Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set A
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set A with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 12 Chemistry issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 12 Chemistry exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry for Set A
1. Define Kraft temperature.
Answer : The temperature above which formation of micelles takes place is called Kraft temperature.
2. The electronic configuration of a transition element in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d7. Find out its atomic number.
Answer : Atomic number = Total number of electrons in neutral atom
= 18 + 7 + 3 = 28
3. Draw the structure of 4-tert-butyl-3-iodoheptane.
Answer :
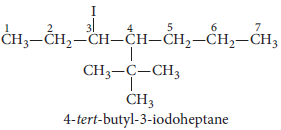
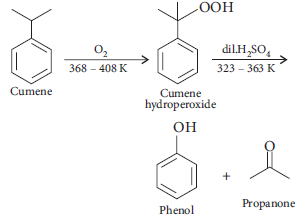
4. Give the equation of reaction for the preparation of phenol from cumene.
Answer :
5. Name the type of semiconductor obtained when silicon is doped with boron.
Answer : When silicon is doped with boron, p-type semiconductor is obtained.
6. The two complexes of nickel, [Ni(CN)4]2– and [Ni(CO)4], have different structures but possess same magnetic behaviour. Explain.
Answer :
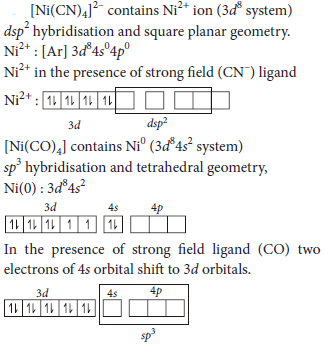
It has no unpaired electrons hence, it is diamagnetic. Thus, [Ni(CN)4]2– and [Ni(CO)4] have different structures but same magnetic behaviour.
OR
A chloride of fourth group cation in qualitative analysis gives a green coloured complex [A] in aqueous solution which when treated with ethane-1,2-diamine (en) gives pale -yellow solution [B] which on subsequent addition of ethane-1,2-diamine turns to blue/purple [C] and finally to violet [D]. Write the structures of complexes [A], [B], [C] and [D].
Answer : Aqueous solution of NiCl2 gives a green colour due to the formation of following complex :
NiCl2 + 6H2O → [Ni(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 2Cl–
(A)
When ethane-1,2-diamine (en) is added to above complex, the colour changes to pale-blue, which on further addition of ethane-1,2-diamine changes to blue/purple and finally to violet. This occurs due to the following ligand replacement reactions :

7. Account for the following :
(i) XeF2 is linear molecule without a bend.
(ii) The electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for fluorine is less than that of chlorine, still fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine.
Answer : (i) The electronic arrangement in XeF2 is trigonal bipyramidal. The shape is linear because the lone pairs prefer to occupy the equatorial positions. The molecule XeF2 has 3 lone-pairs and 2 bondpairs.
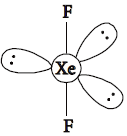
(ii) Fluorine has higher standard reduction potential than chlorine, so it is more easily reduced and hence, it is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine.
8. Derive the relationship between relative lowering of vapour pressure and mole fraction of the volatile liquid.
Answer : Let us assume a binary solution in which the mole fraction of the solvent be x1 and that of the solute be x2, p1 be the vapour pressure of the solvent and p1° be the vapour pressure of the solvent in pure state.
According to Raoult’s law : p1 = x1p1° …(i)
The decrease in vapour pressure of the solvent (Δp1) is given by :
⇒ Δp1 = p1°– p1
⇒ Δp1 = p1° – p1° x1 [using equation (i)]
⇒ Δp1 = p1° (1 – x1)
Since we have assumed the solution to be binary solution, x2 = 1 – x1
⇒ Δp1 = p1° x2 ⇒ x2 = Δp1/p1°
9. After 24 hours, only 0.125 g out of the initial quantity of 1 g of a radioactive isotope remains behind. What is its half-life period?
Answer :

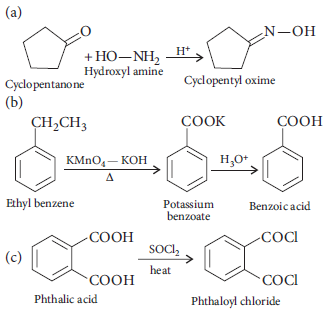
10. Write the IUPAC names of the following :

Answer :
11. The edge length of a unit cell of a metal having molar mass 75 g/mol is 5 Å which crystallises in a cubic lattice. If the density is 2 g/cm3, then find the radius of the metal atom.
Answer :

