Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Chemistry teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 13 Amines Class 12 Chemistry Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines are very important and should be revised daily.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Write the structure for N-ethylmethylamine.
Answer.

Question. Draw the structure of N, N-diethylethanamine.
Answer.

Question. Rearrange the following in an increasing
order of their basic strengths :
C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C6H5)2NH and CH3NH2
Answer.

Question. Why primary aromatic amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Answer.Aromatic amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
Question. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of solubility in water :
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2H5NH2
Answer.C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH2
1° amines are more soluble in water than 2° amines. Aniline due to large hydrophobic benzene ring is least soluble.
Question. Write IUPAC name of the following compound: (CH3CH2)2NCH3
Answer.
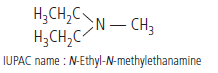
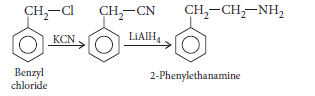
Question. Write chemical equations for the following conversion :
Benzyl chloride to 2-phenylethanamine.
Answer.
Question. Propanamine and N, N-dimethylmethanamine contain the same number of carbon atoms, even though propanamine has higher boiling point than N, N-dimethylmethanamine. Why?
Answer.Primary amines (R – NH2) have two hydrogen atoms on nitrogen which can undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding whereas no such hydrogen bonding is present in
tertiary amines (R3N). So, primary amines boil at a higher temperature than tertiary amines.
Question. How will you convert the following :
Aniline into N-phenylethanamide
(Write the chemical equations involved.)
Answer.

Question. What carbylamine reaction ?
Answer.Carbylamine reaction is the reaction in which 1° amines produce a bad smelling compound when treated with chloroform in the presence of alkali.

It is the test for primary amines.
Short Answer Type Questions
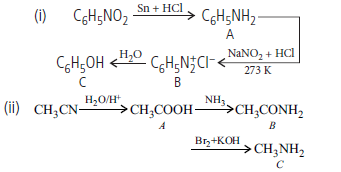
Question. Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :
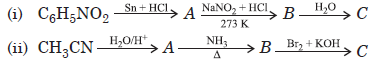
Answer.
Question. Acetamide is less basic than ethanamine. Why?
Answer.
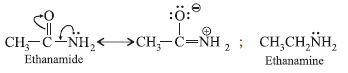
In acetamide, lone pair on nitrogen atom is involved in resonance and hence is not free for donation as in the case of ethanamine.
Question. How will you convert the following :
(i) Nitrobenzene into aniline
(ii) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
Answer.

Question. Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions :
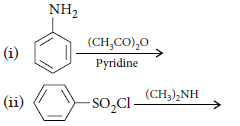
Answer.
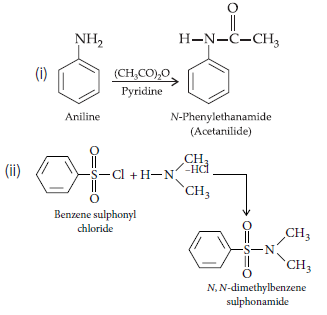
Question. Give the structure of of products A and B in the given sequence of reactions.
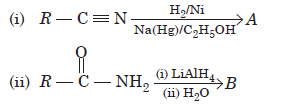
Answer.
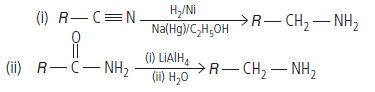
Question. How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) CH3CH2Cl to CH3CH2CH2NH2
(ii) Benzene to aniline
Answer.
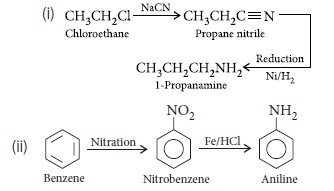
Question. Account for the following :
(i) Tertiary amines do not undergo acylation reaction.
(ii) Amines are more basic than comparable alcohols.
Answer.(i) In tertiary amines there are no acidic hydrogen due to which they do not undergo acylation reaction.
(ii) N being less electronegative than O gives lone pair of electron more easily than O atom. Therefore amines are more basic than alcohols.
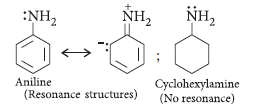
Question. How would you account for the following :
(i) Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine.
(ii) Methylamine in aqueous medium gives reddish-brown precipitate with FeCl3.
Answer.
(i) Aniline is weaker base than cyclohexylamine because of resonance. Due to electromeric effect, the lone pair on nitrogen is attracted by benzene ring. Hence, donor tendency of —NH2 group decreases. There is no resonance in cyclohexylamine.
Electron repelling nature of cyclohexyl group further increases the donor property of NH2 group. So, cyclohexylamine is a stronger base.
(ii) Methylamine forms hydroxide ions when dissolved in water
due to the following acid – base equilibrium.
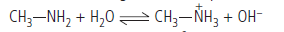
These OH– ions react with Fe3+ ions to form ferric hydroxide.
2Fe + 6OH– → 2Fe(OH)3
Question. Complete the following reactions :

