MCQs for Chemistry Class 11 with Answers Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Students of class 11 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 11 Chemistry NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 11 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 11 Chemistry. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 11 Chemistry examination
Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ with Answers Class 11 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 11. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 11 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. Which of the following compounds represents 2,2,3 – trimethyl hexane?
(a) CH3C (CH3)2 CH2CH2CH(CH3)2
(b) CH3C (CH3)2 CH2CH(CH3)2 CH2CH3
(c) CH3C (CH3)2 CH (CH3)CH2 CH2CH3
(d) CH3C (CH3)2 CH2C (CH)2 CH3
Answer
C
Question. The structural formula of 2-oxo-3-methyl-(N-bromo) butanamide is
(a) CH3 — CH2 —CO —CO — NH — Br
CH3
|
(b) CH3 — CH —CO —CO — NH — Br
CH3
|
(c) CH3CH —CO —CO — NOBr
(d) (CH3)3 C —CO —CO — NHBr
Answer
B
Question. On the basis of hybridisation and resonance effect, the correct order of bond length of the following is
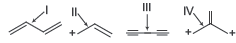
(a) II> IV> III> I
(b) I> III> IV> II
(c) II> IV> I> III
(d) III> I> IV> II
Answer
A
Question. The maximum number of isomer for an alkene with the molecular formula C4H8 is
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer
C
Question. The IUPAC name of neopentane is
(a) 2-methylbutane
(b) 2, 2- dimethylpropane
(c) 2-methylropane
(d) 2, 2-dimethylbutane
Answer
B
Question. The correct stability order for the following species is
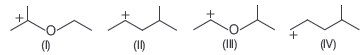
(a) (II) > (IV) > (I) > (III)
(b) (I) > (II) > (III) > (IV)
(c) (II) > (I) > (IV) > (III)
(d) (I) > (III) > (II) > (IV)
Answer
D
Question. In which of the following functional group isomerism is not possible?
(a) Alcohols
(b) Aldehydes
(c) Alkyl halides
(d) Cyanides
Answer
C
Question. Identify the compound that exhibits tautomerism
(a) 2-butene
(b) lactic acid
(c) 2-pentanone
(d) ethane
Answer
C
Question.
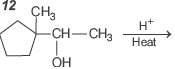
Consider the above written reaction. The product is
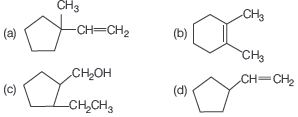
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds will show metamerism?
(a) CH3COOC2H5
(b) C2H5 —S—C2H5
(c) C2H5 —O—C2H5
(d) CH3 —O—C2H5
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of increasing basicity of the given conjugate bases (R = CH3 ) is
(a) RCOO <HC =C < R NH2
(b) R < HC =C < RCOO <NH2
(c) RCOO <NH2 < HC =C <R
(d) RCOO <HC =C <NH2 <R
Answer
D
Question. The IUPAC name of the compound shown below is
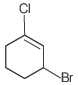
(a) 2-bromo-6-chlorocyclohex-1-ene
(b) 6-bromo-2-chlorocyclohexene
(c) 3-bromo-1-chlorocyclohexene
(d) 1-bromo-3-chlorocyclohexene
Answer
C
Question. The distillation technique most suited for separating glycerol from spent lye in the soap industry is
(a) fractional distillation
(b) steam distillation
(c) distillation under reduced pressure
(d) simple distillation
Answer
C
Question. For the estimation of nitrogen, 1.4 g of an organic compound was digested by Kjeldahl’s method and the evolved ammonia was absorbed in 60 mL of M/10 sulphuric acid. The unreacted acid required 20 mL of M/10 sodium hydroxide for complete neutralisation. The precentage of nitrogen in the compound is
(a) 6%
(b) 10%
(c) 3%
(d) 5%
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is most stable?
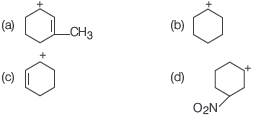
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of nucleophilicity is
(a) I− > Br− > Cl−> F−
(b) Cl−> F− > Br− > I−
(c) F− > Cl− > Br− > I−
(d) I− > Cl− > Br− > F−
Answer
A
Question. The order of stability of the following carbocations

