Notes Chapter 16 Relational Databases
Introduction
- A Database System is basically a record keeping system.
- Collected form of data is known as database.
- “Database is actually a collection of interrelated data so that it can be used by various applications.
- Some of the Popular database softwares are-
- MySQL (open Source)
- ORACLE Database
- MS SQL Server
- SQLite (open Source)
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL (open Source)
Aim of DBMS
- Database Management System (DBMS) is a software whose purpose is to store databases, maintaining databases and using databases.
- Its prime purpose is to perform operarions on databses and to provide data when required.
- DBMS reduces Data Redundancy.
- It improves data security.
- it stores data n organized and Integrated form.
- Data remains error free.
- Data is available as and when required.
- Database follows a standard.
Relational Database Model
- In Relational Data model, data remains in the form of tables.
- A table is a combination of rows and columns which is also known as Relation .
- In a table, a row shows relationship between values. A table is a collection of this relationship.
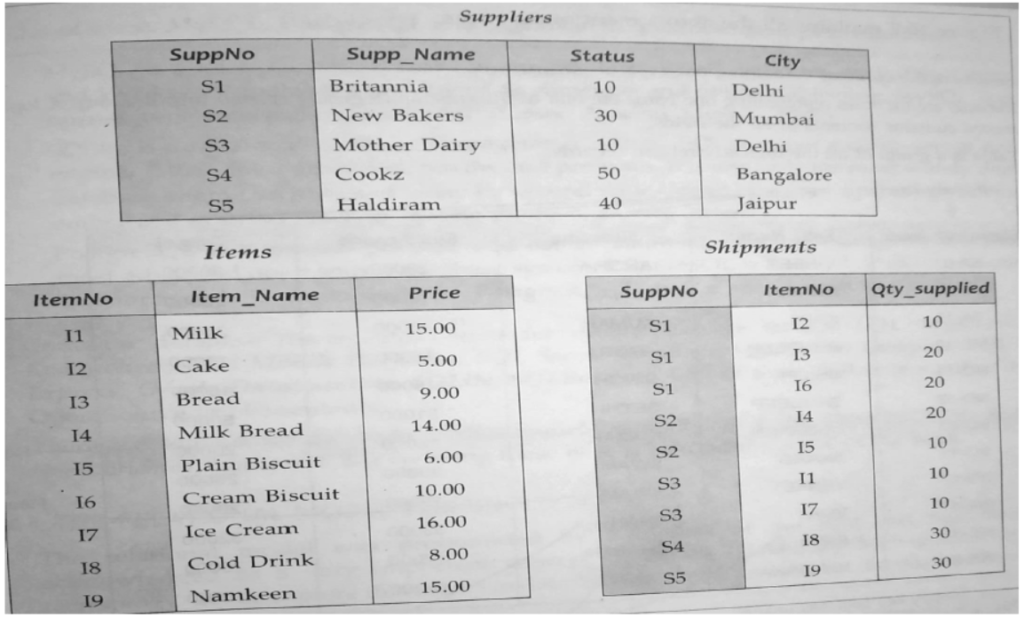
- Imagine a database has three tables- Suppliers, Items and Shipments :
Suppliers (SuppNo., Supp_name, Status, City)
Items (ItemNo., Item_name, Price)
Shipments (SuppNo., ItemNo., Qty_Supplied)

Relational Database Model
Components Of a Relation
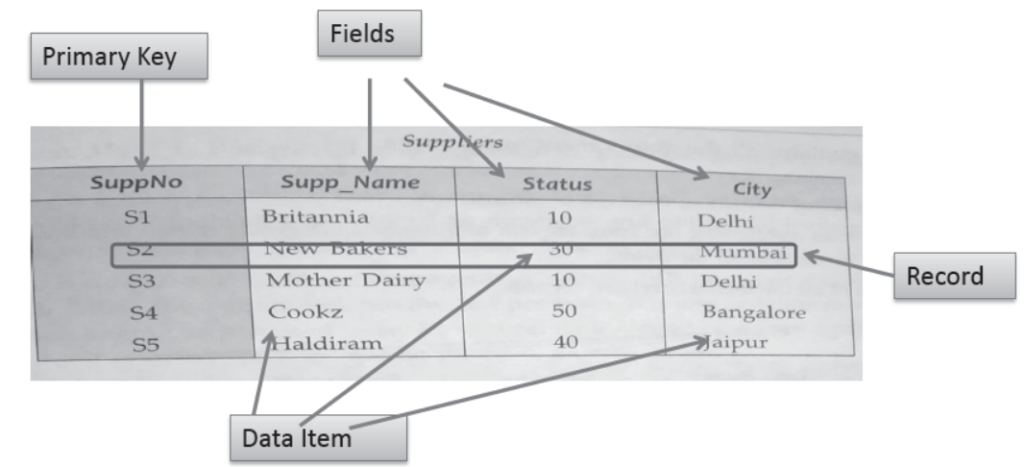
Byte: A group of 8 bits used to store a charater is known as byte.
