Sample Paper Class 10 Science Term 2 Set A
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 10 Science Term 2 Set A with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 10 Science issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 10 Science exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 10 Science for Term 2 Set A
SECTION – A
1. X, Y and Z are the three elements, each one belongs to any one of the groups IA, IIIA and VA. The oxide of X is amphoteric, the oxide of Y is highly acidic, and the oxide of Z is highly basic. Identify the groups to which these elements X, Y and Z belong?
Ans. Oxides of metals are basic while the oxides of non-metals are acidic. As we move from left to right in a period, basic character of oxides decreases while the acidic character of oxides increases. Thus, element X belongs to IIIA, Y belongs to VA and Z belongs to IA.
2. (a) Write the condensed formulae for neo-pentane and iso-butane.
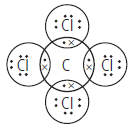
(b) Give the electron dot structure for CCl4.
Ans.
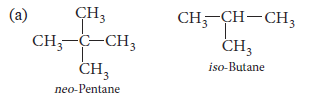
(b) Carbon has 4 valence electrons and chlorine has 7 valence electrons. The electron dot structure of CCl4 is drawn as follows :
3. What are the benefits of using mechanical barriers during sexual act?
Ans. Mechanical barriers like condoms have the following advantages :
(i) They prevent the sperms from reaching the egg.
(ii) They also prevent the transmission of infections during sexual act.
4. Why sexual reproduction is considered advantageous over asexual reproduction?
Ans. Sexual reproduction has the following advantages over asexual reproduction:
(i) Variation: Sexual reproduction involves fusion of gametes hence, genetic recombination takes place resulting in variation.
(ii) Adaptation: The offspring produced due to sexual reproduction adapt better to the changing environmental conditions.
5. “The chromosome number of the sexually reproducing parents and their offspring is the same.” Justify this statement.
Ans. Human males and females have 46 chromosomes. However, both male and female gametes are haploid (n), i.e., contains 23 chromosomes. During fertilisation, both male (23 chromosomes) and female (23 chromosomes) gametes fuse to give rise to a zygote having diploid (2n) i.e., 46 chromosome.
OR
“Human males are heteromorphic while females are homomorphic”. Explain.
Ans. Human males have XY sex chromosomes, where X chromosome is morphologically distinct from Y chromosome. Y chromosome is smaller than X chromosome. Hence they are dissimilar or heteromorphic. Human females have XX sex chromosomes, thus they are homomorphic.
6. (a) Two magnets are lying side by side as shown below. Draw magnetic field lines between poles P and Q.

(b) What does the degree of closeness of magnetic field lines near the poles signify?
Ans.

(b) The degree of closeness of magnetic field lines near the poles signify that field is stronger, i.e., the pole of another magnet when placed in the magnetic field experiences a greater force in the region where the field lines are crowded.
OR
A magnetic field that varies in magnitude from point to point but has a constant direction (east to west ) is set up in a chamber. A charged particle enters the chamber and travels undeflected along a straight path with constant speed. What can you say about the initial velocity of the particle?
Ans. If a charged particle moves parallel or antiparallel to the magnetic field, no magnetic force will act on it and it is undeflected. So, in the given condition either the charged particle enters east to west or west to east.
7. Explain briefly about CFCs. Name two gases which have replaced CFCs.
Ans. CFCs (Chloroflurocarbons) are synthetic, gaseous compounds of carbon and halogen which are odourless, non-toxic, non-inflammable, chemically inert propellants used in refrigerators and air conditioners, in aerosol sprayers, etc. Once released in the air, these harmful chemicals produce active chlorine which destroy the ozone by converting it into oxygen. CFCs are being replaced by Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrochloroflurocarbons (HClFCs).
OR
An ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising of living organisms and physical factors.
(a) How do biotic and abiotic components differ from each other?
(b) Write any four examples of abiotic components of an ecosystem.
Ans. (a) Biotic components are the living organisms of an ecosystem which obtain inorganic nutrients and energy from abiotic components whereas abiotic components are non living physicochemical factors of an ecosystem which affect the distribution and structure of organisms, behaviour and inter-relationship.
(b) The abiotic components of ecosystem are: temperature, soil, rainfall and minerals.
SECTION – B
8. What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Ans. The two important properties of carbon that lead to huge number of carbon compounds are as follows :
(i) Catenation : Carbon has the unique property of self linking which is known as catenation. In fact, any number of carbon atoms can be linked to one another by covalent bonds. This is on account of the stability of C — C bonds since the size of the carbon atom is quite small.
(ii) Linking of carbon with other atoms : Carbon is tetravalent in nature and can readily unite with atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, etc. by electron sharing.
9. (a) Explain law of octaves with example.
(b) What was the position of isotopes in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
Ans. (a) When the elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic mass, the properties of eighth element (starting from a given element) are the repetition of the properties of first element. e.g., if we start from lithium (Li), then the eighth element is sodium (Na) and further eighth element is potassium (K). The above elements have similar chemical and physical properties. Similarly, Be and Mg, B and Al, C and Si, etc., have similar chemical and physical properties.
Li, Be, B, C, N, O
Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S
(b) Mendeleev’s original periodic table does not explain the position of isotopes. Isotopes are the atoms of the same element having different atomic masses. Therefore, according to Mendeleev’s classification these should be placed at different places depending upon their atomic masses. For example , hydrogen isotopes with atomic masses 1, 2 and 3 should be placed at three places. However, isotopes have not been given separate places in the periodic table because of their similar properties.
OR
(a) On what basis an element can be classified as a metal or a non-metal?
(b) Name the most electropositive and most electronegative element of the periodic table.
