Exam Question for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem
Class 12 students can refer to Chapter 14 Ecosystem notes given below which is an important chapter in the class 12 Biology book. These notes and important questions and answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Our team of Business Studies teachers has prepared these notes for class 12 Biology for the benefit of students so that you can read these revision notes and understand each topic carefully.
Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes for Class 12 Biology
Objective Questions
Question. Which of the following is/are example(s) of man-madeecosystem?
(a) Herbarium
(b) Crop fields
(c) Aquarium
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is not an abiotic component?
(a) Temperature
(b) Decomposers
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Answer
B
Question. Two main structural features of an ecosystem are
(a) species composition and stratification
(b) species composition and productivity
(c) productivity and energy flow
(d) nutrient cycling and stratification
Answer
A
Question. Primary productivity
(a) is equal to the standing crop of an ecosystem.
(b) is greatest in freshwater ecosystems.
(c) is the rate of conversion of light to chemical energy in an ecosystem.
(d) is inverted in some aquatic ecosystems.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following most often limits the primary productivity of the ecosystem ?
(a) Solar radiation/light
(b) Oxygen
(c) Consumers
(d) Nitrogen
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following process help the watersoluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts?
(a) Fragmentation
(b) Leaching
(c) Catabolism
(d) Humification
Answer
B
Question. Energy flow in an ecosystem is
(a) unidirectional
(b) bidirectional
(c) multidirectional
(d) all of these
Answer
A
Question. Ecosystems are ______ because resources ____ move from one ecosystem to another.
(a) open; can
(b) closed; cannot
(c) one-way; can
(d) one-way; cannot
Answer
A
Question. The primary difference between sedimentary and atmospheric cycles is that in _____ cycles the nutrient does not _____.
(a) sedimentary; leave the terrestrial environment
(b) sedimentary; leave the aquatic environment
(c) atmospheric; leave the aquatic environment
(d) sedimentary; enter the atmosphere
Answer
D
Question. Ecosystem is
(a) Functional unit of nature where living organism interact among themselves
(b) Functional unit of nature where living organism interact with their surrounding physical environment
(c) Both the statements
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is considered as man made ecosystem?
(a) Estuary
(b) Crop field
(c) Grassland
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The autotrophic component in a pond ecosystem is
(a) Zooplanktons
(b) Solar inputs
(c) Phytoplanktons
(d) Fungi
Answer
C
Question. In pond ecosystem zooplanktons exist in which form
(a) Free swimming
(b) Bottom dwelling
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Pond as an ecosystem perform which of the following functions?
(a) Conversion of inorganic to organic material by using solar radiant energy by autotrophs
(b) Consumption of autotrophs by heterotrophs
(c) Decomposition and mineralization of the dead matter to release them back for reuse by the autotrophs
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Amount of biomass produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis is called
(a) Primary production
(b) Secondary production
(c) Tertiary production
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The rate of biomass production is called
(a) Primary production
(b) Secondary production
(c) Tertiary production
(d) Productivity
Answer
D
Question. Net primary productivity is
(a) Respriation loss by the plant
(b) Total organic matter production rate
(c) Gross primary productivity minus respiration loss of plant
(d) Rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers
Answer
C
Question. Rate of formation of new organic matter by consumer is called
(a) Gross primary productivity
(b) Secondary productivity
(c) Net primary productivity
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The annual primary productivity of whole biosphere is approximately
(a) 170 millions tons
(b) 170 x 103 million tonnes
(c) 17 billions tons
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions
Question. Consider the following statements.
(i) An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature and comprises abiotic and biotic components.
(ii) Abiotic components are organic materials.
(iii) Biotic components are producers, consumers and decomposers.
(iv) Energy flow is bidirectional.
which two statements are correct ?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statement is correct?
(a) Warm and moist environment favour decomposition whereas low temperature and anaerobiosis inhibit decomposition.
(b) Warm and moist environment inhibit decomposition whereas low temperature and anaerobiosis favour decomposition.
(c) Warm moist environment and anaerobiosis inhibit decomposition whereas low temperature favours
decomposition.
(d) Warm and low temperature inhibit decomposition whereas anaerobiosis favours decomposition.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not true for a pyramid of productivity?
(a) Only about 10% of the energy in one trophic level is passed into the next level.
(b) Because of the loss of energy at each trophic level, most food chains are limited to three to five steps.
(c) The pyramid of productivity of some aquatic ecosystems is inverted because of the large zooplankton primary – consumer level.
(d) Eating grain-fed beef is an inefficient means of obtaining the energy trapped by photosynthesis.
Answer
C
Question. Which two of the following statements regarding food chains are correct ?
(i) Removal of 80% tigers resulted in increased growth of vegetation.
(ii) Removal of most carnivores resulted in increased population of deer.
(iii) Length of food chain is limited to 3 – 4 trophic levels due to energy loss.
(iv) Length of food chain may vary from 2 – 3 trophic levels.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Food chains differ from food webs in that
(i) food chains are single sequence of who eats whom in a community.
(ii) food chains better represent the entire community.
(iii) food webs represent the complex interaction among food chains.
(iv) food chain is the flow of energy in a population.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(i) An important characteristic of all communities is that their composition and structure constantly change in response to the changing environmental conditions.
(ii) The climax community remains stable as long as the environment remains changed.
(iiii) The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area are called sere(s).
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following factors influence communities ?
(i) Climate
(ii) Species interaction
(iii) Feeding relationships among organisms
(iv) Succession
(a) (i) and (iii) (b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) (d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about biogeochemical cycle?
(i) Gaseous exchanges of phosphorus between organism and environment are negligible
(ii) All biogeochemical cycles include both organisms and non-living components.
(iii) Most elements remain longest in the living portion of their cycle.
(iv) The chemical elements used by organisms in large quantities cycle back and forth between organisms
and environment.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Assertion/Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Net primary productivity is gross primary productivity minus respiration.
Reason : Secondary productivity is produced by heterotrophs.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : A network of food chains existing together in an ecosystem is known as food web.
Reason : An animal like kite cannot be a part of a food web.
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Primary succession | I. Autotrophs |
| B. Climax community | II. Community that has completed succession |
| C. Consumer | III. Colonization of a new environment |
| D. Producer | IV. Animals |
(a) A – III; B – II; C – IV; D – I
(b) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(c) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
A
Question. Match the following and choose the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Phosphorus | I. Atmosphere |
| B. Carbon | II. Producers |
| C. Goat | III. Rock |
| D. Grasses | IV. T2 |
(a) A – III; B – II; C – IV; D – I
(b) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(c) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
B
Question. Match the following and choose the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Presence of 3-4 storey | I. Blue-green algae of plants grown in a forest |
| B. A biome having grasses | II. Stratification with scattered trees |
| C. Man made ecosystem | III. Savannah |
| D. Pioneer in hydrosere | IV. Dam |
(a) A – III; B – II; C – IV; D – I
(b) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(c) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
D
Diagram Type Questions
Question. Refer the given diagrammatic representation of trophic levels in an ecosystem some spaces are marked A, B, C and D. Identify A, B, C and D.

