Notes Chapter 7 Directing
Class 12 students can refer to Chapter 7 Directing notes given below which is an important chapter in the class 12 Business Studies book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Business Studies teachers has prepared these notes for class 12 Business Studies for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Directing Notes Class 12 Business Studies
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Directing which is really useful and has been recommended by Class 12 Business Studies teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books.
DIRECTING:
Directing as a function of management, refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation to achieve its objectives.
Features:
1. Directing initiates action:
2. Directing takes place at every level of Management (Pervasive):
3. Directing is a continuous process
4. Directing flows from top to bottom:
Importance
1. Initiates Action: It helps to initiate action by the people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives. The employees start working only when they get instructions and directions from their superiors. It is the directing function which starts actual work to convert plans into results.
2. Integrates Employee’s Efforts: All the activities of the organisation are interrelated so it is necessary to coordinate all the activities. It integrates the activities of subordinates by supervision, guidance and counselling.
3. Means of motivation: It motivates the subordinates to work efficiently and to contribute their maximum efforts towards the achievement of organisational goals by satisfying their needs.
4. Facilitates change: Employees often resist changes due to fear of adverse effects on their employment and promotion. Directing facilitates adjustment in the organisation to cope with changes in the environ-ment. Directing instills the spirit of cooperation and commitment among work force.
5. Stability and balance in the organisation: Managers while performing directing function instruct, guide, supervise and inspire their subordinates in a manner that they are able to strike a balance between individual and organisational interests.
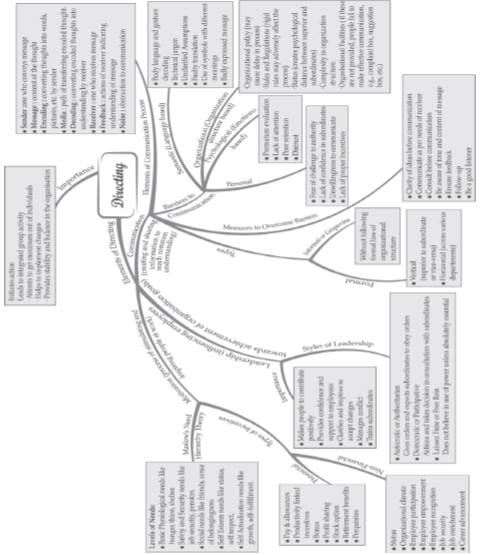
ELEMENTS OF DIRECTING:
1. Supervision: It means observing the subordinates at work to see that they are working in accordance with plans and to help them in solving their problems.. Supervisor’s position is immediately above the worker.
2. Motivation: In the context of an organisation motivation means stimulating employees of all levels to work with greater enthusiasm and more efficiency for the accomplishment of the objectives of the enterprises.
3. Leadership: Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for organisational goals. Leadership indicates the ability of an individual to maintain good interpersonal relations with followers and motivate them to contribute for achieving organisational objectives.
4. Communication: It is the process of exchange of information between two or more persons to reach common understanding.
Motivation Features
1. Motivation is an Internal feeling: Motivation is an internal feeling which means it cannot be forced on employees. The internal feeling such as need, desire, aspiration etc. influence human behaviour to behave in a particular manner.
2. Goal Directed Behaviour: It induces people to behave in such a manner so that they can achieve their goals. A motivated person works towards the achievement of desired goals.
3. Motivation can be either positive or Negative: Positive motivation means inspiring people to work better and appreciating a work that is well done e.g., pay increase, promotion, recognition.
4. Complex Process: It is a complex and difficult process. Individuals differ in their needs and wants and moreover human needs change from time to time.
5. Continuous Process: Human needs are unlimited and so they keep on changing continuously,
satisfaction of one need gives rise to another.
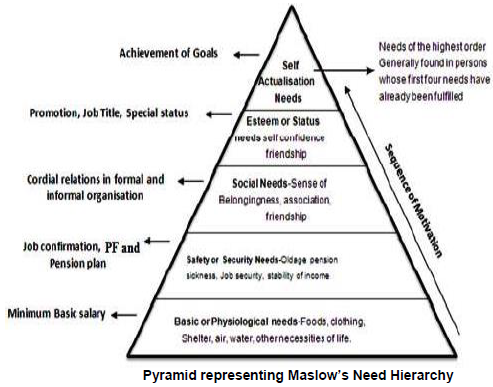
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy-Theory of Motivation:
It on the needs as the basis for motivation. It classifies human needs into five categories.
It helps managers to realise that need level of employees should be identified to provide motivation to them. It is based on the following assumptions:
(i) People’s behaviour is based on their needs.
(ii) People’s needs are in hierarchical order.
(iii) A satisfied need can no longer motivate a person.
(iv) A person moves to the next higher level of hierarchy only when the lower need is satisfied.
Financial and Non-Financial Incentives: Incentive means all measures which are used to motivate people to improve performance.
Financial Incentives (which can be calculated in terms of money)
1. Pay and allowances: Salary is the basic monetary incentive. It includes basic pay, dearness allowance and other allowances.
2. Productivity linked wage incentives: Aims at linking payment of wages to increase in productivity.
3. Bonus: An incentive offered over and above the wages/salary.
4. Profit sharing: It means to provide a share to employees in the profits. It creates a feeling of ownership to employees.