Ans. (a) The metallic character of an element is due to its tendency to release electrons. By losing electrons, metal atoms change to positive ions or cations. Hence, metals are electropositive in nature.
M – e– → M+
Non-metallic character of an element is due to its electron accepting tendency. By accepting electrons, non-metal atoms change to negative ions. Hence, nonmetals are electronegative in nature.
E + e– → E–
(b) Caesium is the most electropositive (metallic) and fluorine is the most electronegative (non-metallic) element.
10. Mendel was first to explain the mechanism of transmission of characters from one generation to other. Write the basic features of mechanism of inheritance.
Ans. The basic features of mechanism of inheritance are as follows:
(i) Characters are controlled by genes and each genecontrols one character.
(ii) Chromosomes are gene carrier and genes are basic unit of heredity.
(iii) One form of gene may be dominant on other, i.e., genes are allelic in nature.
(iv) The two forms of alleles separate at the time of gamete formation, i.e., they do not mix with each other.
(v) Two allelic forms of a gene are brought together ina zygote.
11. What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
Ans. (i) When a number of electrical devices are connected in parallel, each device gets the same potential difference as provided by the battery and it keeps on working even if other devices fail. This is not so in case when the devices are connected in series because when one device fails, the circuit is broken and all devices stop working.
(ii) Parallel circuit is helpful when each device has different resistance and requires different current for its operation as in this case the current divides itself through different devices. This is not so in series circuit where same current flows through all the devices, irrespective of their resistances.
12. (a) (i) Two circular coils P and Q are kept close to each other, of which coil P carries a current. If coil P is moved towards Q, then will some current be induced in coil Q? Give the reason for your answer and name the phenomenon involved.
(ii) What happens if coil P is moved away from Q?
(b) State few methods of inducing current in a coil.
Ans. (a) (i) When coil P is moved towards Q, then current will be induced in coil Q. This is because on moving P, the magnetic field associated with Q increases and so a current is induced. The phenomenon is electromagnetic induction.
(ii) If P is moved away from Q, then the magnetic field associated with Q will decrease and a current will be induced but in the opposite direction.
(b) Some of the methods of inducing current in the coil are as below:
(i) Moving a magnet towards or away from the coil.
(ii) Moving a coil towards or away from a magnet.
(iii) Rotating a coil within a magnetic field.
OR
(a) State four factors on which the strength of magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid depends.
(b) Draw circuit diagram of a solenoid to prepare an electromagnet.
Ans. (a) Strength of magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid depends upon the following factors:
(i) number of turns in the coil
(ii) amount of current flowing through it
(iii) radius of coil
(iv) material of core of the solenoid.
(b) A strong magnetic field produced inside a solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material, like soft iron, when placed inside the coil. The magnet so formed is called an electromagnet.
13. In a cage with plenty of plants, three animals P, Q and R were kept together. The changes in their population over time have been plotted in the given graph.
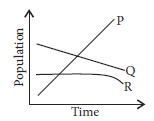
(a) Identify the carnivore and herbivore animal among these.
(b) The population of R remains stable for a longer time as compared to P and Q. What is the most likely reason for this?
Ans. (a) According to the given graph, P could be carnivore and Q and R are herbivores.
(b) The population of R remains stable for a longer time compared to P and Q, because R is a herbivore which is not eaten by P.
SECTION – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (a, b and c). Parts a and b are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part c.
14. The Australian monk Gregor Johannes Mendel worked on a plant due to its unique features like shorter life cycle, well defined contrasting characters over other plants.
(a) Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment.
(b) What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 generation when he crossed the tall and short plants?
(c) Write the phenotypic and genotypic ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
Ans. (a) Mendel selected garden pea (Pisum sativum) for his series of hybridisation experiments.
(b) He first selected two pureline plants (tall plant having gene TT and short plant having gene tt) and then crossed such plants having contrasting characters. In the F1 generation, he observed that only one of the two contrasting characters appeared, he called this character as dominant and the one which does not get expressed in F1 was called recessive.
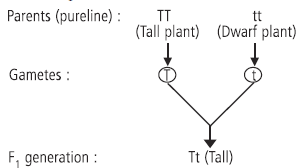
(c) The plants of F1 generation will be all tall plants and after selfing the ratio of tall and dwarf plants that Mendel obtained in F2 generation plants is 3 (Tall) : 1 (Dwarf). Genotypic ratio of F2 generation is 1 (TT) : 2 (Tt) : 1 (tt).
OR
Write the dominant characters studied by Mendel in his experiments.
Ans. Dominant characters studied by Mendel were:
(i) Plant height – Tall (T)
(ii) Flower position – Axillary (A)
(iii) Pod colour – Green (G)
(iv) Pod shape – Full or inflated (I)
(v) Flower colour – Violet (V)
(vi) Seed shape – Round (R)
(vii) Seed colour – Yellow (Y)
15. Study the I-V graph for four conductors A, B, C and D having resistance RA, RB, RC and RD respectively, and answer the following questions :
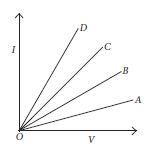
(a) If all the conductors are of same length and same material, which is the thickest?
(b) If all the conductors are of same thickness and of same material, which is the longest?
(c) Which one of these is a best conductor?
Ans. (a) Area of cross-section ∝ 1 / Resistance
So, D is the thickest.
(b) Resistance ∝ length. So, A is the longest.
(c) Slope = I / V = 1 / R is least for RA.
So, RA > RB > RC > RD
D is the best conductor, as it has the least resistance among A, B, C and D.
OR
If the dimensions of all the conductors are identical, but their materials are different which one would you use as (a) resistance wire, (b) connecting wire?
Ans. (a) Resistance wire –A
(b) Connecting wire – D

