Notes for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 3 Financial Statements of a Company
Commerce students can refer to the Financial Statements of a Company Notes Class 12 Accountancy given below which is an important chapter in class 12 accountancy book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Accountancy teachers have prepared these notes for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Financial Statements of a Company Notes Class 12 Accountancy
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Financial Statements of a Company which are really useful and have been recommended by Class 12 Accounts teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books for Class 12 Accounts.
Question. Debenture redeemable after 12 years of the issue are shown as
(a) Long term borrowings
(b) Short term borrowings
(c) Other short-term liabilities
(d) Other long-term liabilities
Answer
Long term borrowings
Question. As per companies act, the Balance sheet is required to be presented
(a) Vertical Form
(b) Horizontal Form
(c) Either Vertical Form or Horizontal Form
(d) Any of the above
Answer
Vertical Form
Question. Sales is termed as
(a) Employee benefit expenses
(b) Revenue from operation
(c) Cost of material Consumed
(d) None of the above
Answer
Revenue from operation
Question. Income statement is termed as –
(a) Statement of profit and loss
(b) Trading Account
(c) Balance sheet
(d) Profit and loss
Answer
Statement of profit and loss
Question. Provision for tax appears in a company’s Balance sheet under the sub head –
(a) Long term provision
(b) Short term provision
(c) Other current liability
(d) None of the above
Answer
Short term provision
Question. Revenue from sales of goods is shown in the statement of profit and loss as-
(a) Other Income
(b) Revenue from operation
(c) Any of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer
Revenue from operation
Question. The prescribed form of balance sheet for the companies has been given in the schedule:
(a) III, Part I
(b) VI, Part I
(c) VI, Part II
(d) None of these
Answer
III, Part I
Question. Maximum amount of capital mentioned in the memorandum of association is known as
(a) Subscribed capital
(b) Authorised capital
(c) Called up capital
(d) Paid up Capital
Answer
Authorised capital
Question. Which statement is not included in final accounts of a company?
(a) Balance sheet
(b) Statement of profit and loss
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
None of the above
Question. List the items Shown under the head ‘Long term borrowings.
Answer
- Debentures
- Bonds
- Long term loans from Bank
Question. List any three items that can be shown under the heading ‘Reserves and surplus’ in a company’s balance sheet
Answer
- Security premium reserve
- General Reserve
Debenture redemption reserve
Question. List the sub heading which are shown under the headings ‘Current Liabilities ‘as per Schedule III part-1 of the companies Act.2013.
Answer.
(a) Short term borrowings
(b) Trade payables
(c) Other current liability
(d) Short term provision
Question. Prepare balance Sheet of XYZ Ltd. As at 31st March, 2013 from the details given below.


Solution:
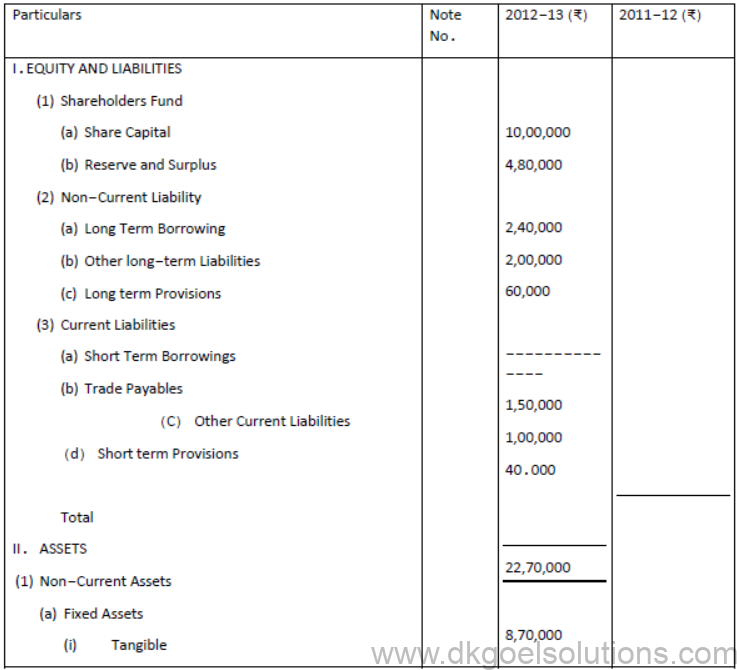
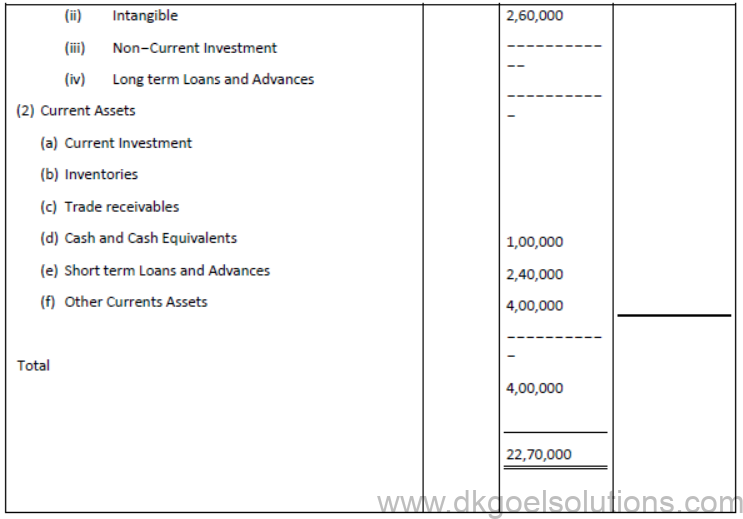
Question. From the following Information, Prepare Balance sheet of Goel Ltd:

