. = Sum of protons + Sum of neutrons
35 = Sum of protons + 18
Sum of protons = 35– 18
Sum of protons = 17
Hence, we can say that the atomic number of element X is 17.
Its electronic configuration will be 2, 8, 7.
Thus it is clear that element X belongs to the 3rd Period and the 17th Group.
Question: Arrange the following elements in increasing order of their atomic radii:
(A) Li, Be, F, N (B) Cl, At, Br, I
Answer: (A) F < N < Be < Li.
Li, Be, F and N belong to the same period of the modern periodic table. As we move from left to right in the periodic table, the atomic radii of elements decreases due to high atomic charge and the same number of shells. Thus, the atomic radii of Li, Be, F and N increase in the order: F < N < Be < Li.
(B) Cl < Br < I < At.
Cl, At, Br and I belong to the same group of the modern periodic table that is group 17.
As we move down in a group, the atomic radii of elements increases due to increase in the number of shells. Thus, the atomic radii of Cl, At, Br and I increase in the order:
Cl < Br < I < At.
Question: List the limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves?
Answer: Limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves:
(1) It was not applicable for all the elements.
It was applicable only till calcium, as after calcium every eighth element did not possess properties similar to that of the first.
(2) It was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future.
But, later on, several new elements were discovered, whose properties did not fit into the Law of Octaves.
(3) Cobalt and nickel are placed in the group of halogens with the elements fluorine and chlorine (F, Cl) which have different properties and it was not explained for the same.
(4) Placing of iron far away from cobalt and nickel, which have similar properties as iron, could also not be explained.
Thus, Newlands’ Law of Octaves worked well with lighter elements only.
Question: An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 16 of the modern periodic table.
(i) Determine the number of valence electrons and valency of ‘X’.
(ii) Molecular formula of the compound, when ‘X’ reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot structure.
(iii) Name the element ‘X’ and state whether it is metallic or non-metallic.
Answer:
(i) The element is S(16)—2, 8, 6, The number of valence electrons—6, Valency—2.
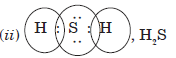
(iii) Sulphur, non-metallic.
Question: An element ‘M’ with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with NO3–, SO42– and PO43– radicals. Write the formulae of three compounds so formed. To which group and period of modern periodic table, ‘M’ belongs to? Will ‘M’ form covalent or ionic compounds? Give reason to justify your Answer:
Answer:
Mg(NO3)2, MgSO4, Mg3(PO4)2
It belongs to Group 2, 3rd period of the periodic table.
It will form ionic compounds because it can lose 2 electrons easily to form Mg2+ ions.
Question: In the following table, the position of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are given as they are in the modern periodic table as follows:

On the basis of above table, answer the following Question:s:
(i) Name the element which form only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a metal with the valency of 3.
(iii) Name the non-metal with the valency of 3.
(iv) Out of B and C, whose atomic size is bigger and why?
(v) Write the common name for the family to which the elements D and F belongs to.
Answer:
(i) E, (ii) B, (iii) C, (iv) B, … It has more number of shells, (v) Noble gases
Question: Based on the group valency of elements, state the formula of the following, giving justification for each.
(i) Oxides of Group 1 elements.
(ii) Halides of the elements of Group 13.
(iii) Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of Group 16.
Answer:
(i) Group 1 elements can lose one electron to become stable, so its valency is equal to 1, M2O.
(ii) Group 13 elements have valency equal to 3, MCl3.
(iii) Group 2 elements have valency equal to 2, Group 16 elements have 6 valence electrons.

valency = 2
Question: In the following table, are given eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H (here letters are not the usual symbols of the elements) of the Modern Periodic Table with atomic numbers of the elements in parenthesis.
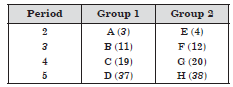
(i) What is the electronic configuration of F?
(ii) What is the number of valence electrons in the atom F?
(iii) What is the number of shells in the atom F?
(iv) Write the order of size of the atoms of E, F, G and H in decreasing order.
(v) State whether F is a metal or a non-metal.
(vi) Out of the three elements B, E and F, which one has the biggest atomic size?
Answer:(i) F(12) 2, 8, 2; (ii) 2; (iii) 3;
(iv) H > G > F > E; (v) F is a metal;
(vi) B has biggest atomic size.
Question: Table given below shows a part of the periodic table:

Using this table, explain why
(i) Li and Na are considered as active metals?
(ii) Atomic size of Mg is less than that of Na?
(iii) Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine?
Answer:(i) Li and Na can lose electrons easily due to their large size and hence are more reactive.
(ii) Mg has more effective nuclear charge than Na.
(iii) Fluorine can gain electrons more easily than chlorine, due to smaller atomic size.
Question: What is the position i.e. group number, period number of element, iodine (atomic number 53)? What is the physical state and nature of this element (metal or non metal)?
Answer:I(53): 2, 8, 18, 18, 7
It belongs to group 17, 5th period.
It is a solid. It is a non-metal.
Question: Consider the following and answer the Question:s that follow:

(i) Amongst A, D and G, which is not electropositive and why?
(ii) Atomic size of H is bigger than B. Why?
(iii) Write the formula of compound formed by the element E and fluorine.
Answer:
(i) ‘A’ is not electropositive because it is hydrogen which is considered as a non-metal.
(ii) ‘H’ has more number of shells than ‘B’, therefore it has bigger atomic size.
(iii) EF2 is the formula of fluoride of ‘E’.
Question: Explain the basic character of oxides of elements down the group and across the period.
Answer:
Basic character of oxides increases from top to bottom in a group because metallic character increases down the group due to increase in tendency to lose electrons.
Basic character of oxide decreases along a period from left to right because the atomic size decreases,tendency to lose electrons decreases, metallic character decreases.
Question: The atomic number of Na and Mg is 11 and 12 respectively and they belong to same period.
(a) Which one would have smaller atomic size?
(b) Which one would be more electropositive?
(c) To which group would each one belongs?
Answer:
(a) Magnesium has smaller size than Na.
(b) Na is more electropositive than Mg.
(c) Na belongs to Group 1, Mg belongs to Group 2.
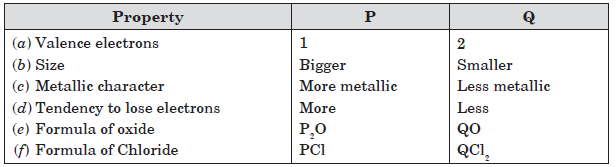
Question: Two elements ‘P’ and ‘Q’ belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in Group 1 and 2 respectively. Compare the following characteristics in tabular form:
(a) The number of valence electrons in their atom.
(b) Their metallic character (c) The size of their atoms
(d) The formulae of their oxides (e) Their tendency to lose electrons
(f) The formula of their chloride
Answer:
Question: Given below are some elements of modern periodic table. Atomic number of elements are given in parenthesis:
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
(a) Select the element that has one electron in outermost shell. Also write the electronic configuration of this element.
(b) Which two elements amongst there belong to the same group? Give reason for your Answer:
(c) Which two elements amongst there belong to the same period? Which one of the two has bigger atomic radius?
Answer:
(a) D(19) has one valence electron. Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 8, 1.
