Exam Question for Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Economics teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Economics and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Economics exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 3 Production and Costs Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 Economics Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs are very important and should be revised daily.
Exam Question Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. When does the producer increase the supply of a good at given price, give two reasons.
Answer. Due to change in other factor like improvement in technology, decrease in price
of inputs.
Question. Why does average cost fall as output rises?
Answer. AC falls due to operation of the law of increasing returns to a factor as output rises.
Question. What do you mean by individual supply schedule?
Answer. Individual supply schedule is a tabular representation showing various quantities of a commodity which a firm is ready to sell at different prices during a given period of time.
Question. What will be the behaviour of Average revenue when total revenue increases at constant rate?
Answer. Average revenue remains constant.
Question. Does fixed cost affect marginal cost? Give the answer with reason.
Answer. No, because fixed cost is not subject to change and it is not considered while calculating MC.
Question. What do you mean by implicit costs?
Answer. Implicit cost is the cost of self owned resources of producer.
Question. What would be the effect of increase in the output on the TFC?
Answer. There would not be any effect of increase in the output on the TFC, It will be constant at different levels of production.
Question. What is the relation between average and marginal product when average product is falling?
Answer. MP falls but it falls at faster rate than AP
Question. Define marginal cost.
Answer. Marginal cost is the net addition to total cost when one additional unit of output is produced.
Question. What do you mean by marginal revenue?
Answer. Marginal revenue is net additions to total revenue by sale of one additional unit of output.
Question. What happens to TPP when marginal productivity of variable input is negative?
Answer. TPP falls.
Question. Define Market Supply
Answer. It refers the sum of total quantity supplied by all the firms in a market.
Question. Why does the difference between average total cost and average variable cost falls with increase in output?
Answer. It is because average fixed cost goes on falling with increase in output.
Question. Define Revenue.
Answer. Revenue is the amount received from sale of output.
Question. What causes an extension in supply?
Answer. Increase in price of a commodity.
Question. Define production function.
Answer. Diminishing return to a factor
Question. When is TPP maximum in relation to MPP?
Answer. When MPP is zero.
Question. Define supply.
Answer. Supply refers to the amount of the commodity that a firm or seller is willing to offer for sale in a given period of time at various prices.
Question. What effect does an increase in input price have on the supply curve?
Answer. The supply curve will shift towards left-hand side.
Question. Define average production.
Answer. AP is a per unit output of a variable factor.
Question. Name two determinants of supply.
Answer. 1. Number of firms
2. Change in technology
Question. What is meant by elasticity of supply?
Answer. Price Elasticity of Supply (Es) is a measure of degree of response of supply for a good to change in its price.
Question. What type of change in price is the cause of upward movement along a supply curve?
Answer. Due to increase in price.
Question. Why does average cost curve and averages variable cost curve never intersect each other?
Answer. Because AFC can never be zero at any level of output.
Question. What happens to MPP when TPP is declining?
Answer. MPP declines and remains negative.
Question. What will be the behavior of total product when marginal product of variable input is falling but is positive?
Answer. Total product increases at diminishing rate.
Question. What is meant by leftward shift of supply curve?
Answer. Due to change in other factors the supply of a commodity falls at same price than supply curve shifted to leftward.
Question. How does a decrease in price of input effect supply curve of the commodity?
Answer. As a result of decrease in price of input production cost falls then producers profit margin will increase so producer will increase the supply of commodity.
Question. Which cost curve is parallel to ox-axis? Why?
Answer. Total fixed cost because TFC remain constant at all level of output.
Question. What is meant by change in supply?
Answer. Change in supply refers to increase or decrease in supply of a commodity due to change in factors other than price like technology, price of inputs, Goal of producer, Number of firms etc.
Question. Define explicit costs.
Answer. Those monetary payments by producer on factor and non factor payments is called explicit cost. Which are not owned by himself.
Question. State any two conditions of producers equilibrium according to marginal revenue and marginal cost approach.
Answer. 1. MR = MC
2. Rising portion of Marginal cost curve intersects marginal revenue curve.
Question. Why MC curve is in short run U-shaped?
Answer. MC Curve in short run is U-shaped due to operation of the law of returns to a factor.
Question. How does fall in MPP affect TPP?
Answer. TPP increases at decreasing rate.
Question. What will be the behaviour of total revenue when marginal revenue is zero?
Answer. Total revenue will be maximum.
Question. When does the elasticity of supply of commodity called equal to unity?
Answer. When percentage change in price is equal to percentage change in supply.
Question. What effect does a cost saving technical progress have on the supply curve?
Answer. Supply curve will shift to the right.
Question. If marginal revenue falls, will total revenue fall?