12. (i) A mixture of X and Y was loaded in the column of silica. It was eluted by alcohol water mixture. Compound Y eluted in preference to compound X. Compare the extent of adsorption of X and Y on column.
(ii) Why copper matte is put in silica lined converter? Write the reactions involved?
(iii) Name the method used for the refining of Zr.
Answer : (i) Extent of adsorption is inversely proportional to elution. Hence, X is more strongly adsorbed than Y.
(ii) Copper matte contains small amount of FeO as impurity which is removed as FeSiO3 slag when reacts with silica. Therefore, it is put in silica lined converter.
FeO + SiO2 →(slag)FeSiO3
(iii) van Arkel method is used for refining of Zr.
13. (i) Complete the following chemical equations :
(a) NH4Cl(aq.)+ NaNO2 (aq.) →
(b) P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O →
(ii) Why is Ka2 << Ka1 for H2SO4 in water?
Answer : (i) (a) NH4Cl(aq) + NaNO2(aq) →N2(g) + 2H2O(l) + NaCl(aq)
(b) P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O → 3NaH2PO2 + PH3
(ii) H2SO4 is a very strong acid in water because of its first ionisation to H3O++ and HSO4– . The ionisation of HSO4– to H3O+ and SO42– is very less as it is difficult to remove a proton from a negatively charged ion.
Therefore, Ka2 << Ka1.
14. Write the correct formulae for the following coordination compounds :
(i) CrCl3.6H2O (violet with 3 chloride ions precipitated as AgCl)
(ii) CrCl3.6H2O (light green colour, with 2 chloride ions precipitated as AgCl )
(iii) CrCl3.6H2O (dark green colour, with 1 chloride ion precipitated as AgCl )
Answer : (i) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(ii) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2·H2O
(iii) [Cr(H2O)4(Cl)2]Cl·2H2O
15. Give reasons for the following observations :
(i) p-Dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than those of o- and m-isomers.
(ii) Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
(iii) The treatment of alkyl chloride with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohol but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkene is the major product.
Answer : (i) The melting point of p-dichlorobenzene is higher than that of o-and m-isomers. This is because, p-isomer has symmetrical structure and therefore, its molecules can easily pack closely in crystal lattice. Hence, it has stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than o- and m-isomers.
(ii) In haloarenes the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring and the following resonating structures are possible.
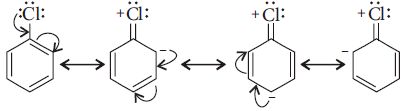
C – Cl bond acquires a partial double bond character due to resonance. As a result, the bond cleavage in haloarenes is difficult than in haloalkanes and therefore, they are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
(iii) Alkoxide ion present in alcoholic KOH is not only a strong nucleophile but also a strong base. So, it reacts with alkyl halide to give alkene as the major product.
R—CH2—CH2—Cl alc. KOH R—CH CH2
On the other hand, aqueous KOH is a good nucleophile and when it reacts with alkyl chloride it forms alcohol.
R—CH2—CH2Cl aq. KOH R—CH2—CH2—OH
16. (i) Why does leather get hardened after tanning?
(ii) On the basis of Hardy-Schulze rule explain why the coagulating power of phosphate is higher than chloride.
(iii) Do the vital functions of the body such as digestion get affected during fever? Explain your answer.
Answer : (i) Animal hides are colloidal in nature having positively charged particles. When soaked in tannin which contains negatively charged colloidal particles, mutual coagulation occurs, which results in the hardening of leather.
(ii) Greater the valency of flocculating ion added, greater is its power to cause precipitation. Valency of phosphate ion is three while that of chloride is one. Hence, phosphate has higher coagulating power than chloride.
(iii) The optimum temperature range for enzymatic activity is 298-310 K. Hence, beyond this temperature range (during fever), the activity of enzymes may be affected.
17. Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molarmass 40 g/mol) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
Answer : Vapour pressure of pure liquid = p°
80% of p° = ps = 80 × p°/100 = 0.8 p°
ps = p° × xsolute
Mass of solute = x g
Mass of solvent = 114 g
Molar mass of solute = 40 g/mol
Molar mass of solvent (octane) = 114 g/mol
Number of moles of solute = x/40 = 0.025x
Number of moles of solvent = 114/114 = 1 mole
Mole fraction of solvent = 1/(1 + 0.025x)
0.8p° = p° × 1/(1 + 0.025x)
or, (1 + 0.025x) 0.8p° = p° …(i)
On dividing equation (i) by 0.8p° we get,
1 + 0.025x = 1.25
On subtracting both side by 1 we get, 0.025x = 0.25 Now, dividing by 0.025, we get x = 10 g
OR
At 300 K, 36 g of glucose (C6H12O6) present per litre in its solution has an osmotic pressure of 4.98 bar. If the osmotic pressure of another glucose solution is 1.52 bar at the same temperature, calculate the concentration of the other solution.
Answer : From formula of osmotic pressure, πV = CRT where, p = osmotic pressure
V = Volume of solution, C = Concentration
R = gas constant, T = Temperature
So, 4.98 = 36/180 × R × 300 = 60R …(i)
1.52 = C × R × 300 …(ii)
Putting the value of R from (i) in (ii) we get, C = 0.061 M
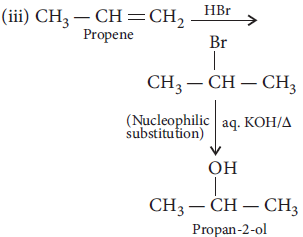
18. Carry out the following conversions :
(i) Phenol to benzoquinone
(ii) Propanone to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Propene to propan-2-ol
Answer :