Data Item: Smallest unit of data.
Record: It is a complete information composed of data item.
Table: A table is a collection of logical records.
Relational Model Terminology
- Relational Model was given by E. F. Codd of IBM.
- Terminology of Relation Model is-
- Relation: Basically a relation is a table. Its a collection of data in rows and columns. A relation has following features-
- In a table, data in one column should be of same data type. Different columns can have data of different data types.
- The value for each row and each column should be stomic. A column in a row can not have multiple values.
- In a relation, each row is distinct. Any two rows can ot have exactly same data.
- There is no specific order of rows in a relation.
- In a Relation, there is no specific order of columns.
Relational Model Terminology
- Domain: The pool of values for a column is known as Domain.
- Tuple : rows of a table are known as tuples.
- Attribute : columns of a table are known as attributes.
- Degree : In a relation, number of attributes or columns is known as its Degree.
- Cardinality : In a relation, number of tuples or rows is known as its Cardinality.
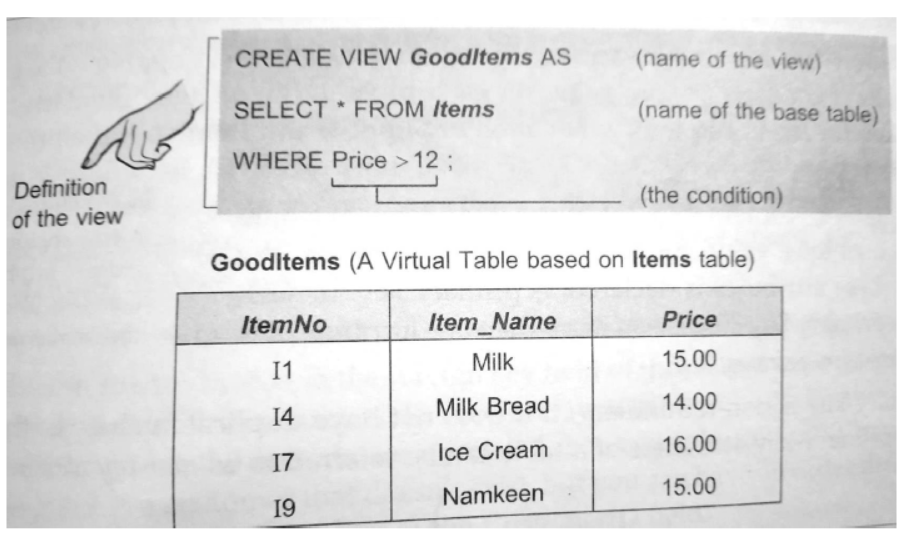
Views
- A View is a Virtual table which is based on some or specific data of a table.
- Command for creation of a View is
Keys
- Some attributes has some properties because of that those attributes are known as keys.
- Primary Key : It is a group of one or more attributes which are used to uniquely identify records of a relation and can be used to establish relationship with other relation. It is a mixture of unique constraint and not null constraint. Generally all master tables have primary keys. For ex- EmpCode in Employee table.
- Candidate Key : Its a group of attributes which have the properties to be selected as a primary key i.e. These attributes shows their candidature to be a Primary Key. For ex- RollNo, EnrollmentNo etc in student table.
- Alternate Key : A candidate key which is not a primary key is known as alternate key.
- Foreign Key : In a table, a non-key attribute which is derived from primary key of some other table is known as foreign key in present table.
Keys
- Referential Integrity: Referential integrity is a system of rules which is used by a DBMS to ensure that there is a valid relationshio between related tables or not. Refrential integrity is
- possible only when follwoing conditions gets completed-
- Primary key should have unique index.
- Related fields should have same datatype.
- All tables should be of same database.
- Primary key of Master table should have a refrence with forgien key of transaction table.
- Entry of that record in transaction table is not possible whose
- forgien key value does not exist in primary key of master table.
- Deletion of that record from primary key table is not possible which has a related record in foreign key table.
- Change in related records of primary key is not possible.
MySQL
- MySQL is an open source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) which makes use of SQL (Structured Query Language).
- It can be downloaded from www.mysql.org.
- In MySQL, information is stored in the form of tables.
- A MySQL database can have multiple tables and thousands of records simultaneously.
- It is a better option to store fast, reliable and big amount of data.
- MySQL was developed by MySQL AB company which is now a part of Sun Microsystems.
- SERVER : which responds to the requests of clients.
- CLIENTS : these are the programs which are attached to database server and send requests to server.
MySQL Features
- Fast Speed
- Easy to use.
- Free of cost.
- Support of SQL.
- Portability.
- Various Data types.
- Secure.
- Can handle large data (Scalability and limits).
- Connectivity : uses various protocols to get connected with clients.
