Exam Question for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Sectors of The Indian Economy
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Sectors of The Indian Economy. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 10 Social Science teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 10 Social Science exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 10th.
Chapter 2 Sectors of The Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Sectors of The Indian Economy are very important and should be revised daily.
Exam Question Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Sectors of The Indian Economy
Objective Type Questions
Question. GDP of a country is based on
(a) Total value of good and services
(b) Final value of goods and services
(c) Initial value of goods and services
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. Which sector helps in the development of the primary and secondary sector?
(a) Public sector
(b) Private sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Choose the correct option from the following.

Answer
C
Question. In which of the following organisations people cannot expect job security?
(a) Organised sector
(b) Unorganised sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. Which among the following activities is not related to primary sector?
(a) Fishing
(b) Natural gas extraction
(c) Making of sugar
(d) Mining
Answer
C
Question. The secondary sector is also known as as this sector produces useful items from natural products.
(a) Manufacturing
(b) Producing
(c) Building
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Under which economic sector does the production of a community through the natural process come?
(a) Public sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Secondary sector
(d) Public sector
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following profession belongs to the tertiary sector of economy?
(a) Fishermen
(b) Farmer
(c) Factory worker
(d) Teacher
Answer
D
Question. Choose the correct option from the following.

Answer
C
Question. The value of which of the following should be added while calculating the national income?
(a) Final goods
(b) Final services
(c) Final goods and services
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. ATM service is an example of
(a) Primary sector
(b) Secondary sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Identify reasons why economic activities are interdependent.
I. If the companies decide not to buy cotton from Indian producers then the Indian cotton cultivation will become less profitable and may even go bankrupt. In this case it is clear that primary sector is dependent on the secondary sector.
II. In case farmers refuse to sell sugarcane to a particular sugar mill then the mill have to shutdown. It is clear in this case that secondary sector is dependent on the primary sector.
III. In case transporters are on strike then the primary sector and secondary sector will face loss.
Options:
(a) I and II
(b) III only
(c) II and III
(d) I, II and III
Answer
D
Question. Study the given data in graph and find out what it shows from the given options.
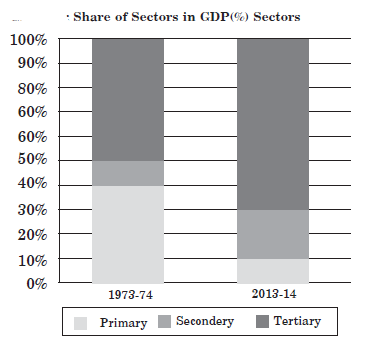
(a) It presents percentage share of the three sectors in GDP.
(b) It shows the share of employment in the three sectors.
(c) It shows the tertiary sectors share largest GDP in 2013-14.
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. The value of each final goods and service produced within the country during a participate year is called as:
(a) Average Income
(b) GDP
(c) National Income
(d) NDP
Answer
B
Question. In the last 100 years, the sector gaining prominance is
(a) Secondary sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Places of work which follow rules and regulation are termed as
(a) Organised sector
(b) Unorganised sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) Secondary sector
Answer
A
Question. All economic activities that directly involve conversion of natural resources are classified under
(a) Secondary sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) Government sector
Answer
B
Question. Which among the following workers are not very productive in tertiary sector?
(a) Educated and trained professionals
(b) Repair persons and daily wage earners
(c) People in defence services
(d) People working in health centres and hospitals
Answer
B
Question. Converting iron is a part of
(a) Primary activity
(b) Secondary activity
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. Hidden unemployment is also called
(a) Organised sector
(b) Disguised unemployment
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) Contractual unemployment
Answer
B
Question. Animal husbandry is a part of which of the following sectors?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Public health is responsibility of
(a) Primary sector
(b) Government
(c) Private sector
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. A labourer working under a contractor, is in which type of sector?
(a) Public sector
(b) Unorganised sector
(c) Service sector
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. MGNREGA guarantees job poor for
(a) 100 days
(b) 90 days
(c) 60 days
(d) 50 days
Answer
A
Question. The task of collection of data in all the three sectors of the economy is done by which of the following organisation.
(a) NSSO
(b) BPO
(c) KPO
(d) UNDP
Answer
A
Question. The type of unemployment in which more number of people work than actually needed is known as
(a) Disguised unemployment
(b) Seasonal unemployment
(c) Underemployed
(d) Over employed
Answer
A
Question. Which among the following is responsible for the education facilities?