5. Co-partnership/Stock option: employees are offered company’s share at a price which is lower than market price.
6. Retirement benefits: Such as provident fund, pension and gratuity etc.
Non-Financial Incentives (which cannot be calculated in terms of money)
1. Status: Status means ranking of positions in the organisation. Psychological, social and esteem needs of an individual are satisfied by the status given to their job.
2. Organisational climate: Employees can be motivated with favourable atmosphere.
3. Career advancement opportunity: Works as a tonic and encourages employees to exhibit improved performance.
4. Job enrichment: If jobs are enriched and made interesting, the job itself becomes a source of motivation to the employees.
5. Employees recognition programmes: Most employees feel that what they should be recognised by the higher authorities.
6. Job security: Employees want their job to be secured and it is a strong motivator but on the other hand it makes the employees lazy.
7. Employee participation: It means involving employees in the decision making.
8. Employee empowerment: Means giving more autonomy and powers to subordinates.
Leadership: Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives. Managers at all levels are expected to be the leaders of their subordinates.
Features of leadership
a) Leadership indicates ability of an individual to influence others.
b) Leadership tries to bring change in the behaviour of others.
c) Leadership indicates interpersonal relations between leaders and followers.
d) Leadership is exercised to achieve common goals of the organistion.
e) Leadership is a continuous process.
Types of leadership
1.Autocratic or Authoritarian Leader
An autocratic leader gives orders and insists that they are obeyed. He determines the policies for the group without consulting them.He does not give information about future plans but simply tells the group what immediate steps they must take. Under this style, all decision making power is centralized in the leader. He does not give the subordinates any freedom to influence his decisions
2. Democratic or Participative Leader
Democratic leader gives order only after consulting the group and worksout the policies with the acceptance of the group.
He never asks people to do things without working out the long term plans on which they are working. He favours decision making by the group as shown in the diagram. This improves the attitude of the employees towards their jobs and the organization thereby increasing their morale.
3. Laissez Faire or Free Rein Leader
Free rein leader gives complete freedom to the subordinates. Such a leader avoids use of power. He depends largely upon the group to establish its own goals and work out its own problems. Group members work themselves as per their own choice and competence. The leader exists as a contact man with the outsiders to bring information and the resources which the group requires for accomplishing the job.
Communication
It is the process of exchange of information between two or more persons to reach common understanding.
Communication plays key role in the success of a manager. Directing abilities of manager mainly
depend upon his communication skills. That is why organization always emphasizes on improving communication skills of managers as well as employees.
Elements of Communication Process
1. Sender: Who conveys his thoughts or ideas.
2. Message: Ideas, feelings, suggestions, order etc.
3. Encoding: Converting the message into communication symbols such as words/pictures etc.
4. Media: Path/Channel through which encoded message is transmitted to receiver e.g., face to face, phone call, internet etc.
5. Decoding: Converting encoded symbols of the sender
6 Receiver: Who receives communication of the sender.
7 Feedback: All those actions of receiver indicating that he has received and understood
the message of the sender.
Importance of Communication
1. Acts as basis of coordination: It provides coordination among departments, activities and persons in the organisation.
2. Helps in smooth working of an enterprise: communication is basic to an organisation existence right from its birth through its continuing life.
3. Act as basis of decision making: Communication provides needed information for decision making.
4. Increases managerial efficiency: Communication is essential for quick and effective performance of managerial functions.
5. Promotes cooperation and Industrial Peace: The two-way communication promotes cooperation and mutual understanding between the management and workers and brings peace in the organisation.
6. Establishes effective leadership: Effective communication helps to influence subordinates. While influencing, a leader should possess good communication skills.
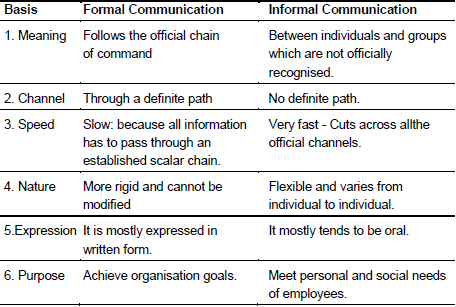
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION:
I. FORMAL COMMUNICATION.
II. INFORMAL COMMUNICATION
I. Formal Communication: refers to official communication which takes place following the chain of command. Classification of formal communication-
1. Vertical Communication: Flows vertically i.e., upwards or downwards through formal channels.
(i) Downward Communication: Higher to lower level like plans, policies, rules etc.
(ii) Upward Communication: Subordinate too superior like suggestions, grievances, reports etc.
2. Horizontal/lateral Communication: between persons holding positions at the same level of the organisation e.g., production manager may contact marketing manager about product design, quality etc.
Merits and demerits of formal communication Merits :
1. Orderly flow of information
2. Easy knowledge of source of information
3. Fixation of responsibility
4. Easy in control
Demerits:
1. Slow process
2. Lack of personal interest
3. Rigidity
4. Overload of work
II. Informal Communication: Communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication is said to be informal communication. There is no fixed direction or path for the flow of information. It is based on informal relations and arises out of personal and social needs of the employees.
Merits and demerits of Informal communication Merits :
1. Fast communication
2. Improved relation
3. Social satisfaction
4. Fill the gaps
Demerits :
1. Misrepresentation of messages
2. Carry rumours
3. Unorganised and irregular
4. Leakage of important facts
Difference between Formal & Informal Communication