(a) A – Primary producer; B – Secondary consumer; C – Man / Lion; D – Plants
(b) A – Secondary consumer; B – Primary producer; C – Man / lion; D – Plants
(c) A – Primary producer; B – Secondary consumer; C – Plants; D – Man / lion
(d) A – Secondary consumer; B – Primary producer; C – Plants; D – Man / lion
Answer
D
Question. In the given food web few organisms are marked as (1), (2), (3) and (4). Identify (1), (2), (3) and (4).

Answer
A
Question. Given below is one of the types of ecological pyramids. This type represents
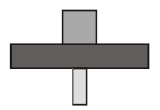
(a) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland
(b) Pyramid of biomass in a fallow land
(c) Pyramid of biomass in a lake
(d) Energy pyramid in a spring
Answer
C
Question. Two food chains are given below.

Answer
C
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Which one is the correct food chain ?
(a) Eagle → Snake → Grasshopper → Grass → Frog
(b) Frog → Snake → Eagle → Grasshopper → Grass
(c) Grasshopper → Grass → Snake → Frog → Eagle
(d) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Answer
D
Question. If CO2 is removed totally from the biosphere, which organisms will be affected first ?
(a) Consumers
(b) Secondary consumers
(c) Producers
(d) Primary producers
Answer B
B
Question. Productivity at the second trophic level is always
(a) greater than the productivity at the first trophic level.
(b) less than the productivity at the first trophic level.
(c) equal to the productivity at the first trophic level.
(d) extremely variable compared to the productivity at the first trophic level.
Answer
B
Question. The transfer of energy from one trophic level to another is governed by the 2nd law of thermodynamics. The average efficiency of energy transfer from herbivores to carnivores is
(a) 5%
(b) 10%
(c) 25%
(d) 50%
Answer
B
Question. Grasslands can support greater grazing rates by herbivores than forests because
(a) net production of grassland is greater.
(b) more of the grassland is above the ground.
(c) grasslands receive more sunlight.
(d) grasslands produce less woody plant tissue.
Answer
D
Question. There is no difference between
(a) secondary consumers and herbivores.
(b) primary consumers and herbivores.
(c) first trophic level and herbivores.
(d) primary carnivores and second trophic level.
Answer
B
Question. In an upright pyramid of biomass, the herbivores generally occupy which of the following position ?
(a) First position
(b) Second position
(c) Third position
(d) Fourth position
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compartments of the global ecosystem would be characterized by very slow movement of materials within the compartment ?
(a) Oceans
(b) Fresh water
(c) Atmosphere
(d) Land
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is not a function of an ecosystem?
(a) Energy flow
(b) Decomposition
(c) Productivity
(d) Stratification
Answer
D
Question. In a food web, each successive trophic level has
(a) increased total energy content
(b) less total energy content
(c) more total energy content
(d) non-estimated energy content
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the most stable ecosystem ?
(a) Mountain
(b) Desert
(c) Forest
(d) Ocean
Answer
D
Question. In ecological succession from pioneer to climax acommunity, the biomass shall
(a) decrease
(b) increase and then decrease
(c) no relation between these communities
(d) increase continuously
Answer
D

