Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science Notes
Students should read Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science Notes provided below. These notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and books issued by NCERT, CBSE and KVS. These important revision notes will be really useful for students to understand the important topics given in the chapter Carbon and Its Compound in Class 10 Science. We have provided class 10 science notes for all chapters.
Revision Notes Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science
Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound is an important chapter in Class 10 Science. The following notes will help you to understand and easily learn all important points to help you score more marks.
Carbon and its Compounds
Chapter map
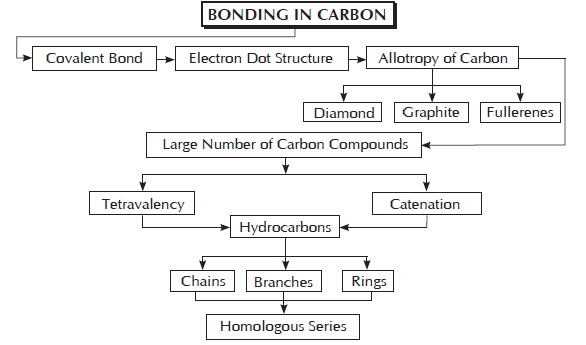
Topic 1. Bonding in Carbon: The Covalent Bond and Versatile
Nature of Carbon
Carbon: Carbon has atomic number 6, mass number 12. It has 6 protons, 6 electrons and 6 neutrons. Its electronic configurations is 2, 4. It has four valence electrons. It belongs to group 14 and second period of the periodic table.
Organic Compounds: Those compounds which contain carbon essentially alongwith hydrogen and mostly, oxygen, sulphur, nitrogen, halogen, etc.
Covalent bond: The bond which is formed by equal sharing of electrons is called covalent bond.
Covalency of Carbon: Carbon has four valence electrons. It cannot lose 4 electrons because high energy is needed to remove 4 electrons. It can share four electrons to form four covalent bonds, therefore its covalency is equal to 4, i.e. it shows tetravalency.
Single Covalent bond: The bond formed by sharing one electron each is called single covalent bond, e.g. the following molecules have single bonds.

Double Covalent bond: When two atoms share two electrons each, double covalent bond is formed.

Triple covalent bond: When two atoms share three electrons each, triple covalent bond is formed.

Properties of Covalent Compounds:
(i) They are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
(ii) They do not conduct electricity as they do not form ions.
(iii) They have low melting and boiling points.
(iv) They exist in solid, liquid as well as in gaseous state.
Allotropes: The property due to which one element exist in more than one form, which differ in physical properties but have similar chemical properties. These forms of element are called allotropes.
Allotropes of Carbon: Diamond, Graphite and Fullerenes are crystalline allotropes of carbon.
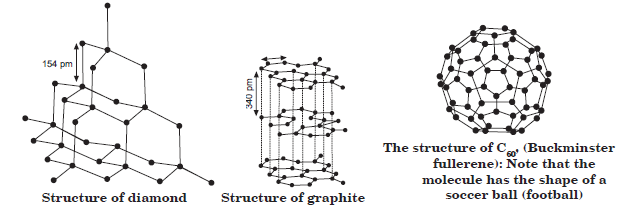
Catenation: The property due to which an atom can form stable covalent bond with the atoms of same element.
Topic 2. Homologous Series
Isomerism: Those compounds which have same molecular formula but different structural formula are called isomers. This phenomenon is called isomerism.
Straight Chain Compounds: Those compounds which have carbon atoms linked in a straight chain are called straight chain compounds, e.g.

Branched Chain Compounds: Those compounds which have carbon atoms linked as branched chains, e.g.