19. (i) Illustrate the following reactions :
(a) Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction
(b) Coupling reaction
(ii) Write a chemical test to distinguish between aniline and methylamine.
Answer : (i) (a) Hoffmann bromamide degradation :
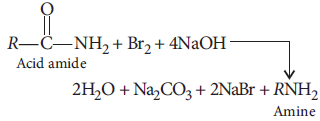
Acid amide on reaction with bromine and alkali such as NaOH, an amine is formed which has one carbon atom lesser than the initial amide molecule.

When arenediazonium chloride reacts with electron rich species like phenol, it undergoes coupling reaction to form p-hydroxyazobenzene.

Aniline will give azo dye test whereas methylamine will not.
20. (i) Name the common types of secondary structure of proteins and give one point of difference.
(ii) Give one structural difference between amylose and amylopectin.
Answer : (i) a – helix structure : In this type of structure, the long peptide chains undergo formation of H – bonding between the
bonds of different peptide groups within the same chain. As a result the polypeptide chain gets coiled up to form a right handed helix.
β-pleated sheet : n this structure, the long peptide chains lie side by side to form a flat sheet. Each chain is held by the two neighbouring chains by H-bonds (N – H …….. O C).
(ii) Amylose is a straight chain polymer of D-glucose whereas amylopectin is branched polymer.
21. Observe the graph in diagram and answer the following questions :