(a) NGOs
(b) Government
(c) Private sector
(d) People themselves
Answer
B
Question. In terms of ownership, enterprises owned by individuals are known as .
(a) Public sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Unorganised sector
(d) Private sector
Answer
D
Question. As per the workers in different sectors (in millions) the data shown only for organised sector is
• Primary Sector — 0.012% (approx.)
• Secondary Sector — 50%
• Tertiary Sector — 48.8% (approx.)
Out of the three sectors, why did employment in the secondary sector increase?
(a) An increase in machinary on farms.
(b) People tend to migrate to urban areas to get jobs in factories.
(c) Most people are engaged in agricultural activities.
(d) all of the above are correct reason.
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following is a feature of unorganised sector?
(a) Fixed number of work hours
(b) Paid holidays
(c) Employment is insecure
(d) Registered with the government
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following organisations the provision of appointment letter is not there?
(a) Unorganised sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Organised sector
(d) Service sector
Answer
A
Question. Study the graph and answer the question that follows:
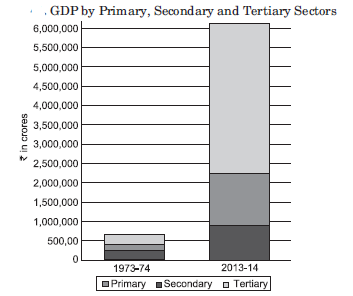
Which one of the following options best signifies this graph?
(a) Primary sector was the largest producing sector in 1973-74.
(b) Tertiary sector is the largest producing sector in 2013-2014.
(c) Tertiary sector has grown the most over 40 years.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. The sector in which the productive units are owned, maintained and managed by government
(a) Organised sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Public sector
(d) Industrial sector
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following may not continue their production or business unless government encourages it?
(a) Public sector
(b) Private sector
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The goods that are used as raw materials for further production are known by which name?
(a) Final goods
(b) Consumer goods
(c) Material goods
(d) Intermediate goods
Answer
D
Question. The sum total of production of all goods and services in the three sectors are combinedly
(a) NDP
(b) NI
(c) GNI
(d) GDP
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): There are several goods and services that the society needs; however, the private sector does not produce all of them.
Reason (R): Private sector is profit-driven.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Several services such as hospitals, educational institutions and police stations are some examples of tertiary activities.
Reason (R): These activities generate services rather than goods.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): The Government of India buys wheat and rice from farmers at fair price.
Reason (R): Public sector contributes to the economic development.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): The development of agriculture and industry leads to the development of service sector.
Reason (R): As the primary and secondary sectors develops, the demand for transport, storage structures, banks, insurance, etc. increases.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Not every good or service that is produced and sold needs to be counted to know the total production in each sector.
Reason (R): The value of final goods already includes the value of all the intermediate goods.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): When calculating the total value of goods and services produced in a country, the value of final goods and services of production is calculated.
Reason (R): At each stage of production some value is added to a good or service, therefore, the value added at each stage of production is added to derive the total value of gods and services in an economy.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Maximum workers in India works in the primary sector.
Reason (R): Tertiary sector has emerged the largest producing sector of India.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): In India, over the forty years between 1973-74 and 2013-14, while production in all the three sectors has increased, it has increased the most in the tertiary sector.
Reason (R): Tertiary sector is the only organized sector in the economy so the government spends a lot of money for creating jobs in tertiary sector.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): An individual who manufactures flour from wheat is engaged in secondary sector.
Reason (R): When some process of manufacturing is used the product is a part of secondary sector.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): In India, the primary sector is the largest employer.
Reason (R): The demand for services has increased enormously.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): There are a limited number of services that employ highly skilled and educated workers.
Reason (R): Not all of the service sector is growing equally well.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): GDP shows how big an economy is.
Reason (R): GDP is the value of all goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country in a year.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): The primary sector continues to be the largest employer even now.
Reason (R): Not enough job were created in the secondary and tertiary sectors.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Since the 1990s, it is also common to see a large number of workers losing their jobs in the organised sector.
Reason (R): Organised factories closed due to facing heavy competition with multinational companies.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): After primary of secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector.
