Sample Paper Class 12 Economics
Get Class 12 Economics Sample Papers free pdf download which is based on the latest pattern of CBSE and NCERT. It involves every one of the points given in NCERT class 12 Economics book. You can easily download sample paper accounts class 12 is given below.
Download 12th Economics Question paper in PDF free of charge. It will help you to make your preparation better to score higher marks in exams. These Class 12 Economics Sample Papers PDFs are prepared by our expert teacher.
This 12th Economics Question Paper PDF assists you with revising the complete chapter in minutes. One of the best tips suggested by teachers is Solving the sample papers during exam time.
We bring here the latest collection of Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics prepared as per the latest examination pattern issued by CBSE. Students can refer to the latest paper below available with answers and also download the suggested guess papers in PDF format for free. Students should solve the papers in exam type environment at home and then compare their results with the answers provided below. Students should regularly solve questions given in DK Goel Class 12 book and also solve the papers given below
Sample Paper Class 12 Economics Term 1 Set A
Section A
1. When government takes decision related to the economic problems of what, how and for whom to produce, this refers to ……… economic structure.
(a) capitalist
(b) socialist
(c) mixed
(d) None of these
Answer
B
2. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Disinvestment of public sector unit is an example of revenue receipts.
Statement II Disinvestment results in decrease in assets of the government for a particular fiscal year.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
3. The upper limit imposed on import of goods during the initial economic reform is known as ……… .
(a) Tariff
(b) Quota
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
B
4. Which of the following functions of money has simplified the process of borrowings and lendings?
(a) Medium of exchange
(b) Unit of account
(c) Story of value
(d) Standard of deferred payments
Answer
D
5. The schedule C of IPR 1956 was left for ……… companies.
(a) public sector
(b) private sector
(c) Both (a) and
(b) (d) None of these
Answer
B
6. Choose the correct pair from given below.
Column I Column II
A. Market determination of exchange rate (i) Fixed exchange rate
B. Planned determination of exchange rate (ii) Managed floating exchange rate
C. Devaluation of currency (iii) Balance of trade surplus
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) All of these
Answer
C
7. ……… is the most important component of the process of human capital formation.
(a) Right to information
(b) Right to work
(c) Defence
(d) Education
Answer
D
8. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Colonial government made no efforts to count the number of poors in the country.
Statement II Jail cost of living index developed by Dadabhai Naoroji was used to compute poverty line during the colonial rule in India.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
9. Farmers need credit for variety of purposes, ……… is the reason for taking medium term credit.
(a) personal expenditures
(b) purchase of seeds, pesticides etc
(c) purchases of fixed assets
(d) None of these
Answer
B
10. India experienced high infant mortality rate during colonial rule owing to which of the following reasons?
(a) Poor health infrastructure
(b) Low level of literacy
(c) Lack of public investment
(d) All of these
Answer
D
11. Increase in foreign exchange rate leads to ……… in balance of payments.
(a) improvement
(b) deterioration
(c) No impact
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer
A
12. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Indian goods and services tax model is based upon the Australian model of indirect tax reform.
Statement II GST replaced all existing direct taxes in the country.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
D
13. Asmall-scale industry is presently defined as the one whose investment does not exceed ₹ 5 crores. During the initial reform, the limit was only ₹ 5 lakhs and gradually increased later on. What other provision(s) were made by the government to protect SSI?
(a) Reservation of goods for SSI
(b) Subsidies
(c) Protected from foreign competition
(d) All of these
Answer
D
14. Fiscal policy of the government budget is comprised of ……… .
(a) revenue policy
(b) expenditure policy
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
15. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Revenue deficits need not be always inflationary in nature.
Statement II A deficit in budget leads to inflation when the money is used for consumption purposes.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
16. Import substitution means substituting imports with domestic production. Imports were protected by the imposition of tariff and quotas which protect the domestic firms from foreign competition. Choose the most appropriate reason for opting this strategy.
(a) Save foreign exchange reserve
(b) Allow domestic industries to grow
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
17. Cross-boarder transactions are recorded in ……… .
(a) government budget
(b) balance of trade
(c) balance of payments
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
C
18. The time period between 1991 to 2003 is known for ……… in agricultural sector in India.
(a) green revolution
(b) golden revolution
(c) white revolution
(d) blue revolution
Answer
B
19. In general terms, minimising the deficits are considered as a good measure but in the context of government budget which of the following types of deficits should never be equal to zero?
(a) Revenue deficit
(b) Fiscal deficit
(c) Primary deficit
(d) All of these
Answer
C
20. Purchase of shares of Microsoft by Tata will be recorded in ……… account and ……… side of balance of payments account.
(a) current account and credit
(b) current account and debit
(c) capital account and credit
(d) capital account and debit
Answer
D
21. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Supply of foreign exchange is inversely proportional to foreign exchange rate.
