Exam Question for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Biology teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Biology and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Biology exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare are very important and should be revised daily.
Exam Question Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
Objective Questions
Question. The bioactive molecule cyclosporin A is used in the treatment of
(a) Whooping cough
(b) Diptheria
(c) Vitamins
(d) Organ transplant patients
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is not true about antibiotics?
(a) First antibiotic was discovered by Alexander Flemimng
(b) The term ‘antibiotic’ was coined by S. Waksman in 1942
(c) Some people can be allergic to a particular antibiotic
(d) Each antibiotic is effective only against one particular pathogen
Answer
D
Question. What are the advantages of gobar gas over conventional utilization?
A. It is most efficient source of energy
B. It is used as good fertilizer
C. It reduces the chances of spreading of pathogens
Options :
(a) A and B only
(b) B and C only
(c) A and C only
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The given table contains tyoes of microbe (Column i),Scientific name (Column ii ) and commercial product (Column iii). Some names are replaced by A,B,Cand D. Identify the correct names
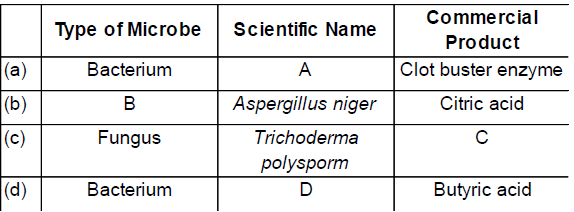
(a) A-Streptococcus ,B – Fungus ,C- Cyclosporin-A, D-Clostridium butylicum
(b) A-Clostridium butylicum,B-Streptococcus, C-Fungus,D-Cyclosporin-A
(c) A-Cyclosporin-A, B-Clostrium butylicum, C-Streptococcus, D-Fungus
(d) A-Fungus ,B-Cyclosporin, C-Clostridium butylicum, D-Streptococcus
Answer
A
Question. Symbiotic asociation is exhibited by
A. Mycorrhiza
B. Rhizobium
C. Heterocyst
D. Yeast
Options :
(a) A, C, D
(b) A, B, C, D
(c) B, C, D
(d) A, B
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is common to Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Anabaena , Nostoc and Oscillatoria?
(a) Prokaryotes
(b) Nitrogen fixers
(c) Both(a) and (b)
(d) Eukaryotes
Answer
C
Question. Pollution from animal excreta and organic wastes from kitchen can be most profitably minimised by
(a) Storing them in underground storage tanks
(b) Using them for producing biogas
(c) Vermiculture
(d) Using them directly as biofertilizers
Answer
B
Question. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of
(a) Gas Authority of India
(b) Oil and Natural Gas Commission
(c) Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi and Village Industries Commission
(d) Indian Oil Corporation
Answer
C
Question. What would happen if oxygen availability to activated sludge flocs is reduced?
(a) It will slow down the rate of degradation of organic matter.
(b) The centre of flocs will become anoxic, which would cause death of bacteria and eventually breakage of flocs.
(c) Flocs would increase in size as anaerobic bacteria would grow around flocs.
(d) Protozoa would grow in large numbers.
Answer
B
Question. A nitrogen-fixing microbe associated with Azolla in rice fields is :
(a) Spirulina
(b) Anabaena
(c) Frankia
(d) Tolypothrix
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is an example of carrying out biological control of pests/ diseases using microbes ?
(a) Trichoderma sp. against certain plant pathogens
(b) Nucleopolyhedrovirus against white rust in Brassica.
(c) Bt-cotton to increase cotton field.
(d) Lady bird beetle against aphids in mustard.
Answer
C
Question. Which pigment gives a pinkish hue to rhizobium induced root nodules.
(a) Leghaemoglobin
(b) Carotenoid
(c) Mauveine
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The free-living fungus Trichoderma can be used for
(a) killing insects
(b) biological control of plant diseases
(c) controlling butterfly caterpillars
(d) producing antibiotics
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is not a nitrogenfixing organism?
(a) Anabaena
(b) Nostoc
(c) Azotobacter
(d) Pseudomonas
Answer
D
Question. Glomus form a symbiotic relationship with plant …………….
(a) leaves
(b) stem
(c) root
(d) stem and root
Answer
C
Question. Conversion of milk to curd improves its nutritional value by increasing the amount of :
(a) Vitamin D
(b) Vitamin E
(c) Vitamin B12
(d) Vitamin A
Answer
C
Question. Match the items in Column ‘A’ and Column ‘B’ and choose correct answer. (Image 68)
The correct answer is :
(a) a – (ii), b – (iv), c – (iii), d – (i)
(b) a – (iii), b – (iv), c – (ii), d – (i)
(c) a – (iv), b – (i), c – (ii), d – (iii)
(d) a – (iii), b – (ii), c – (i), d – (iv)
Answer
B
Case Based MCQs
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Yeast and certain bacteria play a key role fermentation to breakdown carbohydrates into ethanol and carbon dioxide which then further used to prepare acetic acid with the help of bacterium Acctobacter aceti. Alcoholic fermentation in anaerobic process, but the conversion of alcohol to acetic acid is aerobic one.