Solution:

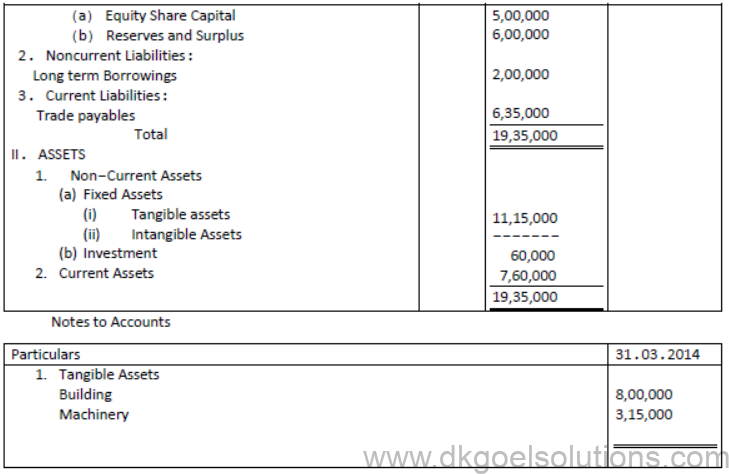
Question. XYZ Ltd. Has the following balances on 1st April 2013:

During the year ending 31st March 2014, it incurred a loss of ₹ 75,000. Show how these items will be shown in the balance sheet the company and Notes to accounts
Solution:


Question. Compute the change in Inventory of Stock in Trade if
Opening Inventory of stock in Trade ₹80,000
Closing Inventory of Stock in Trade ₹50,000
Solution: Opening Inventory of Stock in Trade 80,000
Less: Closing Inventory of Stock in Trade 50000
Change in Inventory of stock in Trade 30,000
Question. Under which major heads of the statement of profit and loss of a company following items will be shown –
(i) Material Purchased
(ii) Sales
(iii) Wages and Salaries
Answer. Material Purchased- Cost of Material Consumed
Sales- Revenue from operation
Wages and Salaries – Employee benefit expenses
Question. Out of the following, Identify the items that are shown in the Notes to accounts on employee benefit expenses –
(a) Wages
(b) Salaries
(c ) Entertainment expenses
(d) Bonus
(e) Gratuity Paid
(f) Conveyance Expenses
Answer. Wages, Salaries, Bonus and Gratuity Paid
Question. Out of the following, Identify the items that are shown in the Notes to accounts on Finance Cost
(a) Interest paid on term loan
(b) Interest paid on overdraft
(c) Interest received on fixed deposits
(d) Bank Charges
(e) Discount on Issue of debentures written off
Answer. Interest paid on term loan , Interest paid on overdraft, Discount on Issue of debentures written off
Question. Identify which of the following items are to be shown in the notes to accounts on other expenses
(a) Wages and Salaries
(b) Internet expenses
(c) Rent for Factory
(d) Depreciation on furniture
(e) Rent for office
(f) Audit Fees
(g) Staff welfare Expenses
(h) Courier expenses
Answer. Internet expenses, Rent for Factory, Rent for office, Audit Fees, Courier expenses
Question. Under which major head of the statement of profit and loss of a company following items will be shown
(i) Bonus
(ii) Material Purchased
(iii) Wages
(iv) Purchase of stock in trade
(v) Sales
(vi) Sale of Scrap
(vii) Interest earned
(viii) Gratuity Paid
Answer.

