Notes Chapter 8 Controlling
Class 12 students can refer to Chapter 8 Controlling notes given below which is an important chapter in the class 12 Business Studies book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Business Studies teachers has prepared these notes for class 12 Business Studies for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Controlling Notes Class 12 Business Studies
Refer to the notes and important questions given below for Controlling which is really useful and has been recommended by Class 12 Business Studies teachers. Understanding the concepts in detail and then solving questions by yourself will help you to learn all topics given in your NCERT Books.
CONTROLLING
Meaning & Definition
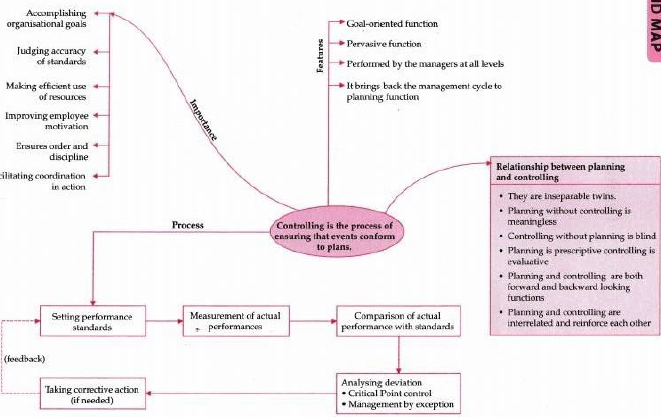
Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals.
It can be defined as comparison of actual performance with the planned performance.
. Nature of Controlling/Features of Controlling
1. Controlling is a goal oriented function: Controlling as a function of management ensures that the overall directions of individuals and groups are consistent with short and long range plans of the organization.
2. Controlling is an all pervasive function: Controlling is a function which is applicable to all types of organizations business and non-business and at all managerial levels.
3. Controlling is a continuous function: Control is not a one time activity. Rather, it is a dynamic process that involves constant analysis of actual and planned performance.
4. Controlling is both a backward looking as well as forward looking function: Under controlling past performance is analysed, therefore controlling is backward looking. On the basis of this past performance analysis, remedial action is taken to make future performance better, in this way controlling is forward looking.
5. Controlling is a dynamic process: Since controlling requires taking reviewable methods, changes have to be made wherever possible.
Importance of Controlling
1. Controlling helps in achieving organizational goals: The controlling function measures progress towards the organizational goals and brings to light/indicates corrective action.
2. For Evaluating/Judging accuracy of standards: A good control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate or not by careful check on the changes taking place in the organizational environment.
3. Making efficient use of resources: By the process of control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage of resources.
4. Improves employee’s motivation: A good control system ensures that employees know well in advance what they are expected to do & also the standard of performance. It thus motivates & helps them to give better performance.
5. Facilitating Coordination in action: In controlling each department and employee is governed by predetermined standards which are well coordinated with one another. Control provides unity of direction.
6. Ensuring order and discipline: Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organization by keeping a close check on the activities of its employees.
Q NO 1. If planning is done carefully and accordingly other functions of management are going in the right direction, then there is no need of the controlling function of management. Do you agree with this statement? Give reasons in support of your answer.
[Hint- Controlling is still required to check whether performance is as per plans or not.]Controlling Process
1. Setting Performance Standards: Standards are the criteria against which actual performance would be measured. Thus standards become basis for comparison and the manager insists on following of standards.
Standards can be set in both quantitative as well as qualitative terms. Is is important that standards should be flexible enough to be modified whenever required. Standards should be SMART as:
S – Simply Expressed M – Measurable
A – Attainable
R – Reasonable T – Time bounded
2. Measurement of Actual Performance: Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner which includes personal observation, sample checking. Performance should be measured in same terms in which standards have been established, this will facilitate comparison.
3. Comparing Actual Performance with Standard: This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired performance. If the performance matches the standards it may be assumed that everything is under control.
4. Analysing Deviations: The deviations from the standards are assessed and analysed to identify the causes of deviations.
Page99
Deviations are analysed in the light of pre-determined deviation tolerance limit and key result areas.
a) Critical point control (CPC): It is neither economical nor easy to have a check on all the activities of an organisation. Hence, the manager should pay more attention on those activities which are important and critical to the success of an organisation. These are known as Key Result Areas- KRA’s.
Example: 2% increase in stationery cost is not critical. But 2% increase in wages Salaries is critical.
b) Management by Exception (MBE): A manager should take corrective action only when there is exceptional deviation i.e. when they cross the permissible limit or acceptable range. Deviations within acceptable range are ignored.
Example: Wastage within Normal Wastage Range may be ignored. But if wastage crosses this limit and becomes Abnormal then management should control.
5. Taking Corrective Action: The final step in the controlling process is taking corrective action. No corrective action is required when the deviations are within the acceptable limits. But where significant deviations occur corrective action is taken.
Q NO 2. “Comparing the actual performance with laid standard, finding out deviations and taking corrective action is an important process of a function of management.” Name the process.
[Hint- Controlling Process]Limitations of Controlling
1. Little control on external factors: Generally no enterprise can control external factors such as government policies, technological changes, competitions etc.
2. Resistance from employees: Control is often resisted by employees. They see it as a restriction on their freedom e.g. Employees may resist and go against the use of cameras to observe them minutely.
3. Costly affair: Control is a costly affair as it involves a lot of expenditure of time and efforts.
4. Difficulty in setting quantitative standards: Control system looses some of its
effectiveness, when standards cannot be defined in quantitative terms. In the absence of quantitative standards, comparison with standards becomes difficult.