Reason (R): These activities do not help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): An individual who manufactures flour from wheat is engaged in secondary sector.
Reason (R): When some process of manufacturing is used the product is a part of secondary sector.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Reliance industries is a privately-owned firm.
Reason (R): Government is a major stakeholder is reliance industries.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Arrange the correct sequence of Column I against the Column II.
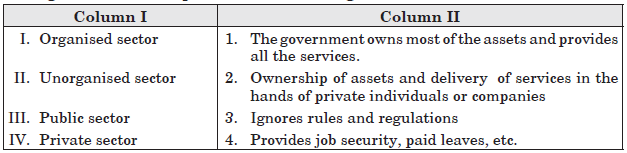
Choose the correct answer.
(a) IV-2, II-4, III-1, I-3
(b) II-3, IV-2, I-4, III-1
(c) I-2, III-4, IV-3, II-1
(d) III-2, I-4, II-1, IV-3
Answer
B
Question. Arrange the following in correct sequence
(i) The biscuit company uses the flour and things such as sugar and oil to make four packets of biscuits. It sells biscuits in the market to the consumers.
(ii) The mill grinds the wheat.
(iii) Farmer sells wheat to a flour mill.
(iv) The flour is sold to a biscuit company.
Choose the correct option.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
(c) (i), (iv), (iii), (ii)
(d) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Read the information given below and select the appropriate option.
There are many activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources. Take, for example, the cultivation of cotton. It takes place within a crop season. For the growth of the cotton plant, we depend mainly, but not entirely, on natural factors like rainfall, sunshine and climate. The product of this activity, cotton, is a natural product. Similarly, in the case of an activity like dairy, we are dependent on the biological process of the animals and availability of fodder etc. The product here, milk, also is a natural product.
When we produce a product by natural activity. It is an activity of the–
(a) industrial sector
(b) primary sector
(c) service sector
(d) agriculture sector
Answer
B
Question. Many people work in the unorganised sector. Which of the following statements about this sector is correct?
(a) It provides medical benefits.
(b) It ensures security of employment.
(c) It is one where the terms of employment are regular.
(d) Jobs are low paid and some kind of work is seasonal in nature.
Answer
D
Question. Read the information given below and select the appropriate option.
Similarly, we know that nearly half of India’s children are malnourished and a quarter of them are critically ill. We have read about Infant Mortality Rates. The infant mortality rate of Odisha (41) or Madhya Pradesh (47) is higher than some of the poorest regions of the world. Government also needs to pay attention to aspects of human development such as availability of safe drinking water, housing facilities for the poor and food and nutrition.
It indicates the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year. It is called:
(a) Child sex ratio
(b) Infant mortality rate
(c) Net attendance ratio
(d) Child mortality rate
Answer
B
Question. The most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing, forestry, this sector is also called–
(a) industrial and related sector
(b) service sector
(c) agriculture and related sector
(d) secondary sector
Answer
C
Question. Read the information given below and select the appropriate option.
After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a goods but they are an aid or a support for the production process. For example, goods that are produced in the primary or secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in wholesale and retail shops. At times, it may be necessary to store these in godowns.
Which of the following is the correct option for classification on the basis of nature of activity?
(a) Organised sector and Unorganised sector
(b) Public sector and Private sector
(c) Primary sector, Secondary sector and Tertiary sector
(d) Agriculture-related sector and Industrial sector
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following objectives is not mentioned in the MGNREGA 2005?
(a) To give at least 100 days of guaranteed work in rural areas.
(b) It is required to provide employment within 10 km of an applicant’s home and to pay maximum wage.
(c) If government fails in its duty to provide employment, it will give unemployment allowances to the people.
(d) To flourish durable assets like roads, canals, ponds and wells.
Answer
B
Question. Read the information given below and select the appropriate option.
Laxmi owning about two hectares of unirrigated land dependent only on rain and growing crops like jowar and arhar. All five members of her family work in the plot throughout the year. In case the government can spend some money or banks can provide a loan to construct a well for her family to irrigate the land. Laxmi will then be able to irrigate her land and take a second crop, wheat.
You see that everyone is working, none remains idle in the two hectares of land, but in actual fact, their labour effort gets divided. Each one is doing some work but no one is fully employed. This is the situation of
(a) Underemployment
(b) Rotational employment
(c) Cycle unemployment
(d) Rotational employment
Answer
A
Question. Along with water, which of the following will help the farmer like Laxi for farming to improve?