(i) If slope is equal to –2.0 × 10–6 sec–1, what will be the value of rate constant?
(ii) How does the half-life of zero order reaction relate to its rate constant?
Answer : (i) From the graph, it is clear that it is first order kinetics.
For first order,
log [R] = −kt log/2.303 + log [R]0
Comparing it with general straight line equation, y = mx + c
Slope(m) = − k/2.303
k = – 2.303 × – 2.0 × 10–6 s–1 = 4.606 × 10–6 s–1
(ii) Half-life of zero order reaction is directly proportional to initial concentration as shown, t1/2 = [R]0/2k
22. (i) Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers : Terylene, Bakelite, Polyvinyl chloride, Polythene.
(ii) Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S.
Answer : (i) Addition polymers : Polyvinyl chloride, polythene Condensation polymers : Terylene, Bakelite
(ii) Buna-N is a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile and Buna-S is a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene.
23. Ali’s brother likes taking medicines. He sometimes even takes cough syrups even when he is not ill. One such day, he took cough syrup when he was healthy. After some time he started feeling nausea, headache and his body
started itching. Ali’s father did not take him to the doctor and wanted to give medicine on his own. Ali insisted that his father should not give medicine to his brother on his own but should take him to a doctor.
After reading the above passage, answer the
following questions :
(i) Mention the values shown by Ali.
(ii) Why did his body start itching and what kind of medicine will doctor prescribe him?
(iii) Why medicines should not be taken without consulting doctor?
(iv) Give one point of difference between agonist and antagonist.
Answer : (i) Caring, empathetic, awareness, application of knowledge at right place.
(ii) Because of production of histamine his body starts itching. So, doctor will prescribe antihistamine.
(iii) Medicines should not be taken without consulting doctor because medicines can be potent poisons which depends upon how vital that medicine is and in how much quantity it is taken.
(iv) An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor and activates the receptor to produce a biological response whereas antagonist is a drug that blocks a receptor.
24. (i) State the relationship amongst cell constant of a cell, resistance of the solution in the cell and conductivity of the solution. How is molar conductivity of a solution related to conductivity of its solution?
(ii) A voltaic cell is set up at 25°C with the following half cell; Al/Al3+ (0.001 M) and Ni/Ni2+ (0.50 M). Calculate the cell voltage. ( E°Ni2+/Ni = − 0.25 V , E°Al3+/Al = − 1.66 V)
Answer : (i) Conductivity of the solution is the ratio of cell constant and resistance of a cell and can be written as
k = G/R
Molar conductivity of a solution is related to conductivity as,
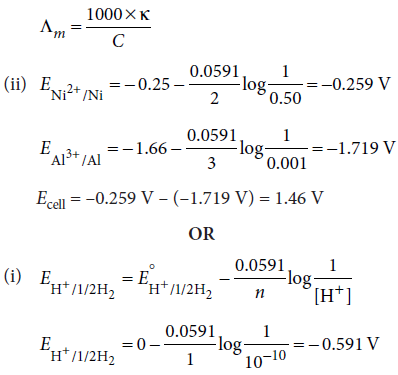
OR
(i) Calculate the potential of hydrogen electrode in contact with a solution whose pH is 10.
(ii) State Faraday’s laws of electrolysis. How much charge in terms of Faraday is required for reduction of 1 mol of Cr2O72– to Cr3+?
Answer :
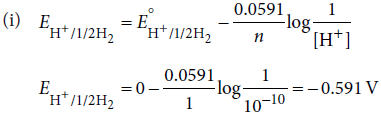
(ii) Faraday’s first law of electrolysis states that, the chemical deposition due to flow of current through an electrolyte is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity (coulombs) passed through it, i.e., w ∝ Q or w = ZQ.
Faraday’s second law of electrolysis states that, when the same quantity of electricity is passed through several electrolytes, the mass of the substances deposited are proportional to their respective chemical equivalent or equivalent weight.
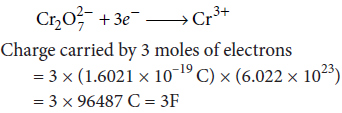
25. (i) Is the variability in oxidation number of transition elements different from that of non-transition elements? Illustrate with examples.
(ii) Give reasons :
(a) d-block elements exhibit more oxidation states than f-block elements.
(b) Orange solution of potassium dichromate turns yellow on adding sodium hydroxide to it.
(c) Zirconium (Z = 40) and Hafnium (Z = 72) have almost similar atomic radii.
Answer : (i) Variability of oxidation states of transition metals arises due to incomplete filling of d-orbitals and it differs from each other by unity e.g., V(V), V(IV), V(III), V(II). In p-block elements oxidation states differ generally by a unit of two. e.g., Sn(II), Sn(IV), PCl3, PCl5, etc.
(ii) (a) d-block elements exhibit more oxidation states because of comparable energy gap between (n – 1) d and ns subshell whereas f-block elements have large energy gap between (n – 2)f and (n – 1) d subshell.
(b) When an alkali such as NaOH is added to orange solution of potassium dichromate, it turns yellow due to the formation of chromate.
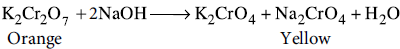
(c) Due to lanthanoid contraction, Zr (230 pm) and Hf (225 pm) have almost same atomic radii.
OR
(i) Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate from pyrolusite ore. Write balanced chemical equation for one reaction to show the oxidising nature of potassium permanganate.
(ii) Draw the structures of chromate and dichromate ions.
Answer : (i) Preparation of potassium permanganate : Potassium permanganate is prepared by the fusion of MnO2 (pyrolusite) with potassium hydroxide and an oxidising agent like KNO3 to form potassium manganate which disproportionates in a neutral or acidic solution to form permanganate.
2MnO2 + 4KOH + O2 → 2K2MnO4 + 2H2O
3K2MnO4 + 4HCl → 2KMnO4 + MnO2 + 2H2O + 4KCl
A reaction to show oxidising nature of potassium permaganate is,

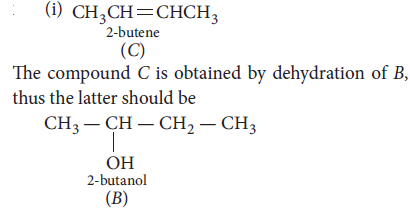
26. (i) A ketone A which undergoes haloform reaction gives compound B on reduction. B on heating with sulphuric acid gives compound C, which forms mono-ozonide D. The compound D on hydrolysis in presence of zinc dust gives only acetaldehyde. Write the structures and IUPAC names of A, B and C. Write down the eactions involved.
(ii) Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with following reagents :
(a) PhMgBr and then H3O+.
(b) Tollens’ reagent.
Answer :


OR
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products :
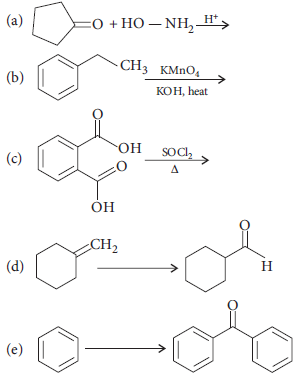
Answer :