Statement II Increase in foreign investment leads to rightward shift in the demand curve for foreign exchange.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
D
22. Floating exchange rate is fixed by ……… .
(a) government
(b) central bank
(c) market forces
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
C
23. Under managed floating exchange rate, when exchange rises more than the desired level, which of the following steps central bank should take?
(a) Supply foreign exchange from its stock
(b) Demand for more foreign exchange in the market
(c) No intervention in the market
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer
A
24. Marketable surplus refers to ……… in agriculture sector.
(a) production for self-consumption
(b) production for selling in market
(c) selling of excess crops in market
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Section B
25. Assertion (A) A balanced budget indicates a balanced development of the country.
Reason (R) A budget is said to be balanced when estimated revenue is equal to estimated expenditure.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
26. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Autonomous items are independent of state of balance of payments.
Statement II Accommodating transactions are done to earn profit from rest of the world.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
A
27. Assertion (A) Stability in the economy promotes both economic growth and development.
Reason (R) Price and interest rate stability brings stability in overall economic situation.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
28. Assertion (A) Unilateral transfers are one-way transactions recorded in capital account of BoP.
Reason (R) Items which impact the liabilities or assets of the country at a given point of time, are recorded in capital account of BoP.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Both are false
Answer
C
29. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Central bank and central government works in isolation of each other.
Statement II Economic growth leads to increase in demand for money in the economy.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
30. Choose the correct pair from given below.
Column I Column II
A. Promotion of multilateral trade (i) Objective of WTO
B. Production on contractual trade (ii) Outsourcing
C. Trade between two countries (iii) Bilateral trade
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) All of these
Answer
D
31. ……… is/are the most critical problem(s) in the process of human capital formation in India.
(a) Lack of proper manpower planning
(b) Growth rate of population
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
B
32. Assertion (A) When CRR is increases, credit creation capacity of commercial banks reduces.
Reason (R) With increase in reserve ratios, banks have less funds available for loans.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
33. Institutional agricultural reforms introduced during 1950s are comprised of which of the following?
(a) Abolition of intermediaries
(b) Land reforms
(c) Removal of land removal systems
(d) All of these
Answer
D
34. Which of the following statements is/are true about the state of India’s industry during colonial rule?
(a) Deindustrialisation of handicraft industries
(b) Lack of capital goods industries
(c) Lack of public investment
(d) All of these
Answer
D
35. Assertion (A) Public expenditure generates investment-friendly environment in the economy for both domestic investors and foreign investors.
Reason (R) Increase in public expenditure leads to infrastructural development.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
36. Match the correct pairs of column I and column II given below.
Column I Column II
A. Sustained source of living (i) Golden revolution
B. Rise in the production of fruits and vegetables (ii) Diversification
C. Production of different types of crops together (iii) Non-farm activity
Codes
A B C A B C
(a) (i) (ii) (iii) (b) (ii) (i) (iii)
(c) (iii) (i) (ii) (d) (ii) (iii) (i)
Answer
C
37. Assertion (A) Land reform policy of India during first phase of economic reforms, faced a major setback.
Reason (R) People with money and power misused the loopholes in the systems and delayed the process of implementation of institutional reforms in agriculture.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
38. In ……… states, land reforms were successfully implemented.
(a) Haryana
(b) Kerala
(c) West Bengal
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
39. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Fixing a cap in the maximum holding of land is known as land ceiling.
Statement II Land ceiling policy was introduced to stop the role of intermediaries in agriculture.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
D
40. Choose the true statement from given below.
(a) Land reforms gives ownership right to the actual tillers of the soil
(b) Land redistribution from the people having more than to those having no land is the process of land ceiling
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
41. Through which of the following way, large landowners created hurdles in the process of implementation of land reforms?
(a) By challenging the policy in court
(b) By registration of land in the name of close relative
(c) By bribing the authorities
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
42. ……… is not a cause of poverty.
(a) Debt trap
(b) Unemployment
(c) Economic growth
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
C
43. Reducing inequality of income and wealth is one of the major objectives of budget by which it reduces the difference between the states. Economic development is not possible without development of all regions. Which of the following fiscal tools are used for the attainment of this objective?
(a) Taxes
(b) Subsidies
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
44. Assertion (A) Green revolution introduced in India during 1960s was a partial success and limited to fewer regions.
Reason (R) Most of the farmers in the country are small and marginal who cannot afford to buy expensive equipments required in modern farming methods.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
45. Assertion (A) Liberalisation policy in India was imposed by the international monetary fund and not intentionally implemented.