(b) A(4), E(20) belong to same group because they have same number of valence electrons.
(c) A and B belong to same period, A is bigger than ‘B’.
D and E also belong to same period, ‘D’ is bigger than E.
Question: The elements Be, Mg and Ca are having two electrons in their outermost shells are in periods 2, 3 and
4, respectively of the modern periodic table. Answer the following Question:s, giving justification in each case.
(i) Write the group to which these elements belong.
(ii) Name the least reactive element.
(iii) Name the element having largest radius.
Answer:(i) They belong to Group 2 because they have 2 valence electrons.
(ii) Be is the least reactive element due to smallest size and least tendency to lose electrons.
(iii) Ca has largest radius because it has the most, four shells (2, 8, 8, 2).
Question: What is meant by ‘group’ in the modern periodic table? How do the following changes occur on moving from top to bottom in a group?
(i) Number of valence electrons (ii) Number of occupied shells
(iii) Size of Atoms (iv) Metallic character of elements
(v) Effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons.
Answer:
The vertical columns of periodic table are called Groups.
(i) Number of valence electrons remains the same.
(ii) Number of occupied shells goes on increasing.
(iii) Size of atoms increases down the group.
(iv) Metallic character of elements increases down the group.
(v) Effective nuclear charge decreases.
Question: Write the number of periods and groups in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving (i) from left to right in a period, and (ii) down a group? Give reason to justify your Answer:
Answer:In the Modern Periodic Table, there are 18 vertical columns known as Groups and 7 horizontal rows known as Periods.
Metallic character: It is defined as the tendency of an atom to lose electrons.Across the period i.e., from left to right: Metallic character decreases.Down the group i.e., from top to bottom: Metallic character increases.
Reason: Across the period, the effective nuclear charge increases, thus decreasing its atomic radius.This favours the increase of electronegativity and therefore the tendency to lose electrons is less. This accounts for the decrease in the metallic character along the period.But as we move down the group the number of shells keep on increasing and therefore the atomic size increases. This means that the electronegativity decreases. This enhances the ability to lose electrons and therefore the metallic character increases down the group.
Question: Na, Mg and Al are the elements of the 3rd period of the Modern Periodic Table having group number 1, 2 and 13 respectively. Which one of these elements has the (a) highest valency, (b) largest atomic radius, and (c) maximum chemical reactivity? Justify your answer stating the reason for each.
Answer:Given are the three elements Na, Mg and Al belonging to group 1 , 2 and 13 respectively.
The electronic configurations of the three elements are as follows:

(a) The element having the highest valency signifies the maximum number of electrons present in the valence shell of an atom. Hence, as per the given electronic configurations, the element having highest valency is aluminium (Al).
(b) As we move across the period, i.e., from left to right the atomic radius decreases. Therefore the element having the largest atomic radius will be sodium (Na).
(c) The given three elements are metals. So, the chemical reactivity of a metal is determined by its metallic character which is the tendency of an atom to lose its electrons. We know that the metallic character of element decreases across the period, i.e., from left to right. So, the element having highest chemical reactivity is sodium (Na).
Question: Two elements X and Y have atomic numbers 12 and 16 respectively. To which period of the modern periodic table do these two elements belong? What type of bond will be formed between them and why? Also give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
Answer:Electronic configuration of X: 2,8,2, Y: 2,8,6
Both X and Y belong to 3rd period because they have 3 shells.
Ionic bond will be formed.
Reason: X will lose 2 electrons and Y will gain 2 electrons to complete their octet and become stable.
Formula is
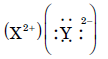
Question: Write the names given to the vertical columns and horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving down a vertical column? How does the size of atomic radius vary on moving left to right in a horizontal row? Give reason in support of your answer in the above two cases.
Answer:In the Modern Periodic Table, there are 18 vertical columns known as Groups and 7 horizontal rows known as Periods.
As we move down the group, the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer-most electron decreases due to increase in the distance between them. This happens because, on moving down the group, a new shell is added. So the valence electrons can be easily lost by the element. As we know, metallic character is characterised by the ease of loss of electrons, thereby, metallic character increases on moving down the group in the Modern Periodic Table.
When we move across a period, the number of electrons in the same shell increases. This leads to greater electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer-most electron. This increased attraction pulls the outer-most electron closer to the nucleus, thereby decreasing the atomic size.
Question: The electronic configuration of an element ‘X’ is 2,8,6. To which group and period of the modern periodic table does ‘X’ belong .State it valency and justify your answer in each case.
Answer:X – 2, 8, 6
(a) Since ‘X’ has three energy shells and period number of an element is equal to the number of energy shells. So, X belongs to 3rd period.
(b) X has 6 valence electrons so, it belongs to group 16.
(c) Valency will be 2. To acquire noble gas configuration it will gain 2 electrons.
Question: Based on the group valency of elements write the molecular formula of the following compounds giving justification for each
(i) Oxides of first group elements
(ii) Halides of group 13 and
(iii) Compound formed when an element A of group 2 combines with element B of group 17
Answer:(i) Group 1 elements have valency equal to 1.
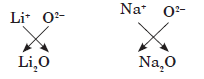
(ii) Group 13 elements have 3 valence electrons,valency equal to 3
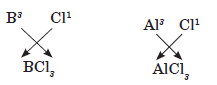
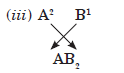
… A has valency equal to 2 and B has valency equal to 1.
Question: How is possible valency of element determined with the help of electronic configuration of its atom? Determine the valency of ‘X’ whose atomic number is 15.
Answer:Valency is equal to number of valence electrons or 8–valence electrons. X has electronic configuration 2, 8, 5.
Its valency is equal to 3 because it can gain 3 electrons to become stable.
Question:22. The following table shows the position of five elements A, B, C, D and E in the modern periodic table.
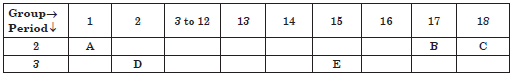
Answer the following giving reasons:
(i) Which element is a metal with valency two?
(ii) Which element is least reactive?
(iii) Out of D and E which element has a smaller atomic radius?
Answer:
(i) D, As it is on the left side of the table in group 2.
(ii) C, as it is in the group 18/ Noble gas.
(iii) E, as we move from left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases.
Question: Answer the following:
(A) Name any three halogens.
(B) Mention the group to which they belong and their valency.
(C) What type of compounds will they form with elements of group 1?
Answer: (A) Three halogens are Fluorine, Chlorine and Bromine.
(B) They belong to the Halogen group or Group 1?? of the periodic table. Their valency is 1.
(C) All the alkali metals react vigorously with halogens to produce salts, the most industrially important of which are NaCl and KCl.
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) ??→ 2NaCl(s)
Question: Out of lithium and potassium, which one has stronger metallic character and why?
Answer: On going down in a group of the periodic table, the metallic character of elements increases.
Therefore, potassium has stronger metallic character than Lithium.
The reason behind is that as we go down in a group of the periodic table, one more electron shell is added. As a result, the size of the atom increases. The valence electrons move away from the nucleus at regular intervals. The holding capacity of the nucleus on valence electrons decreases. Due to this the atom can lose valence electrons more easily to form positive ions, and hence the metallic character increases.
