Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Chemistry teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers are very important and should be revised daily.
Very short Answer type Questions:
Question. Which of the following reagents cannot be used to oxidise primary alcohol to aldehyde ?
(a) CrO3 in anhydrous medium
(b) KMnO4 in acidic medium
(c) Pyridinium chlorochromate
(d) Heat on the presence of copper at 573 K
Answer
B
Question. Monochlorination of toulene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields
(a) o-Cresol
(b) m-Cresol
(c) 2,4-Dihydroxytoluene
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer
D
Question. Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols:
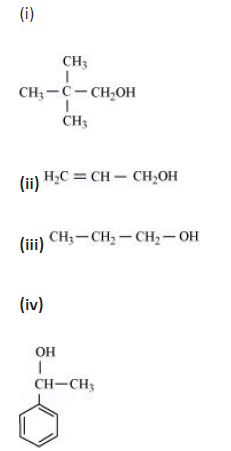
Answer. Primary alcohol → (i), (ii), (iii)
Secondary alcohol → (iv), (v) Tertiary alcohol → (vi)
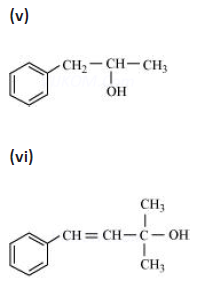
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following:
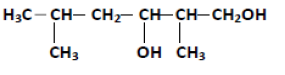
Answer. 2,5 dimethylhexane-1,3-diol
Question.

Answer. 1-Methoxy-2-methylbutane
Question.

Answer. hex-1-en-3-ol
Question. Write the structure of the molecule of a compound whose IUPAC name is 1- Phenylpropan-2-ol
Answer.
Question. Write the structure of the molecule of a compound whose IUPAC name is 2- methyl-2-ethoxypentane.
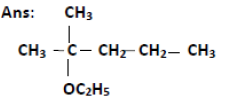
2 Marks Questions
Question. Explain the mechanism of the following reaction:
Answer.

Question. Write mechanism for hydration of alkene.
Answer.

Question. How will you convert the following?
i. Propan-2-ol to propanone
ii. Phenol to 2,4,6-tribromophenol
Answer.

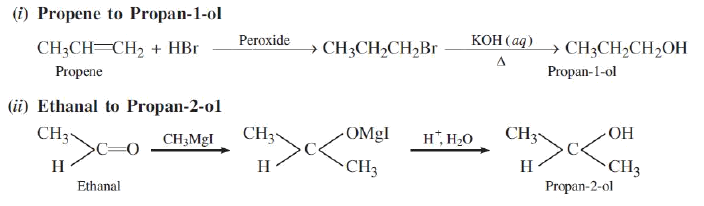
Question. How will you convert:
a) Propene to Propan-2-ol?
b) Ethanal to Propan-2-ol?
Answer.
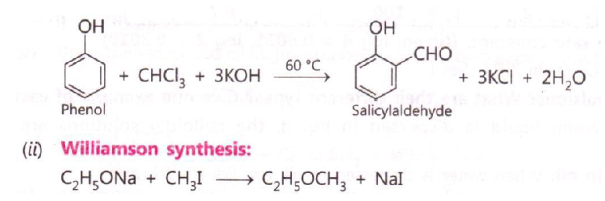
Question. Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer – Teimann Reaction
(ii) Williamson synthesis
Answer. (i) Reimer – Teimann Reaction
Question. Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
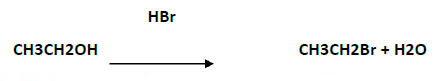
Answer.