Question. Under which major heads of the statement of Profit and Loss of a company following Items will be shown
(i) Interest on public deposits
(ii) Entertainment Expenses
(iii) Discount on issue of debentures written off
(iv) Interest paid on debentures
(v) Profit on sale of Investment
(vi) Contribution of Provident Fund
(vii) Revenue from service rendered
(viii) Goodwill written off
Answer.

Solution:
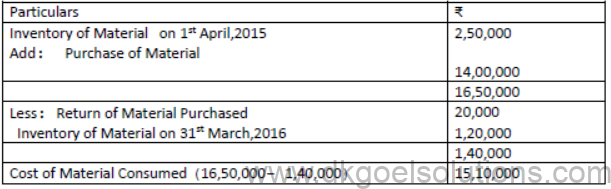
Question.Calculate Revenue from operation, other Income, and total revenue for a non- financial company from the following information

Solution:
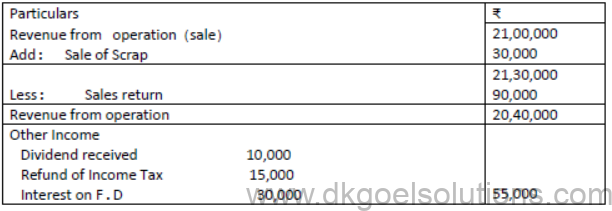
Question. From the following Information of Aroma Ltd, Prepare Statement of Profit and Loss as on 31st March 2016:


Solution:

Notes to Accounts

Question. From the following information Prepare Notes to accounts on Finance Cost :

Solution: Notes to accounts


Question. Prepare Statement of Profit and loss from the following particulars as on 31st March,2013

Notes for Financial Statements Of A Company class 12 Accountancy
Financial Statements are the end products of accounting process and are prepared at end of the accounting period to reveal the financial position of the enterprise at a particular date and the result of its business operations preparing an accounting period.
As per Section 2(40) of the Companies Act, 2013 Financial Statements includes:
1. Balance Sheet or Position Statement
2. Statement of Profit and Loss or Income Statement
3. Notes to Accounts.
4. Cash Flow Statement.
Balance Sheet: It is a statement of assets, liabilities and equities of a business and it is prepared to show the financial position of the company at particular date.
The balance sheet of a company is prepared as per the formal prescribed in part I of Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013.
The Schedule III prescribes only the vertical format for presentation of financial statements. Thus, a company will now not have an option to use horizontal format for the presentation of financial statements.
At contents of Balance Sheet
An asset is a resource controlled by the enterprise as a result of past events Pam which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise.
Liabilities is a present obligation of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources embodying economic benefits.
Equity is the residual interest in the assets of the enterprise after deducting all its liabilities.
Part I – Form of Balance Sheet