(a) Government efforts
(b) Cheap agricultural loan
(c) Hard working farmers
(d) Skill labours
Answer
B
Question. Read the information given below and select the appropriate option.
The central government in India made a law implementing the Right to Work in about 625 districts of India. It is called Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 (MGNREGA 2005). Under MGNREGA 2005, all those who are able to, and are in need of, work in rural areas are guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year by the government.
Every year we can give additional employment to more than 35 lakh people. Recognising this, government of India passed an act in 2005. It is called:
(a) Right to Work Act
(b) MGNREGA
(c) PMRY
(d) Central Employment Scheme
Answer
B
Question. An economy is best understood when we study its components or sectors. Sectoral classification can be done on the basis of several criteria. Which of the following is/are correct about the secondary sector?
(a) It covers the activities in which natural products are changed into other forms.
(b) Here some process of manufacturing is essential.
(c) It is also called as manufacturing sector.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Read the information given below and select the appropriate option.
Kanta works in an office. She attends her office from 9:30 a.m. to 5:30 p.m. She gets her salary regularly at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, she also gets provident fund as per the rule laid down by the government. She also gets medical and other allowances. Kanta does not go to office on Sundays. This is a paid holiday. When she joined work, she was given an appointment letter starting all the terms and conditions of work.
Like Kanta, people who work in the organised sector–
(a) do not worry about medical benefits and pensions
(b) do not get security of employment
(c) do not get overtime
(d) are not sure about their paid leaves, medical benefits, etc.
Answer
A
Question. Read the information given below and select the correct option.
Kamal is Kanta’s neighbour. He is a daily wage labourer in a nearby grocery shop. He goes to the shop at 7:30 in the morning and works till 8:00 p.m. in the evening. He gets no other allowances apart from his wages. He is not paid for the days he does not work. He has therefore no leave or paid holidays. Nor was he given any for mal letter saying that he has been employed in the shop. He can be asked to leave anytime by his employer.
‘This sector includes a large number of people who are employed on their own doing small jobs like Kamal’. The statement is talk about:
(a) Unorganised sector
(b) Private sector
(c) Service sector
(d) Organised sector
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following characteristics is related to the unorganised sector?
(a) It has small and scattered units which are largely outside the control of the government.
(b) Jobs here are low paid and often not regular.
(c) A lot of workers depend on the whims of the employer.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following states has lowest and highest infant mortality rates in India?
(a) Goa and Kerala respectively
(b) Manipur and Madhya Pradesh respectively
(c) Goa and Madya Pradesh respectively
(d) Kerala and Uttar Pradesh respectively
Answer
C
Table Based Questions
Question. Read the following data and information carefully and select the most appropriate answer from the given option.
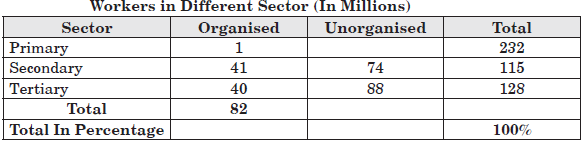
The table shows the estimated number of workers in India in the organised and unorganised sectors. If we look at the country as a whole we find that 82.7% of the workers in India are in the unorganised sector. Find out how many percent of workers in India employ in organised sector?
(a) About 18.4%
(b) About 19.3%
(c) About 16.8%
(d) About 17.3%
Answer
D
Question. Study the table and find out the occupations that come under primary sectors from the options given below.

(a) Tailor, Milk vendor, Priest, Courier, Moneylender, Call centre employee
(b) Flower cultivator, Fishermen, Gardener, Potter
(c) Basket weaver, Workers in match factory, Bee-keeper
(d) Milk vendor, Flower cultivator, Bee-keeper, Fishermen
Answer
B
Question. Study the given table and find out the ways for generating more employment in the city rather than in unorganised sector by the government from the options given below.

(a) Opening a cold storage
(b) Invest some money in transportation
(c) Increase vocational education courses
(d) Provide cheap agricultural credit
Answer
C
Question. Read the following information given in table carefully and select the most appropriate answer from the given options.