Answer.
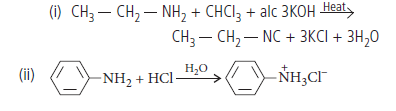
Question. Give the chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Methylamine and dimethylamine
(ii) Aniline and N-methylaniline
Answer.
(i) Methylamine gives carbylamine test, i.e., on treatment with alc. KOH and chloroform, followed by heating it gives offensive odour of methyl isocyanide. Dimethylamine does not give this test.
(ii) Aniline gives carbylamine test, i.e., on treatment with alc. KOH and chloroform followed by heating it gives offensive odour of phenylisocyanide but N-methylaniline being secondary amine, does not show this test.
Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question. (a) Give one chemical test to distinguish between the compounds of the following pairs :
(i) CH3NH2 and (CH3)2NH
(ii) (C2H5)2NH and (C2H5)3N
(b) Why aniline does not undergo Friedel–Crafts reaction?
Answer.(a) (i) Methylamine gives carbylamine test, i.e., on treatment with alc. KOH and chloroform, followed by heating it gives offensive odour of methyl isocyanide. Dimethylamine does not give this test.
(ii) (C2H5)2NH and (C2H5)3N can be distinguish by Hinsberg’s reagent.
(b) (i) In Friedel Crafts reaction, AlCl3 is added as a catalyst which is a Lewis acid. It forms a salt with aniline due to which the nitrogen of aniline acquires positive charge. This positively charged nitrogen acts as a strong deactivating group, hence aniline does not undergo Friedel Crafts reaction.

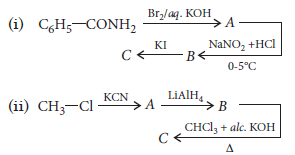
Question. A compound X (C7H7Br) reacts with KCN to give Y (C8H7N). Reduction of Y with LiAlH4 yields Z (C8H11N). Z gives carbylamine reaction, reacts with Hinsberg’s reagent in the presence of aq. KOH to give a clear solution. With NaNO2 and HCl at 0°C (Z) gives a neutral compound which gives red colour with ammonium cerric nitrate. What are X, Y and Z ?
Answer.
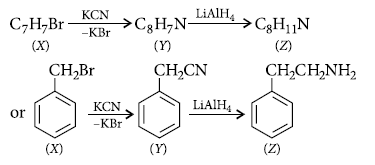
Question. How are the following reactions carried out?
Write the equations and conditions.
(i) Acetic acid to ethylamine
(ii) Bromocyclohexane to cyclohexanamine.
(iii) Methylamine to dimethylamine.
Answer.
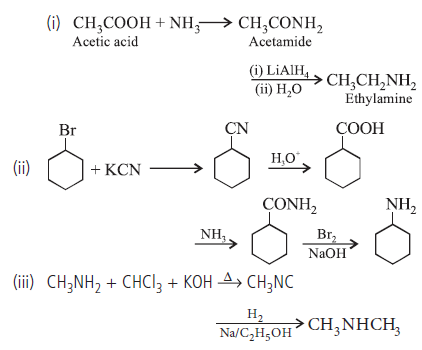
Question.35. Give reasons :
(i) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
(ii) CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
(iii) Although —NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline.
Answer.(i) After acetylation of aniline, acetanilide is formed in which due to the presence of