1. EQUITY AND LIABILITIES
I. (1) Shareholders’ funds
Under this head, following line items are to be disclosed:
• Share capital
• Reserves and surplus
• Money received against share warrants
(1)b.Reserves and Surplus
(i) Reserves and Surplus shall be classified as :
(a) Capital Reserves;
(b) Capital Redemption Reserve;
(c) Securities Premium Reserve;
(d) Debenture Redemption Reserve;
(e) Revaluation Reserve;
(f) Share Options Outstanding Account;
(g) Other Reserves – (Specify the nature and purpose of each reserve and the amount in respect thereof such as Tax Reserve);
(h) Surplus i.e. Balance in statement of Profit & Loss.
(i) Debit balance of Statement of Profit and Loss shall be shown as a negative figure under the head ‘surplus’. Similarly, the balance of ‘Reserves and Surplus’, After adjusting negative balance of surplus, if any, shall be shown under the head ‘Reserves and Surplus’ even if the resulting figure is in the negative.
1.3 Non-current liabilities
A liability shall be classified as non-current if it is not a current liability. The following items shall be disclosed under non-current liabilities.
Long-term borrowings Deferred tax liabilities (Net) Other Long term liabilities Long-term provisions
1.3.a. Long-termborrowings :
1.3.a. 1. Long-term borrowings shall be classified as :
(a) Bonds/debentures;
(b) Term loans; From banks;
From other parties;
(c) Deferred payment liabilities;
(d) Deposits;
(e) Loans and advances from related parties;
(f) Share Options Outstanding Account;
(g) Other loans and advances (Specify nature).
1.3.c Other Long-term liabilities
This should be classified into :
(a) Trade payables; (payable after 12 months from date of Balance sheet or after operating cycle); and
(b) Others.
A payable shall be classified as ‘trade payable’ if it is in respect of amount due on account of goods purchased or services received in the normal course of business operations.
1.3.c. Long-termProvisions
This amounts shall be classified as :
(a) Provision for employee benefits. Example: Provision for Provident Fund
(b) Other (specify nature). Example: Provision for Warranties.
I.4. Current Liabilities
1. A liability shall be classified as current when it satisfies any of the following criteria:
(a) it is expected to be settled in the company’s normal operating cycle; or
(b) it is held primarily for the purpose of being traded; or
(c) it is due to be settled within twelve months after the reporting date; or
(d) the company does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting date. Terms of a liability that could, at the option of the counter party, result in its settlement by the issue of equity instruments do not affect its classification.
2. An operating cycle is the time between the acquisition of an asset for processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. Where the normal operating cycle cannot be identified, it is assumed to have a duration of 12 months.
Short-term borrowings
Trade payables
Other Current liabilities
Short-term provisions
1.4.a. Short-term borrowings
Short-term borrowings are the borrowings which are payable within 12 months from the date of Balance Sheet or within the period of operating cycle. The following items are included in short term borrowings:
(a) loans repayable on demand;
(b) Bank overdraft and cash credit limit form banks;
(c) Loans from other parties repayable within 12 months;
(d) Deposits; and
(e) Other loans and advances (Specify nature).
1.4.c. Other current liabilities
The amounts shall be classified as :
(a) Current maturities of long-term debt;
(b) Current maturities of finance lease obligations;
(c) Interest accrued but not due on borrowings;
(d) Interest accrued and due on borrowings;
(e) Income received in advance;
(f) Unpaid dividends;
(g) Application money received for allotment of securities and due for refund and interest accrued thereon;
(h) Unpaid matured deposits and interest accrued thereon;
(i) Unpaid matured debentures and interest accrued thereon;
(j) Calls-in-Advance
(k) Other payables (specify nature).
1.4.d. Short-term Provisions
Provisions which are expected to mature within 12 months are classified as short term provisions.
The amounts shall be classified as :
(a) Provision for employee benefits;
(b) Others (specify nature).
Others would include Proposed Dividend, Provision for Taxation, Provision for expenses,
Warranty Provisions, etc. These amounts should be disclosed separately specifying nature thereof.
II. Assets
I. Non-Current Assets
(a) Fixed assets
(i) Tangible assets
(ii) Intangible assets
(iii) Capital work-in-progress
(iv) Intangible assets under development
(b) Non-current investments
(c) Deferred tax assets (net)
(d) Long-term loans and advances
(e) Other non-current assets
II. 1.a.i. Tangible assets
Tangible assets are the assets which have a physical existence. Assets that can be touched and seen are known as tangible assets.
The company shall disclose the following in the notes to accounts as per Part
I of the Schedule III :
(a) Land;
(b) Buildings;
(c) Plant and Equipment;
(d) Furniture and Fixtures;
(e) Vehicles;
(f) Office equipment;
(g) Other (specify nature).
II.1.a.ii. Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets are the assets which do not have a physical existence. These assets cannot be seen and touched.
(h) Classification shall be given as:
(a) Goodwill;
(b) Brands/trademarks;
(c) Computer software;
(d) Mastheads and publishing titles;
(e) Mining rights;
(f) Copyrights, patents and other intellectual property rights, services and operating rights;
(g) Recipes, formulae, models, designs and prototypes;
(h) Licenses and franchise;