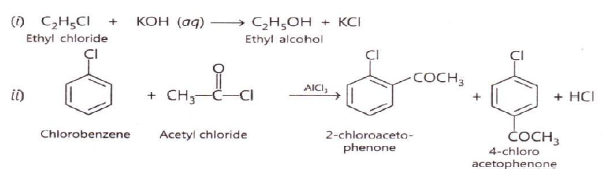
Question. Write chemical equations when :
i. Ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH
ii. Chlorobenzene is treated with CH3COCl in presence of anhydrous AlCl3
Answer.
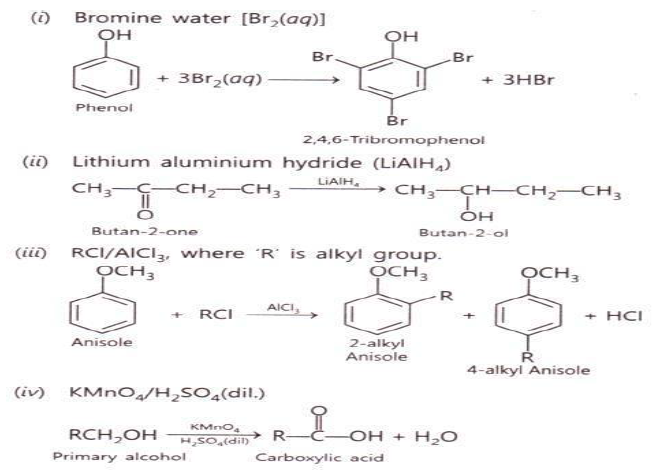
Question. Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
i. Bromination of phenol to 2.4.6-tribromophenol
ii. Butan-2-one to Butan-2-ol
iii. Friedel- Crafts alkylation if anisole
iv. Oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
Answer.
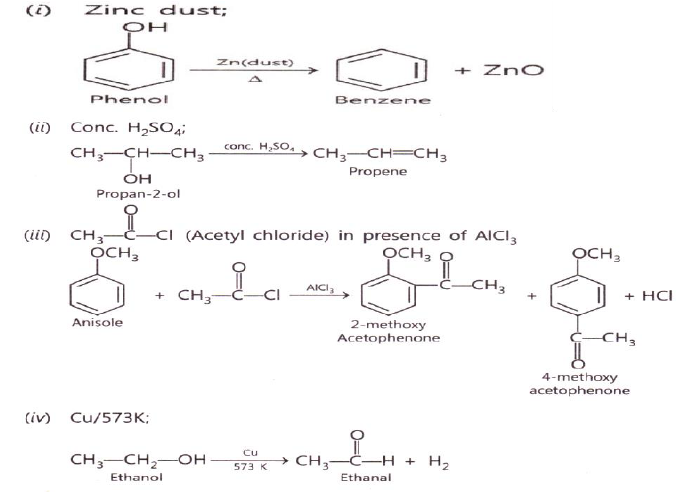
Question.Name the different reagents needed to perform th following reactions:
i. Phenol to Benzene
ii. Dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene
iii. Friedel- Crafts acetylation of anisole
iv. Dehydrogenation of ethanol to ethanol
Answer.
Question. Convert
1. Phenol to 2,4,6 tri nitro phenol
2. Butanal to butanol 1
3.Anisol to 2-methoxyacetophenone
4.ethanol to ethanal
Answer.

Short Answer type Questions:
Question. Explain the mechanism of the following reactions:
(i) Addition of Grignard’s reagent to the carbonyl group of a compound forming an adduct followed by hydrolysis.
(ii) Acid catalysed dehydration of an alcohol forming an alkene.
(iii) Acid catlysed hydration of an alkene forming an alcohol.
Answer.


Question. Explain the following observations:
(1) The boiling point of Methanol is higher than that of methoxymethane.
(2) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
(3) O- and p-nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol.
Answer. (I) It is because ethanol is associated with intermolecular H-bonding. Therefore, ethanol has higher boiling point than that of methoxymethane which is not associated with Intermolecular H-bonding.
(ii) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol because phenoxide ion is more stable due to resonance as compared to ethoxide ion which is unstable due to positive inductive effect of ethyl group.
(iii) It is because -NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group (-R effect), it increases the stability of o- and p- nitro phenoxide ion as compared to phenoxide.
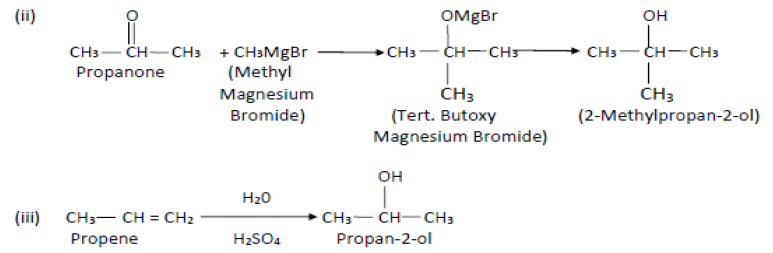
(ii) Propene to propan-2-ol
Question. How would you convert the following?
(i)Phenol to benzoquinone
(ii) Propanone to 2- methylpropan-2-ol
Answer.

Question. Account for the following:
i. Propanol has higher boiling point than Butane.
ii. Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol.
iii. Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method.
Answer. (i) It is because alcohols can form H-bonds with water molecules, whereas hydrocarbons do not.
(ii) It is because NO2 group is electron withdrawing and OCH3 group is electron releasing. Therefore, o-nitro phenoxide ion is more stable than o-methoxy phenoxide ion.
(iii) It is because secondary and tertiary alcohols on dehydration lead to the formation of alkene and not ethers due to the stability of 2° and 3° carbocation.
Question. Account for the following:
i. The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methanol.
ii. Phenol is a stronger acid than an alcohol.
iii. The boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols.
Answer.
i. It is due to the higher molecular weight, more surface are, more vander Waal’s forces of attraction in C2H5OH than CH3OH.
ii. Phenol is a stronger acid than alcohol because phenoxide ion is more stable than ethoxide ion.
iii. It is because ethers are not associated with intermolecular H- bonding, whereas ethanol is associated with intermolecular H-bonding.
Question. Account for the following:
i. The boiling points of alcohols decrease with increase in branching of the alkyl chain.
ii. Phenol does not give protonation reaction readily.
iii. Phenylmethyl ether reacts with HI to give Phenol and Methyl iodide and not Iodobenzene and methyl alcohol.
Answer.
i. It is because branched chain alcohols have minimum surface area therefore minimum force of attraction, hence, they have lower boiling point.
ii. It is due to +ve charge on 3 out of 5 resonating structures of Phenol. It cannot be protonated easily.
iii. It is because phenoxide ion is stabilized by resonance, whereas, methoxide ion is not.
Question. Draw the structure and name of the product formed if the following alcohols are oxidized. Assume that and excess of oxidizing agent is used.
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (ii) 2-butenol (iii) 2-methyl-1-propanol
Answer.

