MCQs for Chemistry Class 12 with Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Students of class 12 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 12 Chemistry NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 12 Chemistry. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 12 Chemistry examination
Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ with Answers Class 12 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 12. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 12 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. An example of a compound with functional group – O – is :
(a) acetic acid
(b) methyl alcohol
(c) diethyl ether
(d) acetone
Answer
C
Question. Butane-2-ol is
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary alcohol
(c) tertiary alcohol
(d) aldehyde
Answer
B
Question. CH3CH2OH can be converted into CH3CHO by _______________.
(a) catalytic hydrogenation
(b) treatment with LiAlH4
(c) treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate
(d) treatment with KMnO4
Answer
C

(a) A, B, C, D
(b) A, D
(c) B, C
(d) A
Answer
C
Question. IUPAC name of m-cresol is _______________.
(a) 3-methylphenol
(b) 3-chlorophenol
(c) 3-methoxyphenol
(d) benzene-1, 3-diol
Answer
A
Question. Phenol is less acidic than _______________.
(a) ethanol
(b) o-nitrophenol
(c) o-methylphenol
(d) o-methoxyphenol
Answer
B
Question. Ethylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent to give
(a) ethane
(b) ethyl alcohol
(c) ethylene glycol
(d) None of these
Answer
C

Answer
B
Question. The C—O bond length in phenol is less than that in methanol due to
(a) partial double bond character in aromatic ring
(b) sp2 hybridised carbon
(c) sp3 hybridised carbon
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Which is the correct order of acid strength of the following?
(a) C6H5OH > H2O > ROH > HC≡CH
(b) C6H5OH > ROH > H2O > HC≡CH
(c) C6H5OH > HC≡CH > H2O > ROH
(d) C6H5OH > H2O > HC≡CH > ROH
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH?
(a) H2/Pd
(b) LiAlH4
(c) NaBH4
(d) Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis
Answer
A
Question. The order of reactivity of the alkenes, (i) (CH3)2C—CH2 , (ii) CH3CH—CH2 , (iii) CH2—CH2, when subjected to acid catalysed hydration is:
(a) (i) > (iii) > (ii)
(b) (i) > (ii) > (iii)
(c) (ii) > (i) > (iii)
(d) (iii) > (ii) > (i)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?
(a) ΘOH
(b) ΘOR
(c) ΘOC6 H5Θ
(d) ΘNO2
Answer
B
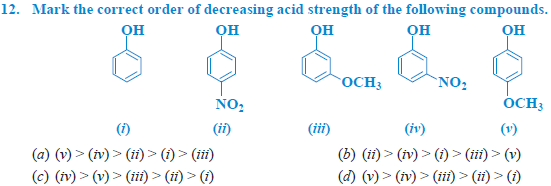
Answer
B
Question. Sodium salt of benzene sulphonic acid on fusion with caustic soda gives
(a) Benzene
(b) Phenol
(c) Thiophenol
(d) Benzoic acid
Answer
B
Question. Acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes except ethene leads to the formation of
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary or tertiary alcohol
(c) mixture of primary and secondary alcohols
(d) mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohols
Answer
B
Question. In the reaction given below, X is:
Neopentyl alcohol→H2SO4 X
(a) 2-methylpent-2-ene
(b) 2-methylpentane
(c) 2-methylbut-2-ene
(d) neopentane
Answer
C
Question. An alcohol on oxidation is found to give CH3COOH and CH3CH2COOH. The structure of the alcohol is:
(a) CH3CH2CH2OH
(b) (CH3)2C(OH)CH2—CH3
(c) CH3(CH2)3CH2OH
(d) CH3CHOHCH2CH2CH3
Answer
C
Question. HBr reacts fastest with
(a) 2-Mehtylpropan-1-ol
(b) 2-Methylpropene-2-ol
(c) propan-2-ol
(d) propan-1-o
Answer
B