Reason (R) India was a highly indebted country before 1990s with huge burden of interest payments and BoP crisis.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
46. Planning commission was replaced in year ……… .
(a) 1990
(b) 2010
(c) 2015
(d) 2020
Answer
C
47. Assertion (A) Poverty leads to loss of human capital formation leading to the loss of resources for the economy.
Reason (R) Prolonged unemployment and poverty lead to developing the sense of hopelessness and loss of confidence.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
48. Observe the picture given below carefully.
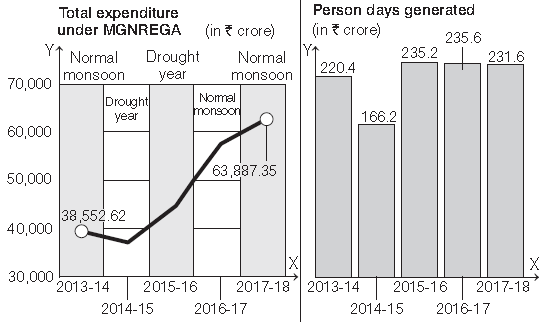
What is total expenditure on MGNREGA in a normal monsoon season?
(a) 38,552.62 crores
(b) 63,887.35 crores
(c) 220.4 crores
(d) 231.6 crores
Answer
B
Section C
Direction : – Read the following case study and answer questions 49 to 54 on the basis of the same.
During the independence, money lenders and traders played a significant role in exploiting the small and marginal farmers and landless labourers by lending to them on high interest rates and by manipulating the accounts to keep them in a debt-trap. It was only during 1969, when a major change occurred when India adopted social banking and multi-agency approach to adequately meet the needs of rural credit.
The institutional structure of rural banking today consists of a set of multi-agency institutions, namely, commercial banks, regional rural banks, cooperatives and land development banks. They are expected to dispense adequate credit at cheaper rates.
In recent times, self-help groups have emerged to fill the gap in the formal credit system. The SHGs promote thrift in small proportions by a minimum contribution from each member. From the pooled money, credit is given to the needy members to be repayable in small installments at reasonable interest rates.
By May 2019, nearly 6 crore women in India have become member in 54 lakh women SHGs. About ₹ 10-15,000 per SHG as a community investment support fund are provided as part of renovating fund to take up self-employment for income generation.
49. Institutional credit excludes which of the following institutions given below?
(a) Land development banks
(b) Reginal rural banks
(c) Self-help groups
(d) All of these
Answer
C
50. Assertion (A) Commercial banks in rural areas played an insignificant role to bridge the gap between formal and informal lending.
Reason (R) Commercial banks work to earn profit and the incidence of defaults are high in rural banking.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
51. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Institutional credit availability is imperative for development of rural areas.
Statement II Reserve Bank of India is the apex institution in rural banking to regulate the banking system.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
A
52. Which of the following is not an advantage of institutional credit?
(a) Varying maturity
(b) Fixed interest rate
(c) Non-manipulation of accounts
(d) All of these
Answer
A
53. As of May, 2019, how many women SHGs are functional in the country?
(a) 15,000
(b) 6 lakhs
(c) 54 lakhs
(d) 60 lakhs
Answer
C
54. SHGs becomes eligible to get credit from formal source when
(a) they are regular for more than one year
(b) they are consisting of large number of members
(c) they are comprised of both men and women
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Direction : – Read the following case study and answer questions 55 to 60 on the basis of the same.
India money supply surge signals pandemic-related uncertainty, not growth. Heightened uncertainty in India caused by the coronavirus pandemic has led to a surge of currency in circulation as people hoard cash or park money in accessible deposits to safeguard themselves against salary cuts or job losses.
According to RBI data, India’s M3 money supply rose 6.7% in the first five months of this year as compared to the same period last year, the highest growth in seven years.
Currency in circulation, which measures money with the public and in banks has also surged.
A rise in money supply usually is seen as a leading indicator of growth in consumption and business investments, but the rise this time is unlikely to bolster either, analysts said. Source The Economic Times, 23rd June, 2020.
55. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Money supply in an economy is a flow variable.
Statement II Quantum of money in the economy changes overtime.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
56. As mentioned in the above paragraph that India’sM3 rose by 6.7% during first five months of 2020,M3 is a ……… .
(a) component of money supply
(b) measure of money supply
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
B
57. Assertion (A) Rise inM3 increased economic growth during first half of 2020.
Reason (R)M3 is considered as broad money and less liquid as it is comprised of components which cannot be converted in cash easily.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
C
58. The most liquid measure of money supply,M1 is also known as ……… .
(a) broad money
(b) narrow money
(c) base money
(d) high powered money
Answer
B
59. A rise in money supply is an indicator of which of the following in general times?
(a) Growth in consumption
(b) Business investment
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
60. As per the data given above,M3 rose by 6.7% during the first five months of this year.
Which of the following will be the impact of this move in the economy as a whole?
(a) Increase in money supply
(b) Increase in purchasing power of money
(c) Decrease in purchasing power of money
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D