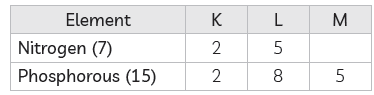
Question: Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative? Why?
Answer: Electronic configurations of the two elements are:
Element K L M
Nitrogen (7) 2 5
Phosphorus (15) 2 8 5
Both these elements have ?? electrons in their respective valence shell and thus have a tendency to gain 3 more electrons to form negative ions by completing their respective octet. Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorus. On moving down a group, the number of shells increases. Therefore, the valence electrons move away from the nucleus and the effective nuclear charge decreases.
This causes the decrease in the tendency to attract electrons and hence electro- negativity decreases.
Question:An element ‘X’ (Atomic number = 19) burns in the presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(A) Identify the element and write its electronic configuration.
(B) State its group number and period number in the modern periodic table.
(C) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction when this oxide is dissolved in water.
Answer: (A) The element ‘X’ is potassium (K) Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 8, 1
(B) Group number 1
Since it has valence electron So it belongs to group Period number 4
Explanation: Since there are four shells as number of shells determine the period number.
(c) K2O (s) + H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq)
Question: Name two elements you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium.
What is the basis for your choice?
Answer: Magnesium (Mg) belongs to group 2 known as alkaline earth family. The two other elements belonging to the same group are Calcium (Ca) and Strontium (Sr) which are expected to show chemical reactions similar to Magnesium (Mg).
The basis of choice is the electronic distribution in the valence shell of these elements. All of them have two valence electrons each.
Explanation: Since chemical properties are due to valence electrons, they show same chemical reactions.

Question: Answer the following:
(A) Why do elements in a group show similar property?
(B) An element M is in the third group of the periodic table. Write the formulae of its chloride and oxide.
Answer: (A) All the elements present in a group have same electronic configuration of the atoms.
The physical and chemical properties of elements depend on the number of valence electrons. Elements present in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. Therefore, elements present in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties.
Explanation: Elements two groups are:
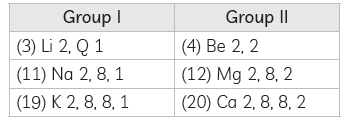
Elements in group I have same number of valence electrons, so have same properties.
(B) Element M is in the third group, therefore it will have a valency of 3.
Its chloride and oxide are MCl3 and M2O3 respectively. (∴ O and Cl have valencies of
–2 and –1 respectively).
Explanation:

Question: Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative? Why?
Answer: Electronic configurations of the two elements are:
Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorus. On moving down a group, the number of shells increases. Therefore, the valence electrons move away from the nucleus and the effective nuclear charge decreases.
This causes the decrease in the tendency to attract electrons and hence electronegativity decreases.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question: (A) In this ladder (figure), symbols of elements are jumbled up. Rearrange these symbols of elements in the increasing order of their atomic numbers in the periodic table.
(B) Arrange them in the order of their group also.

Answer: (A) The symbols of elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers are:
H, He, Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K and Ca.
(B) The symbols of elements in increasing order of their group numbers are as follows:
Group 1 — H, Li, Na, K
Group 2 — Be, Mg, Ca
Group 13 — B, Al
Group 14 — C, Si
Group 1?? — N, P
Group 1?? — O, S
Group 1?? — F, Cl
Group 18 — He, Ne, Ar
Question: Based on the group valency of element write the molecular formula of the following compounds giving ??ustification for each:
(A) Oxide of first group element.
(B) Halide of the element of group thirteen, and
(C) Compound formed when an element, , A of group 2 combines with element, B of group seventeen.
Answer: While writing the formula of compounds, we need to take the valencies of the combining elements into account.
(A) First group elements have a valency one, as they have one valence electron. Oxygen belongs to group 16 and has a valency of 2 as it has ?? valence electrons.
The molecular formula of compound formed by oxides of first group element will be X2O, where X is the first group element. Example of such a compound is Na2O.
(B) Elements of group 13 have a valency 3, as they have 3 valence electrons. Halogens belong to group 1?? and have a valency of 1, as they have ?? valence electrons.
The molecular formula of halide of elements of group 13 will be YX3, where Y is the element of group 13 and X is a halogen.
Example of such a compound is AlCl3.
(C) All ele ments of group 2 have a valency 2, as they have 2 valence electrons. Group 17 elements are halogens, having a valency of 1.
Therefore, valency of A is 2 and that of B is 1.
The molecular formula of compound formed when A combines with B will be AB2. Example of such a compound is MgCl2.
Question: (a) Which two criteria did Mendeleev use to classify the elements in his Periodic Table?
(b) State Mendeleev’s periodic law.
(c) Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table?
(i) Sizes of their atoms
(ii) Their metallic characters
(iii) Their valencies in forming oxides
(iv) Molecular formulae of their chlorides
(d) How and why does the atomic size vary as you go
(i) from left to right along a period?
(ii) down a group?
Answer. (a) (i) Increasing order of atomic mass as physical property and similarities in chemical properties of elements.
(ii) The formulae and nature of hydrides and oxides formed by elements was treated as basic chemical property for its classification.
(b) Properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses.
(c) It is because it resembles both alkali metals as well as halogens.
(d) (i) Atomic size goes on decreasing from left to right because one proton and one electron is being added successively therefore, force of attraction between . valence electrons and nucleus increases hence, the atomic size decreases.
(ii) The atomic size goes on increasing from top to bottom in a group because number of shells keep on increasing therefore, distance between nucleus and valence electrons increases.
Question: Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of element D is almost neutral. Answer the following questions based on the information given herein:
(a) To which group or period of the periodic table do the listed elements belong?
(b) Which one of the eight elements is likely to be a noble gas?
(c) Which one of the eight elements would have the largest atomic radius?
(d) Which two elements amongst these are likely to be non¬metals?
(e) Which one of these eight elements is likely to be a semi-metal or metalloid?
Answer. (a) A and B belong to group 1 and 2 because they form basic oxides. C belongs to group 13 as it has 3 valence electrons. D belongs to group 14 as it forms almost neutral oxide. E and F belong to group 15 – and 16 as they form acidic oxides, G belongs to group 17 as it has 7 valence electrons and H belongs to group 18. They belong to 3rd period of Periodic Table because sodium belongs to 3rd period and AG is NaCI, ionic compound of sodium which can be obtained from sea water and A(Na) and G(CI) belong to 3rd period.
(b) H belongs to noble gas.
(c) A has the largest atomic radius.
(d) E and F are likely to be non¬metals.
(e) D is likely to be metalloid or semi-metal.
Question: (a) Did Mendeleev have gaps in his periodic table?
(b) Write any three limitations of Mendeleev’s classification.
(c) Does electronic configurations of atoms change in a period with increase in atomic number?
Answer. (a)Gaps were left for undiscovered elements in the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
(b) (i) Position of hydrogen was not justified.
(ii) Increasing order of atomic mass could not be maintained.
(iii) Isotopes have similar chemical properties but different atomic masses, they cannot be given separate places.
(c) Number of shells remains the same, number of valence electrons goes on increasing from left to right in a period till octet is comilete,e.g.