Imagine what would happen to cotton cultivation if companies decide not to buy from the Indian market and import all cotton they need from other countries. Indian cotton cultivation will become less profitable and the farmers may even go bankrupt, if they cannot quickly switch to other crops. Cotton prices will fall.
Identify the example for which the statement is based on–
(a) This is an example of primary sector which is dependent on secondary sector.
(b) This is an example of only primary sector.
(c) This is an example of sectary sector that dependent on primary sector
(d) This is an example of tertiary sector which is dependent on secondary and primary both sectors.
Answer
A
Case/Source Based Questions
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. In India, the mammoth task of measuring GDP is undertaken by a central government ministry. This Ministry, with the help of various government departments of all the Indian states and union territories, collects information relating to total volume of goods and services and their prices and then estimates the GDP.
Question. How is GDP calculated?
(a) The value of intermediate goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year and the sum of production in the three sectors.
(b) The value of intermediate goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the approximate production of the sector for that year.
(c) The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of sector for that year, and the sum of production in the three sectors.
(d) The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during last three years provides the total production of the sector for that year.
Answer
C
Question. What do final goods and services mean?
(a) Production of goods and services
(b) Those goods and services that finally reach the consumers
(c) Those goods and services that are out of reach of consumers
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. In how many sectors does the sum of production give GDP of a country?
(a) Two
(b) Five
(c) Four
(d) Three
Answer
D
Question. Who is responsible for collecting data for the GDP in India?
(a) Central Government Ministry
(b) State Government Ministry
(c) Mayor
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Read the following statements and final the INCORRECT from the given options.
I. GDP is the monetary value of all finished goods and services.
II. GDP provides an economic snapshot of a country.
III. GDP is the most commonly used measure of social activity.
Options:
(a) II and III
(b) I and III
(c) I only
(d) III only
Answer
D
Question. In India, the mammoth task of measuring GDP is undertaken by a _________ ministry.
(a) State government
(b) Central government
(c) Independent body set up
(d) Economic survey set up
Answer
B
2. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
The various production activities in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors produce a very large number of goods and services. Also, the three sectors have a large number of people working in them to produce these goods and services. The next step, therefore, is to see how much goods and services are produced and how many people work in each sector. In an economy there could be one or more sectors which are dominant in terms of total production and employment, while other sectors are relatively small in size. Remember, there is one precaution one has to take. Not every goods (or services) that is produced and sold needs to be counted. It makes sense only to include the final goods and services. Take, for instance, a farmer who sells wheat to a flour mill for ₹ 8 per kg. The mill grinds the wheat and sells the flour to a biscuit company for ₹ 10 per kg. The biscuit company uses the flour and things such as sugar and oil to make four packets of biscuits. It sells biscuits in the market to the consumers for ₹ 60 (₹ 15 per packet).
Question. The passage given above relates to which of the following options?
(a) Comparing three sectors
(b) International competition
(c) Comparing only primary and secondary sectors
(d) Increased employment
Answer
A
Question. According to the passage, which among the following options is called as intermediate goods?
(a) Goods and services that finally reach to the consumers.
(b) Goods and services that intermediately reach to the consumers.
(c) Goods that used in the production of final goods and services.
(d) Goods that used in initially to produced a material.
Answer
C
Question. It is calculated by summing the value of all the final goods and services produced in all the three sectors in a country in a financial year. It is called as–
(a) Gross National Product(GNP)
(b) Net National Product (NNP)
(c) Gross Decentralised Product (GDP)
(d) Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following sectors provides maximum number of job opportunities?
(a) Primary Sector
(b) Secondary Sector
(c) Tertiary Sector
(d) Quaternary Sector
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following sectors has emerged as the largest producing sector?
(a) Primary sector
(b) Industrial sector
(c) Secondary sector
(d) Tertiary sector
Answer
D
Question. The tertiary sector is also called the _________ sector.
(a) Industrial
(b) Service
(c) Administrative
(d) None of these
Answer
B
3. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
In the rural areas, the unorganised sector mostly comprises of landless agricultural labourers, small and marginal farmers, sharecroppers and artisans (such as weavers, blacksmiths, carpenters and goldsmiths). Nearly 80 per cent of rural households in India are in small and marginal farmer category. These farmers need to be supported through adequate facility for timely delivery of seeds, agricultural inputs, credit, storage facilities and marketing outlets. In the urban areas, unorganised sector comprises mainly of workers in small-scale industry, casual workers in construction, trade and transport etc., and those who work as street vendors, head load workers, garment makers, rag pickers etc. Small-scale industry also needs government’s support for procuring raw material and marketing of output. The casual workers in both rural and urban areas need to be protected. We also find that majority of workers from scheduled castes, tribes and backward communities find themselves in the unorganised sector. Besides getting the irregular and low paid work, these workers also face social discrimination. Protection and support to the unorganised sector workers is thus necessary for both economic and social development.