Answer. It may fall when MR falls and becomes negative. If MR falls but remains positive then TR may increase with diminishing rate.
Question. What effect does an increase in excise tax have on the supply curve?
Answer. Supply curve will shift to the left.
Question. What causes a downward movement along a supply curve?
Answer. Decrease in price.
Question. At what rate average and marginal revenue falls, with fall in per unit price of a good?
Answer. Marginal revenue falls twice the rate of average revenue.
Question. What happens to TP when MP is zero?
Answer. TP is maximum.
Question. What is the price elasticity of supply of a commodity whose straight line supply curve passes through the origin forming an angle of 75º?
Answer. Price elasticity of supply will be equal to one when a straight line supply curve passes through the origin; angle does not matter anything.
Question. What do you mean by fixed factors of production? Give example.
Answer. These factors of production which cannot be varied in short period e.g. machine, land.
Question. What do you mean by producer’s equilibrium?
Answer. Producer’s equilibrium is a situation where he gets maximum profit.
Question. What do you mean by cost?
Answer. Cost is the sum of explicit and implicit cost.
Question. What happens to MPP when TPP increases at decreasing rate?
Answer. MPP falls but remains positive.
Question. Why does fixed cost not influence marginal cost?
Answer. Because marginal cost does not include fixed cost.
Question. Why does a supply curve have a positive slope?
Answer. Because of positive relation between price and supply.
Question. When a seller sells his entire output at a fixed price, what will be the shape of AR & MR curves?
Answer. Both AR & MR are equal and coincide with each other on a horizonta
Question. Define marginal product.
Answer. Marginal product is net addition to total product when one additional unit of variable factor is used.
Question. If the price of a commodity falls by 10% and, consequently, the quantity supplied decreases by 20%. What will be its price elasticity of supply?
Answer.

Question. As the variable input is increased by one unit, total output falls. What would you say about of marginal productivity labour?
Answer. Marginal productivity of labour is negative.
Question. What effect does an increase is tax rates have on supply of a commodity?
Answer. As a result of increase in tax rates production cost increase, so the profit margin of producer will fall and producer will decrease the supply.
Question. What is the price elasticity of supply, if supply curve is parallel to y-axis.
Answer. Perfectly elastic.
Question. By which behaviour of marginal product will total product be maximum
Answer. When marginal product of a factor is zero, then total product will be maximum.
Question. How does fall in total product affects marginal product?
Answer. When total product falls, marginal product becomes negative.
Question. Show that average revenue equals price.
Answer.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question. With the help of example distinguish between total fixed cost and total variable cost.
Answer.

Question. What is producer’s equilibrium? Explain the conditions of produce’s equilibrium through the ‘marginal cast and marginal revenue’ approach. use diagram/schedule.
Answer. Producer’s equilibrium refer’s the stage under which with the help of given factor’s of production producer attain that level of production of which he is getting maximum profit. The conditions of producer’s equilibrium through the marginal cost and marginal revenue approach are as follows.
1. Marginal cost should be equal to marginal revenue.
2. With the increase in output after equilibrium marginal cost should be greater than marginal revenue.

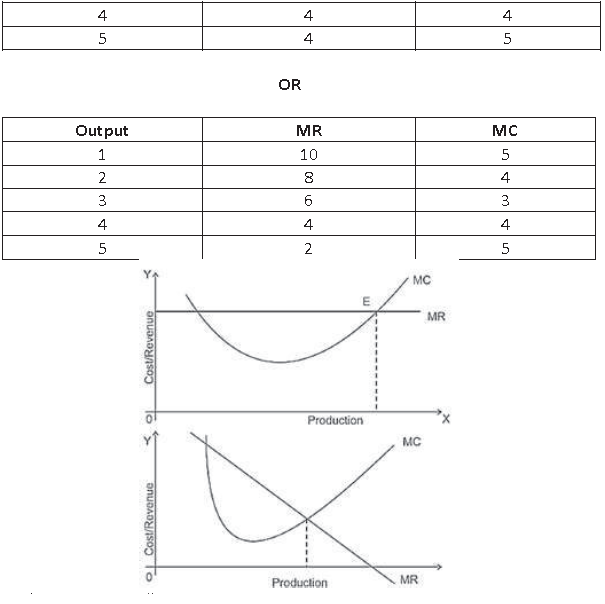
Explanation of conditions :–
1. So long as MC is less than MR, it is profitable for the producer to go on producing more because it adds to its profits. He stops producing more when MC becomes equal to MR.
2. When MC is greater than MR after equilibrium it means the profit will decline if producer will produce more units of the good.