Question: Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This compound is added in a small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of D is almost neutral. Based on the above information answer the following questions:
(a) To which group or period of the Periodic Table do the listed elements belong?
(b) What would be the nature of compound formed by a combination of elements B and F?
(c) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
(d) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature?
(e) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G be 3 and 7 respectively, write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Answer. (a) A and B belong to group 1 and 2 because they form basic oxides. C belongs to group 13 as it has 3 valence electrons. D belongs to group 14 as it forms almost neutral oxide. E and F belong to group 15 and 16 as they form acidic oxides, G belongs to group 17 as it has 7 valence electrons and H belongs to group 18. They belong to 3rd period of the Periodic Table because AG is NaCI, added in a small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking and Na and Cl belong to 3rd period.
(b) Ionic compounds will be formed because ‘B’ is metal and ‘F’ is non-metal. ‘B’ can lose two electrons and ‘F’ can gain two electrons.
(c) A and B are definitely metals as they form basic oxides.
(d) G and H are gaseous at room temperature.
(e) CG3 is the formula of the compound formed by combination of C and G.
Question: Complete the following crossword puzzle (Figure).
Across:
(1) An element with atomic number 12.
(3) Metal used in making cans and member of group 14.
(4) A lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell.
Down:
(2) Highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept in kerosene.
(5) The first element of the second period.
(6) An element which is used in making florescent bulbs and is the second member of group 18 in the modern periodic table.
(7) A radioactive element which is the last member of the halogen family.
(8) Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air?
(9) The first metalloid in modern periodic table whose fibres are used in making bullet-proof vests.
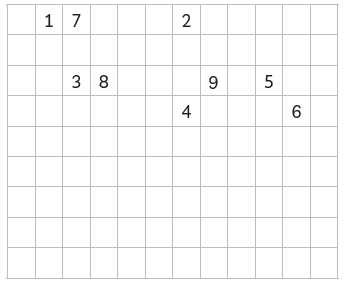
Answer: Across:
(1) An element with atomic number 12 is magnesium
(3) Metal used in making cans and member of group 14 is tin
(4) A lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell is iodine.
Down:
(2) Highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when sub??ected to flame and is kept in kerosene is sodium.
(5) The first element of the second period is lithium.
(6) An element which is used in making fluore-
scent bulbs and is the second member of group18 in the modern periodic table is neon.
(7) A radioactive element which is the last member of the halogen family is astatine.
(8) Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air is iron.
(9) The first metalloid in modern periodic table whose fibres are used in making bullet-
proof vests is boron.

Question: Two elements A and B have atomic numbers 11 and 19 respectively.
(A) State their position in the moden periodic table.
(B) Which element has a bigger atomic radius?
(C) What is the nature of their oxides?
Answer: (A) Electronic configuration of A: 2, 8, 1 Electronic configuration of B: 2, 8, 8, 1 From its electronic configuration, it is clear that element A belongs to Group 1 (since valence electron is 1) and Period 3 (since it has 3 electron shells).
Similarly, we can say that the element B belongs to Group 1 and Period 4.
(B) The atomic radius of element B is bigger as compared to element A. This is because the atomic radius increases (due to the presence of more shells) as we move down in a group.
(C) They form basic oxides.
Question:Explain giving ??ustification the trends in the following properties of elements, on moving from left to right in a period, in the Modern periodic Table.
(A) Variation of valency.
(B) Change of atomic radius.
(C) Metallic to non-metallic character.
(D) Electronegative character.
(E) Nature of oxides.
Answer: The trends in the properties of elements, on moving from left to right in a period, in the Modern periodic Table are given below:
(A) Variation of valency: On moving from left to right, the valency increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to 0 as the valency is determined by the number of valence electrons.
(B) Change of atomic radius: On moving from left to right in a period, the atomic radius decreases because the number of electrons and protons increases. Due to the large positive charge on the nucleus, electrons are pulled more strongly towards the nucleus.
(C) Metallic to non-metallic character: The metallic character decreases and non- metallic character increases as we move from left to right in a period because the tendency to lose electrons decreases as the effective nuclear charge on the valence shell electrons increases.
(D) Electronegative character: The electronegative character, or the tendency
to gain electrons, increases on moving from left to right along a period because of the
increase in effective nuclear charge on the valence shell.
(E) Nature of oxides: The basic nature of oxides decreases and the acidic nature increases as we move from left to right since metals form basic oxides whereas non-metals form acidic oxides.
Question: (A) How is the valency of an element determined if its electronic configuration is known? Determine the valency of an element of atomic no. 9.
(B) Given below are some elements of the Modern Periodic Table.
Atomic numbers of the elements are given in parentheses:
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
(i) With the help of the electronic configuration, find out which one of the above elements will have one electron in its outermost shell.
(ii) Which two elements belong to the same group? Give reasons for your answer.
(iii) Which one of the above elements belonging to the fourth period has bigger atomic radius and why?
Answer: (A) Valency of an element is the number of electrons an element can donate or gain or share in order to complete its valence or outermost shell.
The electronic configuration of an element of atomic number 9 is (2, 7). As this element requires only 1 electron (8 – 7 = 1) to complete its valence shell, its valency is 1.
(B) The electronic configuration of the elements given is as under:
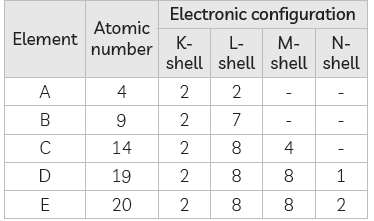
(i) Element D will have one electron in its outermost shell.
(ii) Elements A and E belong to the same group as they have the same number of valence electrons.
(iii) D has bigger atomic radius than E as E has more number of electrons and protons as compared to D. Due to the larger positive charge on its nucleus, electrons are pulled more strongly towards the nucleus in E than D.
Question: (A) What was the basis of Mendeleev classification of elements?
(B) List two achievements of Mendeleev periodic tables.
(C) List any two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev periodic law.
Answer: (A) Atomic Mass of elements was the basis of Mendeleev’s classification of elements.
(B) Achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table:
(1) Mendeleev’s periodic law predicted the existence of some elements that had not been discovered at that time. He therefore left some gaps in his Periodic Table
(2) Mendeleev’s periodic table could predict the properties of several elements on the basis of their positions in the periodic table.
(3) It could accommodate noble gases when these gases were discovered in a new group without disturbing the existing order.
(C) Two observations that posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s periodic law:
(1) The position of isotopes could not be explained since the elements are arranged according to their atomic masses.
(2) Wrong order of atomic masses of some elements could not be explained. For example, cobalt (atomic mass 58.9) appeared before nickel (atomic mass 58.7).
(3) A correct position could not be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table.
(4) The atomic masses do not increase in a regular manner in going from one element to the next.
Question: Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G andH have the same number of electronic shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound.
This compound is added in small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking.
The oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic.
The oxide of D is almost neutral. Based on the above information answer the following questions:
(A) To which group or period of the periodic table, do the listed elements belong?
(B) What would be the nature of the compound formed by a combination of elements B and F?
(C) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
(D) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature?
(E) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of element C and G are 3 and 7 respectively, write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Answer: Element A is sodium (Na) and element G is chlorine (Cl). They form an ionic compound NaCl (also called common salt), which is added to dishes.