(i) Other (specify nature).
1.a.iii. Capital Work-in-progress
It includes Fixed Assets which are under construction by the company itself.
II.1.a.iv. Intangible Assets under Development
Intangible Assets under development should be disclosed under this head provided they can be recognized based on the criteria laid down in AS-26. Examples are patents, computer software under development.
II.1.b. Non-CurrentInvestments
(i) Non-currents investments shall be classified as :
i. Trade investments; and ii. Other investments.
Trade investments
The “trade investment”is an investment mad by a company in shares or debentures of another company, to promote the trade or business of the first company.
Non-Current Investments is further classified as :
(a) Investment in property;
(b) Investment in Equity Instruments;
(c) Investment in preference shares;
(d) Investment in Government or trust securities;
(e) Investment in debentures or bonds.
(f) Investment in Mutual Funds;
(g) Investment in partnership firms;
(h) Other non-current Investments (specify nature)
Note :If a debenture is to be redeemed partly within 12 months and balance after 12 months, the amount to be redeemed within 12 months should be disclosed as current and balance should be shown as non-current.
1. d. Long-term loans & advances
Loans and advances that are not expected to be received back in cash or in the form of an asset within 12 months are known as Long-Term loans and advances.
(i) Long-term loans and advances shall be classified as :
(a) Capital Advances;
(b) Security Deposits;
(c) Loans and advances to related parties (giving details thereof);
(d) Other loans and advances (specify nature)
Capital advances are advances given for procurement of fixed assets which are non-current assets.
II.1.e. Other Non–CurrentAssets
Other non-current assets shall be classified as :
(i) Long Term Trade Receivables (including trade receivables on deferred credit terms);
(ii) Other (Specify nature)
A receivable shall be classified as ‘trade receivable’ if it is in respect of the amount due on account of goods sold or services rendered in the normal courses of business.
Important: The Schedule III does not contain any specific disclosure requirement for the unamortized portion of expense items such as share issue expenses, ancillary borrowing cost and discount or premium relating to borrowings.
We should disclose the unamortized portion of such expenses as “Unamortized expenses”, under the head ‘Other current assets”, depending on whether the amount will be amortized in the next 12 months or thereafter.
I.2. Current Assets
1. An asset shall be classified as current when it satisfies any of the following criteria :
(a) it is expected to be realized in, or is intended for sale or consumption n the company’s normal operating cycle; or
(b) it is held primarily for the purpose of being traded; or
(c) it is expected to be realized within twelve months after the reporting date; or
(d) it is cash or cash equivalent unless it is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least twelve months after the reporting date.
All other assets shall be classified as non-current.
2. An operating cycle is the time between the acquisition of an asset for processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. Where the normal operating cycle cannot be identified, it is assumed to have a duration of 12 months.
II.2.a. CurrentInvestments
Current Investments are the investments which are held to be converted into cash within, short period, i.e., within 12 months.
Current investments shall be classified as :
(a) Investment in Equity Instruments;
(b) Investment in preference shares;
(c) Investment in Government or trust securities;
(d) Investment in debentures or bonds.
(e) Investment in Mutual Funds;
(f) Investment in partnership firms;
(g) Other Investments (specify nature)
II.2.b. Inventories
Inventories shall be classified as :
(a) Raw materials;
(b) Work-in-progress;
(c) Finished goods;
(d) Stock-in-trade (in respect of goods acquired for trading);
(e) Stores and spares;
(f) Loose tools;
(g) Other (specify nature)
The heading Finished Goods should comprise of all finished goods other than those acquired of trading purposes.
II.2.c. Trade Receivables (current)
A receivable shall be classified as a ‘trade receivable’ if it is in respect of the amount due on account of goods sold or services rendered in the normal course of business.
A trade receivable will be treated as current if it is likely to be realized within 12 months from the date of Balance Sheet or Operating cycle of the business.
II.2.d. Cash and Cash Equivalents
As defined in AS-3, Cash flow Statement, cash and cash equivalents are share term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into known amount cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of change in value.
(i) Cash and cash equivalents shall be classified as :
(a) Balances with banks;
(b) Cheques, drafts on hand,
(c) Cash in hand;
(d) Other (specify nature)
II.2.e. Short–termLoans and Advances
(i) Short-term Loans and Advances shall be classified as :
(a) Loan and advances to related parties (giving details thereof):
(b) Other (specify nature)
(ii) Allowance for bad and doubtful loans and advances shall be disclosed under the relevant heads separately.
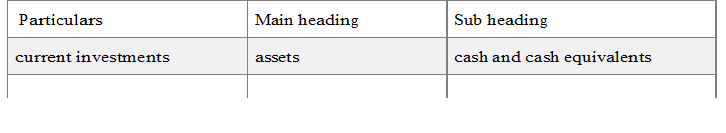
II.2.e.f. Other CurrentAssets (specify nature)
This is an all-inclusive heading, which incorporates current assets that do not fit into any other asset, categories e.g. Unbilled Revenue, Unamortized Premium on Forward Contracts, prepaid expenses, dividend receivable, advance taxes etc.
for example-