Question. Draw average cost, average variable cost and marginal cost curves on a single diagram and explain their relations.
Answer.
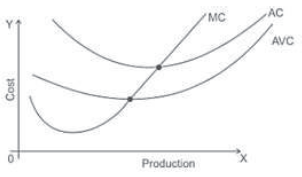
Relation of AC, AVC and MC
1. MC intersects to AC and AVC at their minimum level
2. AC and AVC decreases before the intersection by MC, but remain greater than MC.
3. AC and AVC starts to increase after the intersection by MC, and becomes less than MC.
4. As output increases, AC and AVC tends to be closer but the difference between AC and AVC can never be zero.
Question. Explain how does change in price of input affect the supply of a good.
Answer. A. Increase in price of input : increase in price of input is cause of a decrease in the supply of a good because the production cost of a good will increase due to increase in price of input. It will reduced the profit. So producer will decrease the supply of the good.
B. Decrease in price of Input : Decrease in price of input is a cause of increase in supply because when the price of input decrease the production cost of a good also also decreases. Decrease in cost increases the profit margin. It motivate to producer to increase the supply of the good.
Question. Draw average cost, average variable cost and average fixed cost curves on a single diagram and explain their relation.
Answer.
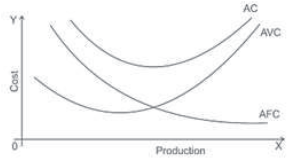
1. AC is the vertical summation of AVC and AFC
2. The difference between AC and AVC falls as output increases but the difference of AC and AFC increases.
3. As output increases AC and AVC tends to be closer but their curves do not interect each other because AFC always remains more than zero.
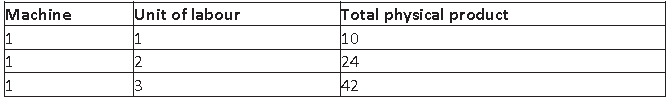
Question. Explain the likely behaviour of total product under the stage of increasing return to a factor with the help of numerical example.
Answer. Increasing return to a factor is the first phase of the Law of return to a factor. When more and more units of a variable factor is combined with fixed factor up to a certain level total physical product increases with increasing rate.
Question. Explain the relation between average revenue and marginal revenue when a firm can sell an additional unit or a good by lowering the price.
Answer. 1. AR and MR both decreases.
2. MR decrease at the rate of twice than AR.
3. MR become zero and negative but AR can never be zero.
Question. Explain how changes in prices of other products influence the supply of a given product.
Answer. The supply of a good is inversly influenced with the change in price of other product which can explain as fallows.
A. Rise in price of other product :– When there is rise in the price of other product the production of these product become more profitable due to unchanged cost in comparison of the production of given produce. As a result the producer will produce more quantity of other product so the supply of given good will decrease.
B. Fall in the price of other product :– When there is fall in the price of other product the production of these product become less profitable due to unchanged cost in comparison of the production of given product. As a result producer will produce less quantity of other product so the factors of production shifted for the production of given good. It cause an increase in supply of given good.
Question. What are the factors which give rise to increasing returns to variable factors?
Answer. 1. Fuller utilization of the fixed factors- Generally fixed factors are indivisible and underutilized. With greater application of variable factor these factors are better utilized its MPP tends to rise.
2. Increased efficiency of variable factor- Application of specialization and division of labour among the units of variable factors leads to greater efficiency and increase in MPP.
Question. What will be the price elasticity of supply if the supply curve is a positively sloped straight line?
Answer. Es = 1 if the curve starts from the origin point.
Es>1 if the curve starts from the y-axis and E<1 if the curve starts from the x-axis.
Question. Explain how technological advancement influence the supply of a given product.
Answer. Technological advancement brings a positive impact in the supply of a given product. It reduces per unit cost and increase the productivity of given factors of production. Due to these reasons production of given product becomes more profitable.
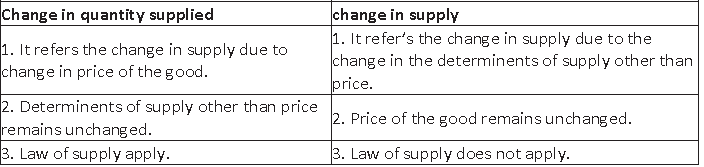
Question. Distinguish between change in quantity supplied and change in supply.
Answer.

Question. Explain the law of variable proportion with the help of diagram schedule.
OR
What is the likely behaviour of total product/marginal product when only one input is increased for increasing production? Use diagram/ schedule.
Answer. Law of variable proportion state the impact of change in unit of a variable factor on the physical output. When more and more unit of a variable factor combined with fixed factor physical product passes though following phases.
