Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Chemistry teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 14 Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules are very important and should be revised daily.
Question. The sugar present in milk is
(a) Sucrose
(b) Maltose
(c) Glucose
(d) lactose
Answer
D
Question. α-D (+) glucose and β-D (+) – glucose are
(a) Enantiomers
(b) Geometrical isomers
(c) Anomers
(d) Epimers
Answer
C
Question. Amylopectin is a polymer of
(a) β-D-glucose
(b) α-D-glucose
(c) β-D-frutose
(d) α-D-fructose
Answer
B
Question.Hydrolysis of sucrose gives
(a) Glucose only
(b) Glucose + fructo
(c) Glucose and galactose
(d) Maltose
Answer
B
Question. DNA and RNA differ in
(a) Sugar
(b) Purines
(c) Pyrimidines
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Keratin present in hair is an example of
(a) Fibrous protein
(b) Globular protein
(c) Conjugated protein
(d) Derived Protei
Answer
A
Question. Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins with examples.
Answer.
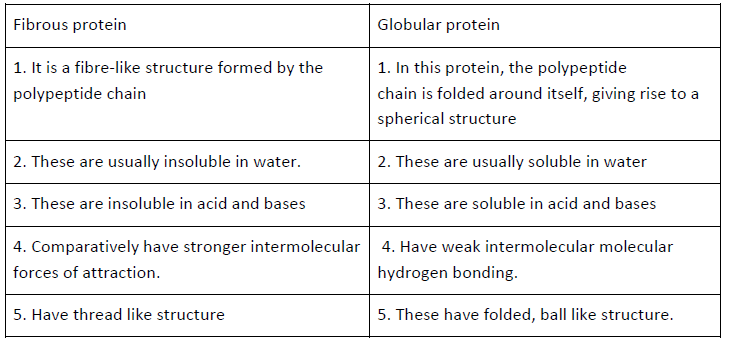

Question. What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
(i) HI (ii) Bromine water (iii) HNO3
Answer.
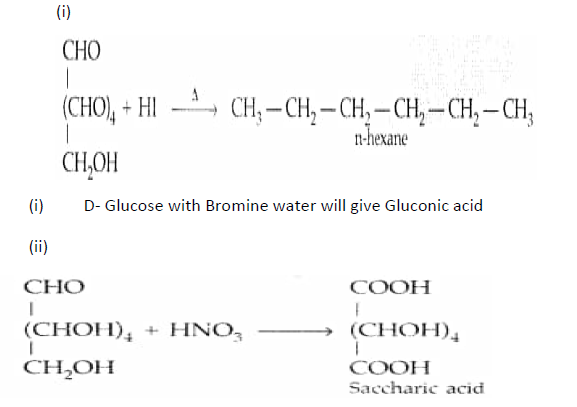
Question. How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids?
Answer.Amino acids have both acidic (carboxyl) group and basic (amino) group in the same molecule.
In the aqueous solution the carboxyl group losses proton while amino group accepts that proton.
This results to formation of zwitter ion.
This zwitter ionic form of α amino acid shows amphoteric behaviour, i.e. act both as acid and base.
Question. Define the following as related to proteins
(i) Peptide linkage (ii) Primary structure (iii) Denaturation.
Answer.(i) Peptide linkage: A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O). This is a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids.
Primary structure: The primary structure of a protein is the specific sequence in which various amino acids are present in it. It is the sequence of linkages between amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The sequence in which amino acids are arranged is different in each protein. A change in the sequence creates a different protein. Also the sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its function and biological activity.
(iii) Denaturation: In a biological system, a protein is found to have a unique 3-dimensional structure and a unique biological activity. This is said to be native form of protein. When any protein present in its native form is subjected to a physical change (Change in temperature) or chemical changes like change in pH, its hydrogen bonds are broken. This disturbance unfolds the globules and uncoils the helix of the protein molecule. This makes the protein lose its biological activity. This loss of biological activity by the protein is known as denaturation. During denaturation, the secondary and tertiary structures of the protein get destroyed, but the primary structure remains unaltered. Due to denaturation the globular proteins are converted into fibrous proteins. Hence denaturation leads to coagulation. One of the examples of denaturation of proteins is the coagulation of egg white when an egg is boiled.
Question. Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg?
Answer.When an egg is boiled, the proteins present inside the egg get denatured (the process of loss of biological activity of protein like hydrogen bonding when subjected to a physical change) and coagulate (the process of a liquid changing to a solid or semi-solid state). After boiling the egg, the water present in it gets absorbed by the coagulated protein through H-bonding.
Question. What is meant by ‘reducing sugars’?
Answer.Reducing sugar contains aldehydic or ketonicgroup in the hemiacetal and hemiketal forms and can reduce Tollen’s reagent or Fehlmg’s solution.
Example: Glucose and Fructose.
Question. Name the four bases present in DNA. Which one of these is not present in RNA?
Answer.The four bases present in DNA are :
(i) Adenine (A)
(ii) Guanine (G)
(iii) Cytosine (C)
(iv) Thymine (T)
In RNA, Thymine (T) is absent. It has Uracil (U) in place of Thymine.
Question. What are essential and non-essential amino acids in human food? Give one example of each type.
Answer.Essential amino acids : Amino acids which the body cannot synthesize are called essential amino acids.
Example : Valine, leucine etc. Therefore they must be supplied in diet.
Non-essential amino acids : Amino acids which the body can synthesize are called non-essential amino acids. Therefore, they may or may not be present in diet.
Example : Glycine, alanine etc.
Question. What are Biomolecules and Carbohydrates.?
Answer.Biomolecules: Complex lifeless chemical substances which not only build up the living system but are also responsible for their growth, maintenance and their ability to reproduce is called Biomolecules.
Carbohydrates : Carbohydrates may be defined as optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones or the compounds which produce such units on hydrolysis
Question. Give an example of non-reducing sugar.
Answer.Sucrose