It is said in the question that the oxides of A and B are basic in nature. Since we now know that element A is sodium (Na), it combines with Na to form sodium oxide (Na2O), which is basic in nature.
Similarly, element B could be magnesium (Mg), which forms a basic oxide called magnesium oxide (MgO).
It is said that oxides of E and F are acidic in nature, which could probably be aluminium oxide and sulphur dioxide.
On the basis of this knowledge, let us answer the questions:
(A) A: 1st Group and 3rd Period
B: 2nd Group and 3rd Period
C: 13th Group and 3rd Period
D: 14th Group and 3rd Period
E: 15 th Group and 3rd Period
F: 16 th Group and 3rd Period
G: 17 th Group and 3rd Period
H: 18 th Group and 3rd Period
(B) Ionic compound: magnesium sulphate MgSO4.
(C) A and B (sodium and magnesium)
(D) H (argon)
(E) CG3
Question: Give reasons for the following:
(A) K atom is bigger than Na atom even though both these elements belong to the same group.
(B) The metallic character of elements increases as we move down a group.
(C) Mg atom is smaller than Na even though these elements belong to the same period.
Answer: (A) On moving down in a group of the periodic table, the atomic radius of elements increases.
When we go from top to bottom in a group, a new shell of electrons is added to the atoms regularly. In this way, the number of electron shells in the atoms
increases gradually due to which the size of atoms also increases. For example, a sodium atom (Na) has three electron shells K, L and M in it and a potassium atom (K) has four electron shells K, L, M and N, and hence it is bigger than a sodium atom.
(B) The metallic character of elements increases as we move down a group because one more electron shell is added to the atom. As a result, the size of the
atom increases. The valence electrons move away from the nucleus at regular intervals. The holding capacity of the nucleus on valence electrons decreases.
Due to this, the atom can lose valence electrons more easily to form positive ions, and hence the metallic character increases.
(C) Mg atom is smaller than Na because on moving from left to right in a period of the periodic table, the atomic radius of elements decreases. This happens because the number of protons and electrons in the atoms increases. Due to a large positive charge on the nucleus, electrons are pulled in close to the nucleus and the size of atom decreases.
Question: Consider the following elements of the Modern Periodic Table:
Be(4); O(8); Cl(17); K(19); Ca(20)
(A) Select from these an element having only one valence electron.
Write the electronic configuration of this element.
(B) Select from these, two elements of the same group and state the reason for your answer.
(C) Select from these, two elements of the same period and state the reason for your answer.
Answer: The electronic configuration of the elements given is as under:
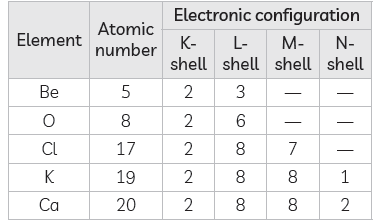
(A) The element having only one valence electron is Potassium (K).
Electronic configuration of K is (2, 8, 8, 1).
(B) Be (Atomic No. 4) and Ca (Atomic No. 20) belong to the same group 2 as they both have the same number of valence electrons 2.
(C) Be and O belong to the same period 2 as they both have the same number of occupied shells, which is 2.
K and Ca belong to the same period 4 as they both have the same number of occupied shells, which is 4.
Question: (A) Why do we classify elements?
(B) What were the two criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his periodic table?
(C) Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in his periodic table?
(D) In Mendeleev’s periodic table, why was there no mention of noble gases like helium, neon and argon?
(E) Would you place the two isotopes of chlorine, Cl-35 and Cl-37 in different slots because of their different atomic masses or in the same slot because their chemical properties are the same? Justify your answer.
Answer: (A) Elements are classified to systematize
their study and make the understanding of properties of elements and compounds simpler.
(B) The two main guiding factors for Mendeleev in the classification of the then known elements were:
(1) increasing atomic masses, and
(2) grouping together of elements having similar properties.
(C) These gaps were left for the elements which had not been discovered at that time. Mendeleev thought that these elements would be discovered later on in the future.
The modern periodic table does not have any gaps because new elements were discovered later on, which were placed correctly in the gaps left by Mendeleev.
(D) Noble gases were not known at that time. So, there was no group of noble gases in Mendeleev’s original periodic table.
(E) Both the isotopes of chlorine, Cl-35 and Cl-37, have the same atomic number of 17. Therefore, they have same chemical properties. Hence, both of them can be put at one place in the same group of the periodic table.
Question: Why is atomic number considered to be a more appropriate parameter than atomic mass for the classification of elements in a periodic table? How does the metallic character of elements vary as we move (i) from left to right in a period, and (ii) top to ottom in a group in the modern periodic table? Give reasons to justify your answers.
Answer: When elements were arranged on the basis of increasing atomic number, prediction of their properties could be made with more precision.
Moreover, many anomalies of the Mendeleev’s periodic table, such as position of isotopes, position of elements such as Cobalt and Nickel, could be explained.
(1) The metallic character decreases as we move from left to right in a period. Because when we move from left to right in a period, the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases and therefore the tendency to lose electrons also decreases.
(2) The metallic character increases as we move from top to bottom in a group because when we go down a group, the effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons decreases since distance of valence electrons from the nucleus increases.
(i) Position of isotopes : All the isotopes of an element have the same atomic number. Therefore, They can be place at one place is the same group of the periodic table. e.q. C-12, C-14 are placed is group 14.
(ii) Anomalous position of some pairs of elements.
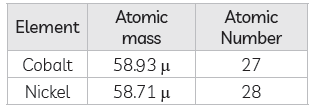
In mendeleev’s periodic table, cobalt with slightly higher atomic mass (58.93 μ) war placed before nickel with slightly lower atomic mass (58.71 μ). But the atomic number of Co is less than that of Ni, as Modern Periodic Law is based on atomic number so this anomaly was explained
• For example:
In third period: Mg is smaller than Na because on moving form left to right in a period, atomic radius of element decreases. This happens because the number of protons and electrons is the atoms increases.
Due to a large positive charge on the nucleus, electrons are pulled close to the nucleus and size of atom decreases and metallic character decreases.
• For example: In the first group Na (Sodium) atom has three electron shells K, L, and M and K atom has four electrons shells K, L, M and N and K (Potassium) atom is bigger than Na because when we go from top to bottom in a group, a new shell of electrons is added to the atom, due to which the size of atoms
increases and metallic character also increases.
Question: (A) Write the number of groups and periods in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the atomic size vary down a group in the periodic table? State its reason.
(B) The electronic configurations of four
elements A, B, C and D are as follows:
A – (2, 8, 7); B – (2, 8, 1); C – (2, 8, 2); D – (2, 8, 8, 2)
(i) Which amongst these elements will form acidic oxide and why?
(ii) Which amongst these elements has the smallest atomic radius and why?
(iii) Out of these select those two elements which have same valency and form compounds by ionic bonds.
Answer: (A) The number of groups in the Modern Periodic Table are 18 and the number of periods are 7.
The atomic size increases as we go down in a group as a new shell is added to the atoms when going from top to bottom in a group which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus.
(B) (i) Element A (2, 8, ??) will form an acidic oxide as it is a non-metal and forms an oxide which on dissolution with water gives an acid.