(a) III > II > I
(b) II > III > I
(c) I > II > III
(d) III > I > II
Answer
D
Question. Nitroethane can exhibit one of the following kind isomerism.
(a) Metamerism
(b) Optical activity
(c) Tautomerism
(d) Position isomerism
Answer
C
Question. Identify the compound that exhibits tautomerism.
(a) 2-butene
(b) lactic acid
(c) 2-pentanone
(d) Phenol
Answer
C
Question. The maximum number of possible optical isomers in 1-bromo-2-methyl cyclobutane is
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 8
(d) 16
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is the most energetic conformation of cyclohexane?
(a) Boat
(b) Twisted boat
(c) Chair
(d) Half chair
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the correct order of priority of groups in D -glyceraldehyde?
(a) OH (1), CHO (2), CH2OH (3) and H (4)
(b) OH (1), CH2OH (2), CHO (3) and H (4)
(c) CH2OH (1), CHO (2), OH (3) and H (4)
(d) CHO (1), OH (2), CH2OH (3) and H (4)
Answer
A
Question. The structures (CH3)3 CBr and CH3 (CH2)3Br represent
(a) chain isomerism
(b) position isomerism
(c) chain as well as position isomerism
(d) functional isomerism
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds exhibit rotamers?
(a) 2-butene
(b) Maleic acid
(c) Butane
(d) Fumeric acid
Answer
A
Question. The total number of cyclic isomers possible for a hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C4H6 is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 7
Answer
C
Question. Which among the following statements is correct with respect to the optical isomers?
(a) Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images
(b) Diastereomers are superimposable min-or images
(c) Enantiomers are superimposable mirror image
(d) Meso-fonns have no plane of symmetry
Answer
A
Question. The total number of cyclic structural as well as stereoisomers possible for a compound with the molecular formula C5H10 is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 7
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds will show metamerism?
(a) CH3 —CO—C2H5
(b) C2H5—S—C2H5
(c) CH3 —O—CH3
(d) CH3—O—C2H5
Answer
B
Question. The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is
(a) propene
(b) 2-methyl propene
(c) 2-butene
(d) 2-methyl-2-butene
Answer
C
Question. Racemic compound has
(a) equimolar mixture ofenantiomers
(b) 1 : 1 mixture of enantiomer and diastereomer
(c) 1 : 1 mixture of diastereomers
(d) 1 : 2 mixture of enantiomers
Answer
A
Question. Out of the following, the aikene that exhibits optical isomerism is
(a) 3-methyl-2-pentene
(b) 4-methyl-1-pentene
(c) 3-methyl-1-pentene
(d) 2-methyl-2-pentene
Answer
C
Question. Angle strain in cyclopropane is
(a) 24°44′
(b) 9°44′
(c) 44′
(d) – 5° 16′
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following does not contain chiral carbon atom?
(a) Lactic acid
(b) 2-chlorobutanoic acid
(c) Tartaric acid
(d) Succinic acid
Answer
D
Question. A molecule having three different chiral carbon atoms, how many stereoisomers it will have?
(a) 8
(b) 3
(c) 9
(d) 6
Answer
A
Question. Example of geometrical isomerism is
(a) 2-butanol
(b) 2-butene
(c) butanal
(d) 2-butyne
Answer
B
Question. The total number(s) of stable conformers with non-zero dipole moment for the following compound is/are

(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
A
Question. The number of isomeric pentyl alcohols possible is
(a) two
(b) four
(c) six
(d) eight
Answer
D
Question. The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular fommla
CH3 —CH= CH—CH(OH)—Me is
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
C
Question. The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals is
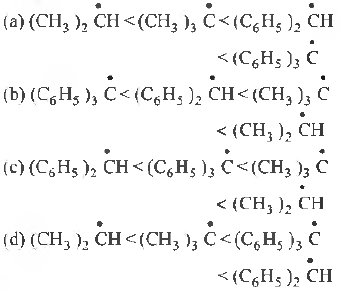
Answer
C
Question. The number of isomeric alkanes having the molecular fommla C5H12 is
(a) three
(b) five
(c) nine
(d) thirty two
Answer
A
Question. The most stable free radical is
(a) PhCH2CH2
(b) MeCH2
(c) Me2CH
(d) PhCHMe
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following free radical is most stable?

Answer
A
Question. The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular formula
CH3 — CH == CH — CH(OH) Me is
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
C
Question. Correct order of nucleophilicity is
(a) CH3− < NH2− < OH− < F−
(b) F− < OH− < CH3− < NH2−
(c) OH− < NH2−< F− < CH3−
(d) F− < OH− < NH2− < CH3−
Answer
D
Question. Which is the most stable carbocation?