This process can be represented by following equation :
Question. Distilled alcohol with 95% ethanol content is called
(a) absolute alcohol
(b) rectified spirit
(c) gin
(d) brandy.
Answer
B
Question. A number of chemicals are produced at the time of alcoholic fermentation with the change of nutrient media, pH and aeration. Select such by-product from the following.
(a) Butanol
(b) Succinic acid
(c) Acetaldehyde
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. is used in the preparation of vinegar.
(a) toddy
(b) acetic acid
(c) butter
(d) both (a) and (b).
Answer
D
Question. The rate of alcohol production is measured on the basis of
(a) amount of sugar present in the medium
(b) amount of CO2 produced per unit time
(c) amount of yeast added in the medium
(d) all of these.
Answer
B
Question. During alcoholic fermentation of cereals and potato, the crushed food mixed with hot water for obtaining malt is called
(a) juice
(b) mash
(c) wort
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 51-60, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Azotobacter fixes nitrogen in symbiotic form.
Reason : Rhizobium form root nodules in the roots of leguminous plants.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Azolla is used as a biofertiliser in rice fields.
Reason : Azolla shows the presence of N2 – fixing bacteria in its leaf cavities.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Whisky develops colour during the aging process.
Reason : Vodka is colourless.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : An organism which acts as herbicide is called bioherbicide.
Reason : Phytophthora palmivora is a mycoherbicide.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Saccharomyces ellipsoidens is Brewer’s yeast.
Reason : Brewer’s yeast produces beer not wine.
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the metabolic pathway associated with the rising of dough in making bread. What makes the dough rise?
Answer : When Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker’s yeast) is added to dough it causes its fermentation and releases CO2 gas which is responsible for puffed up appearance of dough.
Question. Which of the following is a free living bacteria that can fix nitrogen in the soil?
Answer : Azospirillum is a free living nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Question. Write the commercial use of lipases.
Answer : Lipases are used in detergents formulations and are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry.
Question. Write the biochemical reaction of yeast fermentation of molasses for alcohol production.
Answer : The biochemical reaction for anaerobic fermentation is
C6H12O6 → Yeast fermentation 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Question. Name the group of organisms and the substrate they act on to produce biogas.
Answer : Methanogenic bacteria or methanogens are the group of anaerobic microbes which digest organic mass as well as aerobic microbes of the sludge to produce a mixture of gases containing methane, H2S and CO2 called biogas.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What makes the Nucleopolyhedrovirus a desirable biological control agent?
Answer : Nucleopolyhedrovirus a genus of baculoviruses are useful in controlling many insects and other arthropods. They are species specific narrow spectrum bioinsecticides with no side effects on plants, mammals, birds, fish and non-target insects. Therefore, they serve as an important component of integrated pest management programme in dealing with ecological sensitive areas. These properties are useful in organic farming.
Question. How has the fungus, Trichoderma polysporum proved to be very essential to organtransplant patients?
Answer : Trichoderma polysporum produces a bioactive molecule known as cyclosporin–A which has antifungal, antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It inhibits activation of T-cells and therefore, prevents rejection reactions in organ transplantation.
Question. Name the genus to which baculoviruses belong. Describe their role in the integrated pest management programmes.
Answer : Nucleopolyhedrovirus a genus of baculoviruses are useful in controlling many insects and other arthropods. They are species specific narrow spectrum bioinsecticides with no side effects on plants, mammals, birds, fish and non-target insects. Therefore, they serve as an important component of integrated pest management programme in dealing with ecological sensitive areas. These properties are useful in organic farming.
Question. How does the application of the fungal genus, Glomus, to the agricultural farm increase the farm output?
Answer : Many members of the genus Glomus form symbiotic associations with plants to form mycorrhiza. Glomus helps to absorb phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plant. Plants having such associations show other benefits also, such as resistance to root-borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity and drought and an overall increase in plant growth and development. Therefore, Glomus increases the farm yield.
Question. Name the source of streptokinase. How does this bioreactor molecule function in our body?
Answer : Streptokinase is produced by bacterium Streptococcus. Streptokinase is modified by genetic engineering which is further used as a ‘clot bluster’ for removing clots from the blood vessels of the patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack.
Question. State one reason for adding blue-green algae to the agricultural soil.
Answer : A number of free living and symbiotic blue green algae or cyanobacteria have the property of nitrogen fixation and are photosynthetic. Therefore, they add organic matter as well as extra nitrogen to the soil. Hence, blue green algae serve as biofertilisers and are added to agricultural fields such as cotton, maize, jowar, rice, etc.
Question. Name the organism that fixes nitrogen in symbiotic association with a water fern. Where does it live in such plant?