group having–I effect, electron density on N-atom decreases and hence, activation effect of aniline gets reduced.
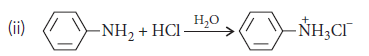
(iii) Nitration is carried out with conc. HNO3 in the presence of conc. H2SO4. In the presence of these acids, the –NH2 group of aniline gets protonated and is converted into –NH3+group. This positively charged group acts as a strong electron withdrawing and meta-directing group. Hence, the incoming electrophile goes to m-position.
Question. Amit wants to manufacture aniline for the synthesis of dye stuff. For this he has selected tin and hydrochloric acid as reducing agent for the reduction of nitrobenzene. But his friend suggested to use iron scrap and hydrochloric acid as the reducing agent.
Now answer the following questions :
(i) Write the chemical equation for the reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline.
(ii) Why Amit’s friends has suggested to use scrap iron and HCl in place of tin and HCl?
Answer.
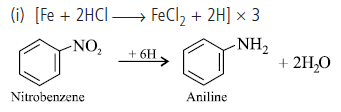
(ii) Amit’s friend has suggested to use scrap iron and hydrochloric acid because in this reaction FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl during the reaction. Thus only small amount of HCl is required to initiate the reaction and scrap iron is also cheaper.
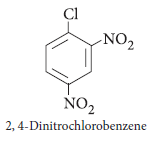
Question. Write the structure of 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene.
Answer.
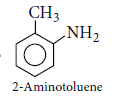
Question. Write the structure of 2-aminotoluene.
Answer.
Question. Which amine in each of the following pairs is a stronger base? Give reason.
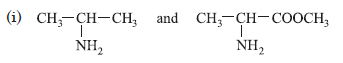
(ii) CH3CH2CH2NH2 and CH3NHCH2CH3
Answer.
withdrawing group which decrease the electron density on nitrogen atom.
(ii) 2° amines are more basic than 1° amines, because in 2° amine there are two electron releasing groups and in 1° amine only one electron releasing group is present, so, CH3NHCH2CH3 is more basic than CH3CH2CH2NH2.
Question. Account for the fact that although N,N-dimethyl aniline is only slightly more basic than aniline, 2, 6-dimethyl N, N-dimethyl aniline is much more basic than 2, 6-dimethyl aniline.
Answer.Extended p bonding between the amino nitrogen and the ring requires the s bonds on N atom to become coplanar with the ring and its ortho bonds.
Presence of bulky substituents in the ortho positions (2, 6-positions) sterically hinder the attainment of this geometry (coplanarity) and thus interferes with the base—weakening extended p bonding.
Because of this effect, (called steric inhibition of resonance) 2, 6-dimethyl N, N-dimethyl aniline is much more basic than 2, 6-dimethyl aniline.
Question. Write the structures of A, B and C in the following sequence of reactions :
Answer.

Question. (a) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between aniline and N, N-dimethylaniline.
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point :
C2H5NH2, C2H5OH, (CH3)3N
Answer.(a) Aniline undergoes isocyanide test (carbylamine reaction) whereas, N, N – dimethylaniline does not.
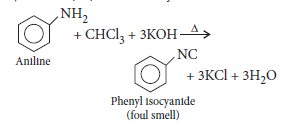
(b) Increasing order of boiling points :
(CH3)3N < C2H5NH2 < C2H5OH
Tertiary amine does not have hydrogen to form hydrogen bonding and hydrogen bonding in alcohol is stronger than that of amines because oxygen is more electronegative than
nitrogen.
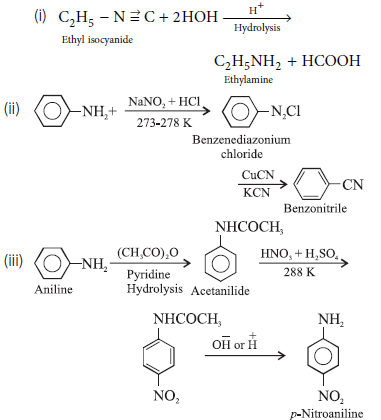
Question. Write the chemical equations for the following conversions :
(i) Ethyl isocyanide to ethylamine.
(ii) Aniline to benzonitrile
(iii) Aniline to p-nitroaniline.
Answer.
Question. Write the structure of N-methylethanamine.
Answer.CH3CH2NHCH3
Question. An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.
Answer.Formula of the compound ‘C’ indicates it to be an amine.Since it is obtained by the reaction of Br2 and KOH with the compound ‘B’ so compound ‘B’ can be an amide. It is also indicated because ‘B’ is obtained from compound ‘A’ by reaction with ammonia following by heating. So compound ‘A’ could be an aromatic acid. Formula of compound ‘C’ shows that it is aniline, then ‘B’ is benzamide and compound ‘A’ is benzoic acid. The sequence of reactions can be written as follows :

