Notes for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Financial Statements I
Students can refer to Notes for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Financial Statements I given below. These notes have been prepared keeping into consideration the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE and NCERT. Class 11 Chapter 9 Financial Statements I Notes is important to understand the topic and solve all questions given in DK Goel Class 11 Textbook
Unit at a glance:
• Meaning of Financial Statements
• Users of Accounting information
• Capital Nature Items
• Revenue Nature Items
• Operating Profit and Net Profit
• Trading Account
• Profit and Loss Account
• Balance Sheet
• Important Adjustments with their treatments in financial statements
• Generally Students commits these mistakes please avoid
“Financial Statements of a company shows its financial position for the current year”
Meaning :
The financial statement provide a summary of the accounts of a business enterprise.
Financial statement include two statements include two statements :
i) ‘Trading and Profit and Loss Account’ or Income Statement’ (To Know Profit or loss)
ii) Balance Sheet (To know value of assets and liabilities on the closing date of an accounting period)
Users of Accounting Information :
Internal Users : Management, Employees, Current owners
External Users : Potential Investors Government, Banks/Lenders, Stock Exchange, Suppliers and Trade Creditors, Public.
Capital Nature Items:
Capital Expenditure : Those expenditures which are incurred in acquiring and increasing the value of fixed assets. Ex.
1. Purchase of fixed assets or bringing into existence of fixed assets
2. Expenditure incurred on erection of a fixed asset
3. Payment of goodwill
4. Decrease in long term debts.
5. Capital Receipts : Any receipt from the sale of fixed assets is known as capital receipt.
Revenue Nature items :
Revenue Receipts : Receipts in the business of recuirring nature are called as Revenue receipts ex: rent received, discount received, commission received.
Revenue Expenditures : Recurring nature of expenditure done in the business which are done in order to earn profit are known as revenue expenditure ex.:
1. Purchase of goods during the year
2. Money spent in acquiring or manufacturing goods like freight, carriage, wages etc.
Any expenses for meeting day to day business like wages, salaries, postage etc.
OPERATING PROFIT AND NET PROFIT
After getting Gross Profit from the business. Profit may be divided into two parts :
1. Operating Profit, 2 Net Profit
Operating Profit : Operating profit is that profit which is earned through the normal activities of the business. It can be ascertained by deducting aqll operating expenses from the gross profit.
2. Net Profit : Net profit is that profit which is earned after deducting all operating as well as non operating expenses from the Gross Profit.
Trading Account :
Trading account is prepared to know the result of manufacturing and trading activities :
Ex: Prepare A Trading Account from the following particulars for the year ender March 31, 2007.

Solution :

Profit and Loss Account :
Profit and loss account is prepared to know the result of the business in the term of net profit Question for Practice:
Prepare Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2010 from the following particulars :
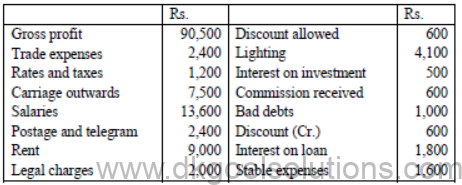
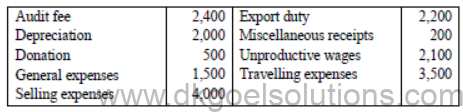

Question for Practice :
From the following trial balance of Raj & Co. prepare trading and profit and loss A/c for the year ending 31st March 2011 .
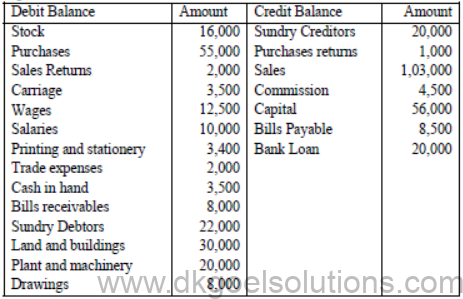

Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet is a statement prepared for showing the financial position of the business summarising its assets and liabilities at a given date.
Important Adjustments with their treatments
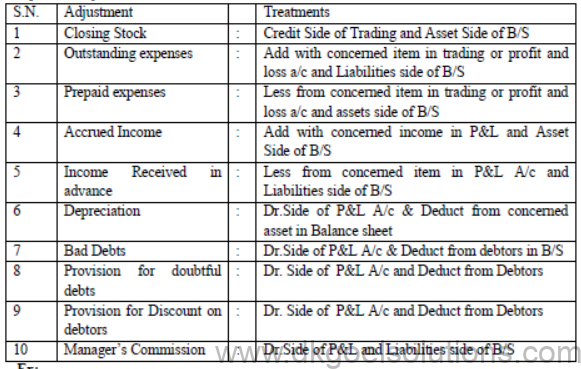
Ex:
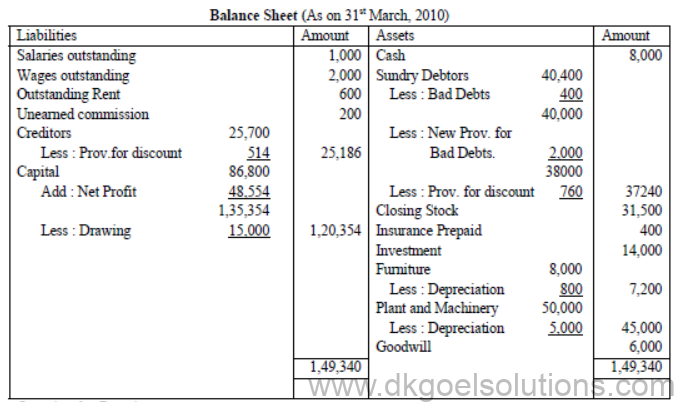
From the following figures prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2010 and a Balance Sheet as on that date :