Question.8. Explain the following reactions:
Answer.
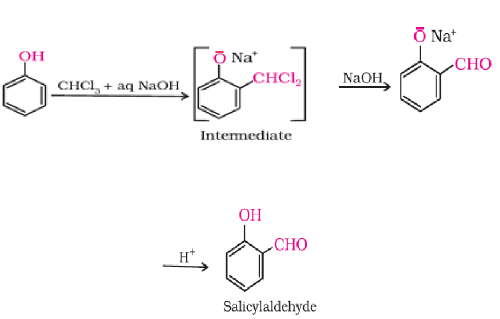
A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
On treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide, a – CHO group is introduced at ortho position of benzene ring.
The intermediate substituted benzal chloride is hydrolysed in the presence of alkali to produce salicylaldehyde.
B) Kolbe’s reaction
Phenoxide ion generated by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide and then undergoes electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide, Ortho hydroxy benzoic acid is formed as the main reaction product on hydrolysis.

C) Williamson synthesis
In this method, an alkyl halide is allowed to react with sodium alkoxide to prepare ether.

Question. Write a chemical test to distinguish between following:
(a) Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols e.g. Butanol, Butan-2-ol and 2-Methylpropan2-ol
(b) Ethanol and methanol
(c) Ethanol & phenol
(d) 1-Propanol and ethanol
Answer.
(a) Primary ,secondary and tertiary alcohols : LUCAS TEST
When 1o , 2o , 3o alcohol treated with Lucas reagent [Conc HCl + anhydrous ZnCl2] at room temp
i) If turbidity appears immediately alcohol is tertiary
ii) If turbidity appears in five minutes alcohol is secondary
iii) If turbidity appears only upon heating the given alcohol is primary.
(b) Ethanol and methanol –
Halo form test
Compounds treated with NaOI, yellow ppt of iodoform will be given by molecule having– CO – CH3 group. Ethanol gives yellow ppt.
(c) Ethanol & phenol:
Neutral ferric chloride test.
Ethanol on treating with NaOH and I2 give yellow coloured iodoform but not 1-propanol Phenol gives violet colouration when we treated it with neutral ferric chloride.
(d)1-Propanol and ethanol:
Iodoform test → Ethanol on treating with NaOH and I2 give yellow coloured iodoform but not 1-proponol
LONG ANSWERS:
Question. Give reasons:
Question. Ethanol has higher boiling point in comparison to methoxymethane .
Answer. Due to presence of intermolecular hydrogenbond in ethanol.
Question. Phenols are more acidic than alcohols.
Answer. Due to –R effect of phenoxide ion produced after the loss of proton from phenol, phenoxide ion is more stable than alkoxide ion
Question. o-nitrophenol is steam volatile while p-nitrophenol not.
Answer. Due to presence of intramolecular hydrogen bond
Question. Cleavage of phenyl alkyl ether with HI always gives phenol and alkyl iodide
Answer. Due to resonance C-O bond of phenyl will acquire double bond character hence difficult to break.
Question. Arrange the following as property indicated: –
Question. pentan-1-ol, pentanal, ethoxyethane (increasing order of boiling point)
Answer. n-butane <ethoxyethane < pentanal < pentan-1-ol
Question. pentan-1-ol, phenol, 4-methylphenol, 3-nitrophenol ( increasing order of acid strength)
Answer. pentan-1-ol < 4-methylphenol < phenol < 3-nitropheno
Question. Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Phenol and Benzoic acid. (ii) Propan-1-ol and Propan-2-ol.
Answer.

Question. A compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C4H10O is a unreactive towards sodium metal . It does not add Bromine water and does not react with NaHSO3 solution .On refluxing ‘A’ with excess of HI gives ‘B’ which react with aq. NaOH to form ‘C’. ‘C’can be converted into ‘B’ by reacting with P and I2 . ‘C’ on heating with aqueous alkali to form ‘E’ which form ‘F’ on heating with conc. H2SO4. ‘F’ decolourises bromine water . Identify A to F and write the reactions involved.
Answer.- ‘A’is not alcohol therefore it does not react with Sodium metal . ‘A’ is not aldehyde and ketone as it does not react with NaHSO3 ‘A’ is not unsaturated hydrocarbon as it does not add Br2 (aq) . It is likely to be ether.

