MCQs for Chemistry Class 12 with Answers Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
Students of class 12 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 12 Chemistry NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 12 Chemistry. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 12 Chemistry examination
Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds MCQ with Answers Class 12 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 12. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 12 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. The geometry of Ni(CO)4 and [Ni(PPh3)2Cl2] are
(a) both square planar
(b) tetrahedral and square planar, respectively
(c) both tetrahedral
(d) square planar and tetrahedral, respectively
Answer
C
Question. What is the denticity of the ligand ethylenediaminetetra actetate ion?
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 1
Answer
C
Question. The type of isomerism present in Pentaminenitrochromium (III) chloride is
(a) optical
(b) linkage
(c) ionisation
(d) polymerisation.
Answer
B
Question. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent ?
(a) thiosulphato
(b) oxalato
(c) glycinato
(d) ethane – 1, 2-diamine
Answer
A
Question. Central atoms/ions in coordination compounds are.
(a) Lewis acid
(b) Lewis bases
(c) Neutral molecules
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following has highest molar conductivity?
(a) potassiumhexacyanoferrate(II)
(b) hexaaquachromium(III)chloride
(c) tetraamminedichloridocobalt (III)chloride
(d) diamminechlorido platinum (II)
Answer
A
Question. A bidenate ligand always
(a) has bonds formed to two metals ions
(b) has a charge of +2 or – 2
(c) forms complex ions with a charge of +2 or –2
(d) has two donor atoms forming simultaneously two sigma () bonds.
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following ligands forms a chelate
(a) Acetate
(b) Oxalate
(c) Ammonia
(d) Cyanide
Answer
B
Question. Choose the correct statement.
(a) Coordination number has nothing to do with the number of groups or molecules attached to the central atom
(b) Coordination number is the number of coordinating sites of all the ligands connected to the central atom or the number of coordinate bonds formed by the metal atom with ligands
(c) Werner’s coordination theory postulates only one type of valency
(d) All the above are correct
Answer
B
Question. An ambident ligand is one which
(a) is linked to the metal atom through two donor atoms
(b) has two donor atoms, but only one of them has the capacity to form a coordinate bond [or a sigma () bond]
(c) has two donor atoms, but either of two can form a coordinate bond
(d) forms chelate rings.
Answer
C
Question. According to the postulates of Werner for coordination compounds
(a) primary valency is ionizable
(b) secondary valency is ionizable
(c) primary and secondary valencies are non-ionizable
(d) only primary valency is non-ionizable.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following postulates of Werner’s theory is incorrect?
(a) Primary valencies are satisfied by negative ions.
(b) Secondary valencies are satisfied by neutral molecules or negative ions.
(c) Secondary valence is equal to the coordination number and it depends upon the nature of ligand attached to metal.
(d) The ions/ groups bound by the secondary linkages to the metal have charecteristic spatial arrangements
Answer
C
Question. When 0.1 mol CoCl3(NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, 0.2 mol of AgCl are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to
(a) 1:3 electrolyte
(b) 1:2 electrolyte
(c) 1:1 electrolyte
(d) 3:1 electrolyte
Answer
B
Question. When 1 mol CrCl3.6H2O is treated with excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl are obtained. The formula of the complex is:
(a) [CrCl3(H2O)3]3H2O
(b) [CrCl2(H2O)4]Cl2H2O
(c) [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2H2O
(d) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
Answer
D
Question. Violet colour of [Ti(H2O)6]Cl3 on heating changes to___.
