Notes for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Cash Flow Statement
Commerce students can refer to the Cash Flow Statement Notes Class 12 Accountancy given below which is an important chapter in class 12 accountancy book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Accountancy teachers have prepared these notes for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Cash Flow Statement Notes Class 12 Accountancy
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Cash Flow Statement which are really useful and have been recommended by Class 12 Accounts teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books for Class 12 Accounts.
Question 1. Classify the following into (i) Operating Activities, (ii) Investing Activities (iii) Financing Activities and (iv) Cash and Cash Equivalents while preparing Cash Flow Statement:
a. Cash Sales
b. Purchase of Building
c. Cash received from Trade Receivable
d. Sale of Building
e. Issue of shares
f. Dividend paid
g. Interest paid on Debenture by Finance Company
h. Cash Purchases
i. Depreciation
j. Selling and Distribution Expenses
k. Dividend received on share by finance company
l. Sale of investment by non-finance company
m. Current investment
n. Income tax Paid
Solution:
a. Operating Activities
b. Investing Activities
c. Operating Activities
d. Investing Activities
e. Finance Activities
f. Finance Activities
g. Operating Activities
h. Operating Activities
i. Operating Activities
j. Operating Activities
k. Operating Activities
l. Investing Activities
m. Cash and Cash Equivalents
n. Cash and Cash Equivalents
Question 2. On March 31st 2020 Ramesh and Co. indicated a profit of ₹ 1,25,000, after considering the following:

Additional Information

Solution :
Cash in hand will not affect Cash flow from operating activities.
Bank Overdraft is a financing Activities, hence it will not appear Cash Flow from Operating Activities.
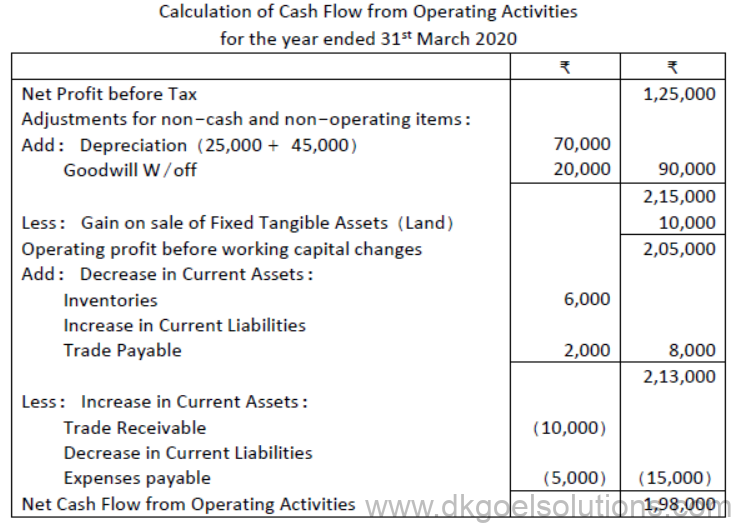
Question 3.From the following figures calculate cash from operating activities

Solution:

Note:

Question 4. Prateek Ltd. Made a profit of ₹ 5,00,000 after considering the following items:

Additional Information

Ascertain the net cash flow / use from operating activities.
Solution:
Calculation of Cash Flow from Operating Activities

Question 5. Prepare a Cash Flow Statement on the basis of the information given in the Balance Sheet of Neelakshi Trading Co. as at 31.03.2020 and 31.03.2019.
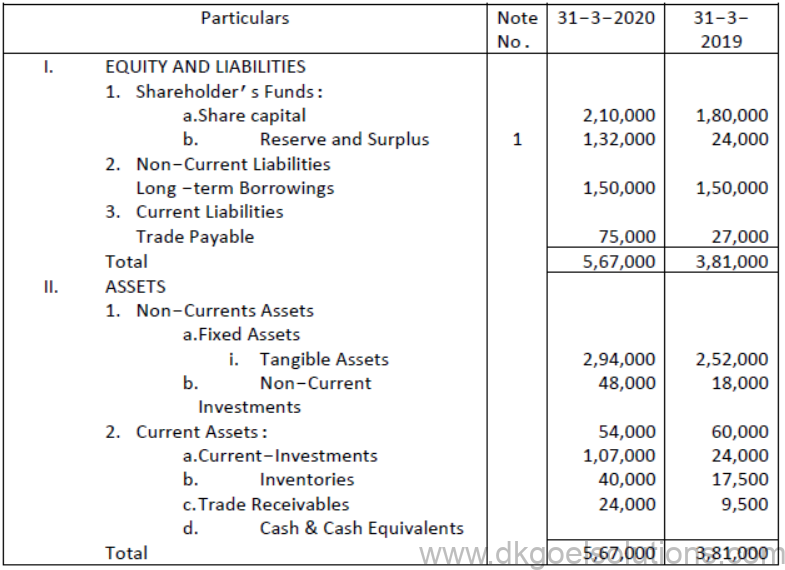
Notes:

Solution:

Notes

Question 6. Prepare a Cash Flow Statement on the basis of the information given in the Balance Sheet of Riddhiman Trading Co. as at 31.03.2020 and 31.03.2019

.Notes:

Additional Information:
- Depreciation provided on tangible assets (Machinery) during the year ₹ 8,000
- Interest paid on debentures ₹ 5,000.
Solution:


Notes

Notes for Cash Flow Statement class 12 Accountancy
Meaning: It is a statement that shows flow (Inflow or outflow) of cash and cash equivalents during a given period of time.
As per Accounting Standard-3 (Revised) the changes resulting in the flow of cash & cash equivalent arises on account of three types of activities i.e.,
(1) Cash flow from Operating Activities.
(2) Cash flow from Investing Activities.
(3) Cash flow from Financing Activities.
Cash: Cash comprises cash in hand and demand deposits with bank.
Cash equivalents: Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investment that are readily convertible into known amount of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of change in the value e.g. short-term investment. Generally these investments have a maturity period of less than three months.
Some examples of cash equivalent: Short-term deposits, marketable securities. Treasury bills, commercial papers, money market funds, money market funds, investment in preference shares if redeemable within three months provided that there is no risk of the failure of the company.
Cash flow exclude movements between items that constitute cash or cash equivalents because these components are part of the cash management of an enterprise rather than part of its operating, investing and financing activities.
Some types of transaction which are considered movement between cash and cash equivalents are given below:
1. Cash deposited into bank.
2. Cash withdrawn from bank.
3. Sale of cash equivalent securities (e.g. Sale of short-term investment, sale of commercial papers)
4. Purchases of cash equivalent securities (e.g. Purchase of short-term investment Purchases of Treasury bills).
The above types of transaction are part of cash and equivalents, so these are included in opening and closing cash and cash equivalent only. So these types of transaction no to be included in cash flow from different activities like perating investing, financing activities.
Preparation of cash flow statement

Note: The student should ensure that the Cash & Cash equivalent at the end of the year as calculated above will be same as cash & cash equivalent given in closing balance sheet.
Objectives of Cash Flow Statement
1. To ascertain how much cash or cash equivalents have been generated or used in different activities e., operating/investing/financing activity.
2. To ascertain the net changes in cash and cash equivalents.
3. To assess the causes of difference between actual cash & cash equivalent and related net earnings/income.
4. To help in formulation of financial policies such as dividend policy, fixed assets policy, capital structure related policy.
5. To help in short-term financial planning.
6. To ascertain the liquidity of enterprises.
Limitations of Cash Flow Statement
1. Non cash transaction are not taken into consideration like shares or debentures issued to vendors, depreciating charged during the year.
2. It is a statement related with past data.
3. It is not used for judging the profitability of enterprise.
4. Accrual accounting concept is ignored in this statement e.g. credit sales, credit purchases, outstanding expenses, accrued income are not included.
Computation of Cash flows from different activities.
(1) Cash flow from operating activities: Operating activities are the main revenue generating activities of the enterprises. It also includes all those transactions which are not included in investing and financing activities.
Indirect Method of calculating the cash flow from Operating Activities: Under this method Net Profit before Tax and Extra-ordinary Item is the starting point for further calculations. Calculation of Net Profit before Tax and Extra-ordinary Item:
Difference between closing balance and opening balance of Balance in statement of Profit & Loss A/c…………….
Add:
1. Proposed dividend for current year…………….
2. Interim Dividend paid during the year …………….
3. Profit Transferred to Reserve…………….
(If reserve of current year increased from previous year) …………….
4. Provision for Taxation made during the year…………….
5. Preference Dividend…………….
6. Extra Ordinary Item if any Debited to Statement of Profit & Loss…………….
Less:
1. Refund of Tax credited to Statement of P & L (………….)
2. Extraordinary-item if any Credited to Statement of P& (………….)
3. Reserves transferred back to statement of Profit and Loss(…………)
Net Profit before Tax and Extra-ordinary item (………….)
Extraordinary items: These items are not related to normal business operation
Format Cash Flow from Operating Activities


For the calculation of Proposed Dividend during the current year the proposed dividend account is to be prepared as follows:
Proposed Dividend Account

For the calculation of Provision for Taxation made during the current year the provision of Taxation account is to be prepared as follows:
Provision for Taxation Account

Illustration 1:
Cash Flow From Operating Activities


2. Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Investing activities are those activities which related to the acquisition (busying) and disposal (selling) of fixed assets and investment (other than cash equivalents). It also includes income from fixed assets and investment like rent received, interest received on investment, dividend received on investment in shares and mutual funds.

For the calculation of sale or purchase of fixed assets and investment, the following accounts are prepared:
1. Fixed Assets Account2.Investment Account
Fixed Assets Account: Fixed assets accounts may be prepared by two methods:
(a) At written down value method (when provision for depreciation account/accumulated depreciation account is not maintained):
Fixed Assets Account (at written down value)

(b) Fixed Assets (at cost); When provision for depreciation account or accumulated depreciation account has been separated maintained. In this method two separate account named Fixed Assets Account and Provision for Depreciation account are maintained.
Fixed Assets Account (at original cost)

Provision for Depreciation Account

Preparation of Investment Account:
Investment Account

3. Cash Flow from financing Activities
Financing activities are those activities that result in the changes in size and composition of the share capital (equality and preference) and borrowed fund of the business enterprises. Generally cost related to these funds also included in financing activities like interest paid on loans and debentures and dividend paid on equity and preference capital.


Note:
1. Bonus shares worth Rs. 5,00,000 issued to equity shareholder are not to be shown in the cash flow statement because there is no flow of cash by this activity.
2. If any other information is not given in the question about final dividend paid amount then the previous year proposed dividend is assumed as dividend payable in current year.
Current year proposed dividend amount is assumed as proposed dividend in current year and to be added in operating activities to calculated net profit before tax and extraordinary
item.
3. Previous year proposed dividend- unpaid divided = Final dividend paid during the current year is cash used in financing activities.
Financing Business Enterprise Transaction Treatment in Cash Flow statement Financing business enterprises are the business enterprises which deal in finance like investment companies, mutual fund house, banks. These enterprises purchase and sale of securities as their stock, so it is treated as operating activities and interest revived, dividend received and interest paid are considered as routine business activities and included in their operating activities.
Comprehensive

Also download : Question Papers for Class 12 Accountancy