Answer : Anabaena azollae (blue green alga) fixes nitrogen in symbiotic association with a water fern. It resides in the leaf cavities of the fern.
Question. Distinguish between the roles of flocs and anaerobic sludge digesters in sewage treatments.
Answer : Aerobic bacteria and fungi constitute ‘flocs’. Flocs are masses of aerobic bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh like structures. These microbes digest a lot of organic matter converting it into microbial biomass and releasing a lot of minerals. This reduces biochemical oxygen demand or BOD.
In anaerobic sludge digesters, aerobic microbes present in the sludge get killed. Anaerobic microbes digest the organic mass as well as aerobic microbes of the sludge. During this digestion, bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. These gases form biogas which can be used as source of energy as it is inflammable. The spent sludge of anaerobic sludge digester can be used as manure or part of compost.
Question. Why biogas is more suitable and advantageous in rural areas?
Answer : Biogas is more suitable and advantageous in rural areas as :
(i) It provides both energy and manure.
(ii) Biogas has wider applications than the direct burning of organic wastes.
(iii) The energy value of biogas is lower than that of organic matter but due to more efficient handling, the net energy output is roughly equal to the output in direct burning of organic wastes.
(iv) It minimises the chances of spread of faecal pathogens.
(v) The fertiliser value of the manure produced in biogas plants is similar to that of manure formed directly from organic wastes.
(vi) Biogas use does not add to pollution.
Question. Name the bacterium responsible for the large holes seen in “Swiss Cheese”. What are these holes due to?
Answer : Bacterium responsible for large holes in Swiss cheese is Propionibacterium shermanii. Large holes in Swiss cheese are due to CO2 gas produced by these bacteria.
Question. Why are some molecules called bioactive molecules? Give two examples of such molecules.
Answer : Bioactive compounds are those compounds that have an effect on living organisms tissues or cells. Bioactive compounds are found in both plant and animal products
or can be synthetically produced. Two examples of bioactive compounds are cyclosporin A and statins.
Question. (a) Why are the fruit juices bought from market clearer as compared to those made at home?
(b) Name the bioactive molecules produced by Trichoderma polysporum and Monascus purpureus.
Answer : (a) The fruit juices sold in market or bottled juices are treated with pectinases and proteases which makes them clearer than those made at home.
(b) Cyclosporin A is obtained from fungus Trichoderma polysporum whereas statin is obtained from yeast Monascus purpureus.
Cyclosporin A has immunosuppressive properties. It inhibits activation of T cells and therefore prevents rejection of transplants. Statin inhibits cholesterol synthesis and is therefore used in lowering blood cholesterol.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the site of nitrogen fixation in legumes.
List and describe the biochemical components at this site.
Answer : Symbiotic nitrogen fixation is carried out by bacteria frequently found in the root nodules of leguminous plants. The different components and their role in symbiotic nitrogen fixation are as follows:-
(i) Rhizobium : They are symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria commonly present in root nodules of leguminous plants and carry out conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous salts to make it available for absorption by plants.
(ii) Lectin : Lectins are the key proteins involved in the Rhizobium-legume symbiotic association. Bauer (1981) proposed that these lectins interact selectively with microbial cell carbohydrates (or glycoproteins) found in the capsule of bacteria and serve as determinants of recognition or host specificity.
(iii) Tryptophan : Leguminous plants release tryptophan in the soil which is absorbed by Rhizobium and is metabolised to produce IAA.
(iv) Root hair curling factor : The rhizobia produce another characteristic substance called root hair curling factor that causes deformation and twisting of root hairs.
(v) Leghaemoglobin : The nodule contains a pink coloured pigment leghaemoglobin which is like true haemoglobin combines with oxygen and CO2 gets readily oxidised into brown form with a trivalent iron.
(vi) Nitrogenase : Process of nitrogen fixation, involves reduction of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia (NH3) by the enzyme nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is made up of two protein components, one containing iron and molybdenum, known as Mo-Fe protein or molybdo-ferredoxin (component I) and the other containing only iron called Fe-protein or azoferredoxin. Nitrogenase is extremely sensitive to oxygen. The enzyme remains active under anaerobic conditions. The leghaemoglobin binds with oxygen and protect nitrogenase from O2 inactivation. At the same time it is able to make O2 available to bacteroids for ATP production, required for nitrogen fixation.
Question. Prior to sowing rice, a legume crop was cultivated and ploughed back in the field, why? Explain.
Answer : Prior to sowing rice, a leguminous crop was cultivated and ploughed back in the field. The root nodules of leguminous plants contain Rhizobium bacteria. Rhizobium is one of the most important source of biofertilizer. It forms an efficient symbiotic relationship with leguminous plants and can fix upto 100 – 500 kg nitrogen per hectare of land. The fixed nitrogen is used up by the leguminous plants. However, a sizeable amount of fixed nitrogen is left behind in the soil in the form of residue which can be utilized by the succeeding crop.