(a) Green
(b) Colourless
(c) White
(d) Red
Answer
B
Question. The octahedral complex of a metal ion M3+ with four monodentate ligands L1, L2 ,L3 and L4 absorb wavelengths in the region of red, green, yellow and blue, respectively. The increasing order ofligand strength of the four ligands is
(a) L4 < L3 < L2 < L1
(b) L1 < L3 < L2 < L4
(c) L3 < L2 < L4 < L1
(d) L1 < L2 < L4 < L3
Answer
B
Question. The equation which is balanced and represents the correct product (s) is
(a) Li2O + 2KCI → 2LiCl + K2O
(b) [COCl(NH3 )5]+ 5H+ → Co2+ + SNH4+ + c1-
(c) [Mg(H2O)6 ]2+ + (EDTA)4-
→Excess NaOH [Mg (EDTA)]2+ + 6H2O
(d) CuSO4 + 4KCN → K2[Cu(CN)4 ] + K2SO4
Answer
B
Question. In which one of the pairs of ion given, there is an ion that forms a coordination compound with both aqueous sodium hydroxide and ammonia and an other ion that forms a coordination compound only with aqueous sodium hydroxide ?
(a) Pb2+, Cu2+
(b) Zn2+, Al3+
(c) Cu2+,zn2+
(d) AI3+,Cu2+
Answer
B
Question. The oxidation state and covalency of Al in [AlCI(H2O)5 )2+, respectively are
(a) + 6,6
(b) + 3,6
(c) + 2,6
(d) + 3,3
Answer
B
Question. What is the oxidation number of Pt in K[PtNH3Cl5]?
(a) 0
(b) + 1
(c) + 2
(d) + 4
Answer
D
Question. EDTA can form complex with how many number of donor atoms ?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Six
(d) Three
Answer
C
Question. EDTA4- is ethylenediarninetetraacetate ions. The total number of N—CO—O bond angles in [Co(EDTA)– complex ion is
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 2
(d) 10
Answer
A
Question. The atomic number of cobalt is 27. The EAN of cobalt in Na3 [Co(NO2 )4Cl2] is
(a) 24
(b) 36
(c) 34
(d) 35
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is a negatively charged bidentate ligand ?
(a) Cyano
(b) Ethylenediamine
(c) Acetato
(d) Dimethylglyoxime
Answer
B
Question. Oxidation state of Fe in [Fe(H2O)5 NO+ ]SO4 is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
D
Question. The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDT A) is
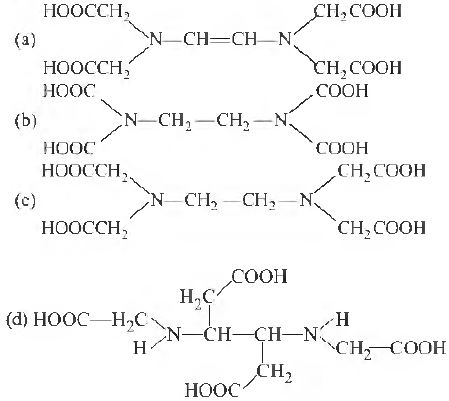
Answer
C
Question. A group of atoms can function as a ligand only when
(a) it is a small molecule
(b) it has an unshared electron pair
(c) it is a negatively charged ion
(d) it is a positively charged ion
Answer
B
Question. Which complex compound obeys 18-electron rule ?
(a) [V(CO)5 ]
(b) [Fe(NH3 ) 6 ]2+
(c) [Ni(CO)6 ]
(d) [Mn(H2O)6 ]2+
Answer
B
Question. The oxidation state of Fe in the brown ring complex [Fe(H2O)5 NO]SO4 is
(a) + 3
(b) 0
(c) + 2
(d) + 1
Answer
D
Question. The name of the ring structure complex compound formed between metal ion and polydentate ligand is
(a) simple complex
(b) chelate complex
(c) polynuclear complex
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following system is most stable for a chelate?