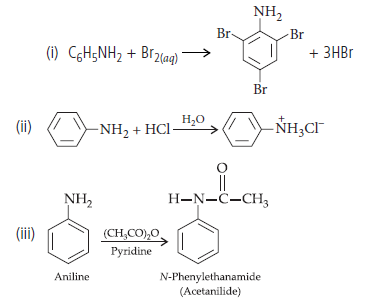
Question. Write the structures of main products when aniline reacts with the following reagents :
(i) Br2 water
(ii) HCl
(iii) (CH3CO)2O/pyridine
Answer.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a)

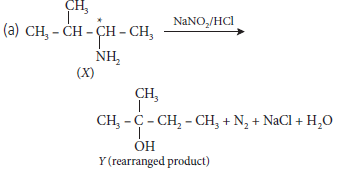
Find X and Y. Is Y optically active? Write the intermediate steps.
(b) Which of the following is more acidic and why?
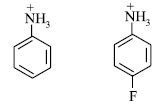
Answer.

Question. Give plausible explanation for each of the following :
(i) Why are amines less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses?
(ii) Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
(iii) Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than aromatic amines?
Answer.(i) In alcohols, the hydrogen atom is attached to more electronegative oxygen atom whereas nitrogen of amines is less electronegative. After the loss of H+ ion, the negative
charge is more easily accommodated on oxygen than in case of nitrogen in amines. Hence, amines have lesser tendency to lose H+ ions, so they are less acidic than alcohols.
R − NH2 → R – NH–+ H+
R – O – H → R – O– + H+
(ii) Primary amines (R – NH2) have two hydrogen atoms on nitrogen which can undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding whereas no such hydrogen bonding is present in tertiary amines (R3N). So primary amines boil at a higher temperature than tertiary amines.
(iii) In aromatic amines, the lone-pair of electrons on nitrogen atom is involved in resonance with the benzene ring as shown below for aniline.
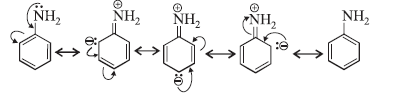
It shows that this pair of electrons is less available for protonation. In case of aliphatic amines electron releasing alkyl groups increase electron density on nitrogen atom. So, aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines.
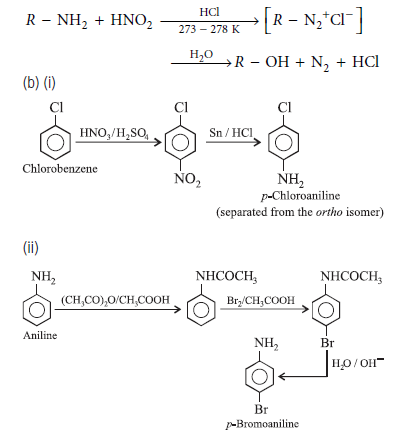
Question. (a) Write the reactions of (i) aromatic and
(ii) aliphatic primary amines with nitrous acid.
(b) Write the chemical equations for the following conversions
(i) Chlorobenzene to p-chloroaniline
(ii) Aniline to p-bromoaniline
Answer.(a) (i) Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts.

(ii) Aliphatic primary amines also form diazonium salts on reaction with nitrous acid but they are unstable and decompose to give the corresponding alcohols as the major product with the evolution of nitrogen.
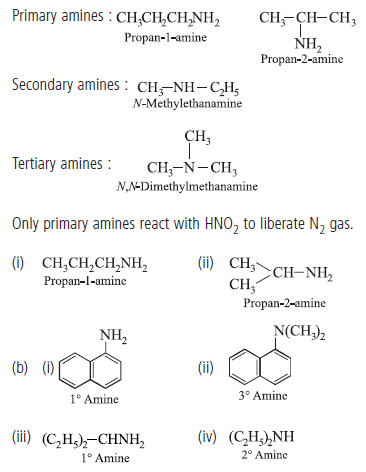
Question. (a) Write structures of different isomers corresponding to the molecular formula, C3H9N.
Write IUPAC name of the isomers which will liberate nitrogen gas on treatment with nitrous acid.
(b) Classify the following amines as primary, secondary and tertiary :
Answer.(a) In all, four structural isomers are possible. These are as follows :
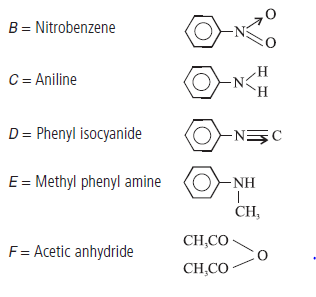
Question. 39. Write the structure of the reagents/organic compounds A to F in the following sequence of reactions :

Answer.Structure of reagents/organic compounds :