Saturated Closed Chain Compounds: Compounds having carbon atoms arranged in the form of a ring, e.g. cyclohexane has the formula C6H12. It has single bonds only.
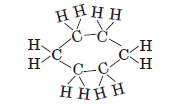
Aromatic, Closed Chain Compounds: If closed chain compounds contain double or triple bonds, they are called unsaturated closed chain compounds, e.g. Benzene (C6H6). It is also called an aromatic hydrocarbon.
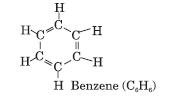
Hydrocarbons: The compounds formed by carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons.
Heteroatoms: In a hydrocarbon chain if one or more hydrogen atoms is replaced by halogens, oxygen, nitrogen or sulphur, then these atoms replacing hydrogen are called heteroatoms
Functional groups: These are the atoms or groups of atoms or reactive part of the compound which determines the properties of organic compounds, e.g.
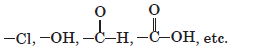
The functional group is attached to the carbon chain by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms.
Homologous series: The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
Characteristics:
(i) Each series has a general formula, e.g. alkane has CnH2n+2 as general formula.
(ii) Each series has same functional group, e.g. alcohols has –OH group.
(iii) Successive members differ by CH2 unit, e.g. CH4 and C2H6 differ by CH2 unit.
(iv) Successive members differ by 12 + 2 = 14 u by weight, e.g. CH4 has 16 u, C2H6 has 30 u weight.
(v) There is a gradation in physical properties, e.g. there is an increase in boiling point with the added carbon chain, i.e. with the increase in molecular weight.
General Formula: The formula from which all the members of homologous series can be derived, e.g. CnH2n is the general formula of alkenes, CnH2n–2 is the general formula of alkynes.
MCQ Questions Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science
Question. Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of:
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Sulphur
(c) Carbon
(d) Tin
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structure of nitrogen?
(a) N N
(b) N N
(c) N N
(d) N N
Answer
D
Question. A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has:
(a) Only single bonds
(b) Only double bonds
(c) Only triple bonds
(d) Two double bonds and one single bond
Answer
A
Question. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is:
(a) H O H
(b) H O H
(c) H O H
(d) H O H
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H8
(d) C4H8
Answer
D
Question. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of:
(a) Only carbon monoxide
(b) Carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) Only carbon dioxide
(d) Coal
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of C4H10?
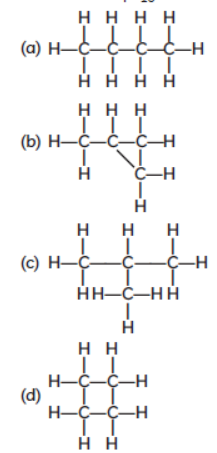
(i) (a) and (c)
(ii) (b) and (d)
(iii) (a) and (b)
(iv) (c) and (d)
Answer
A
Assertion-Reason Questions In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A) : Chemical bonds in organic compounds are covalent in nature.
Reason (R) : Covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons in the bonding atoms
Answer : (a)
Question. Assertion (A) : Carbon has a strong tendency to either lose or gain electrons to attain noble gas configuration.
Reason (R) : Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell and has the tendency to share electrons with carbon or other elements.
Answer : (d)
Question. Assertion (A) : Carbon forms covalent compounds with other atoms.
Reason (R) : Carbon can gain 4 electrons forming C4- anion.
Answer : (c)
Question. Assertion (A) : Following are the structural isomers of butane.

