HOTS Accountancy Class 12 Chapter 4 Analysis of Financial Statement
Students of Class 12 Commerce should refer to the HOTS Accountancy Class 12 Analysis of Financial Statement with solutions given below, this will help them to understand the concepts and related questions given in Class 12 Accountancy DK Goel textbook. It’s very important to understand High Order Thinking Skills questions and answers to get better marks in examinations. Also dont forget to refer to dk goel class 12 accountancy solutions
Question: Under What heads will you classify the followings:
1) Proposed Dividends
2) Interest Accrued and due on secured loans
3) Interest Accrued and due on unsecured Loans
4) Provision for Taxation
5) Arrears of fixed accumulative dividends
6) Security premium Account
7) Share Forfeiture account.
Answer:
1) Provisions :- Proposed Dividend
2) Secured Loans : – Interest Accrued and due on Secured Loans
3) Unsecured Loans:- Interest Accrued and due on unsecured Loans
4) Provision : Provision for Taxation
5) Contingent Liabilities :- Arrears of Fixed Cumulative dividend
6) Reserves & Surplus :- Security Premium Account
7) Share Capital Account: – Share forfeiture Account.
Question: Under What headings will you show the following items in the Balance sheet
of a company
1) Securities Premium account
2) Preliminary Expenses
3) Bills Receivable
4) Goodwill
5) Authorised share Capital
Answer:
1) Securities Premium Account :- Under Reserves & Surplus,
Liabilities side
2) Preliminary Expenses :- Under Miscellaneous Expenditures,
Assets side
3) Bills Receivables :- Under Loans & Advance on assets side.
4) Goodwill :- Under Fixed Assets, Assets side
5) Authorised Capital :- Under Share Capital, Liabilities side
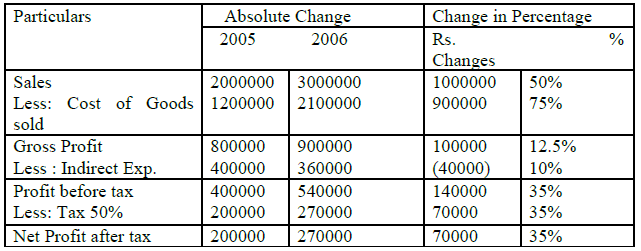
Question: Prepare a Comparative Income statement with the help of the following
information
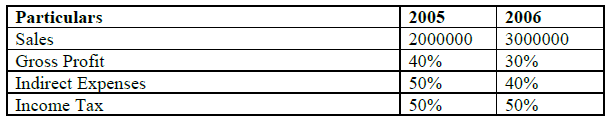
Answer:
Comparative Income Statement
For the year ended 31st Dec, 2006
Question: Explain three purposes or objectives of Financial Analysis.
Answer: Following are the purposes of Financial Analysis:
1) Judging earning capacity of business
2) Judging managerial efficiency of business
3) Judging short term long term Solvency
Question: Mention three limitations of financial statement Analysis.
Answer: Following are the Limitation of Financial statement Analysis
1) Historical Analysis
2) Ignore price level changes
3) Quantities aspect ignored
Q.6 From the following Balance Sheets U.K Ltd. on 31st Dec 2006 & 2007.Prepare
comparative Balance Sheet.
Balance Sheet
As on 31st Dec 2006 & 2007

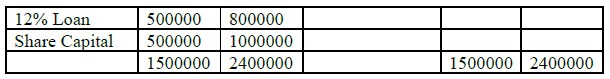
Answer:
Comparative Balance Sheet
For the year ended 31st Dec, 2006 & 2007

Question: (a) The ratio of current Assets (Rs. 600000) to current Liabilities ( Rs.
400000) is 1.5:1.The Accountant of the firm is interested in maintaining a
current Ratio be 2:1 by paying off a part of Liabilities. Calculate the amount of
Current Liabilities that should be paid.
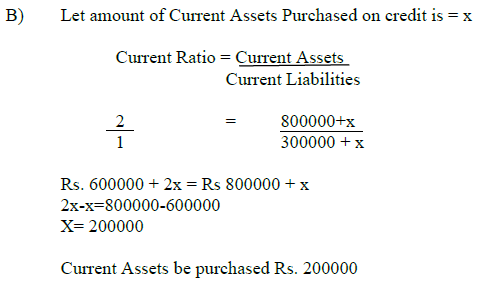
(b) The Current Assets to Current Liability of a firm is Rs. 800000 to Rs.
b. The Accountant of the firm wishes that current Ratio be 2:1 by
acquiring current assets on credit. Calculate the amount of current Assets.
Answer: A)
a) Let Current Liabilities = X
b)
Current Ratio after making payment of x is 2:1
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
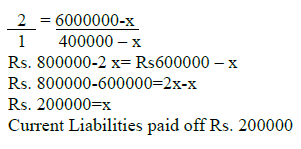
Question: (a) A business has current Ratio of 4:1 & a Quick Ratio of 1.2:1 . If
working capital is Rs. 180000. Calculate total current Assets and Stock
(b) Calculate current Ratio and Quick Ratio from the followings:
Working capital Rs. 150000, Total Debts Rs.400000, Long term debts Rs.
310000, Stock Rs. 110000, Prepaid Expenses Rs. 10000
Answer:


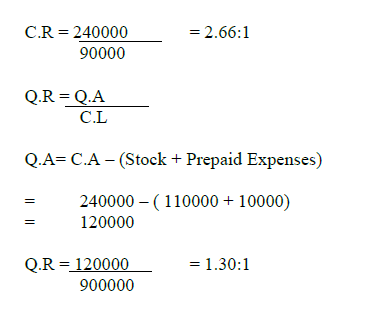
Question:(a) Calculate current Ratio and Quick Ratio from the following
information:
Total Assets Rs. 350000
Fixed Assets Rs. 175000
Investment Rs. 70000
Fictitious Assets Rs. 5000
Share holders fund Rs. 200000
Long term Debts Rs. 100000
Inventory Rs. 45000
(b) From the following information calculate the stock turnover ratio.
Sales Rs. 200000, G.P 25% on cost, Opening Stock was 1/3rd of the
value of closing stock
Closing stock was 30% of sales
(3 + 3)=6 Marks
Answer: A) Total Assets = Fixed Assets + Investment + Current Assets +
Fictitious Assets
350000 = 175000+70000+Current Assets +5000
Current Assets = 350000-250000
Current Assets = 100000
Liquid Assets = Current Assets – Inventory
= 100000 – 45000 = 55000
Total Assets = Total Liabilities
Total Assets = Shareholders Fund + Long Term Debts +Current
Liabilities
350000 = 200000+100000+Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 350000- 300000
Current Liabilities = 50000


Question: (a) Determine the amount of gross profit and sales from the followings:
Debtors Turnover Ratio = 4 Times
Loss of goods sold = Rs. 640000
Gross Profit Ratio = 20%
Closing Debtors were Rs. 20000 more than at the beginning.
Cash sales being 33 1/3 % of credit sales.

Cost of Sales = 60000 * 6 = 360000
Case 1)
Let Cost of Sale = 100
G.P = 25 % above Cost
Sales = 125
If Cost of Sale 100 Sale = 125
If Cost of Sale 1 Sale = 125/100
If Cost of Sale 360000 = 125/100 * 360000
= 450000
Gross Profit = 450000 – 360000
= 90000
Case 2)
Let Sales= 100
G.P = -25/75
If Cost of Sale 75 Sales = 100
If Cost of Sale 1 Sale = 100/75
If Cost of Sales 360000 Sales = 100/75 * 360000
= 480000
Gross Profit = 480000 – 360000 = 120000
B) 1) Sales = Cost of Goods Sold – Gross Profit
Let Sales = 100
G.P = -20
Cost of Goods Sold = 80
If Cost of Good Sold 80 G.P = 20
If Cost of Goods Sold 1 G.P = 20/80
If Cost of Goods Sold 640000 G.P = 20/80*640000
= 160000
Thus Sales = 640000-160000 = 800000
2) Let Credit Sale = 100
Cash Sale = 33 1/3 = 100/3
Total Sale = 100 + 100/3 = 400/3
If Sales 400/3 Credit Sales = 100
If Sales 1 Credit Sales = 100* 3/400 = ¾
If Sale 800000 Credit Sales = ¾ * 80000 = 600000

Question: (a) If Current Ratio is 2:1 state giving reason of the following transaction would
(i) Improve (ii) Reduce or (iii) Not change Current Ratio
(1) Bills Receivable drawn
(2) Bills Receivable Dishonoured
(3) Bills Receivable endorsed to Creditors
(4) Sales of Goods for cash at par
(5) Sales of Goods for cash at Profit
(6) Sales of Assets for Cash
(7) Bills Payable given to creditors
(b) If the Liquid ratio is 1:1, find whether the following transactions
would
(ii) Improve (ii) Reduce or (iii) Not change Liquid Ratio
1) Purchase of goods for cash
2) Purchase of goods on credit
3) Payment of Tax Provision
4) Sales of short term investment at par
5) Sales of Investment at profit
Answer: A)
1) Not Change
2) Not Change
3) Improve
4) Not Change
5) Improve
6) Improve
7) Not Change
B)
1) Reduce
2) Reduce
3) Improve
4) Not Change
5) Improve
Question: (a) Calculate and Closing stock from the following information:-
Total sales Rs 600000
Gross Profit 25% on Sales
Stock Turnover Ratio = 5 times
Closing stock is Rs. 12000 more than opening stock
(b) Gross Profit Ratio of a company was 25%. Its cash sales were Rs. 200000
and its credit Sales was 90% of the total sales. If the indirect expenses of the
Company were Rs. 20000. Calculate net Profit ratio.
Answer: A) Sales = 600000
G.P = 600000*25/100 = 150000
Cost of Goods Sold = Sales – G.P
= 600000-150000 = 450000

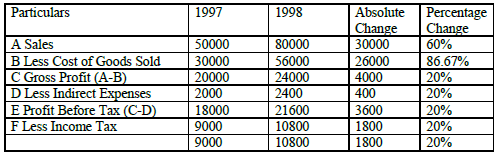
Question: With the help of the following information. Prepare Comparative Income
Statement of XYZ Ltd.
Question: With the help of the following information. Prepare Comparative Income
Statement of XYZ Ltd.

Answer:
Comparative Income Statement of XYZ Ltd.
For the year ended 31st, Dec 1997 & 1998
Question: (a) Calculate Return on Investment from the following
Gross Profit Rs.100000, Office Expenses Rs. 10000, Selling and Distribution
expenses Rs. 25000, Interest on Bank Loan Rs. 8000, Income tax Rs. 12000,
Fixed Assets Rs. 300000, Current Assets Rs. 150000 & Current Liabilities Rs.
125000
(b) Calculate the earning per share from the following data
15000 Equity Share of Rs. 10 each 150000
10 % Preference Share Capital 100000
Net Profit before Tax 55000

Question: The Debt-equity ratio of a company is 1:2, state giving reasons which of the
following would improve, reduce or no change the ratio:-
1) Debenture redeemed for cash
2) Issue new equity shares
3) Payment of Proposed dividends
4) Goods Purchased on Credit
5) Goods Purchased on Cash
6) Redemption of Debentures against the Purchase of a Fixed
Assets
Answer:
1) Reduce
2) Increase
3) Decrease
4) Increase
5) Not Change
6) Increase
7) Increase