Behaviour of TP
(i) TP increases at an increasing rate
(ii) TP increases at diminishing rate
(iii) TP falls
Behaviour of MP
(i) MP increases and becomes maximum.
(ii) MP decreases and becomes zero.
(iii) MP becomes negative.
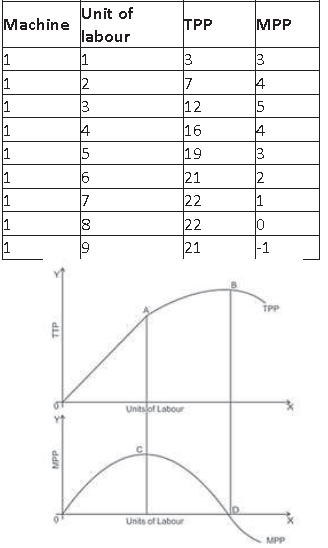
First Phase :– TPP increases with increasing rate upto A point. MPP also increase and becomes maximum of point C.
Second Phase :– TPP increases with diminishing rate and it is maximum on point B. MPP start to decline and becomes zero at D point.
Third Phase :– TPP starts to decline and MPP becomes negative.
Question. Define marginal revenue. State the relation between marginal revenue and average revenue when a firm:
(i) is able to sell more quantity of output at the same price.
(ii) is able to sell more quantity of output only by lowering the price.
Answer. Marginal revenue is the addition to total revenue from producing one more unit of output.
1. MR = AR at all levels of the output. (In case of perfect competitive market)
2. MR will be less than AR at all levels of the output. (In case of monopoly and monopolistic market)
Question. Explain the relationship between AC & MC with diagram.
Answer. (i) When MC < AC, AC falls.
(ii) When MC = AC, AC is minimum.
(iii) When MC > AC, AC rises.
(iv) MC falls & rises faster than AC.
(v) Both can be obtained from TC.

Question. How do changes in MR affect TR?
Answer. 1. If MR increases, TR increases at increasing rate.
2. If MR is constant, TR increases at constant rate.
3. If MR falls, TR increases at diminishing rate.
Question. What is MR? How is it related to AR?
Answer. MR refers to the change in TR due to sale of an additional unit.
Relation –
1. If AR (Price) is constant, MR = AR
2. If AR (Price) falls, MR < AR.
3. If AR (Price) rises, MR > AR.
Question. Explain how do the following determine price elasticity of supply:
(i) Nature of the good (ii) Time period.
Answer. 1. Nature of Commodity – Elasticity of industrial goods is more than that of agricultural goods. Similarly supply of durable goods e.g. table is more elastic than that of perishable goods e.g. vegetables.
2. Time Period- Generally elasticity of supply is more in the long period than in shorter period of time. The reason is that in the long period, all adjustments to the changed price can be made easily and supply of commodity can be varied accordingly.
Question. Why is AC curve in the short run U-shaped?
Answer. AC curve is U-shaped in short run due to operation of law of returns to factors (i.e., law of variable proportion). Initially production is subject to law of increasing returns (i.e. decreasing cost), then law of constant return (i.e. constant cost) and ultimately to law of diminishing return (i.e. increasing cost). As output is increased, AC first falls, reaches its minimum and then rises. Hence, AC curves become Ushaped.
Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question. When does the supply curve shift rightward while price remains constant.
Answer. When the supply of commodity increases due to change in other factors.
Question. Why is total fixed cost curve parallel to ox-axis.
Answer. TFC remains constant at all levels of output.
Question. Why does a producer moves downward along a supply curve due to decrease in price of commodity?
Answer. Because profit margin of firm (producer) decreases.
Question. What behaviour of per unit price will cause the equality of average and marginal revenue.
Answer. Per unit price remains constant.
Question. What is the price elasticity of supply associated with when a supply curve passes through the origin at 40° angle?
Answer. Equal to unity elastic.
Question. What is the price elasticity of supply associated when the supply curve passing through to intersect to x-axis?
Answer. Inelastic.
Question. Why does average fixed cost fall with increase in output?
Answer. AFC can be calculated from TFC. Which remains constant at all level of output.
Question. What effect does an increase in price of competitive good have on the supply of a commodity?
Answer. Supply of the commodity will fall.
Question. Under which situation will MR fall when an additional quantity of a good is sold?
Answer. When per unit price falls by selling an additional unit of a good.
Question. Why is total variable cost curve parallel to total cost curve?
Answer. Total cost is the sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost. TFC remains constant at all levels of output.
Question. Give one differences between law of supply and price elasticity of supply.
Answer. Law of supply reflects the direction of change in supply where as price elasticity of supply measures the magnitude of change in supply.