Question. In the rural areas the unorganised sector comprises of:
(a) Landless agricultural labourers
(b) Small and marginal farmers
(c) Sharecroppers and artisans
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following farmers need to be supported through adequate facility for seeds, agricultural inputs, credit, etc.?
(a) Small and marginal farmer
(b) Landless agricultural farmer
(c) Prosperours farmer
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Small-scale industry needs government’s support for:
(a) Procurring raw material
(b) Marketing of output
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Large scale of labour
Answer
C
Question. Which of the social communities is mostly engaged is urorganised sector?
(a) Scheduled castes
(b) Scheduled tribes
(c) Backward communities
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Besides getting the irregular and low paid work, which of the following workers also face social discrimination?
(a) Scheduled castes
(b) Backward communities
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Marginal worker
Answer
C
Question. Read the following statements and find the CORRECT regarding workers condition from the given options.
I. In urban areas, unorganised sector consists of basically of workers in small-scale industry, casual workers, street vendors, head load workers, garment workers, etc.
II. In rural areas, about 80% of a households in India are in small and marginal farmer category.
(a) I Only
(b) II Only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
Answer
C
4. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
First, in any country several services such as hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, courts, village administrative offices, municipal corporations, defence, transport, banks, insurance companies, etc. are required. These can be considered as basic services. In a developing country the government has to take responsibility for the provision of these services. Second, the development of agriculture and industry leads to the development of services such as transport, trade, storage and the like, as we have already seen. Greater the development of the primary and secondary sectors, more would be the demand for such services. Third, as income levels rise, certain sections of people start demanding many more services like eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospitals, private schools, professional training etc. You can see this change quite sharply in cities, especially in big cities. Fourth, over the past decade or so, certain new services such as those based on information and communication technology have become important and essential. The production of these services has been rising rapidly.
Question. Which one of the following options is considered as basic services?
(a) Village administrative officers
(b) Banks
(c) Educational institutions
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The development of agriculture and industry leads to the development of services such as:
(a) Transport
(b) Trade
(c) Storage
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following changes is quite sharply in cities, especially in big cities?
(a) Private hospitals
(b) Private schools
(c) Tourism
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following services rise rapidly?
(a) Banking and trade
(b) Call centres
(c) Information and Communication Technology
(d) Software companies
Answer
C
Question. Information and Communication Technology is a part of
(a) Tertiary sector
(b) Primary sector
(c) Secondary sector
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reasoning (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option.
Assertion (A): Certain sections of people start demanding many more services like eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospitals, private schools, professional training, etc.
Reason (R): As income level of certain sections of people rise.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
5. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
A study conducted by the erstwhile Planning Commission (now known as NITI Aayog) estimates that nearly 20 lakh jobs can be created in the education sector alone. Similarly, if we are to improve the health situation, we need many more doctors, nurses, health workers etc. to work in rural areas. These are some ways by which jobs would be created and we would also be able to address the important aspects of development. Every state or region has potential for increasing the income and employment for people in that area. It could be tourism, or regional craft industry, or new services like IT. Some of these would require proper planning and support from the government. For example, the same study by the Planning Commission says that if tourism as a sector is improved, every year we can give additional employment to more than 35 lakh people. We must realise that some of the suggestions discussed above would take a long time to implement. For the short-term, we need some quick measures. Recognising this, the central government in India made a law implementing the Right to Work in about 625 districts of India. It is called Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 (MGNREGA 2005). Under MGNREGA 2005, all those who are able to, and are in need of, work in rural areas are guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year by the government. If the government fails in its duty to provide employment, it will give unemployment allowances to the people. The types of work that would in future help to increase the production from land will be given preference under the Act.
Question. In which year the NITI Aayog has been set up?
(a) 2014
(b) 2015
(c) 2017
(d) 2018
Answer
B
Question. According to the given source, which of the following suggestions are suggested by erstwhile Planning Commission to create jobs?