Answer
C
Question. How many chiral compounds are possible on monochlorination of 2-methylbutane?
(a) 8
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
B
Question. The most suitable method for separation of1:1mixture of ortho and para-nitrophenols is
(a) sublimation
(b) chromatography
(c) crystallisation
(d) steam distillation
Answer
D
Question. The most stable carbanion is
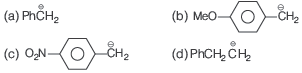
Answer
C
Question. Two solids A and B have appreciably different solubilities in water but their melting points are very close. The mixture of A and B can be separated by
(a) sublimation
(b) fractional crystallisation
(c) distillation
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
B
Question. Arrange the carbanions, in order of their decreasing stability.
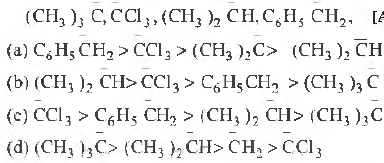
Answer
B
Question. 29.5 mg of an organic compound containing nitrogen was digested according to Kjeldahl’s method and the evolved ammonia was absorbed in 20 mL of 0.1 M HCl solution. The excess of the acid required 15 mL of 0.1 M NaOH solution for complete neutralisation. The percentage of nitrogen in the compound is
(a) 59.0
(b) 47.4
(c) 23.7
(d) 29.5
Answer
C
Question. 3-methylpent-2-ene on reaction with HBr in presence of peroxide forms an addition product. The number of possible stereoisomers for the product is
(a) six
(b) zero
(c) two
(d) four
Answer
D
Question. Among the following, the least stable resonance structure is
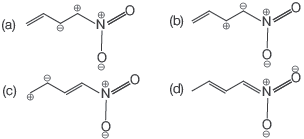
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compound will exhibi geometrical isomerism?
(a) 1- phenyl-2-butene
(b) 3 – phenyl-1-butene
(c) 2 – phenyl-1-butene
(d) 11 , – diphenyl-1-propane
Answer
A
Question. In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is
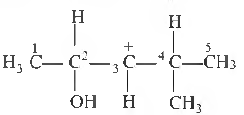
(a) CH3 at C-4
(b) H at C-4
(c) CH3 at C-2
(d) H at C-2
Answer
D
Question. The Lassaigne’s extract is boiled with dil. HNO3 before testing for halogens because
(a) Ag2S is insoluble in HNO3
(b) AgCN is soluble in HNO3
(c) Na2S and NaCN are decomposed by HNO3
(d) silver halides are soluble in HNO3
Answer
C
Question. In Carius method of estimation of halogens 250 mg of an organic compound gave 141mg of AgBr.The percentage of bromine in the compound is (at. mass Ag = 108,Br = 80)
(a) 24
(b) 36
(c) 48
(d) 60
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following molecules is least resonance stabilised?

Answer
D
Question. A gaseous hydrocarbon gives upon combustion 0.72 g of water and 3.08 g of CO2. The empirical formula of the hydrocarbon is
(a) C2H4
(b) C3H4
(c) C6H5
(d) C7H8
Answer
D
Question. The order of the stability of the following carbocations

(a) III > II > I
(b) I > III > II
(c) I > II > III
(d) III > I > II
Answer
D
Question. The compound that does not give a blue colour in Lassaigne’s test is
(a) aniline
(b) glycine
(c) hydrazine
(d) urea
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds will be suitable for Kjeldahl’s method for nitrogen estimation?

Answer
B
Question. 60 g of organic compound on analysis gave following results C = 24 g; H = 4 g andO = 32 g.
The compound can be
(a) CH2O2
(b) C2H2O
(c) C2H2O4
(d) CH2O
Answer
D
1 2
Question. The bond between carbon atom (1) and carbon atom (2) in compound N = C —CH == CH2 involves respectively the hybrid orbitals
(a) sp2 and sp2
(b) sp3 and sp
(c) sp and sp2
(d) sp and sp
Answer
C
Question. Order of reactivity for the following compounds, is