- Localization : server can send error messages to clients in different laguages.
- Clients and Tools. It provides various client and utility programs.
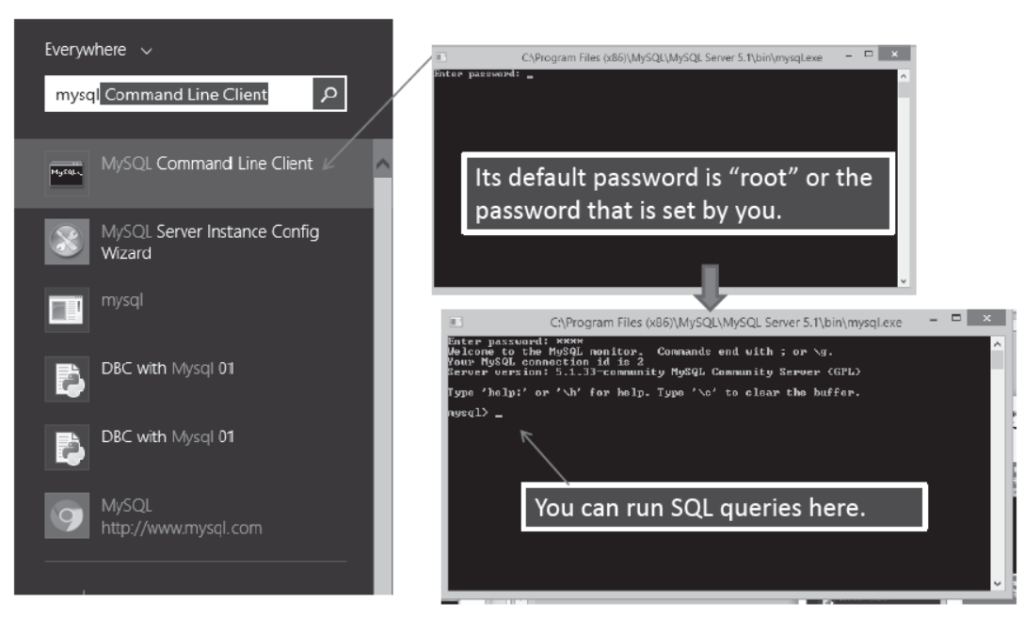
Starting MySQL
SQL
- Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to access any database.
- SQL stores the commands that are to be used in databases which are generally accepted by all RDBMS.
- SQL is a language which provides interface to create relational database and to operate upon them. – Various versions of SQL are available. First version was developed in 1970 by San Jose Research Laboratory of IBM.
- In 1992, 2003, 2008 some updates were added.
- SQL is being used by beginners and skilled users.
Processing Capabilties of SQL
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
2. Interactive Data Manipulation Language(DML)
3. Embedded Data Manipulation Language: these are developed to be used in some programming languages
4. View Definition
5. Authorization
6. Integrity
7. Transaction Control
Data Definition Language (DDL)
- Command under this category are used to create or modify scheme of database. It is used to create data dictionary.
- Data Dictionary is a kind of metadata means Data about Data. A standard DDL should have following functions-
- It should identify the types of data division.
- It should give a unique name of each data item.
- It should specify the proper data type.
- It may define the length of data items.
- It may define the range of values of Data items.
- It may specify means of checking for errors.
- It may specify privacy locks for preventing unauthorized reading or modification of the data.
DDL Commands
Following commands are under this category-
- Create, alter and drop schema Objects
- Create table, create view, create database,
- Alter Table
- Drop Table
- Drop View
- Create Index
- Alter Index
- Grant and Revoke privileges and rolls
- Grant
- Revoke
- Maintenance Commands
- Analyze Table
- Check Table
- Restore Table etc
DDL Commands
Following commands are under this category-
- Create, alter and drop schema Objects
- Create table, create view, create database,
- Alter Table
- Drop Table
- Drop View
- Create Index
- Alter Index
- Grant and Revoke privileges and rolls
- Grant
- Revoke
- Maintenance Commands
- Analyze Table
- Check Table
- Restore Table etc
DML Commands
- DML (Data Manipulation Language) is a kind of language used to access data, insert data and delete data from a data model.
- Data manipulation means-
- Accessing the stored data from a Database.
- Insertion of new information into the Database.
- Deletion of information from the Database.
- modification of information in the Database.
- DMLs are basically of two types-
- Procedural : specifies what data is needed and how to get it.
- Non- Procedural: specifies what data is needed without specifying how to get it.
TCL Commands
- A transaction is one complete unit of work for ex- withdrawl of 2000 Rs. From a bank Account.
- Following commands are used to successfully complete a transaction-
1. COMMIT : it makes all the changes permanent.
2. ROLLBACK : undoes all the changes.
3. SAVEPOINT : it marks a point upto which all earlier statments have been successfully completed.
4. SET TRANSACTION : it establishes properties for the current transactions.