(a) Two fused cyclic system
(b) Three fused cyclic system
(c) Four fused cyclic system
(d) Five fused cyclic system
Answer
D
Question. The oxidation state and effective atomic number (EAN) of cobalt [CoF6 ]2- respectively, are
(a) 3 and 36
(b) 4 and 35
(c) 4 and 37
(d) 2 and 35
Answer
B
Question. A complex compound in which the oxidation number of a metal is zero, is
(a) K4 [Fe(CN)6 ]
(b) K3 [Fe(CN)6 ]
(c) [Ni(CO)4 ]
(d) [Pt(NH3 )4 ]Cl2
Answer
C
Question. A ligand can also be regarded as
(a) Lewis acid
(b) Bronsted base
(c) Lewis base
(d) Bronsted acid
Answer
C
Question. The primary and secondary valencies of chromium in the complex ion, dichlorodioxalatochromium (III), respectively are
(a) 3,4
(b) 4,3
(c) 3,6
(d) 6,3
(e) 4,4
Answer
C
Question. Two isomers X and Y with the formula Cr(H2O)5 CIBr2 were taken for experiment on depression in freezing point. It was found that one mole of X gave depression corresponding to 2 moles of particles and one mole of Y gave depression due to 3 moles of particles. The structural formula of X and Y respectively, are
(a) [Cr(H2O)5 CI]Br2 ; [Cr(H2O)4 Br2 ]Cl· H2O
(b) [Cr(H2O)5 CI]Br2 ; [Cr(H2O)3 CIBr2 · 2H2OJ
(c) [Cr(H2O)5 Br]BrCI; [Cr(H2O)4 CIBr]Br-H2O
(d) [Cr(H2O)5 CI]]Br2 ; [Cr(H2O)4 ClBr ]Br· H2O
(e) [Cr(H2O)4 Br2 ]ClH2O; [Cr(H2O)5 Cl]Br2
Answer
E
Question. Identify the correct statements for the behaviour of ethane- 1, 2-diamine as a ligand.
(i) It is a neutral ligand.
(ii) It is a didentate ligand.
(iii) It is a chelating ligand.
(iv) It is a unidentate ligand.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand?
(a) NO
(b) NH4+
(c) NH2CH2CH2NH2
(d) CO
Answer
B
Question. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?
(a) Thiosulphato
(b) Oxalato
(c) Glycinato
(d) Ethane-1,2-diamine
Answer
A
Question. The terahedral complex [M(A)(B)(X)(Y)], where A,B,X and Y are different ligands and M is a metal ion is
(a) optically inactive
(b) rotate plane polarized light
(c) incomplete information
(d) can’t be said
Answer
B
Question. According to valence bond theory which of the following statement is correct about the complexes Ni(CO)4 and [Ni(CN)4]2– if both are diamagnetic in nature
(a) both are tetrahedral
(b) both are square planar
(c) one is square planar and other is tetrahedral
(d) one is tetrahedral and other is square planar
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is p-acid ligand?
(a) NH3
(b) CO
(c) F –
(d) ethylenediammine
Answer
B
Question. The stabilisation of coordination compounds due to chelation is called the chelate effect. Which of the following is the most stable complex species?
(a) [Fe(CO)5]
(b) [Fe(CN)6]3–
(c) [Fe(C2O4)3]3–
(d) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
Answer
C
Question. According to IUPAC nomenclature sodium nitroprusside isnamed as
(a) Sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III)
(b) Sodium nitroferrocyanide
(c) Sodium nitroferricyanide
(d) Sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (II)
Answer
A
Question. The correct IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is
(a) diamminedichloridoplatinum (II)
(b) diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV)
(c) diamminedichloridoplatinum (0)
(d) dichloridodiammineplatinum (IV)
Answer
A
Question. Coordination isomerism is caused by the interchange of ligands between the
(a) cis and trans structure
(b) complex cation and complex anion
(c) inner sphere and outer sphere
(d) low oxidation and higher oxidation states
Answer
B
Question. Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism.
(a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+
(b) [Pt(NH3)3Cl]
(c) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(d) [CO(CN)5(NC)]3–
Answer
A
Question. Change in composition of co-ordination sphere yields which type of isomers
(a) optical
(b) geometrical
(c) ionisation
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type [Pd(C6H5)2(SCN)2] and [Pd(C6H5)2(NCS)2] are
(a) linkage isomers
(b) coordination isomers
(c) ionisation isomers
(d) geometrical isomers
Answer
A
Question. Atomic number of Mn, Fe and Co are 25, 26 and 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbitalboctahedral complex ions are diamagnetic?