Reason (R) : Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in their structures.
Answer : (i)
Question. Assertion (A) : Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Reason (R) : Covalently bonded molecules have weak intermolecular forces.
Answer : (a)
Question. Assertion (A) : The following belong to the same homologous series:
C2H4, C3H6, C4H8.
Reason (R) : Gradation in physical properties is seen with an increase in molecular mass in any homologous series.
Answer : (b)
Passage Based Questions
Direction: Answer the following questions on the basis of each of your understanding of the following paragraphs and the related studied concepts.
Organic compounds are made up of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and a few other elements.But, the number of organic compounds is far bigger than inorganic compounds that do not form bonds.
Carbon is a chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. Carbon is a versatile element and is found in many different chemical compounds, including those found in space.
Carbon is versatile because it can form single,double, and triple bonds. It can also form chains, branched chains, and rings when connected to other carbon atoms. The versatile nature of carbon can be best understood with its features such as tetravalency and catenation.
(A) What is the atomic number and electronic configuration of carbon?
(B) Why are the bonds formed by carbon with other elements strong?
(C) Name two properties of Carbon which lead to formation of a large number of carbon compounds.
(D) Define catenation and name an element other than carbon which shows this phenomenon to some extent.
Answer : (A) Atomic number of carbon is 6 and its electronic configuration is: K-shell: 2, L-shell: 4 or (2, 4).
(B) The bonds formed by carbon with other elements are strong as the size of carbon atom is quite small which enables its nucleus to hold on to the shared pairs of electrons strongly.
(C) The two properties of Carbon which lead to formation of a large number of carbon compounds are tetravalency and catenation.
(D) Catenation is the property of carbon element due to which its atoms can join or link with one another to form long carbon chains.
An element other than carbon which exhibits catenation is sulphur.
Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science Important Questions
Very Short Anwer Type Questions
Question. State two characteristic features of carbon which when put together give rise to large number of carbon compounds.
Answer: (i) Catenation (ii) Tetravalency of carbon.
Question. Explain why carbon generally forms compounds by covalent bonds or do not form ionic compounds. OR
Give reason why carbon neither forms C4+cations nor C4– anions but form covalent compounds which are bad conductors of electricity and have low melting and boiling points. OR
Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell. How does carbon attain stable configuration?
Answer: Carbon as 4 valence electrons. It cannot lose 4 electrons because very high amount of energy is needed. It also cannot gain four electrons because 6 protons cannot hold 10 electrons.
It can share four electrons to form four covalent bonds. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity because they do not form ions. They have low melting and boiling points due to weak forces of attraction between molecules.
Question. Why are most carbon compounds poor conductors of electricity?
Answer: Carbon compounds form covalent bonds/do not dissociate into ions/do not have charged particles (ions).
Question. Define catenation.
Answer: The property of self-linking of atoms of an element through covalent bonds in order to form straight chain, branched chains or cyclic chains of different sizes is called catenation.
Question. Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point. Why?
Answer: It is because they have weak van der Waal’s forces of attraction between molecules therefore have low melting and boiling points.
Question. An alkene ‘P’ has three carbon atoms and an alcohol ‘Q’ has four carbon atoms. Write the formulae of P and Q.
Answer: ‘P’ is CH3–CH=CH2, ‘Q’ is CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Question. Write the molecular formula of benzene and state the number of double bonds in its structure.
Answer: C6H6, It has three double bonds 2
Question. What is homologous series?
Answer: It is a series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties.
Question. The molecular formula of two members of a homologous series are C3H4 and C6H10. Write the molecular formula of a member of this family with five carbon atoms in a molecule.
Answer: C5H8
Question. Write the general formula of alkenes. Write the name of the simplest alkene.
Answer: CnH2n, Ethene is simplest alkene.
Question. What is a saturated hydrocarbon? Write the formula of any one saturated hydrocarbon.
Answer : A saturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms have only single covalent bonds between them.
Formula of any one saturated hydrocarbon is CH4, C2H6, C3H8, C4H10, C10H12
Question. Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point. Why?
Answer : Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points because they are made up of electrically neutral molecules. So, the force of attraction between the molecules of a covalent compound is very weak.
Question. Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
Answer : Benzene is a cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Short answer Type Questions :
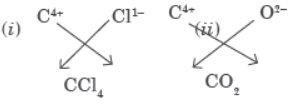
Question. Carbon, group 14 element in the periodic table, is known to form compounds with many elements.
Write an example of a compound formed with (i) Chlorine, (ii) Oxygen.
Answer:
Question. In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
(i) The atomic number of chlorine is 17. Write its electronic configuration.
(ii) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule.
Answer: (i) Cl (2,8,7)

Question. Compare the ability of catenation of carbon and silicon. Give reasons.
Answer: Carbon shows catenation property to more extent than silicon. It is because C–C bond is stronger than Si–Si bond because carbon is smaller in size than silicon.
Question. Give a test that can be used to confirm the presence of carbon in a compound. With a valency of 4, how is carbon able to attain noble gas configuration in its compounds?
Answer: – Burn compound in air/ oxygen; Gas evolved turns lime water milky – By sharing its four valence electrons with other elements.
Question. Which of the following is not observed in a homologous series? Give reason for your choice.
(a) Change in chemical pro perties (b) Difference in CH2 and 14u molecular mass
(c) Gradation in physical properties (d) Same functional group
Answer: (a) It does not occur due to the presence of the same functional group.
Question. How are covalent bonds formed?
Answer: Covalent bonds are formed by equal sharing of electrons.
Question. The number of carbon compounds is more than those formed by all other elements put together. Justify the statement by giving two reasons.
Answer: • Due to self linking ability of carbon/catenation
• Since carbon has a valency of four it can form bonds with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other mono-valent element.
• Due to small size of carbon it forms very strong and (or) stable bonds with other elements
Question. How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of ethane (C2H6)?
Answer: There are 7 covalent bonds.

Question. Write the electron dot diagram of ethane (C2H6) molecule.
Answer:
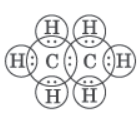
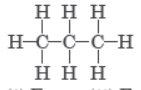
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in propane, C3H8.
Answer: There are 10 covalent bonds.
Question. Atoms of an element contain five electrons in its valence shell. This element is the major component of air. It exists as a diatomic molecule.
(i) Identify the element.
(ii) Show the bond formed between two atoms of this element.
(iii) Write the nature of bond between the two atoms.
Answer: (i) Nitrogen
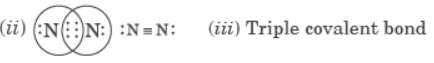
C2H4 is molecular formula of Ethene