(ii) A, B and C belong to 3rd period and A has the smallest atomic radius because as we move from left to right along a period, the nuclear charge increases which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus and hence reduces the atomic size.
(iii) Elements A and B have same valency 1 and form compound by ionic bond.
A is a non-metal whereas B is a metal. B transfers an electron to A thereby forming B+ ion and A forms A– ion by gaining an electron. The formula of the
compound formed is AB.
Question: Write the electronic configurations of two elements P (atomic number 17) and Q (atomic number 19) and determine their group numbers and period numbers in the Modern Periodic Table.
Answer: The electronic configuration of elements P and Q is written below:
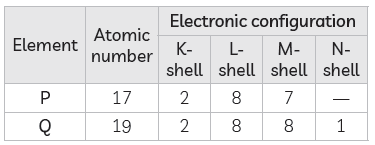
Position of P and Q in the Modern Periodic Table:
P: Group number = 1?? ; Period number = 3
Q: Group number = 1 ; Period number = 4
Question: An element ‘X?? with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with two radicals, (NO3)– and (SO4)2–.
(A) Is ‘X’ a metal or a non-metal ? Write the nature of its oxide.
(B) Write the formula of the compounds of ‘X’ formed by the combination of these
radicals. Are these compounds covalent or electrovalent ?
Answer: (A) ‘X’ is a metal as it has 2 valence electrons. Its oxide is basic in nature.
(B) Valency of X is 2. The formula of compounds formed by X with (NO3)– and (SO4)2– :
a. X(NO3)2
b. XSO4
These compounds are ionic (electrovalent) as these are formed by transfer of electrons.
Question: An element ‘M’ has atomic number 12.
(A) Write its electronic configuration and valency.
(B) Is ‘M’ a metal or a non-metal? Give reason in support of your answer.
(C) Write the formula and nature (acidic/ basic) of the oxide of M. [17-311DC]
Answer: Atomic number of element ‘M’ = 12
(A) Electronic configuration of M: (2, 8, 2), i.e.,
k-shell = 2, L-shell = 8, M-shell = 2 electrons.
Valency of M = 2
(B) M is a metal as it is electropositive, since it has the tendency of losing electrons, thereby forming positive ion.
(C) Formula of the oxide of M: MO Nature of oxide: Basic
Question: The atomic number of an element is 20.
(A) Write its electronic configuration and determine its valency.
(B) Is it a metal or a non-metal?
(C) Write the formula of its chloride.
(D) Is it more reactive or less reactive than Mg (atomic number 12)?
Give reason for your answer.
Answer: (A) The electronic configuration of element having atomic number 20 is 2, 8, 8, 2, i.e., electrons in K, L, M and N shells are 2, 8, 8 and 2 respectively.
Valency of given element = 2
(B) It is a metal as it can lose electrons easily since it is electropositive.
(C) Let us denote the element by M. Since chlorine has valency 1, formula of the
chloride of M is MCl2.
(D) This element, M, is more reactive than Mg as Mg lies in 2nd Group, 3rd period and M lies in 2nd Group but 4th period of the periodic table. M is more electropositive than Mg as the effective nuclear charge experienced by its valence electrons is less than that experienced by valence electrons of Mg because of increase in distance of valence electrons from the nucleus.
Question: What is meant by groups and periods in the Modern Periodic Table? Two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’ belong to group 1 and 2 respectively and are in the same period. How do the following properties of ‘A’ and ‘B’ vary?
(A) Atomic size
(B) Metallic character
(C) Valencies in forming oxides
(D) Formula of their chlorides
Answer: Groups are the vertical Colums Periods are the horizontal rows.
(A) Atomic size: decreases as we go from left to right in a period hence atom of element A is bigger than B.
(B) Metallic Character: A is more metallic than B since metallic character decreases as we go along a period.
(C) Valancies in forming oxides: Valency of group 1 is 1 and valency of group 2 is 2.
(D) Formula of their chloride: ACl, BCl2 Explanation : As we move from left to right
in the period of the periodic table, the number of shells remains same but atomic number increases. So, the attraction over valence electrons also increases which decreases the atomic radius.
Question: The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 7.
(A) What is the group number and period number of this element in the Modern Periodic Table?
(B) Is this element a metal or a non-metal?
Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: (A) Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7. Hence its atomic number is 1?? and this element is chlorine.
(B) This element is a non-metal because it gains the electron to complete their octet.
Question: How does the atomic radius of the elements change on going:
(A) from left to right in a period, and
(B) down a group in the Modern Periodic Table? (Give reasons) in support of your answer.
Answer: (A) The atomic radius decreases on moving from left to right in a period in the Modern Periodic Table as the number of electrons and protons increases. Due to the large positive charge on the nucleus, electrons are pulled more strongly towards the nucleus.
(B) The atomic radius increases on moving from top to bottom in a group, as new shells are being added, which increases the distance between the outermost electrons and the nucleus. So, although the nuclear charge increas, the atomic radius also increases.
Question: An element P (atomic number 20) reacts with an element Q (atomic number 17) to form a compound. Answer the following questions giving reason:
Write the position of P and Q in the Modern Periodic Table and the molecular formula of the compound formed when P reacts with Q.
Answer: In order to answer this question, let us write the electronic configuration of the given elements:
Element P (Atomic Number = 20): 2, 8, 8, 2
Element Q (Atomic Number = 17): 2, 8, ??
Position of P: Period No. 4 and Group No. 2
Position of Q: Period No. 3, Group No. 17
P is a metal having valency of 2 and Q is a non-metal having valency of 1, therefore formula of compound formed by the reaction between P and Q will be PQ2.
Explanations: P and Q will form an ionic bond
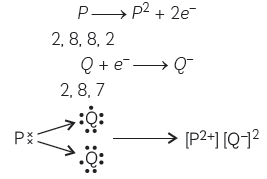
Question: An element ‘X’ belongs to third period and second group of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) Is it a metal or non-metal? Why?
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ reacts with an element
(i) Y of electronic configuration 2, ?? and
(ii) Z with electronic configuration 2,8, 7.
Answer: Element situate in 3rd period means it has 3 shells and in second group means it has
2 electrons in outer most shell. Electronic configuration.
(A) X = 2, 8, 2
(B) Because it is situated on left of periodic table therefore it is a metal.
(C) (i) Compound XY
(ii) Compound XZ2
Explanation : The number of shells gives us the period number and number of valence
electrons tells us the group number to which the element belongs.
(1) The elements having 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons are metals as they can lose
electrons to acquire electropositive character.
(2) Element ‘X’ has 2 valance electrons, it will lose 2 electrons to acquire noble gas
configuration
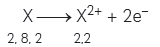
(3) Electronic configuration of elements ‘Y’ is 2, ?? so it needs 2 electrons to complete its octet to acquire noble gas configuration

(4) Electronic configuration of elements ‘Z’ is 2, 8, ?? so it requires, 1 valence electron
to complete its octet to acquire inert gas configuration.
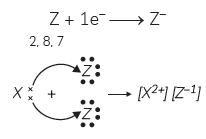
Question: State the main aim of classifying elements.
Which is the more fundamental property of elements that is used in the development of
Modern Periodic Table? Name and state the law based on this fundamental property.