Adjustments :
1. Stock on 31st march 2010 was Rs. 31,500
2. Salary and wages for March 2010 were unpaid.
3. Rent outstanding amounted to Rs. 600 and insurance unexpired amounted to Rs. 400.
4. Commission amounting to Rs. 200 has been received in advance.
5. Write off Rs. 400 as bad debts, create provision for doubtful debts at 5% on sundry debtors and provide 2% provision for discount on debtors and creditors.
6. Depreciate furniture and plant and machinery by 10%.
Solution :

Question for Practice :
Following is the Trial Balance of Rama & Co. for theyear ending 31st December 2010. Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet :
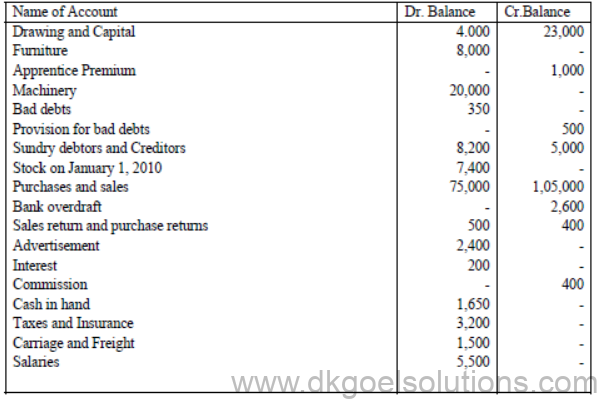
Adjustments :
The following adjustments are to be made :
(i) Stock in hand on 31st December 2010 was value Rs. 8,250/-
(ii) Salary is paid at Rs. 500 for month.
(iii) Tax outstanding Rs. 300 and insurance is prepaid Rs 400.
(iv) Write off furniture bad debts Rs. 200 and create provision for bad debts on debtors at 5%.
(v) Apprentice Premium Rs. 300 is related to 2011.
(vi) Commission Accrued Rs. 100.
Ans. G.P. 29250, NP 18300 and B/S 46000
1- Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold
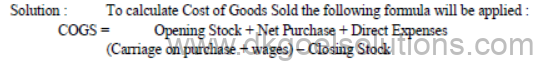
2- Confusion in calculating operating profit :

3- Marshalling and Grouping of Assets and Liabilities :

4- Provision for Bad Debts :
First of all deduct bad debts given in adjustment from the debtors
Calculate provision for doubtful debts on the amount of debtors
Deduct the amount of provision for doubtful debts given in credit side of trial balance
Questions for practice:
1. What are financial statements ?
2. Differentiate Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
3. Differentiate Capital Receipts and Revenue Receipts
4. Prepare Final Accounts of Mr. Sharad for theyear 31-3-09. Trial Balance 31-3-09
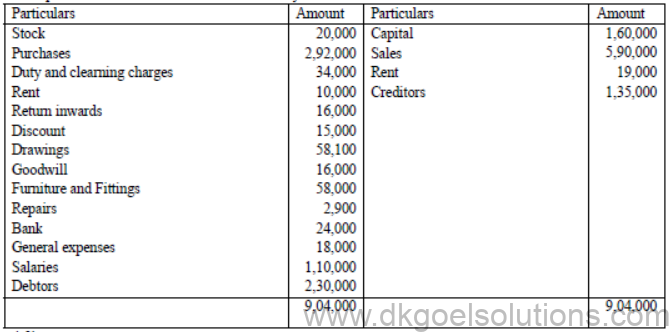
Adjustments :
1. General expenses include Rs. 5,000 chargeable to furniture pursed on ist October 1998.
2. Create a reserve of 5% on Debtors for Bad and Doubtful debts after treating Rs. 30,000 as a Bad Debt.
3. Balance at Bank as ascertained from the pass book is Rs. 22,500, the difference representing bank charges.
4. Rent for 2 months is outstanding.
5. Depreciate furniture and fittings @ 10% p.a.
6. Closing Stock was Rs. 40,000. There was a loss by fire on 20th March to the extent of Rs. 8,000.
Insurance Company admitted the claim in full.
7. Goods costing RS. 2,500 were used by the proprietor.
8. Goods costing Rs. 1,500 were distributed as free samples
Ans. G.P. 2,80,000, N.P. 97050 B/S 3,33,450
5. From the following Trial Balance of Mr.Sarthak for the year ended 31st March 2011.. Prepare Final Accounts.
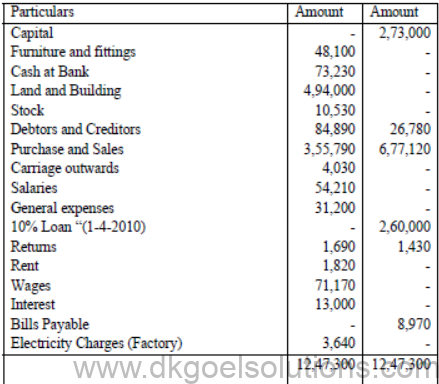
Additional Information :
1. Goods costingRs. 5,200 were taken by Sarthan for the personal use.
2. Salaries include Rs. 2,210 paid for the year ending 31-12-2012.
3. The debtors include Rohan who owned us Rs. 1,690 and has become insolvent and nothing is recoverable from his estate.
4. General expenses include Rs. 2,600 paid for wages.
5. Create a provision for doubtful debts @ 5% p.a.
6. Depreciate land and building @ 10% p.a. and furniture and fittings @ 20% p.a.
7. Closing stock was valued at Rs.20,280.
(Ans. G.P. Rs. 2,58,610 N.P. Rs. 81,290, Balance Sheet Rs.6,57,840)