Question. (i) Explain the formation of calcium chloride with the help of electron dot structure. (At numbers: Ca = 20; Cl = 17)
(ii) Why do ionic compounds not conduct electricity in solid state but conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state?.
Answer:
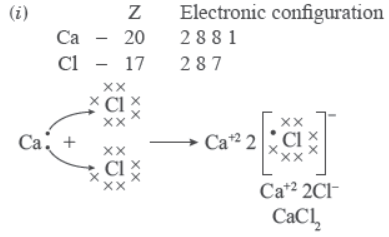
(ii) Ionic compounds do not conduct in solid state due to absence of free ions but they conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state due to presence of free ions.
Question. What are covalent compounds? Why are they different from ionic compounds? List their three characteristic properties.
Answer: Those compounds which are formed by equal sharing of electrons are called covalent compounds.
They are different from ionic compounds since ionic compounds are formed by transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
Properties:
(i) They have low melting and boiling points.
(ii) They do not conduct electricity in molten state and in aqueous solution.
(iii) They are mostly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents except glucose, sugar, urea, ethyl alcohol, etc.
Question. (a) Explain why carbon forms covalent bond? Give two reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds.
(b) Explain the formation of ammonia molecule.
Answer: (a) Carbon has electronic configuration 2, 4. It could gain four electrons forming C-4 anion or lose 4 electrons to form C+4 cation . Both are not possible due to energy considerations. Carbon overcome this problem by sharing electrons and forming covalent compounds. Two reasons for forming large number of compounds:
(1) Catenation (2) Tetra valency
(b) Formation of NH3 molecule
Three hydrogen atoms each share their 1 electron with nitrogen to form three covalent bonds and make an ammonia molecule (NH3).

Question. The general formula of three compounds A, B and C is CnH2n. ‘B’ has the highest boiling point and ‘C’ has the lowest boiling point.
(i) Mention the type of compounds A, B and C.
(ii) Which of these has minimum number of carbon atoms?
(iii) Name the homologous series to which A, B and C belong
Answer: (i) Unsaturated hydrocarbons with double bonds.
(ii) ‘C’ has minimum boiling point, so ‘C’ has minimum no. of C-atoms.
(iii) Alkene
Question. Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell.
Which type of compounds can be formed by carbon atom and why? Give any one example of such compounds.
Answer : Carbon forms covalent compounds with other atoms by sharing electron pairs because of the following reasons:
(1) Carbon cannot form C4+ cation by losing four electrons, as it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons leaving behind a carbon cation with six protons in its nucleus holding on to just two electrons.
(2) Carbon cannot form C4– anion by gaining four electrons, as it would be diffcult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
Example of compounds formed by carbon:
(i) Methane (CH4)
(ii) Ethene (C2H4)
(iii) Propyne (C3H4)
(iv) Ethanol (C2H3OH)
Question. Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity. Why?
Answer : Covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity because these compounds do not have any charged particles as they are made by sharing of electrons.
Question. Write the name and formula of a carbon compound having – OH functional group.
Answer : Name and formula of a carbon compound having – OH functional group:
Question. Select alkenes and alkynes from the following:
C2H4, C3H4, C2H2, C4H8
Write their structural formula also.
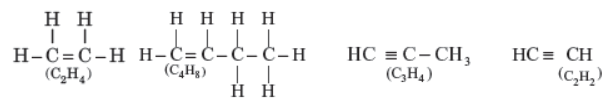
Answer: C2H4 and C4H8 are alkenes, C3H4 and C2H2 are alkynes.
Question. An alkane has molecular weight 86. Write its molecular formula. What will be its physical state?
Answer: C6H14 has molecular weight of 6 × 12 + 14 = 86u.
It is in liquid state at room temperature.
Question. What is homologous series of carbon compounds? Give an example and list its three characteristics.
Answer: The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series. For example,
Alkane: CH4 C2H6 C3H6
Methane Ethane Propane
Characteristics: • Each successive member differ by CH2 unit.
• They have gradation in physical properties.
• They have similar chemical properties due to presence of same functional group.
Question. Carbon, a member of group 14, forms a large number of carbon compounds estimated to be about three million. Why is this property not exhibited by other elements of this group? Explain.
Answer: Carbon shows the property of catenation.
It forms strong covalent bonds with other atoms of carbon forming long straight, branched and closed chain compounds.
Carbon is smallest in size in group 14 with tatravalency, it can form double as well as triple bonds, therefore, it can show property of catenation to maximum extent and forms 3 million compounds other elements cannot show property of catenation to this extent due to larger size form weaker covalent bond and cannot form double or triple bonds.