(a) To improve the health situation, need more doctors, nurses, health workers, etc.
(b) To improve tourism or regional craft industry.
(c) Jobs can also be created in educational field.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. In how many districts in India, Government of India implemented the Right to Work?
(a) About 625
(b) About 535
(c) About 600
(d) About 800
Answer
A
Question. In which year among the following years MGNREGA came into existence?
(a) 2003
(b) 2004
(c) 2005
(d) 2006
Answer
C
Question. MGNREGA is referred to as
(a) Right to Water
(b) Right to Property
(c) Right to Life
(d) Right to Work
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the main objective of MGNGEGA?
(a) It have given rise to the largest employment programme.
(b) It provides a legal guarantee for wage employment.
(c) It is a demand-driven programme where provision of work is triggered by the demand for work by wage-seekers.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
6. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. For example, goods that are produced in the primary or secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in wholesale and retail shops. At times, it may be necessary to store these in godowns. We also may need to talk to others over telephone or send letters (communication) or borrow money from banks (banking) to help production and trade. Transport, storage, communication, banking, trade are some examples of tertiary activities. Since these activities generate services rather than goods, the tertiary sector is also called the service sector.
Question. The source given above relates to which of the following options?
(a) Service sector
(b) Tertiary sector
(c) Secondary sector
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following activities do not produce a goods, but they are an aid or support for the production process?
(a) Tertiary activities
(b) Quinary activities
(c) Secondary activities
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
A
Question. It is a sector that gradually became associated with the different kinds of industries that came up. It is called as–
(a) Primary sector
(b) Secondary sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) Quinary sector
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following are the example of service sector?
(a) Teachers
(b) Doctors
(c) People who do administrative works, etc.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Read the following statements and find the INCORRECT from the given options.
I. There are many activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources come under primary sector.
II. There are many activities where the natural products are changed into other forms come under the tertiary sector.
III. Banking, transport, communication are examples of service sector.
Options:
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) I only
(d) Quinary sector
Answer
B
Question. activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Manufacturing
Answer
C
7. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
The organised sector offers jobs that are the most sought-after. But the employment opportunities in the organised sector have been expanding very slowly. It is also common to find many organised sector enterprises in the unorganised sector. They adopt such strategies to evade taxes and refuse to follow laws that protect labourers. As a result, a large number of workers are forced to enter the unorganised sector jobs, which pay a very low salary. They are often exploited and not paid a fair wage. Their earnings are low and not regular. These jobs are not secure and have no other benefits. Since the 1990s, it is also common to see a large number of workers losing their jobs in the organised sector. These workers are forced to take up jobs in the unorganised sector with low earnings. Hence, besides the need for more work, there is also a need for protection and support of the workers in the unorganised sector. In the urban areas, unorganised sector comprises mainly of workers in small-scale industry, casual workers in construction, trade and transport etc., and those who work as street vendors, head load workers, garment makers, rag pickers etc. Small-scale industry also needs government’s support for procuring raw material and marketing of output. The casual workers in both rural and urban areas need to be protected.
Question. In which one of the following sectors employment opportunities have been expanding very slowly?
(a) Organised Sector
(b) Unorganised Sector
(c) Private Sector
(d) Public Sector
Answer
A
Question. According to the given passage, in the urban areas unorganised sector comprises mainly of workers in–
(a) Small-scale industry
(b) Casual workers in construction
(c) Trade and transport
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following sectors adopt such strategies to evade taxes and refuse to follow laws that protect labourers?
(a) Organised sector enterprises in the unorganised sector
(b) Unorganised sector enterprises in the organised sector
(c) Only unorganised sector
(d) Only organised sector
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following sectors/industries needs government’s support for procuring raw material and marketing of output?
(a) Public Sector
(b) Unorganised Sector
(c) Organised Sector
(d) Small-scale Industry
Answer
D
Question. Mohan is a labourer in a near by shop. He gets unpaid holidays and his working hours are not fixed. He works in–
(a) Private sector
(b) Organised sector
(c) Unorganised sector
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Since the it is also common to see a large number of workers losing their jobs in the sector.
(a) 1990s, organised
(b) 1980s, unorganised
(c) 2000s, organised
(d) 2010s, organised
Answer
A