(a) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(b) [Mn(CN)6]3–
(c) [Fe(CN)6]4–
(d) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Answer
A
Question. The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4– is 18,000 cm–1. The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2– will be
(a) 18,000 cm–1
(b) 16,000 cm–1
(c) 8,000 cm–1
(d) 20,000 cm–1
Answer
C
Question. In spectrochemical series, chlorine is above water, i.e, Cl > H2O. This is due to
(a) large size of Cl than H2O
(b) Good p-acceptor properties of Cl
(c) Strong s-donor and good p-acceptor properties of Cl
(d) Good p-donor properties of Cl
Answer
C
Question. According to Lewis, the ligands are
(a) acidic in nature
(b) basic in nature
(c) some are acidic and others are basic
(d) neither acidic nor basic
Answer
B
Question. How many geometrical isomers are possible for following square planar compound [M (Cl) (Br) (I) (F)] (where M is a metal ion)
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 9
(d) 8
Answer
B
Question. Ligand in a complex salt are
(a) anions linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion
(b) cations linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal or ion
(c) molecules linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal or ion
(d) ions or molecules linked by coordinate bonds to a central atom or ion
Answer
C
Question. The coordination number of a central metal atom in a complex is determined by
(a) the number of ligands around a metal ion bonded by sigma and pi-bonds both
(b) the number of ligands around a metal ion bonded by pi-bonds
(c) the number of ligands around a metal ion bonded by sigma bonds
(d) the number of only anionic ligands bonded to the metal ion.
Answer
C
Question. Some salts although containing two different metallic elements give test for only one of them in solution. Such salts are
(a) complex
(b) double salts
(c) normal salts
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the limitation of valence bond
(a) It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands.
(b) It does not give quantitative interpretation of magnetic data.
(c) It does not explain the colour exhibited by coordination compounds
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Higher CFSE favours formation of high spin complex
(b) Lower CFSE favours formation of low spin complex
(c) t2g orbital are three fold degenerate whereas eg orbitals are two fold degenerate.
(d) A particular metal ion in a particular oxidation state can form either diamagnetic complexes only or paramagnetic complexes only.
Answer
C
Question. An example of ambidentate ligand is
(a) Ammine
(b) Aquo
(c) Chloro
(d) Thiocyanato
Answer
D
Question. CN– is a strong field ligand. This is due to the fact that
(a) it carries negative charge
(b) it is a pseudohalide
(c) it can accept electrons from metal species
(d) it forms high spin complexes with metal species
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following does not form a chelate ?
(a) EDTA
(b) Oxalate
(c) Pyridine
(d) Ethylenediamine
Answer
C
Question. A similarity between optical and geometrical isomerism is that
(a) each gives equal number of isomers for a given compound
(b) if in a compound one is present then so is the other
(c) both are included in stereoisomerism
(d) they have no similarity
Answer
C
Question. The type of isomerism present in nitropentaamminechromium (III) chloride is
(a) optical
(b) linkage
(c) ionization
(d) polymerization
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is an organometallic compound?
(a) Ti(C2H4)4
(b) Ti(OC2H5)
(c) Ti(OCOCH3)4
(d) Ti(OC6H5)
Answer
A
Question. Ziegler-Natta catalyst is TiCl4 dissolved in
(a) triethylaluminium
(b) ether
(c) water
(d) ammonia
Answer
A
Question. Atomic number of Mn, Fe, Co and Ni are 25, 26 27 and 28 respectively. Which of the following outer orbital octahedral complexes have same number of unpaired electrons?
(a) [MnCl6]3–
(b) [FeF6]3–
(c) [CoF6]3–
(d) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
Answer
C
Question. Crystal field stabilization energy for high spin d 4 octahedral complex is
(a) – 1.6 D0 + P
(b) – 1.80 D0
(c) – 1.2 D0
(d) – 0.6 D0
Answer
B

We hope the above multiple choice questions for Class 12 Chemistry for Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Coordination Compounds is an important chapter in Class 12 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 12 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