(a) 1° > 2° > 3°
(b) 1° < 2° > 3°
(c) 3° > 2° > 1°
(d) 3° > 1° > 2°
Answer
C
Question. Methanol and ethanol are miscible in water due to
(a) covalent character
(b) hydrogen bonding character
(c) oxygen bonding character
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following compounds will not react with CH3MgBr?
(a) Ethyl acetate
(b) Acetone
(c) Dimethyl ether
(d) Ethanol
Answer
C
Question. What is the hybridisation of carbon and oxygen in electronic structure of ether?
(a) sp3 and sp2
(b) sp3 and sp3
(c) sp and sp
(d) sp2 and sp2
Answer
B
Question. If the boiling point of ethanol (molecular weight= 46) is 78°C, what is the boiling point of diethyl ether? (molecular weight= 74)
(a) 100°C
(b) 78°C
(c) 86°C
(d) 34°C
Answer
D
Question. Anisole is the product obtained from phenol by the reaction known as
(a) coupling
(b) etherification
(c) oxidation
(d) esterification
Answer
B
Question. One mole of an organic compound A with the formula C3H8 Oreacts completely with two moles of HI to form X and Y. When Y is boiled with aqueous alkali it forms Z. Z answers the iodoform test. The compound A is
(a) propan-2-ol
(b) propan-1 -ol
(c) ethoxyethane
(d) methoxyethane
Answer
D
Question. A simple method to remove peroxides from ethers is to treat them with an aqueous solution of
(a) KI
(b) KCNS
(c) Na2S2O3
(d) Br2
Answer
A
Question. Acetic anhydride reacts with diethyl ether in the presence of anhydrous AlCI3 to give
(a) CH3CH2COOH
(b) CH3CH2COOCH2CH3
(c) CH3COOCH3
(d) CH3COOC2H5
Answer
D
Question. Tert-butyl methyl ether on heating with anhydrous HI in ether gives
(a) CH3 OH + (CH3)3 Cl
(b) CH3I + (CH3)3 COH
(c) CH3I + (CH3)3 Cl
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question.
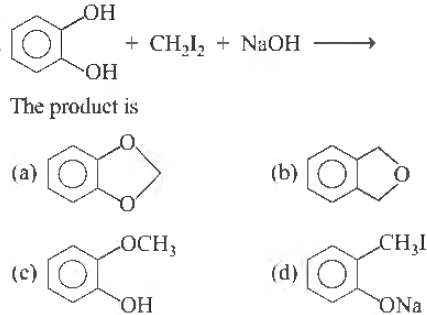
Answer
A
Question. The products obtained when anisole is heated in a sealed tube with HI are