(a) IV < II < III < I
(b) II < IV < III < I
(c) IV < II < I < III
(d) II < IV < I < III
Answer
A
Question. The name of ClH2C — C ==C — CH2Cl according to
Ι Ι
Br Br
IUPAC nomenclature system is
(a) dichloro dibromobutene
(b) dichloro dibromobutane
(c) 1,4- dichloro- 2,3- dibromobut- 2- ene
(d) 2,3- dibromo -1,4- dichlorobut- 2- ene
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following compounds is most acidic?
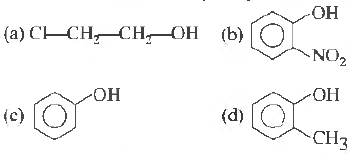
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is wrong?
(a) Using Lassaigne’s test nitrogen or sulphur present in an organic compound can be tested
(b) Using Beilstein’s test the presence of halogen in a compound can be tested
(c) Lassaigne’s test fails to identify nitrogen in diazo compound
(d) In the estimation of carbon an organic compound is heated with CuO in a combustion tube
Answer
D
Question. Arrange the following free radicals in order of decreasing stability.
Methyl (I), Vinyl (II), Allyl (III), Benzyl (IV)
Codes
(a) I > II > III > IV
(b) III > II > I > IV
(c) II > I > IV > III
(d) IV > III > I > II
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following order is true regarding the acidic nature of COOH ?
(a) Formic acid > acetic acid > propanoic acid
(b) Formic acid > acetic acid < propanoic acid
(c) Formic acid < acetic acid > propanoic acid
(d) Formic acid < acetic acid < propanoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Among the following, the least stable resonance structure is
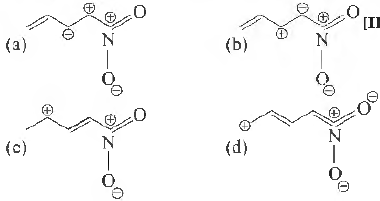
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following orders is not correct regarding −I -effect of the substitutents?
(a) —I< —Cl< —Br< —F
(b) —N+R3 < —O+R2
(c) —N+R2 < —OR < —F
(d) —SR < — OR < —O+R2
Answer
A
Question. Out of the following the alkene that exhibits optical isomerism is
(a) 3-methyl-2-pentene
(b) 4-methyl-1-pentene
(c) 3-methyl-1-pentene
(d) 2-methyl-2-pentene
Answer
C
Question. The rate of the reaction,
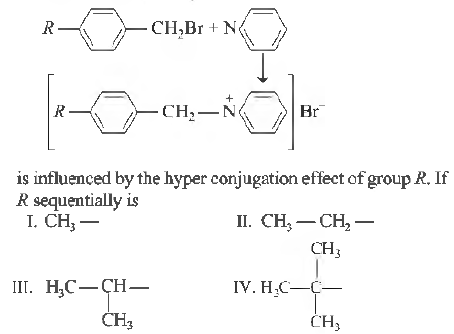
The increasing order of speed of the above reaction is
(a) IV< IIl< II < I
(c) I <IV< IIl <II
(b) I <II <III< IV
(d) III < II < I < IV
Answer
A
Question. Consider the following carbocations.
I. C6H5 C+H2+
II. C6H5CH2 C+H2
III. C6H5 C+H CH3
IV. C6H5 C+ (CH3)2
The correct sequence of the stability of these carbocation is
(a) II<I<III<IV
(b) II<III<I< IV
(c) III<I<II<IV
(d) IV<III<I<II
Answer
A
Question. In Kjeldahl’s method, the gas evolved from 1.325 g sample of fertiliser is passed into 50.0 mL of 0.2030 N H2SO4. 25.32 mL of 0.1980 N NaOH are required for the titration of unused acid. What will be the percentage of nitrogen in fertiliser?
(a) 2.50 %
(b) 5.43 %
(c) 6.48 %
(d) 12.02 %
Answer
B
Question. The electrophile Ee attacks which benzene ring to generate the intem1ediate cr-complex. Which of the following cr-complexes is of lowest energy?
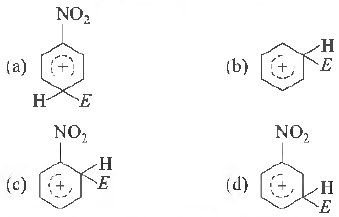
Answer
D
Question. Electronegativity of carbon atoms depend upon their state of hybridisation. In which of the following compounds, the carbon marked with asterisk is most electronegative?
(a) CH2 —CH2 —*CH2 —CH3
(b) CH3 —*CH = CH—CH2
(c) CH3 —CH2 —C = *CH
(d) CH3 —CH2 —CH = *CH2
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds contain only primary hydrogen atoms?
(a) Isobutene
(b) 2, 3 – dimethylbut – 2 – ene
(c) Cyclohexane
(d) Propyne
Answer
B

We hope the above multiple choice questions for Class 11 Chemistry for Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques is an important chapter in Class 11 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for the benefits of class 11 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