On which side of the periodic table one can find metals, non-metals and metalloids?
Answer: (1) Main ob??ective for classification of elements is the systemic study of properties of known element and can guess for future elements.
(2) Basic Property to classify elements is: Atomic number.
(3) Modern Periodic Law: Atomic number is the periodic function for properties of elements.
(4) Metals are situated on left of periodic table.
(5) Non- metals are situated on right of periodic table.
(6) Metalloids are situated on border of metals and non – metals and are placed diagonally.
Question: Write the names given to the vertical columns and horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving down a vertical column? How does the size of atomic radius vary on moving left to right in a horizontal row? Give reason in support of your answer in the above two cases.
Answer: The vertical columns in the Modern Periodic Table are known as ??Groups?? and horizontal rows are known as “Periods”.
The metallic character increases as we move from top to bottom in a group because the electropositive character of elements increases as the tendency of an atom to lose electrons increases.
On moving from left to right in a period, the atomic radius decreases as the number of
electrons and protons increases. Due to the large positive charge on the nucleus, electrons are pulled more strongly towards the nucleus.
Question: An element has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7.
(A) To which group and period of the Modern Periodic Table does it belong?
(B) What is the atomic number of this element?
Is it metallic or non-metallic and why?
(C) Identify the element and name an element chemically similar to this element.
Answer: Electronic configuration 2, 8, 7 (total electrons are 17)
(A) It belong to 17th group and 3rd period of periodic table.
(B) Atomic Number of this element is 1??, it is non-metallic because it gains electrons to complete its octet.
(C) Element is chlorine, Related elements are Bromine, Iodine, etc.
Question: Do you know there are 11?? elements known at present. It is very dif??icult to study the properties of all these elements. Di??ferent scientists started looking for some pattern in this properties.
Dobereiner arranged elements with lame properites into triads. Newlands assumed that when elements are arranged in the increasing order of there atomic mass. The properties of every eighth elements are similar to one. Mendeleev stated that properties of elements are periodic function of their atomic mass. Mosley gave the Modern Periodic Table and it sates that properties of elements are peridic function of their atomic numbers. Solve the questions on the basis of your understanding of the above paragraph and the related studied concepts.
(A) Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table and Modern Periodic Table.
(B) Hygrogen occupies a unique position in modern periodic table. Thus it occupies a unique position in modern periodic table. Justify the statement.
Answer:
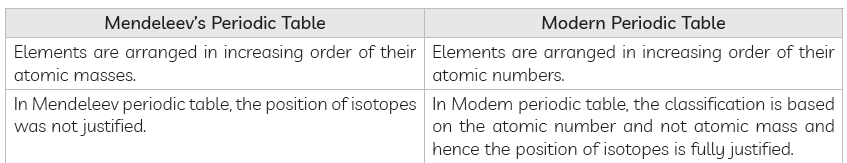
(B) Hyrogen shows similar properties like alkali metals as well as hydrogen.
Question: Calcium is an element with atomic number 20. Stating reason answer each of the following questions:
(A) Is calcium a metal or non-metal?
(B) Will its atomic radius be larger or smaller than that of potassium with atomic number 19?
(C) Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer: (A) Calcium is a metal because it has two electrons in its outermost shell, hence it loses electron easily.
(B) The atomic radius of calcium is smaller than that of potassium because atomic size decreases along the period due to increase in nuclear charge between the electrons.
(C) CaO is the formula of oxide of calcium.
Question: Four elements P, Q, R, S have atomic number 12, 13, 14 and 15 respectively. Answer the following questions giving reasons:
(i) What is the valency of Q?
(ii) Classify these elements as metals and non-metals.
(iii) Which of these elements will form the most basic oxide?
Answer:
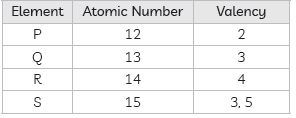
(i) Valency of Q is 3
(ii) Metals are P & Q
Non-metals S
Metalloids R
As we know all metals are basic in nature and produce basic Oxide.
Both P and Q are metals and P is more reactive metal than Q as P has to lose only two electrons whereas Q has to lose 3 electrons to acquire metallic character hence P is will form the most basic oxide.
Question: An element ‘???? with electronic configuration
(2, 8, 2) combines separately with (NO3)–, (SO4)2- and (PO4)3- radicals. Write the formula of the three compounds so formed.
To which group and period of the Modern Periodic Table does the elements ‘M’ belong?
Will ‘M’ form covalent or ionic compounds?
Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: The electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2, Hence the element ‘M‘ is Magnesium (Mg).
It belongs to 2nd group and 3rd period of the modern periodic table and its valency is 2.
The formula of compounds so formed are:
(i) Mg (NO3)2
(ii) Mg SO4
(iii) Mg3 (PO4)2
It will from ionic compound because it has 2 electrons in its outermost shell, so it can loose 2 electrons easily and forms ionic compound.
Question: Taking the example of an element of atomic number 16, explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the modern periodic table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number.
Answer: Electronic configuration of element with atomic no. 16 is 2,8,6.
Since it has 3 shells, the period no. will be 3.
Since the no. of valence electrons is 6, the group no. will be 10 + 6 = 16.
Valency of the element will be 8- valence electrons ie 8 –6 = 2.
Question: Compare the following elements as per the characteristics given in the brackets:
(A) Lithium and Nitrogen (Atomic radii)
(B) Potassium and Chlorine (Electronegativity)
(C) Magnesium and Calcium (Valency)
Give reason for your answer in each case.
Answer: (a) Lithium has larger atomic radius compared to nitrogen,
Reason: Along a period from left to right, there is an increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus. So, size of the atom of the elements decreases from Lithium to
Nitrogen.
(b) Chlorine is more electronegative than potassium.
Reason: Chlorine is smaller in size. So it has tendency to pull bonded electrons towards itself.
(c) Magnesium and Calcium have same valency.
Reason: Both have the same number of valence electrons, i.e. 2.
Question: Two elements ‘P’ and ‘Q’ belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form:
(A) The number of electrons in their atoms
(B) The sizes of their atoms
(C) Their metallic characters
(D) Their tendencies to lose electrons
(E) The formula of their oxides
(F) The formula of their chlorides
Answer:
Property P Q
(A) No. of electrons in the 3 4
atom 11 12
19 20
(any one pair)
(B) Size of the atom Bigger Smaller
(C) Metallic character More Less
metallic metallic
(D) Tendency to lose More Less
electrons
(E) Formula of oxides P2O QO
(F) Formula of chlorides PCl QCl2
Note: For parts (e) and (f) examples using symbols of elements may also be accepted.
Long Answer Type Question:s
Question: Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells, but different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This compound is added in a small amount to almost all the vegetable dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature, while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of D is almost neutral. Based on the above information, answer the following Question:s:
(i) To which group or period of the periodic table do the listed elements belongs to?
(ii) What would be the nature of compound formed by the combination of elements B and F?
(iii) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
(iv) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state, at room temperature?
(v) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G are 3 and 7 respectively, then write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Answer:(i) They belong to the same period but different groups. ‘G’ belongs to Group 17. A and B belong to Group 1 and 2, … their oxides are basic. ‘C’ belongs to Group 13 due to 3 valence electrons. ‘D’ belongs to Group 14. E and F belong to group 15 and 16, respectively. ‘H’ belongs to group 18.