Answer
A
Question. The reaction,
C2H5ONa + C2H5I → C2H5OC2H5 + NaI
is known as
(a) Kolbe’s synthesis
(b) Wurtz’s synthesis
(c) Williamson’s synthesis
(d) Grignard’s synthesis
Answer
C
Question. In Williamson’s synthesis ethoxy ethane is prepared by
(a) passing ethanol over heated alumina
(b) heating sodium ethoxide with ethyl bromide
(c) treating ethyl alcohol with excess of H2SO4 at 430-440 K
(d) heating ethanol with dry Ag2O
Answer
B
Question. Tertiary alcohols on reaction with KMnO4 at elevated temperature form
(a) aldehyde
(b) ketone
(c) mixture of carboxylic acids containing lesser number of carbon atoms
(d) mixture of carboxylic acids containing more number of carbon atoms
Answer
C
Question. The compound that reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
(a) butan-1-ol
(b) butan-2-ol
(c) 2 methylpropan-1-ol
(d) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Answer
C
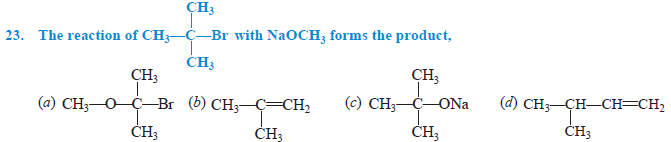
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
(a) C6H5OH
(b) C6H5CH2OH
(c) (CH3)3 COH
(d) C2H5OH
Answer
A
Question. Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields.
(a) o-Cresol
(b) m-Cresol
(c) 2, 4-Dihydroxytoluene
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer
C
Question. If ethanol dissolves in water, then which of the following would be observed
(a) absorption of heat and contraction in volume
(b) emission of heat and contraction in volume
(c) absorption of heat and increase in volume
(d) emission of heat and increase in volume
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds is oxidised to methyl ethyl ketone?
(a) 2-Propanol
(b) 1-Butanol
(c) 2-Butanol
(d) tert. Butyl alcohol
Answer
C
Question. When phenol is heated with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH when salicyladehyde is produced. This reaction is known as
(a) Rosenmund’s reaction
(b) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(c) Friedel-Crafts reaction
(d) Sommelet reaction
Answer
B
Question. Phenol is more acidic than alcohol because
(a) phenol is more stable than water
(b) phenol is aromatic and alcohol is aliphatic
(c) phenoxide ion is resonance stabilised
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Cresol has
(a) Alcoholic – OH
(b) Phenolic – OH
(c) – COOH
(d) – CHO
Answer
B
Question. Which statement is not correct about alcohol?
(a) Molecular weight of alcohol is higher than water
(b) Alcohol of less no. of carbon atoms is less soluble in water than alcohol of more no. of carbon atoms
(c) Alcohol evaporates quickly
(d) All of the above
Answer
B
Question. IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________
(a) 2-methylphenol
(b) 3-chlorophenol
(c) 3-methoxyphenol
(d) benzene-1, 3-diol
Answer
A
Question. Alcohols of low molecular weight are
(a) soluble in water
(b) soluble in water on heating
(c) insoluble in water
(d) insoluble in all solvents
Answer
A
Question. How many isomers of C5H11OH will be primary alcohols ?
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following on oxidation gives a ketone ?
(a) Primary alcohol
(b) Secondary alcohol
(c) Tertiary alcohol
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following has lowest boiling point ?
(a) p-Nitrophenol
(b) m-Nitrophenol
(c) o-Nitrophenol
(d) Phenol
Answer
C
Question. Acidity of phenol is due to
(a) hydrogen bonding
(b) phenolic group
(c) benzene ring
(d) resonance stabilisation of its anion
Answer
C
Question. The ionization constant of phenol is higher than that of ethanol because :
(a) phenoxide ion is bulkier than ethoxide
(b) phenoxide ion is stronger base than ethoxide
(c) phenoxide ion is stabilized through delocalization
(d) phenoxide ion is less stable than ethoxide
Answer
C
Question. Benzyl alcohol is obtained from benzaldehyde by
(a) Fittig’s reaction
(b) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(c) Kolbe’s reaction
(d) Wurtz’s reaction
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reacts with NaOH to give an alcohol?
(a) Propene
(b) Butene
(c) Ethanal
(d) Methanal
Answer
C
Question. By which of the following methods alcohol can be prepared in excellent yield?
(a) From alkenes
(b) By hydroboration-oxidation
(c) From carbonyl compounds
(d) From Grignard reagent
Answer
B
Question. Commercially carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols by converting them to the ______.
(a) esters
(b) aldehydes
(c) ketones
(d) amines
Answer
A
Question. Primary and secondary alcohols on action of reduced copper give
(a) Aldehydes and ketones respectively
(b) Ketones and aldehydes respectively
(c) Only aldehydes
(d) Only ketones
Answer
A
Question. When ethyl alcohol reacts with acetic acid, the products formed are
(a) Sodium ethoxide + hydrogen
(b) Ethyl acetate + water
(c) Ethyl acetate + soap
(d) Ethyl alcohol + water
Answer
B
Question. How many alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O are chiral in nature?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is dihydric alcohol ?
(a) Glycerol
(b) Ethylene glycol
(c) Catechol
(d) Resorcinol
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds is oxidised to preparemethyl ethyl ketone?
(a) 2-Propanol
(b) l-Butanol
(c) 2-Butanol
(d) t-Butyl alcohol
Answer
C

We hope the above multiple choice questions for Class 12 Chemistry for Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Alcohols Phenols and Ethers is an important chapter in Class 12 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 12 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