Statement of Profit and Loss
Statement of Profit and Loss: It is a statement prepared to show the result of business operations during an ccounting period.
It shows the operating performance of a company during the accounting period.
A Statement of Profit & Loss of a Company is prepared as per the format prescribed in Part II of Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013. for example -the main and sub headings for the following are
PART II – FORM OF STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS
Statement of Profit & Loss
For the year ended
(Rs. In………)


CONTENTS OF STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS
1. Revenue from Operations : It refers to the revenue earned by the company from its business operations.
Fox example :
(1) Revenue from sale of products or services
(2) Revenue from sale of scrap.
2. Other Income : It refers to the revenue earned by the company from activities other than its business operations.
For example :
(i) Interest Income
(ii) Dividend Income
(iii) Profit from sale of investments or fixed assets.
(iv) Bad debts recovered
(v) Excess provisions written back etc.
3. Cost of Material Consumed:
= Opening inventory of Raw Materials +Net Purchases of Raw Materials – Closing Inventory of Raw Materials.
Note: Inventory of Work-in-progress, Finished goods and Stock-in-trade are no considered for calculating cost of material consumed.
4. Purchase of Stock-in-Trade: It includes goods purchased for resale purpose in same form e., without any further processing.
5. Changes in Inventories of work-in-progress, finished goods and stock-in-trade.
= Opening Inventories – Closing Inventories
6. Employees Benefit Expenses : It includes all expenses incurred by the company on its employees such as :
(i) Wages, salaries, bonus etc.
(ii) Leave encashment, staff welfare expenses, etc.
(iii) Contribution to employees provident fund and other funds.
7. Finance Cost: It means cost incurred by a company on its borrowings e., debentures issued or loan taken by it.
Borrowing costs such as loan processing fees are also included in finance cost.
8. Depreciation and Amortisation expenses : Depreciation is the cost of tangible fixed assets written of over their useful life such as on building, plant & machinery etc.
Amortisation is the cost of intangible fixed assets written off over their useful life such as on patents, trademarks, computer software etc.
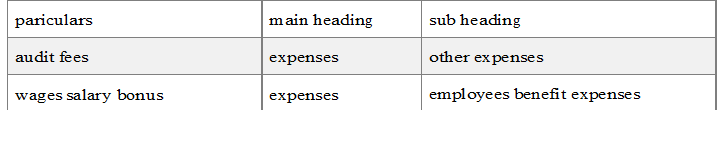
9. Other Expenses: Expenses that are not shown in any of the above mentioned heads are shown here.
For example:
(i) Carriage Inwards/Outwards
(ii) Audit Fees
(iii) Insurance charges
(iv) Rates & taxes
(v) Bank charges
(vi) Advertisement expenses
(vii) Administrative expenses
(viii) Selling and distribution expenses
(ix) Power and electricity expenses]
(x) Repairs of Fixed Assets etc.
(xi) Rent
(xii) Telephone expenses
(xiii) Sundry expenses


Also download : Question Papers for Class 12 Accountancy
And
DK GOEL SOLUTIONS Chapter 1: Financial Statements of a Company (As Per Schedule III)
DK GOEL SOLUTIONS Chapter 2: Financial Statement Analysis