(ii) B and F will form an ionic compound.
(iii) A and B are metals.
(iv) G, H are gases at room temperature.
(v) CG3
Question: The nucleus of five elements D, E, F, G and H are shown below:

(i) Identify D and E.
(ii) Identify the position of F and H in the periodic table.
(iii) What is the cause of similarity among the species D, G, H?
(iv) What will be the formula of compound formed between D and E?
(v) Which is largest in size among D, E, F, G and H?
Answer:(i) ‘D’ is lithium, E is fluorine.
(ii) F belongs to group 17, 3rd period.
H belongs to group 1, 4th period.
(iii) They have the same number of valence electrons, D(3) 2, 1; G(11) 2, 8, 1; H(19) 2, 8, 8, 1.
(iv) DE is the formula of the compound.
(v) H is largest in size due to the presence of four shells.
Question: (i) Which element can lose electrons most easily in 3rd period and why?
(ii) Why does tendency to lose electrons increases down the group?
(iii) What happens to the basic character of oxides down the group and why?
(iv) What happens to the acidic character of oxides along a period and why?
(v) Which group of elements can gain electrons most easily and why?
Answer:(i) Na, it is due to larger atomic size and least effective nuclear charge.
(ii) It is due to increase in atomic size and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
(iii) Basic character of oxides increases down the group due to increase in metallic character.
(iv) Acidic character of oxides increases along a period due to increase in non-metallic character.
(v) Group 17 elements, due to smaller atomic size and more effective nuclear charge.
Question: An element X of group 15 exists as a diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K, in the presence of a catalyst to form a compound ammonia, which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(i) Identify the element X. How many valence electrons does it have?
(ii) Draw the electron dot structure of diatomic molecule of X. What type of bond is formed in it?
(iii) Draw the electron dot structure for ammonia and what type of bond is formed in it?
Answer:(i) ‘X’ is nitrogen. It has 5 valence electrons
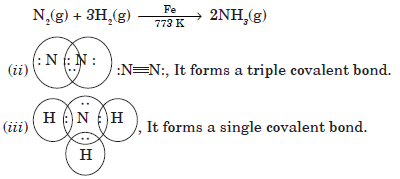
Question: An element X, which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(i) Identify the element X.
(ii) Write the electronic configuration of X.
(iii) Write the balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals.
(iv) What would be the nature (acidic/basic) of the oxides formed?
(v) Locate the position of the element in the modern periodic table.
Answer:(i) ‘X’ is sulphur. (ii) S(16): 2, 8, 6
heat
(iii) 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) SO2 and SO3 are acidic oxides and major air pollutants whereas Fe2O3 is a basic oxide.
(v) It belongs to group 16 and 3rd period.
Question: The atomic radius of element of second period are given below:

(i) Arrange these elements in decreasing order of atomic radius.
(ii) Are the elements now arranged in the pattern of period in the periodic table?
(iii) Name the element which has (a) largest (b) smallest atomic size.
(iv) From the above data, infer how the atomic size or radius of elements changes as we go from left to right in a period.
(v) Name one metal, one non-metal and a metalloid from these elements.
(vi) Why does atomic radius decrease as we move from left to right in a period?
Answer:
(i) Li Be B C N O F
152 111 88 77 74 66 64
(ii) Yes, the elements are arranged in the pattern of a period (2nd period in the periodic table).
(iii) (a) Li is largest in size.
(b) F is smallest in size.
(iv) Atomic radius decreases from left to right in a period.
(v) Metal–Li/Be, Non-Metal-C/N/O/F, Metalloid-Boron.
(vi) Atomic size decreases as we move from left to right in a period because effective nuclear charge increases as one electron and one proton is added successively and number of shells remains the same.
Question: (a) How is valency of an element determined if its electronic configuration is known? Determine the valency of an element of atomic no. 9
(b) Given below are some elements of modern periodic table. Atomic number of elements are given in parentheses.
A (4), B (9), C (14), D (19), E (20)
(i) With the help of electronic configuration, find out which ore of the above elements will have one electron in its outermost shell.
(ii) Which two elements belong to the same group? Give reasons for your Answer:
(iii) Which one of the above element belonging to the fourth period has bigger atomic radius and why?
Answer:(a) Valency is equal to number of valence electrons or 8— number of valence electrons.
F (9): 2,7
Its valency is equal 1 because it will become stable on gaining one electron.
(b) (i) A (4): 2,2 D (19): 2,8,8,1
B (9): 2,7 E (20): 2,8,8,2
C (14): 2,8,4
‘D’ has one valence electron.
(ii) ‘A’ and ‘E’ belong to same group because they have same number of valence electrons.
(iii) ‘D’ has larger atomic radius than ‘E’ because it has 19 protons which attract 19 electrons which is there less strongly than 20 protons can attract 20 electrons as in E.
Question: Explain giving justification the trends in the following properties of elements, on moving from left to right in a period, in the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Variation of valency
(b) Change of atomic radius
(c) Metallic to non-metallic character
(d) Electronegative character
(e) Nature of oxides
Answer:(a) Valency increases from left to right till middle, then decreases because valence electrons goes on increasing.
(b) Atomic radius decreases due to increase in effective nuclear change.
(c) Metallic character decreases, non-metallic character increases due to increase in tendency to gain electrons as atomic size decreases, effective nuclear change increases.
(d) Electronegative character increases due to increase in effective nuclear change.
(e) Acidic character of oxides increases, basic character of oxides decreases because metallic character decreases and non-metallic character increases.
Question: (a) List any three observations which posed a challange to Mendeleev’s periodic table.
(b) How does the mettallic character of elements vary on moving from
(i) Left to right in a period.
(ii) From top to bottom in a group of the Modern periodic table? Give reason for your Answer:
Answer:
(a) (i) Increasing order of atomic mass could not be followed.
(ii) Isotopes cannot occupy different positions as they have same chemical properties but different atomic mass.
(iii) Position of hydrogen was not justified.
(b) (i) Metallic character decreases from left to right in a period because tendency to lose electrons decreases as effective nuclear charge increases.
(ii) Metallic character increases down the group from top to bottom because tendency to lose electron increases due to increase in atomic size and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
Question: The position of certain elements in the Modern Periodic Table are shown below:

Using the above table answer the following Question:s giving reasons in each case:
(i) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a non-metal with valency 2?
(iii) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(iv) Out of H, C and F which has largest atomic size?
(v) To which family does H, C and F belong?
Answer: (i) E will form only covalent compounds.
(ii) B is non-metal with valency 2.
(iii) D is metal with valency 2.
(iv) ‘F’ has largest atomic radius.
(v) It belongs to noble gases.
Question: Define atomic size. Give its unit of measurement. In the modern periodic table what trend is observed in the atomic radius in a group and a period and why is it so?
Answer:
Atomic size is the distance between centre of nucleus and valence shell.
Its unit of measurement is picometre (10–12m) denoted by pm.
Atomic radius increases down the group due to increase in number of shells and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
Atomic radius decreases along a period from left to right because effective nuclear charge increases but number of shells remain the same.